How to determine the relationship between a sore throat and the stomach?
Painful sensations in the throat can occur for various reasons, such as hypothermia, irritation of the respiratory tract with smoke or dry air, or ingestion of a foreign object.
A sore throat is a symptom of diseases such as laryngitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sore throat, and acute respiratory viral disease. A sore throat can be caused by an allergic reaction, smoking, dental disease, or tumors of the larynx and tongue. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract can also lead to discomfort and sore throat. To determine the relationship between a sore throat and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, symptoms should be analyzed. Thus, if discomfort in the throat appears in the morning, goes away after two to three hours and appears again every day for seven or more days, then this may indicate gastrointestinal reflux
It is important to rule out other symptoms that may occur with a viral infection, such as fever, cough, or sore throat. If such signs are present, then there can be no talk of gastric reflux
You should not try to diagnose yourself and prescribe treatment on your own. Doctors should do this, so at the first signs of illness, the patient needs to visit a therapist, who will refer him to a specialist, be it a gastroenterologist or otolaryngologist. The doctor will examine the patient, collect information about the medical history, living conditions and previous diseases. If necessary, he will order laboratory tests and make a diagnosis based on the results.
First of all, you should lead a healthy lifestyle, in which there is no place for alcohol and nicotine. The key to health is proper nutrition, rich in a complex of vitamins and minerals. It is necessary to avoid fried and fatty foods and minimize the consumption of sweets, coffee and strong tea. Eat more fruits and vegetables, making juices and purees from them. Stressful situations and a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to the development of gastritis. Therefore, you should be less nervous and exercise more.
It is important to regularly visit doctors and undergo medical examinations. This will help identify ailments that do not have pronounced symptoms.
A strong immune system can resist diseases. To do this, you should ensure proper sleep and rest, proper nutrition and include exercise in your daily routine. You can strengthen the immune system with the help of hardening, taking a contrast shower during water procedures.
In most cases, discomfort in the throat is associated with inflammation and diseases of the ENT organs, but pain in the stomach often causes similar symptoms. Often the causes of concern are attributed to symptoms of tracheitis or laryngitis.
If the pain is not accompanied by signs of a cold such as fever, runny nose or headache, but appears against the background of stomach pain and heartburn, then gastroesophageal reflux is likely to occur. With this pathology, stomach acid returns through the esophagus and, when it reaches the throat, causes irritation of the larynx, and a dull pain is observed in the navel area.
As a result of the ingress of acid from the stomach, a person experiences a feeling of a lump and bitterness in the throat. Often with this pathology, heartburn, belching and hiccups are observed simultaneously with pain. Discomfort in the stomach is eliminated by taking antacids, and when taking the drugs, the pain in the throat goes away at the same time, since the drugs neutralize the effect of the acid.
A frequent companion to gastric reflux is a dry cough without phlegm, which appears immediately or within 30 minutes after eating. In most cases it is short-lived. In this case, the return of acid into the esophagus leads to a burning sensation in the upper part of the esophagus. After taking medications with an antacid effect, this cough quickly goes away.
Why does the esophagus hurt when swallowing?
Pain when swallowing in the esophagus indicates impaired functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which entails a lot of other symptoms and discomfort.
When a person is experiencing pain when swallowing in the esophagus, in no case should you self-medicate; you should immediately go for a consultation to a hospital, where qualified specialists can identify and eliminate the true cause of the pain.
1. Esophagitis
Pain in the esophagus when swallowing, or, as this condition is called in medicine, dysphagia, is a consequence of esophagitis, an inflammatory pathology that affects the mucous membrane of the esophagus. The disease can occur in acute, chronic, catarrhal, erosive, hemorrhagic, necrotic and pseudomembranous forms.
© shutterstock
Experts have identified a number of factors that cause esophagitis:
- Irritation from hot or cold food;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Acid, alkaline burns;
- Probing;
- Prolonged vomiting;
- Infectious lesions;
- Allergy to certain foods;
- Severe intoxication.
Signs of illness
The initial stage of the disease does not show obvious symptoms. A person occasionally experiences slight discomfort in the esophagus during swallowing.
When the disease becomes acute, esophagitis is expressed:
- Burning pain that radiates to the back, sometimes to the neck;
- Increased salivation;
- Swallowing disorder;
- Bloody vomiting.
If you experience pain in the esophagus when swallowing and other symptoms appear, you should go to the hospital to avoid unforeseen consequences.
The chronic form of the disease manifests itself:
- Heartburn;
- Burning behind the sternum;
- Belching with an unpleasant aftertaste;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Mild pain in the esophagus when swallowing.
Treatment options
Depending on the form of esophagitis, the patient is prescribed inpatient or outpatient treatment, including:
- Special diet;
- Antacids;
- Medicines that relieve heartburn;
- Agents that neutralize excess stomach acid.
In severe cases, doctors resort to surgery.
GERD
Esophageal pain after swallowing is caused by gastroesophageal reflux disease. The disease provokes the release of stomach acid into the esophagus, which is not adapted to such aggressive chemical influences. The walls of the organ begin to become inflamed, ulcers form on them, which causes excruciating pain when swallowing.
© shutterstock
Among the causes of GERD are::
- Improper diet;
- Problems with excess weight;
- Poor gastric motility;
- Problematic saliva production;
- Regular stressful situations;
- Excessive loads;
- Stomach pathologies.
Achalasia cardia
Another cause of pain in the esophagus when swallowing food is achalasia cardia - impaired motility of the esophagus. To be more precise, the disease is a poor reflex opening of the opening between the esophagus and the stomach, as a result of which complete swallowing does not occur.
© shutterstock
Often, achalasia cardia is diagnosed in people over 20 years of age. Unfortunately, to this day scientists have not been able to figure out the causes of the disease.
