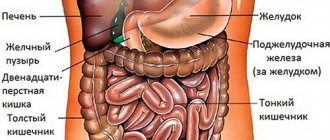
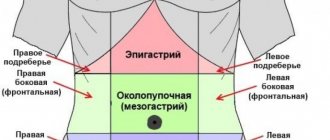
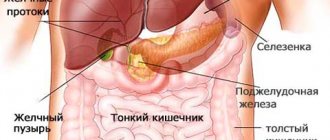
Where is the stomach and how does it hurt? Why do discomfort occur in this area? Now let's look at these issues. Stomach pain bothered almost everyone. These sensations can be caused by a slight malaise and do not always indicate that a serious illness is present in the human body. One of the reasons for unpleasant sensations in the human body is that he drank a lot of liquid or ate a lot of food. You can also determine the disease by where your stomach hurts. But you shouldn’t ignore the pain. Since they may indicate that some kind of disease is developing in the body, which requires timely treatment. Below we will discuss various options for unpleasant sensations. If a person learns to distinguish which pain relates to what, then he will not miss the moment of contacting a medical institution.
What processes can cause discomfort? Where does your stomach hurt?
The reasons for stomach discomfort may be physiological or pathological. It happens that the pain is present for a certain period of time, and then goes away. Where the stomach hurts is also a determining indicator.
The person experiences relief and continues to ignore such unpleasant sensations. This behavior is erroneous. Since this type of pain may indicate that there is a serious disease in the human body that needs to be treated urgently.
How does my stomach hurt?
Unpleasant sensations often occur under the left rib, and can sometimes radiate to the lower back, lower abdomen and heart area. In addition, the pain varies in the nature of its course - intense, pulling, dagger-like, cramping. Depending on the cause of painful spasms, you may also notice the presence of other symptoms. The most common are:
- nausea with vomiting;
- belching of gastric juice;
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- heartburn;
- bowel dysfunction - diarrhea or constipation;
- weakness;
- heat;
- bloating;
- decrease in blood pressure.
Gastritis
What pathological processes can cause stomach pain? For example, it could be gastritis. Where does the stomach hurt with gastritis? This disease is characterized by the fact that its walls become inflamed. With gastritis, the pain is intermittent. It occurs after a person has eaten foods that cause irritation to the inflamed walls of the stomach. If gastritis occurs in an acute form, then immediately after the patient has eaten a food product that he should not eat, sharp pain occurs in the epigastric region. This discomfort goes away quickly. But it resumes after the next consumption of those foods that cause irritation. When gastritis is chronic, a person does not experience severe pain. In this case, the discomfort is aching in nature. There is also a feeling of fullness and bloating.
Diet and prevention
In combination with the main treatment prescribed by the doctor, it is necessary to follow proper nutrition, which should be fractional. In other words, you need to eat in small portions, but often throughout the day. Foods that irritate the gastric mucosa are excluded from the diet: fatty, sweet, alcoholic drinks and sparkling water, sauce, spices.
Prevention of stomach pain is aimed at preventing provoking diseases and consists of maintaining a proper and balanced diet, lifestyle with the exception of alcohol, smoking, drugs, and abuse of potent drugs.
Dyspepsia
Another cause of discomfort is dyspepsia. In this case, where does a person’s stomach hurt? This disease has another name, namely, nervous stomach. The pain with this pathology is spastic. In addition, the person begins to feel sick. He also does not want to eat, and there is a feeling that his stomach is full. The pain syndrome is located in the stomach area. But in fact, the cause of its occurrence comes from the pancreas. Therefore, taking painkillers does not have the desired effect. Painful sensations continue to bother the person.
Ulcer
Now let's look at the signs and symptoms of a stomach ulcer. Where does it hurt with this disease? A stomach ulcer is the next stage in the development of gastritis in the human body. If the latter ailment is not treated properly, the patient begins to develop an ulcer. Where does it hurt with a stomach ulcer? Since this disease is a consequence of gastritis, this suggests that the person is already accustomed to constant unpleasant sensations. Therefore, he may not pay attention to new ones. It is worth saying that pain with an ulcer is more severe. They occur immediately after food enters the stomach. A person should pay attention to the severity of the pain. In this case, it is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible for qualified help.
