What kind of illness?
The duodenum sounds like duodenum in Latin. It got its name back in the old days, in Rus', when there was a measure of calculation in fingers. The disease “duodenitis” received its Russian pronunciation thanks to a translation from Latin. The duodenum is the most important organ of digestion. In it, food is processed by the digestive juices of the pancreas, completing the stage that prepares food for absorption. It also produces some hormones that regulate the activity of the gastrointestinal tract and metabolism in the body.
Since inflammation occurs more often on the intestinal mucosa, you should also know some of the features of the disease. For treatment to be effective, a diet for duodenitis must be applied.
The mucous membrane is unique in that so-called villi appear in the small intestine. These are nothing more than outgrowths containing food enzymes. Thanks to them, the absorption area of microelements beneficial to the body increases tens of times.
In case of diseases, the outgrowths atrophy and die if foci of infection appear nearby. Thus, a person receives less useful substances that are excreted from the body in feces. One of the causes of the disease is the bacterium Helicobacter Pylori.
Additional nutritional recommendations
Lean meat is not included in the list of prohibited foods, but it still cannot be added to your menu at the very beginning of a diet for duodenitis. It is recommended to wait 2 weeks. At this time, it is best to eat soups and cereals. Only after 2 weeks from the start of treatment, experts advise gradually introducing meat into the diet.
Patients often feel hungry before going to bed. It should not be allowed. An effective way to prevent this sensation is to drink a glass of milk before bed. It not only prevents the feeling of hunger, but also restores digestion processes, cleanses the body of toxins, normalizes intestinal microflora, and solves the problem of chronic constipation.
Another tip: you should never give preference to a complex dish consisting of several ingredients. The more products it includes, the longer it stays in the digestive system. To digest such food, the body requires more hydrochloric acid, and this is fraught with increased inflammation of the mucous membrane or the recurrence of this pathological process.
Proper nutrition gradually eliminates the symptoms of duodenitis. However, this does not mean that the disease will not arise again in the future. In order to never again encounter manifestations of duodenitis, it is recommended to always follow the rules of nutrition and lead a healthy lifestyle.
IMPORTANT! Informational article! Before use, you should consult a specialist.
Signs
The disease can occur in acute and chronic form. Let's consider what are the main symptoms of duodenitis in the first case:
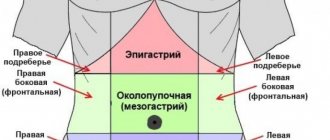
- Pain in the abdomen (stomach area).
- Nausea.
- Weakness.
- Possible internal bleeding; penetration - spread of the disease beyond the initially formed area; perforation - the formation of holes in the mucosa.
There are methods of conservative therapy that will prevent duodenitis from turning into an ulcer. They are usually used in treatment. What are the symptoms of chronic duodenitis? The signs are as follows:
- Pain in the right hypochondrium.
- Cutting sensations in the left side of the abdomen.
- Pain in the pit of the stomach.
- Yellow vomit.
- Diarrhea.
- Loss of appetite.
- Belching with the taste of half-digested food.
Drugs
From year to year, new and new drugs are created, which differ in their composition and method of use. These include drugs to reduce secretion of the digestive tract, enveloping, sedative and sedative drugs, various types of antibiotics, antibacterial drugs aimed at destroying pathogens.
It should be noted that not all drugs are useful. Especially if we consider them from the point of view of their influence on other internal organs and glands of the human body. Massive use of drugs creates the so-called resistant flora. This is a common problem when treating the body from harmful bacteria.
Features of the gut
The peculiarity of the duodenum is that the pancreatic duct flows into it, which injects enzymes - digestive enzymes, which consist of a complex of ribose and protein molecules that help break down food, and thereby speed up the digestive processes. In case of illness, this significantly affects the state of health, since it is necessary to take measures to reduce acidity and release this substance in order to increase the time of intestinal regeneration. Proper nutrition for duodenitis helps reduce acidity. Thus, removing irritability.
The bile duct also flows into the duodenum. It emulsifies fats, transforming them into a state in which they will be absorbed by the body rather than excreted. Simply put, they soften and become accessible to enzymes.