Signs of achalasia cardia
The main signs of the disease include:
- Impaired swallowing;
- Retention of food in the esophagus;
- Vomit;
- Painful sensations behind the sternum;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Suffocation;
- Cough;
- Significant weight loss.
Initially, difficulty swallowing occurs periodically, resulting from severe stress or hasty eating. But over time, the pain becomes regular, preventing a person from drinking even liquids. Esophageal vomiting is becoming more common, making life unbearable.
Due to the danger of the disease, doctors recommend seeking medical help when the esophagus hurts when swallowing.
Dermatomyositis
Pain in the stomach when swallowing food is caused by dermatomyositis, an inflammation of the connective tissues. The disease can occur as an independent disease, or as a consequence of tumor neoplasms.
© shutterstock
Experts have identified some factors contributing to the development of dermatomyositis, including:
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Infectious lesions;
- Various injuries;
- Psychological stress;
- Frequent hypothermia;
- Allergic reactions.
Esophageal carcinoma
Pain occurs when swallowing in the esophagus due to a malignant neoplasm. Cancer is the eighth most common cancer, affecting women and men equally.
© shutterstock
Among the most common types of the disease are squamous cell carcinoma, which arises from the epithelial cells of the mucous membrane, and adenocarcinoma, which develops from the glands of the organ.
Doctors have identified several factors contributing to the development of esophageal cancer:
- Vitamin deficiency;
- Chronic diseases of the organ;
- Tobacco smoking;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Various internal burns.
Chemical burn
In the throat and esophagus, pain may indicate a chemical burn, which occurs due to neglect or loss of self-control.
© shutterstock
Doctors treating pain when swallowing in the esophagus
When the esophagus hurts during swallowing, you need to seek help from a gastroenterologist, since it is this doctor who treats diseases of the esophagus and gastrointestinal tract.
In severe forms of the disease, consultation with a surgeon is often required.
© shutterstock
Less popular causes of pain when swallowing in the esophagus
In addition to the above ailments, there are other causes of pain in the esophagus when swallowing:
- Organ diverticula;
- Scleroderma;
- Lupus erythematosus;
- Portal hypertension;
- Entry of a foreign body;
- All kinds of injuries;
- Tumor of the oropharynx;
- Paralysis;
- Angina;
- Quincke's edema.
Summarizing
If a person experiences pain in the esophagus when swallowing, they should immediately go to the hospital for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
After all, only a highly qualified specialist will be able to determine the true cause of pain when swallowing in the esophagus.
And also do not forget that self-treatment can lead to serious complications in the form of incurable diseases.
Source: https://PrichinyBolej.ru/2111-bolit-pishhevod-pri-glotanii.html
Treatment of sore throat with gastritis of the stomach
If the appearance of a sore throat can be correlated with eating, then it is possible that the cause lies in problems with the digestive system or impaired motility of the esophagus. For example, with a disease such as gastroesophageal reflux, intestinal contents reflux into the esophagus, a feeling of discomfort in the stomach appears, a sour taste in the mouth, and an unpleasant lump rolls up in the throat.
Irritation of the esophagus (spicy foods, alcohol, swallowing a probe during endoscopic examination), as well as hiatal hernia, can also manifest themselves in a similar way. Treatment of food reflux should be carried out simultaneously with changes in diet and lifestyle.
If your throat hurts due to stomach problems, then getting results is possible only after changing your eating habits and lifestyle. Otherwise, taking pharmacological drugs and medications can only provide a short-term effect and the cause of the problem of sore throat will not be solved.
Therapy and prevention of the disease aims to normalize the functioning of the digestive system and reduce the effects of stomach acid. Features of treatment and prescription directly depend on the causes of disruption of the digestive system and the severity of the patient’s symptoms.
Several different groups of drugs are prescribed medicinally:
- blockers of H2 histamine receptors that produce hydrochloric acid - Ranitidine, Famotidine, Cimetidine, should be taken before meals for gastric reflux or after meals for heartburn;
- drugs of the inhibitor group: Omeprazole, Omez, which stop acid production, are taken for 14 days, eliminate the symptoms of gastric reflux and heal the mucous membrane of the esophagus;
- anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of gastritis and other digestive problems;
- drugs that protect mucous membranes;
- prokinetics to provide pressure on the lower esophagus and enzymes to improve digestion.
If there are no other pathologies of the digestive system, then it is enough to neutralize the effect of stomach acid after eating, and the throat will stop hurting.
A necessary action to normalize the patient’s condition is to ensure proper nutrition and eliminate foods from the diet that lead to increased acidity levels. These include any types of citrus fruits, onions, garlic. It is necessary to exclude all fatty and fried foods, pickles, and sweets from the diet.
Treatment with folk remedies for sore throat with gastritis
Not only medications, but also folk remedies are effective for therapy and prevention. Good results are observed with regular drinking of herbal decoctions: yarrow; linden; chamomile; St. John's wort; calendula.
Such medicinal plants improve digestion and help relieve pain in the stomach, which has a beneficial effect on the larynx area and eliminates discomfort in this area. It is recommended to use dry herbs or special teas for recipes, since when using alcohol-containing tinctures, the mucous membranes become irritated and the stomach begins to ache.
For pronounced symptoms, it is recommended to use a herbal decoction recipe. The product is prepared as follows: 2 tbsp. l. flax seed; 200 ml boiling water. The seed mixture is poured with water and left for 8 hours. After filtering, the infusion is taken 0.5 cups for a month before meals.
If your throat hurts due to heartburn or gastritis, then a good effect is observed from using potato juice. It is worth considering that the product must be freshly prepared, otherwise its effectiveness is reduced significantly. This natural medicine is taken ¼ cup 20 minutes before meals.