Benign tumors and polyps
With such pathologies, pain in the stomach may also occur, where it hurts specifically will be discussed later. These formations in the stomach do not pose any danger to the patient’s life. However, they cause quite uncomfortable sensations. Pain comes when food enters the stomach and comes into contact with tumors, causing them to irritate. Also, when a person has eaten too much food, he begins to experience discomfort in the stomach. With this type of pathology, the pain is aching in nature. The patient also has a feeling of fullness in the abdomen. Moreover, this feeling is present even if the patient has eaten a little food. The discomfort goes away after a short time and ceases to bother the patient. Since in this case pain appears immediately after eating, the person becomes afraid of eating food and begins to avoid eating.
Groups of painkillers for the stomach
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs based on acetylsalicylic acid, ibuprofen and diclofenac are prohibited for abdominal pain. Their uncontrolled use can lead to gastritis, duodenal or stomach ulcers. The following are allowed for stomach pain:
- Antacids. These drugs not only relieve abdominal pain, but also treat the cause of its occurrence. They are alkaline, so they interact with the acidic environment of the stomach.
- Antispasmodics. This is the most common group of painkillers for the stomach, the action of which is aimed at relieving spasms of smooth muscles.
- Proton pump blockers. They act at the cellular level, block the synthesis of hydrochloric acid by parietal cells, protecting them from an acidic environment.
- Histamine receptor blockers. These drugs stabilize the production of prostaglandins, gastric mucus, pepsin and bicarbonates.
- Bismuth-containing preparations. Their main purpose is to treat ulcers. This group of drugs exhibits bactericidal activity against Helicobacter pylori.
Antacids
The effect of antacid drugs is to neutralize the acidity of gastric juice and coat the mucous membrane. This helps relieve pain, eliminate heartburn and activate recovery processes. Modern antacid medications contain aluminum and magnesium salts, which increase the effectiveness of these medications. Their main advantage is the minimum of contraindications:
- renal failure;
- individual intolerance to individual components.
The last contraindication concerns magnesium oxide, calcium carbonate, aluminum hydroxide, sodium bicarbonate. These substances are classic active components of antacids. Preparations based on them are used to treat:
- gastritis with high acidity;
- reflux disease, in which stomach contents flow back into the esophagus.
Another advantage of antacids is their local effect. These drugs are not absorbed into the systemic circulation, which is why they have virtually no side effects. Some antacids are capable of adsorbing toxins, so such tablets for stomach pain are also used in cases of food poisoning. Effective drugs in this category are:
- Phosphalugel;
- Rennie;
- Gaviscon;
- Almagel;
- Rutacid;
- Maalox;
- Enterosgel.
Antispasmodics
These are painkillers for gastritis and stomach ulcers. Additionally, antispasmodics help eliminate unpleasant symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux. The main effect of such drugs is to regulate the contractile function of muscles, which helps eliminate their involuntary spasms. This effect is achieved in different ways depending on the type of antispasmodics used:
- Neurotropic. They act on nerve impulses and stimulate muscle function. Suppression of spasm is due to blocking the pain signal. Neurotropic antispasmodics are M-anticholinergics: Methocinium, Hyoscyamine, atropine sulfate, Buscopan.
- Myotropic. They influence biochemical reactions inside muscle cells, which also provides relief from spasms. Papaverine, Spasmomen, Trimedat, Papazol, Drotaverine, No-shpa have this effect.
Antispasmodics for the stomach include both pharmacological tablets and herbal remedies. The latter contain extracts of medicinal herbs: chamomile, oregano, tansy, lily of the valley, mint, belladonna. Both groups of drugs have minimal contraindications:
- enlarged colon;
- certain types of colitis;
- microbial intestinal diseases;
- tuberculosis;
- Crohn's disease.
Proton pump blockers
Proton pump inhibitors or blockers help relieve heartburn. This effect is due to blocking the secretory function of the parietal cells of the stomach, which produce hydrochloric acid. After taking proton pump inhibitors, the processes of regeneration of the digestive system function are started. Additionally, these drugs protect the mucous membrane from high acidity. They are used as pain relievers for stomach ulcers, gastritis, and esophageal reflux. Popular among proton pump blockers are:
- Omeprozole;
- Nolpaza;
- Pantoprazole;
- Lansoprazole.