And all these enzymes enter the intestine we are considering. When suffering from duodenitis, frequent heartburn and a bitter taste in the mouth can also serve as a signal.
If food with enzymes does not pass through a small area, only twelve fingers long, then the entire digestive process will stop. Such cases are sometimes called “gastric arrest.” It turns out that a small area starts the whole process, and that is why a correctly and competently selected diet for duodenitis is so important.
How can you get duodenitis? There is a very common myth that this type of disease can cause stress. But in 1984 this assumption was refuted. This disease can be caused by both poor nutrition and the gram-negative bacterium Helicobacter Pylori.
When diagnosed with duodenitis, cholecystitis develops, and, as a rule, pancreatitis. If the intestine becomes inflamed, the pressure in the pancreas increases and inflammation begins. The same thing happens in the gallbladder system. This is a single zone of vital activity of the digestive system, the so-called “conglomerate of organs”. Therefore, if duodenitis is treated, the risks of chronic diseases in neighboring organs will be reduced. Diagnosis is carried out during gastroscopy.
Basic Rules
The goal of dietary nutrition for duodenitis is to achieve maximum chemical, mechanical and thermal gentle functioning of the digestive tract, and reduce the inflammatory process in the duodenum.
A diet for duodenitis involves limiting carbohydrates in the diet, but remains physiologically complete. According to the classification of treatment tables according to Pevzner, it corresponds to table No. 5. By order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 330, the prescription of a gentle diet (SB) is indicated.
Daily nutrient content:
- proteins – 85-90g, of which 60-70% are proteins of animal origin;
- fats – 70-80g, of which up to 20% are fats of vegetable origin;
- carbohydrates – 300-350g.
The energy value of the diet is 2170-2480 Kcal.
Basic principles of the treatment table for duodenitis:
- diet; Meals should be fractional, up to 5-6 times a day, at the same hours. Frequent meals in small portions can reduce inflammation by reducing the production of gastric juice and pancreatic juices that irritate the duodenum, as well as normalize the entire functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- temperature regime; Food should not be cold or hot (15-60°C), which ensures a gentle thermal effect.
- culinary processing; Dishes should be served pureed, boiled or steamed. Only liquid and mushy foods are allowed.
- salt; Salt in medical nutrition is somewhat limited (up to 8g per day): sodium chloride increases the secretion of gastric juice, which irritates the inflamed intestine.
- alcohol and smoking; During the period of exacerbation of chronic duodenitis or acute duodenitis, there is a categorical ban on alcoholic beverages. Ethanol stimulates gastric secretion and also slows down the regeneration of the duodenal mucosa. In addition, patients should stop smoking.
- chewing food; It is necessary to chew food thoroughly: this increases its mechanical processing and accelerates the onset of satiety. When eating, you should take moderation and not overeat, since the inflamed duodenum will not be able to ensure normal processes of breaking down food, which will aggravate the symptoms of duodenitis.
- product selection; It is necessary to exclude from the diet all foods that have a stimulating effect on gastric secretion and irritate the organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
- composition of dishes; In therapeutic nutrition for duodenitis, simple but varied dishes with a minimum number of ingredients should prevail. Complex dishes linger in the stomach for a long time, which means they increase the secretion of hydrochloric acid.
Products for duodenitis
One of the treatment methods (if the disease is caused by a bacteria) is taking antibiotics with an additional complex of vitamin supplements that restores the intestinal flora. Alternatively, a special diet for duodenitis is followed. What is possible with such a power system? Let's look at it now.
The list of approved products includes the following products:
- Vegetable oils.
- Kefir (non-acidic).
- Protein omelette, steamed (not fried).
- Dried white bread.
- Lean meat (beef, veal, rabbit). You can use it to make steamed cutlets, meatballs, and soufflés.
- Cracker.
- Low-fat and mild cheese varieties.
- The tea is not strong with added milk.
- Milk no more than 1.5% fat content.
- Salads from boiled vegetables.
- Small pasta.
- Scrambled eggs.
- Vegetable or cereal soups.
- Rose hip decoction.
- Boiled cauliflower.
- Milk and puree vegetable soups.
- Side dishes of beets, carrots and potatoes.