Causes and mechanisms
The origin of the pain syndrome is most often associated with some kind of inflammatory process. Children are often exposed to various infections, which can lead to disorders not only in the upper respiratory tract, but also provoke pathology in the abdomen. And not everyone knows what diseases are capable of this. Viruses are the most common pathogens, but there are also cases of bacterial infection. If, along with a sore throat, your stomach also hurts, then you need to think about the following infections:
- Adenoviral.
- Rotavirus.
- Enteroviral.
- Cytomegalovirus.
- Mononucleosis.
- Pseudotuberculosis.
- Hemorrhagic fevers.
Diagnostic features
Most often, therapy is primarily aimed at eliminating problems with the gastrointestinal tract and includes the mandatory cessation of bad habits, in particular, smoking as the main irritant for both the stomach and throat.
In parallel, medications can be prescribed to treat stomach problems, the choice of which depends on the stage of evolution of gastritis. These can be analgesics or antispasmodics, histamines and antacids; in more complex situations, antibiotics are prescribed.
If the symptoms discussed above are present, it is necessary to seek advice from a therapist, who, if necessary, will give a referral to a more specialized specialist - a gastroenterologist, as well as an otolaryngologist to determine the cause of the sore throat.
If you have symptoms of reflux, when gastric juice enters the esophagus, it is recommended to consult a physician. In most cases, the patient is given referrals to two specialists:
- gastroenterologist;
- otolaryngologist.
To confirm the diagnosis, the following studies are prescribed:
- FGDS to identify inflammatory processes, erosive changes in the stomach;
- X-ray of the esophagus to rule out a hernia;
- stomach acidity analysis;
- biopsy if there is a suspicion of cancer in the pharynx.
When a patient informs a doctor about a symptom such as a lump in the throat, it becomes necessary to exclude the possible development of all diseases that have this symptom. For a consultation you will need to visit:
- ENT doctor;
- endocrinologist;
- neurologist;
- psychotherapist;
- gastroenterologist.
The gastroenterologist prescribes a series of examinations and finds out whether the patient has inflammation of the gastric mucosa. When diagnosing gastritis, urine and stool tests are done.
It indicates which parts of the digestive tract are affected by pathology and what its nature is. It is mandatory to determine the acidity of gastric juice and test for bacterial infection in the stomach.
Of the instrumental methods, the most informative are abdominal ultrasound and gastroendoscopy.
Ear, throat, stomach hurts
Probably everyone is familiar with pain. This is a signal from the body about a certain danger, characteristic of many pathological conditions. For parents whose child is ill, it causes anxiety, and therefore should be the subject of an in-depth examination.
Particularly incomprehensible are cases when symptoms from the respiratory and abdominal organs are simultaneously observed. Sore throat, combined with abdominal pain, is a fairly common occurrence in pediatrics.
And before taking any measures, you should understand what led to this condition.
Why does my throat hurt with gastritis?
The feeling of a lump in the throat with gastritis is not accompanied by a rise in temperature, a burning sensation in the throat, a strong cough, the voice does not change and breathing is not difficult, as happens with other diseases.
Lump in throat due to digestive diseases
A sign of gastritis is discomfort in the throat against the background of the following clinical manifestations:
- heaviness in the stomach, especially after eating fatty or spicy foods;
- heartburn and belching with a sour and bitter, rotten aftertaste;
- nausea and gag reflex;
- loss of appetite and even aversion to food;
- white coating on the tongue.
Most often, a sore throat occurs with three pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Reflux esophagitis
Reflux is a return, reverse reflux of food from the epigastrium into the esophagus. The reason may be:
- gastritis with high acidity;
- fullness of the stomach with food;
- weakness of the valve that regulates the communication between the acidic environment of the stomach and the alkaline contents of the esophagus.
The reaction of gastric juice with alkali causes severe irritation of the walls of the esophagus - heartburn. To protect against it, mucus secretion increases in the esophagus. Food thrown out of the stomach with mucus reaches the pharynx, causing a sour taste, belching of air and a lump in the throat, chronic coughing and a sore sensation in the throat.
Peptic ulcer
In 90% of cases of gastritis and gastric ulcers, the cause is the bacterial infection Helicobacter pylori. With advanced disease, the infection can spread to the duodenum. Ulcers appear on the mucous membrane of the digestive system of both sections. In this case, bile contents from the duodenum are thrown into the stomach, causing spasm of its muscles, moving food back to the esophagus. Peptic ulcer disease is accompanied by a complex of symptoms:
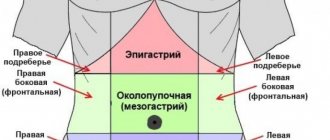
- severe epigastric pain;
- belching with a bitter taste of bile;
- gag reflex with the release of yellow-green mucus;
- spasm of the muscles of the pharynx, causing a painful sensation of a lump in the throat.
Atrophic gastritis
Gastritis with reduced acid secretion develops without pain, but after eating there is a feeling of heaviness in the stomach. The cause of heaviness is stagnation of food in the epigastrium due to lack of hydrochloric acid. The undigested contents of the stomach undergo fermentation and rotting, and gases are released. They provoke belching with a rotten smell, dry coughing, which does not eliminate the feeling of discomfort in the throat.
The cause of low acidity may be the death of a large number of glandular cells as a result of illness or surgery. Hypoacid gastritis develops when the immune system suppresses the formation of glandular cells, replacing them with mucous ones. In this case, they talk about autoimmune gastritis. It develops against the background of systemic hormonal imbalance in the body.
Sore throat and stomach pain: causes
Probably everyone is familiar with pain. This is a signal from the body about a certain danger, characteristic of many pathological conditions. For parents whose child is ill, it causes anxiety, and therefore should be the subject of an in-depth examination.
Particularly incomprehensible are cases when symptoms from the respiratory and abdominal organs are simultaneously observed. Sore throat, combined with abdominal pain, is a fairly common occurrence in pediatrics.