When treating chronic ulcers, they are more effective in combination with antibiotics. After taking proton pump inhibitors, disorders of the visual analyzer are possible, which is often manifested by a decrease in visual acuity. Possible muscle pain, depression, changes in the leukocyte formula. Proton pump blockers have a minimum of contraindications:
- pregnancy;
- lactation;
- malignant tumors of the digestive tract;
- liver and kidney failure;
- gastrointestinal infections.
Histamine receptor blockers
Another name for these drugs is H2-histamine receptor antagonists. They reduce acidity levels, which helps eliminate pain. The action is due to blocking receptors on the surface of cells in the gastric mucosa. Additionally, histamine receptor blockers increase the production of prostaglandins and mucus, which has a beneficial effect on digestion. This group of painkillers for the stomach includes:
- Ranitidine (Zantac, Ranisan, Gistac);
- Nizatidine (Axid);
- Roxatidine (Roxane);
- Famotidine (Famosan, Kvamatel);
- Cimetidine (Cinamet).
Most of these medications must be taken 2 times a day - morning and evening. Histamine receptor blockers are tablets for pain in the stomach and pancreas. The disadvantage of these medications is that they do not effectively suppress the production of gastric juice, which is why the pain syndrome may return. In addition, histamine receptor blockers cause fatigue, vertigo and headache. The list of contraindications to these drugs includes:
- age up to 14 years;
- lactation;
- pregnancy;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- disorders of the liver and kidneys;
- hypersensitivity to the composition of the drug.
Bismuth-containing preparations
The peculiarity of bismuth-containing painkillers for the stomach is the presence of a bactericidal effect against Helicobacter. These microorganisms cause inflammation of the mucous membrane, which can lead to ulceration. In addition to analgesic, bismuth-containing drugs have an anti-inflammatory effect. Examples of such drugs are:
- De-nol;
- Vikalin;
- Vikair;
- Vis-nol.
- What is SNILS and what does it look like, where to get a certificate
- Tea tree oil - properties and uses for the treatment of various diseases
- Makeup for eyes with drooping eyelids
Bismuth preparations affect the pathogen at the cellular level: they prevent the colonization of Helicobacter and reduce the symptoms of gastritis and ulcers. Such medications for stomach pain have an astringent effect, i.e. envelop the mucous membrane with a protective film. This blocks pain and prevents the occurrence of erosions and ulcers. Contraindications to the use of bismuth-based products are:
- allergy to the composition of medications;
- lactation;
- pregnancy;
- renal failure.
Other pathologies. Where does your stomach hurt? Symptoms
In addition to the above reasons for pain in the stomach, there are a number of other reasons that are associated with the physiological processes of the body. Medicine classifies pathologies of organs and systems of the human body into this category. Let's look at them:
- Pathologies of a viral nature. Ailments such as sore throat and pneumonia can cause pain in the human body. If these ailments are present in the patient’s body, then the pain in the stomach will last a short time, namely about 3 days. In addition, the patient also experiences indigestion in the form of diarrhea. In this case, the pain is aching and cutting in nature.
- Infections localized to the bladder, pancreas and gall bladder. The pain is of an intermittent, aching nature.
- An allergic reaction of the body can manifest itself in the form of pain in the stomach. This reaction in the body can be caused by certain foods. The pain lasts as long as the digestion of these products occurs. In this case, discomfort may be present in the form of spasms or severe indistinguishable pain.
- If a person is experiencing stress, then this condition can cause pain in the stomach area. Moreover, these unpleasant sensations may be accompanied by diarrhea and diarrhea.
- The same reaction of the body may be a consequence of the fact that a person is experiencing fear. For example, before some important event.
Pain caused by gastric pathologies
The group is quite extensive.
Gastritis
Aching pain is typical for the chronic form of gastritis with preserved secretory function of the stomach. As a rule, the pathology is characterized by the appearance of pain immediately after eating. The likelihood of its development increases if the food had a sour taste or was rough in consistency.