- Puddings and boiled porridges made from buckwheat, rice and other cereals.
- Condensed milk.
- Non-acidic cottage cheese.
- Boiled and pureed fruits and berries.
- Juices diluted with water.
It is worth noting that the diet for gastritis and duodenitis are completely similar to each other. Products should not be spicy or fried. Since this affects the process of enzyme release. The food will not only be digested slowly, but also irritate the walls of the stomach.
Food list: what you can and cannot eat
Below we will separately analyze some fruits and vegetables that can and cannot be eaten with gastroduodenitis.
Fruits
Persimmon
For gastroduodenitis, it is recommended to eat persimmon in strictly limited quantities. This fruit contains an element such as tannin, the concentration of which is increased in unripe fruits. The astringent effect is achieved thanks to this particular substance, which can lead to pain and heaviness in the abdomen due to poor digestion. If you really want to eat persimmon, then choose a well-ripened fruit with juicy pulp.
Banana
Banana is a wonderful product that envelops the walls of the stomach and eliminates pain even during exacerbation of gastroduodenitis. You can eat bananas with low and high acidity. There are also contraindications - if you have flatulence or bloating, it is better to refuse it.
Apple
As we wrote above, the degree of stomach acidity can be low or high. If you have low acidity, you can eat sour apples, but in limited quantities. If the acidity is high, then only sweet varieties of apples are recommended.
Mandarin
If you suffer from high acidity, then you should not eat tangerines. For low acidity, we recommend approximately 100 ml of freshly squeezed tangerine juice three times a day. But you should be very careful and listen to your body!
Interesting article: Treatment and diet for duodenal bulbitis!
Pomegranate
In the stage of exacerbation of gastroduodenitis, it is necessary to exclude the use of pomegranate grains and juice. If the acute phase of the disease has passed, you are allowed to drink pomegranate juice diluted with water and consume the pulp in small quantities.
Vegetables
Pumpkin
If the acidity is low, raw pumpkin is prohibited.
Boiled is allowed, but only in moderate quantities.
For gastroduodenitis with high acidity, pumpkin becomes an indispensable component of the diet.
It helps relieve heartburn and eliminate discomfort.
Tomato
With increased secretion, the intake of tomatoes should be limited. It is recommended to eat no more than 100 grams per day. Only red ripe tomatoes with the skin removed are allowed for consumption. Yellow and green tomatoes are prohibited. If gas formation occurs, they should be completely abandoned!
Carrot
If you have gastroduodenitis, you should avoid carrots or carrot juice, as this vegetable irritates the gastric mucosa.
Healthy drinks
What can you eat with duodenitis, and at the same time contribute to healing? On an empty stomach, it is recommended to eat lamb or badger fat, which is mixed with garlic and salt. Half a spoon on an empty stomach. Then after 10-15 minutes you can proceed directly to the meal itself. It must be remembered that when the disease occurs, the acid-base balance is disturbed. Milk and tomato juice are mixed one to one (1:1). This drink helps restore pH in the body, and most importantly, eliminates the possibility of the development of harmful bacteria and eliminates inflammatory processes.
First day
So, let's start with Monday. In the morning, on an empty stomach, before the first breakfast (7-8 am) - you should take half a spoon of badger fat. You can soak crackers with it. Then prepare a fruit or vegetable salad, which should not contain eggs, cucumbers or white cabbage.
The second breakfast starts around 9-10 am, and you can cook porridge for it. At lunchtime (13-14 hours) fish soup is best. For an afternoon snack (at 16-17) you can drink diluted peach juice and eat a baked apple. For dinner (at 19-21) - light food, which can consist of mashed potatoes and boiled chicken.
Menu (Power Mode)
The First Table is a physiologically complete diet that can be adhered to constantly. However, it slightly reduces the amount of food taken at one time. The basis of this table is pureed soups. They are boiled in water, adding cereals, potatoes and carrots, pureed and butter added.
For meat dishes, steaming or boiling in a water bath is preferable (souffles, puddings, as well as omelettes, egg porridge). To remove extractive substances from meat or fish, they need to be cooked in small pieces, draining the first broth and bringing it to readiness in new water.
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|