And before taking any measures, you should understand what led to this condition.
Causes and mechanisms
The origin of the pain syndrome is most often associated with some kind of inflammatory process.
Children are often exposed to various infections, which can lead to disorders not only in the upper respiratory tract, but also provoke pathology in the abdomen. And not everyone knows what diseases are capable of this.
Viruses are the most common pathogens, but there are also cases of bacterial infection. If, along with a sore throat, your stomach also hurts, then you need to think about the following infections:
- Adenoviral.
- Rotavirus.
- Enteroviral.
- Cytomegalovirus.
- Mononucleosis.
- Pseudotuberculosis.
- Hemorrhagic fevers.
One should not ignore the fact that such symptoms may not be related to each other. It is likely that there will be a layer of respiratory and intestinal infections (for example, salmonellosis or shigellosis). Abdominal pain with dyspepsia can even be one of the manifestations of the general toxic syndrome, especially in younger children.
The presence of gastroenterological pathology cannot be excluded. Nutritional disorders in childhood often lead to reflux gastritis. Due to the backflow of acidic gastric contents, a reactive inflammation that is not associated with infection forms on the mucous membrane of the pharynx.
But it also causes a sore throat.
If a child has a sore throat and stomach, then first of all you should look for an infection. But the reason may be hidden in other health problems.
Symptoms
The cause of the pain syndrome can be identified only with a complete diagnosis. And it starts with identifying clinical symptoms. Arriving at an appointment with a doctor, the patient is interviewed to find out the main and additional complaints. Then the nature of the pain is assessed:
- Type: sharp or blunt.
- Duration: short-term or permanent.
- Intensity: pronounced, moderate or weak.
- Dependence on certain factors: swallowing, eating, movements.
Problems with the gastrointestinal tract will be indicated by dyspeptic disorders in the form of nausea, decreased appetite, vomiting, bloating and diarrhea. Every detail is assessed, because even mild symptoms, which are practically ignored, can serve as the basis for a preliminary diagnosis.
Adenovirus infection
Intestinal problems due to adenovirus infection most often occur in younger children. The pathology begins rapidly, first there is bloating and rumbling, paroxysmal pain in the abdomen.
Almost simultaneously, the temperature rises to 39.5 degrees, vomiting and frequent loose stools occur. This can cause dehydration.
In adults, diarrhea is much easier and is not accompanied by dehydration of the body.
In the vast majority of cases, signs of an intestinal disorder are combined with respiratory manifestations: the child has a sore and red throat, enlarged tonsils, and nasal congestion.
At the same time, symptoms of conjunctivitis occur. A separate form of adenovirus infection in children is intussusception, which occurs as an obstruction (with retention of stool and gas, pain).
Rotavirus infection
Rotaviruses enter the body with unwashed hands, vegetables and fruits. They multiply and accumulate over several days, and then cause illness. Its onset is acute, with sudden fever, vomiting and diarrhea. The stool often takes on a rather characteristic appearance: gray-yellow in color and clayey consistency. All this is accompanied by symptoms from the upper respiratory tract:
- Nasal congestion and discharge.
- Sore throat when swallowing.
- Redness of the mucous membrane.
In the acute period, symptoms of intoxication appear (general weakness, malaise). With severe diarrhea, dehydration occurs.
Dangerous signs include dry mouth and thirst, decreased skin elasticity, “pointed” facial features, pallor, increased heart rate, drop in blood pressure and decreased diuresis.
It should be noted that adults are practically not susceptible to rotavirus infection, which is associated with more developed protection (high acidity of gastric juice and the level of secretory immunoglobulins in it).
Diarrhea accompanied by fever and a red throat is a good reason to rule out the presence of rotaviruses in the body.
Enterovirus infection
Diarrhea is often caused by other viruses - Coxsackie and ECHO. The infection they cause is characterized by a variety of clinical forms and polymorphism of symptoms. Gastroenteritis mainly occurs in young children.
The temperature rises slightly, but other signs are very well expressed - vomiting, diarrhea and paroxysmal abdominal pain. When the urge to defecate occurs, rumbling occurs in the abdomen, and bowel movements can become more frequent up to 10 times a day. The stool becomes watery, greenish-yellow, foamy, with mucus.
Again, enteroviral diarrhea in adults is much milder.
With great consistency, children are diagnosed with catarrhal symptoms from the upper respiratory tract - red throat, swelling of the soft palate and uvula, granularity of the posterior wall of the pharynx, pain when swallowing. Other variants of enteroviral infection may well develop:
- Herpangina.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Stomatitis.
- Skin rash (exanthema).
- Muscle pain (myalgia).
- Hepatitis and myocarditis.
- Meningoencephalitis.
- Paralysis.
This makes the pathology quite serious and requires early detection. The appearance of alarming symptoms should be a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
Mononucleosis
Infection with the Epstein-Barr virus leads to a disease called infectious mononucleosis. It is characterized by damage to organs containing lymphoid tissue. The incubation period of the pathogen is quite long (up to 50 days).
As a rule, it all begins with nonspecific (prodromal) symptoms: weakness, body aches, loss of appetite. Then a sore throat occurs, which gradually increases. At the same time, the temperature rises to febrile levels.
The younger the child, the less clear the clinical signs of infection (under the age of 2 years it is often asymptomatic).
A characteristic sign of mononucleosis is enlarged lymph nodes. First, the cervical ones increase, then the axillary and inguinal ones. In many children, mesenteric (intra-abdominal) and peribronchial nodes are also affected. In turn, this provokes the occurrence of abdominal syndrome and cough.
But the damage to the reticular tissue does not end there - patients have an enlarged liver and spleen (hepatosplenomegaly). Every tenth case occurs with a skin rash: maculopapular, pinpoint, urticarial. Mononucleosis usually lasts about a month, but recovery may be delayed.