Signs of chronic gastritis are:
- a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the epigastric region that develops immediately after eating;
- belching;
- unpleasant taste of saliva;
- attacks of nausea (vomiting is possible);
- heartburn.
Important! With chronic gastritis, the occasional occurrence of diarrhea is possible. Stool upset may be a sign of damage to the digestive tract.
Peptic ulcer
The leading symptom of gastric ulcer is pain in the epigastric region of varying intensity. The nature of the syndrome is variable and can be described as aching pain. The “pain – food intake” link can be considered as a diagnostic criterion. As a rule, with stomach ulcers they do not form immediately after eating, but after about 60–90 minutes.
Another characteristic sign of the disease is a relapsing course. A person’s condition worsens in spring/autumn and improves in summer/winter. Typical symptoms of a stomach ulcer: frequent heartburn, sour belching, nausea and vomiting, weight loss. Perforation of the ulcer is indicated by the development of severe pain that can put a person in a state of shock. It requires immediate medical attention.
Polyps
Polypous formations in the gastric cavity are quite rare. The disease is not accompanied by the development of any specific symptoms or signs. In the majority of cases, growths on the mucous membrane are detected by chance during a diagnostic examination of the organ for another reason.
Sometimes polyps manifest themselves in the form of attacks of aching pain, unpleasant sensations when trying to palpate the epigastric area, gastric bleeding, nausea and bouts of vomiting.
Oncopathology
Stomach cancer is one of the most common diseases. One of the typical signs of pathology is mild, aching pain, with the stomach aching almost constantly. However, no relationship between the development of the attack and any specific causes can be traced.
At the beginning of its formation, characteristic signs are not observed. Clinical manifestations can only be dyspeptic symptoms and loss of appetite. In addition, a person very quickly eats small portions and complains of a feeling of fullness in the stomach.
Pain in the initial stage of stomach cancer is aching in nature
Doctors consider the following manifestations to be potential signs of the disease:
- anemic conditions;
- painful thinness;
- aversion to meat;
- weight loss; feeling of discomfort in the stomach.
As the disease progresses, pain and symptoms increase. Vomiting in the form of coffee grounds or pure blood, as well as melena (rich black stool) is characteristic.
Infectious bowel pathologies
Aching pain in the stomach area may be a sign of a viral or bacterial infection. But such a manifestation is atypical and occurs quite rarely. The disease is called gastroenteritis (intestinal flu). A sign of the disease, in addition to pain, is the development of diarrhea and vomiting.
Functional disorders
Aching pain in the stomach area can be caused by disturbances in the digestive processes, overeating, or increased tension in the anterior abdominal wall. The cause may also be the abuse of alcoholic beverages of any strength.
Food poisoning
The severity of pain from food poisoning depends on the amount of food consumed, i.e., the amount of toxic substances that enter the digestive tract. The stomach can hurt very much. Signs can appear quite quickly - literally 30 minutes after eating. But most often, signs form within 1–2 hours.
Signs of food poisoning include:
- pain of varying intensity, including aching;
- attacks of nausea, vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- cephalgia;
- dizziness;
- general severe weakness.
Pain due to stressful situations
The cause of aching pain in the stomach can be excessive physical or psycho-emotional stress. This is explained by the fact that on the surface of the gastric mucosa there are many nerve endings, which react to the stimulus with pain. Additionally, vomiting and uncontrollable diarrhea may occur.
Food allergies
The cause may be lactose (milk sugar) intolerance. Against the background of consumption of dairy products and milk, a person develops:
- bloating;
- aching pain in the stomach;
- diarrhea;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting.
Important! In children, lactose intolerance manifests itself in the form of frequent constipation. Babies become restless after eating and often cry.
Causes of pain
You should know that stomach pain can occur due to any pathology that occurs in the body. Its nature can also be different, from aching and dull sensations to acute and sudden forms of manifestation.
In addition, there is such a thing as hunger pain. They usually occur at night and appear when a person’s stomach is empty.
What causes hunger pains? Why does my stomach hurt? The reasons may be as follows:
- The main thing is that hydrochloric acid accumulates in the stomach in an amount that exceeds the norm.
- Presence of pathogenic bacteria.