If a child has enlarged various groups of lymph nodes, has a fever, and has a sore throat, then the first step is to rule out infectious mononucleosis.
Cytomegalovirus infection
The clinical picture of cytomegalovirus infection in older children and adults most often consists of a mononucleosis-like syndrome and damage to internal organs.
The disease begins gradually, with mild symptoms of intoxication: low-grade fever, general malaise and fatigue. Then the temperature rises more strongly - up to 39 degrees, and the throat begins to hurt.
The mucous membrane of the pharynx turns red, which suggests pharyngitis.
Abdominal pain in patients with cytomegalovirus infection may occur with damage to the liver (hepatitis) and pancreas (pancreatitis). They are accompanied by dyspeptic symptoms in the form of nausea and vomiting, and sometimes yellowness of the sclera and skin appears.
The spread of the pathogen in the body leads to damage to other organs with the development of myocarditis, encephalitis, and pneumonia. With normal immune activity, they are not severe.
But in individuals with a decrease in protective mechanisms (for example, with HIV infection), the disease is characterized by pronounced manifestations and generalized forms.
Pseudotuberculosis
The appearance of pain in the abdomen and throat should be the basis for examination for pseudotuberculosis. This is an infection caused by the bacterium Yersinia.
After accumulation in the body (the incubation period is about 10 days), the pathogen provokes a sharp increase in temperature, which can persist for 2 weeks. Among the general toxic manifestations, it is worth noting headaches, aches in muscles and joints.
The intensity of myalgia can become such that it has to be differentiated from acute surgical pathology of the abdominal cavity. The following manifestations will be characteristic of pseudotuberculosis:
- The patient’s appearance is redness and puffiness of the face, scleral injection, “crimson” tongue.
- Respiratory symptoms – pain when swallowing, nasal congestion, cough, “flaming throat”.
- Joint damage - arthralgia, swelling, annular erythema, local hyperthermia.
- Abdominal syndrome - vomiting and diarrhea, intense pain (in the epigastrium, iliac region, near the navel), enlarged liver.
- Skin rash – pinpoint or maculopapular on the trunk and limbs.
- Enlarged lymph nodes - intra-abdominal, submandibular, inguinal.
These symptoms can be observed in various combinations, causing a variety of clinical pictures in each patient. And the more severe the disease, the richer the symptoms.
Hemorrhagic fevers
Infections that are accompanied by hemorrhagic syndrome are extremely dangerous. Lassa, Marburg and Ebola fevers are diseases with extremely high contagiousness and severe course.
The onset of the disease is acute, with a high temperature (up to 40 degrees and above) and other signs of intoxication: weakness, headaches, body aches, malaise.
The further clinical picture is characterized by polymorphism:
- Pain in the abdomen, throat, chest, joints.
- Cough with sputum.
- Dyspepsia (nausea, vomiting and diarrhea).
- Conjunctivitis.
- Swelling of the face and neck.
- Bleeding of mucous membranes.
Severe hemorrhagic syndrome is manifested by bleeding from the gums, uterus, kidneys, and lungs. Together with diarrhea, this creates conditions for dehydration, which aggravates the course of the disease and causes adverse outcomes.
When your throat turns red and your stomach hurts, you shouldn’t forget about quite specific infections – hemorrhagic fevers. They are highly contagious and severe.
Additional diagnostics
The main thing in diagnosing any infection is to identify its causative agent. But in parallel, one should also determine the nature and location of the damage, and understand the severity of the patient’s condition. This determines the need for laboratory tools:
- General blood and urine tests.
- Biochemical tests (inflammatory indicators, immunogram, electrolytes, liver and kidney tests, coagulogram, proteins).
- Nasopharyngeal smear (microscopy, culture, PCR).
- Stool analysis (clinical, bacteriological).
- Serological test (for antibodies).
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
- ECG, etc.
An infectious disease specialist and an ENT doctor must be involved in the diagnosis. And after receiving the results of all studies, a final diagnosis is made. All therapeutic measures aimed primarily at eliminating the cause of the disease are based on it.
Source: https://elaxsir.ru/simptomy/drugie/bolit-gorlo-i-bolit-zhivot.html
Gastritis and lump in throat
If your throat hurts after eating, in this case we can talk about the development of gastritis and other problems with the digestive system in the body. The feeling of a coma during gastritis is associated with the release of stomach contents into the esophagus. Since the contents most often have an acidic environment, it irritates the surface of the esophagus and pharynx and causes associated sensations. If the problem is clearly related to gastritis, then in addition to a lump in your throat you will feel:
- Sourish and unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- Constant belching after eating;
- Chest burning and heartburn.
Unpleasant sensations develop after eating, often accompanied by a feeling of pain or heaviness in the stomach.
You can find out what exactly is causing the lump in the throat with gastritis through medical research. A medical specialist examines the patient, records complaints and visible symptoms and refers the patient for examination. First of all, if gastritis is suspected, it is necessary to take blood and stool tests, which will confirm inflammatory processes in the body.
An examination of the spinal and cervical region is required to identify possible problems with the vertebrae, thyroid gland and lymph nodes.
Based on the results obtained, treatment is prescribed.
Why can't you ignore a sore throat?
A sore throat due to stomach disease is considered one of the signs of a serious illness. At first, signs of disturbances in the body are the appearance of the following signals:
- the appearance of an unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- soreness of the laryngeal mucosa, the presence of a coma;
- difficulty breathing due to heartburn;
- the appearance of a dry cough;
- feeling of nausea.
See also
Inhalations with propolis tincture in a nebulizer for children and adults
Read
In the absence of timely measures, reflux can transform into esophagitis, the appearance of which significantly increases the risk of getting esophageal cancer. This pathology is already difficult to treat, while simple forms of reflux respond well to therapy. The danger also lies in the fact that the main disease is accompanied by other pathologies in the form of obstructive bronchitis, heart pain, rhinitis and pharyngitis.
In most cases, if the larynx is sick due to the stomach, the pathology is accompanied by dental problems that arise as a result of constant exposure to acid on the oral mucosa.
Why does a lump appear?
The main cause of this condition is gastrointestinal disease - gastritis. But a lump in the throat also appears with the following pathologies:
- Emotional, mental instability. Due to constant stress, a lump appears, which manifests itself as a spasm. The problem is not related to the disease itself. Difficulty breathing occurs during stress. When the condition normalizes, the unpleasant symptoms disappear on their own.
- Various gastrointestinal diseases. These include not only gastritis, but also ulcers, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, and metabolic failures. Usually a lump in the throat with gastritis is accompanied by other symptoms. This is pain and a sour taste in the mouth. Can your throat hurt with gastritis? Such sensations often appear in patients.
- Autoimmune disorders. These are diseases of the thyroid gland - autoimmune thyroiditis, Graves' disease.
- Long-term sore throat. With long-term treatment of inflammation, the problem becomes chronic. The condition usually appears from microbes. In this case, not only a lump occurs, but also pain.
- Problems in the spine. With diseases of the spinal column, an unpleasant lump in the throat develops, as there is a constant lack of oxygen.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia. With this disorder, other diseases affecting various parts and organs may occur. With the disorder, dry mouth, lack of oxygen, numbness of the tongue, and the appearance of a lump are observed.
- Neoplasms. As tumors grow, hoarseness in the voice, sore throat, cough, lump, and drooling are observed.
According to doctors, if you have a coma in your throat, it is better to consult a specialist to identify the cause. If the symptom occurs periodically, it may be due to:
- with neck injuries;
- persistent cough;
- negative consequences of drug therapy;
- colds;
- overweight;
- hiatal hernia;
- disruptions of the digestive system due to unbalanced nutrition.
Knowing the causes of a lump in the throat due to various ailments and malfunctions, it is necessary to determine the exact signs of gastritis. With this disease, other symptoms also arise, by which it can be identified and treatment can begin.
Child has sore throat, fever and stomach ache | Pain, hurts
- Adenoviral.
- Rotavirus.
- Enteroviral.
- Cytomegalovirus.
- Mononucleosis.
- Pseudotuberculosis.
- Hemorrhagic fevers.
If a child has a sore throat and stomach, then first of all you should look for an infection. But the reason may be hidden in other health problems.
The cause of the pain syndrome can be identified only with a complete diagnosis. And it starts with identifying clinical symptoms. Arriving at an appointment with a doctor, the patient is interviewed to find out the main and additional complaints. Then the nature of the pain is assessed:
- Type: sharp or blunt.
- Duration: short-term or permanent.
- Intensity: pronounced, moderate or weak.
- Dependence on certain factors: swallowing, eating, movements.
High fever, sore throat and stomach. What to do?
It will be completely different if you have a sore throat. Yes, abdominal pain may also accompany it. We are accustomed to the fact that a sore throat means a swollen throat, the inability to eat or speak. But its forms can be different, and, for example, the herpes variety has the above symptoms.
Rotovirus infection
You can also catch a rotavirus infection, which manifests itself in different ways. One person is tormented by a fever, but his throat does not hurt, another is all at the same time, a third is caused by a lot of trouble with an intestinal disorder that does not allow him to leave the house.
Fake feelings
Sometimes doctors say that it is not the stomach that hurts, but the lymph nodes that are in our body, which was a consequence of pathology. The person thinks that he has an intestinal disorder. Everything is not as simple as it may seem.
First aid
Why do men experience pain in the head of their penis when urinating?
What are the causes of abdominal pain and blood in the urine?
How do worms come out after medication?
Why do worms come out with feces?
The best modern prevention and treatment of gonorrhea
What infections occur in surgery?
How do you get chlamydia?
What are the reasons for pain in the penis when urinating?
I smoked. Not only does the head feel dizzy, but it also staggers
https://infectionlab.com/novosti/105-vysokaya-temperatura-bolit-gorlo-i-zhivot-chto-delat.html No comments yet!
Source: https://doctornebolit.ru/bol-bolit/bolit-gorlo-temperatura-i-bolit-zhivot-u-rebenka.html
Gastro-food reflux
Irritation of the esophagus causes not only pain, but also a dry throat and a burning sensation in the larynx, and there is often a feeling that something is stuck in the throat. There may be several reasons:
- diseases of the digestive system;
- hernia in the esophagus;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- acute gastritis;
- compression of the abdominal cavity due to tight clothing and belts;
- violation of the diet and the development of inflammation in the digestive tract;
- nervous tension due to stress;
- obesity;
- bad habits;
- taking medications for a long time;
- physiological changes during pregnancy;
- physical overload.
The throat can hurt not only due to the reflux of gastric secretions into the esophagus. The following diseases may be the cause:
- angina;
- laryngitis;
- pharyngitis;
- smoking;
- allergy;
- Oncology of the larynx.
In order to associate a sore throat with problems of the digestive tract, a clearer clinical picture and the presence of additional symptoms are necessary:
- the throat usually hurts in the morning;
- pain persists for several weeks;
- after a person gets out of bed, the pain goes away after a few minutes or hours;
- there are no symptoms characteristic of a viral disease;
- cough due to irritated larynx;
- heartburn and dryness in the larynx;
- nausea and problems swallowing food;
- sour taste in the mouth, especially in the morning;
- belching after each meal, becoming more intense in the evening;
- you feel a lump in your throat;
- labored breathing;
- chest pain.
If there is a cough, a sore throat, a fever, a person feels unwell, this is a viral disease that is not associated with the stomach. The reflux of gastric juice into the throat occurs when the diet and diet are violated. Fatty and fried foods often provoke gastric reflux.
When gastritis worsens, especially due to bad habits, the pain that occurs in the stomach can radiate to the throat. Reflux does not go away without a trace, gastric secretions cause irritation of the larynx and this has a bad effect on the mucous membrane of the throat.
The acidic environment of gastric juice can corrode the mucous membrane of the larynx, which will cause the appearance of ulcers and erosions.
Pathogenic microbes, getting on the loose, inflamed mucous membrane, begin to multiply and provoke the development of various diseases, these can be:
- focal sore throat;
- throat cancer;
- laryngitis;
- inflammation of the vocal cords;
- viral diseases of the respiratory system.
The reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus can cause a sore throat. This is due to the production of gastric juice, which contains hydrochloric acid, which breaks down food. Due to the alkaline environment in the esophagus, digestive juice flows back into the esophagus, which leads to irritation of the organ mucosa and gastrointestinal reflux.
When stomach contents flow back into the esophagus, heartburn, dryness and pain begin to bother you, a burning sensation and a sensation of a lump in the throat appear. Often, disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract occur due to poor nutrition. Bad habits, large amounts of fatty and peppery foods consumed can trigger gastric reflux. Exacerbation of gastritis is manifested not only by anxiety in the stomach, but also affects the mucous membrane of the throat.
Reflux can cause chronic inflammation of the pharynx, so the patient should consult an otolaryngologist, who, in turn, will prescribe treatment for both the sore throat and the stomach, prescribing a therapeutic diet. Thus, the patient should limit the amount of alcohol consumed and avoid citrus products, garlic and onions. During an exacerbation of diseases of the digestive system, fatty foods, pickles, chocolate and smoked meats should be excluded from the patient’s menu.
Strong coffee and tea are contraindicated for gastritis; doctors recommend brewing linden or chamomile. During treatment and as a preventive measure for gastrointestinal diseases, it is not recommended to eat large portions of food at night. You should get up from the table feeling slightly hungry. Patients with reflux disease are advised to sleep on an elevated pillow to avoid stomach acid from refluxing into the esophagus. It is necessary to avoid tight-fitting trousers and belts, as they can also provoke reflux, so you should wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing.
Reflux symptoms
The main symptom is heartburn, which can be provoked by errors in diet, or can occur spontaneously, regardless of food intake.
Also, severe heartburn and a lump in the throat can accompany physical activity, especially in an inclined position of the body (gardening, cleaning, lifting weights), and often appears during sleep when the person’s body is in a horizontal position.
Associated symptoms:
- unpleasant taste and odor from the mouth;
- lump in throat or upper esophagus;
- difficulty breathing due to heartburn;
- dry nonproductive cough that occurs 30-40 minutes after eating;
- nausea;
- sore throat, sometimes radiating to the ear;
- hoarseness of voice;
- painful passage of food through the esophagus, especially if the food is rough (stale bread, tough meat, hard fruits);
- pain when swallowing.
Gastroesophageal reflux is a very serious disease that should not be underestimated or attempted to be treated on your own.
If you do not pay due attention to treatment and prevention, the disease threatens to develop into reflux - esophagitis, which, in turn, significantly increases the risk of esophageal cancer.
Esophagitis is an inflammatory process in the esophagus, caused by many factors, among which is constant irritation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus and throat with acid, which is in the gastric juice, which occurs with reflux.
Additional diagnostics
The main thing in diagnosing any infection is to identify its causative agent. But in parallel, one should also determine the nature and location of the damage, and understand the severity of the patient’s condition. This determines the need for laboratory tools:
- General blood and urine tests.
- Biochemical tests (inflammatory indicators, immunogram, electrolytes, liver and kidney tests, coagulogram, proteins).
- Nasopharyngeal smear (microscopy, culture, PCR).
- Stool analysis (clinical, bacteriological).
- Serological test (for antibodies).
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
- ECG, etc.
An infectious disease specialist and an ENT doctor must be involved in the diagnosis. And after receiving the results of all studies, a final diagnosis is made. All therapeutic measures aimed primarily at eliminating the cause of the disease are based on it.
Source
Stomach hurts and goes into throat
Painful sensations in the stomach occur quite often and the patient, by the nature and location of the pain, can most often easily determine the cause of its occurrence - overeating, eating food that is heavy for him or an exacerbation of chronic diseases of the stomach, liver, pancreas.
But it happens that the pain in the stomach radiates to the throat, there is a burning sensation in the esophagus, a coma in the larynx.
Why does this happen? Which symptom indicates a disease and which is a side effect? This article will answer these questions.
What is the connection between stomach pain and sore throat?
Sore throat also occurs for various reasons. Most often, its culprits are a common respiratory viral infection or bacterial inflammation of the ENT organs.
But if a sore throat occurs along with an aching, dull pain in the stomach, heartburn, a feeling that there is a lump in the esophagus or larynx and, moreover, there are no signs characteristic of colds - fever, runny nose, headache, then pathology can be suspected which is called gastroesophageal reflux.
Reflux - (from Latin refluo - to flow back or back). Gastric reflux means that the contents of the stomach (undigested pieces of food along with stomach acid) flow back up the esophagus and can reach the throat.
The acid in the gastric juice irritates the mucous membrane, causing pain in the throat and a feeling as if there is a lump in the throat.
Sometimes such pain radiates to the ear, the disease is accompanied by heartburn, belching, hiccups, and aching pain in the stomach.
Often, taking medications - antacids - eliminates sore throat in this disease, since antacids neutralize the acid and relieve its irritating effect.
Separate mention should be made of cough. This symptom can be misleading, since cough usually accompanies pathologies in the throat, upper and lower respiratory tract.
But a cough can also be one of the signs of reflux disease. How to distinguish such a cough?
With reflux, a cough appears a short time after eating, is accompanied by a burning sensation in the throat and upper esophagus, is non-productive (dry, without mucus production), and quickly disappears after taking an antacid and eliminating heartburn.
But such a cough, especially if it also hurts the throat, is mistaken for a symptom of laryngitis, tracheitis, or tonsillitis and they put off going to the doctor, who could establish the true cause of the ailment and prescribe the correct treatment.
Causes of gastroesophageal reflux
Reflux can develop in a person regardless of his age and gender; even infants sometimes suffer from this disease.
Symptoms can appear occasionally, when exacerbation is provoked by overeating, too fatty, sour or spicy foods, excess alcohol, exercise or pregnancy, or they can occur regularly, significantly reducing the quality of life.
The causes may be:
- overweight;
- poor diet low in plant fiber;
- insufficiently active lifestyle;
- excess salt in the diet;
- too narrow, tight clothes, drawstrings, corsets;
- smoking;
- some medications.
The symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux will always be the same, regardless of the frequency and frequency with which a person suffers from attacks of the disease.
Reflux symptoms
The main symptom is heartburn, which can be provoked by errors in diet, or can occur spontaneously, regardless of food intake.
Also, severe heartburn and a lump in the throat can accompany physical activity, especially in an inclined position of the body (gardening, cleaning, lifting weights), and often appears during sleep when the person’s body is in a horizontal position.
Associated symptoms:
- unpleasant taste and odor from the mouth;
- lump in throat or upper esophagus;
- difficulty breathing due to heartburn;
- dry nonproductive cough that occurs 30-40 minutes after eating;
- nausea;
- sore throat, sometimes radiating to the ear;
- hoarseness of voice;
- painful passage of food through the esophagus, especially if the food is rough (stale bread, tough meat, hard fruits);
- pain when swallowing.
Gastroesophageal reflux is a very serious disease that should not be underestimated or attempted to be treated on your own.
If you do not pay due attention to treatment and prevention, the disease threatens to develop into reflux - esophagitis, which, in turn, significantly increases the risk of esophageal cancer.
Esophagitis is an inflammatory process in the esophagus, caused by many factors, among which is constant irritation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus and throat with acid, which is in the gastric juice, which occurs with reflux.
The disease can be expressed in an acute form, when pain is associated exclusively with food intake; catarrhal, in which the esophageal mucosa swells, the passage of food through it causes severe pain and the person constantly feels a lump in the throat; erosive - the most complex form of esophagitis, when the esophageal mucosa becomes covered with erosions (sometimes with ulcers).
In addition to reflux, esophagitis is caused by other reasons: genetic predisposition, frequent stress, mechanical damage to the esophagus (too hard food, accidental or intentional ingestion of sharp objects, insertion of a probe during FGDS), liver and gallbladder diseases, hiatal hernia.
The symptoms of reflux esophagitis are similar to gastroesophageal esophagitis, but it is much more severe and, if the disease is advanced, complicated or there is no necessary treatment, other, more dangerous manifestations are added.
They may be:
- Obstructive bronchitis, which, if not treated sufficiently, can lead to the development of bronchial asthma.
- Pain in the heart area, reminiscent of angina pectoris, resulting from provoking factors of reflux.
- Rhinitis and pharyngitis. Nasal congestion appears, sore throat and, possibly, ear; there is a risk of otitis media.
- Dental problems. Constant exposure to hydrochloric acid leads to caries.
- Barrett's syndrome - doctors consider it a precancerous condition.
Treating esophagitis can be quite difficult, while uncomplicated reflux has a fairly positive prognosis, provided that all the rules of treatment, diet and lifestyle are followed.
Diagnosis and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux
If the symptoms discussed above are present, it is necessary to seek advice from a therapist, who, if necessary, will give a referral to a more specialized specialist - a gastroenterologist, as well as an otolaryngologist to determine the cause of the sore throat.
To make a diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux, the doctor must find out the full picture of the disease: when pain occurs, its nature and location, what serves as a provoking factor for the pain, whether there are chronic diseases of the throat and stomach; what food the patient eats, in what cases a lump in the throat or heartburn appears.
Therefore, before going to the doctor, it is a good idea to study your symptoms.
To confirm the diagnosis, additional examination is prescribed:
- FGDS - detects inflammation, erosion and other changes in the stomach and esophagus
- An x-ray of the esophagus will show the presence of a hernia
- a study of changes in the acidity of gastric juice will indicate a possible cause of the disease
- examination using radioisotopes is very expensive and is prescribed in cases where other methods do not bring results
- biopsy – if cancer is suspected
Treatment of uncomplicated forms of reflux is possible at home. To alleviate the condition, antacid medications are prescribed to relieve heartburn and eliminate throat discomfort (Almagel, Rennie, Gastal); prokinetics to improve peristalsis (Motilium, Motilak, Perinorm).
If it is determined that a sore throat is caused by reflux, there is no need for additional treatment with special medications; neutralizing the stomach acid will be sufficient.
Folk remedies also give good results. If you use them at the very beginning of the disease, while changing your diet and regimen, you can avoid many health problems.
At the initial stage of the disease, herbal medicine can be used: yarrow, chamomile, St. John's wort, calendula, plantain herbs. Infusions and decoctions of these herbs will relieve stomach pain, nausea, and help digestion.
Source: https://ormira.ru/bolit-zheludok-otdaet-v-gorlo/
Diagnostics
To determine the child’s condition, doctors carry out a comprehensive diagnosis, which includes:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- coprogram;
- general urinalysis, additional testing for diastasis;
- nasopharyngeal swab for flora;
- bacteriological analysis of stool;
- serological studies;
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
Diagnosis of these diseases is carried out with the involvement of a pediatrician, infectious disease specialist, and otolaryngologist.