- Gastrinoma. This is the name of the formation, the area of localization of which is the pylorus of the stomach. This formation is benign. Gastrinoma secretes gastric juice. It contains a large amount of hydrochloric acid.
- Wrong diet, namely, eating at night. Here we are talking about the constant violation of eating hours. A one-time late dinner will not cause pain in a person.
- The presence of malignant tumors in the body. You should know that they tend to develop at night.
How does the diagnosis process work for pain that is localized in the stomach?
When a person goes to a medical facility, the doctor listens to his complaints. To make a diagnosis, an examination is necessary.
Stages of patient examination:
- First of all, the doctor does a survey. He asks about the nature of the pain, when it appeared, what is its frequency and at what time of day it bothers the patient. It also finds out whether they depend on food intake or not.
- The patient is required to be given a referral for an ultrasound scan. An ultrasound examination of the digestive system will reveal whether the patient has pathological changes in organs and tissues.
- Esogastroduodenography. This type of examination is not very pleasant. Since the patient will need to swallow a special device on which the camera is located. Through this examination method, the doctor can see a picture of what is happening in the patient's stomach.
- MRI. Today, this research method is considered the most effective for making a diagnosis. Computed tomography allows a patient to be diagnosed with high accuracy. Since the examination results will show all the pathological changes that are present in the body. This method is considered the most expensive. But if there is an opportunity to use it, then you should definitely do it. It should also be said that MRI does not require special preparation from the patient.
What will happen next?
After an initial examination and medical history, the doctor can establish several differential diagnoses. Diagnostic measures will help confirm one of them:
- analysis of feces and urine - allows you to assess the completeness of food digestion, the presence of an inflammatory process in the body;
- general and biochemical blood tests - reflect the state of the body as a whole, determine the complication of the underlying pathology;
- ultrasound or magnetic resonance examination helps to study the condition of the stomach, intestines, pancreas and liver;
- gastroduodenosopia - examination of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and colon using optical equipment;
- analysis of gastric contents - reflects the composition of the chyme, the acidity of the medium, and the presence of undesirable impurities. The particles are collected using a gastroscope;
- biopsy of the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum - performed during gastroscopic examination of neoplasms on the mucous membrane in order to identify their nature;
- X-ray contrast examination of the gastrointestinal tract – provides information about the condition of the intestines and allows you to assess the functioning of the digestive tract as a whole.
The examination is carried out on the direction of a doctor; independent diagnosis is excluded. The specialist will be able to comprehensively evaluate the diagnostic results, compare them with each other and accurately determine the diagnosis.
Watch yourself!
We have already found out where the stomach hurts and why. Now we will give advice if problems arise.
A person who experiences discomfort in the stomach area is advised to monitor his own well-being. Namely, for a week, record at what time and under what circumstances the pain occurs.
You should also remember or write down the nature of the pain. Namely, dull or sharp pain is present in a person. You also need to remember how long it was present in the human body, whether it is repeated or not, and so on. If the patient provides the doctor with such a description of his feelings, he can make a diagnosis based on this data.
It is also worth paying attention to factors that can trigger pain, such as sneezing or taking deep breaths.
Treatment recommendations
If the pain is spastic in nature, then the person can take antispasmodics. They will relieve pain. However, it is worth remembering that such treatment has a temporary and emergency effect.
In order to completely get rid of pain, the cause of its occurrence must be identified. Also, do not self-medicate. What is good for one person may be dangerous for another. Therefore, the doctor should prescribe a treatment regimen after examining the patient.
Nutrition
If you have pain localized in the stomach, you need to monitor your diet and limit yourself from some food. Follow these guidelines:
- You can consume low-fat dairy products.
- It is worth giving up fatty meat.
- Also remove canned food, pickled and salty foods from the menu. This category of products can cause discomfort in people with a healthy stomach. And for those who have pathological abnormalities, pickles will cause pain and worsen their condition.
- Under no circumstances should you eat before bed. If the feeling of hunger is strong, it is recommended to drink a glass of milk with honey.
- It is better to switch to diet food. This includes porridge, soups, and steamed food.
What to do for stomach pain at home?
If the pain in the stomach occurs as a spasm, then for its emergency relief you can take an antispasmodic. This drug will help, but for a short time. A doctor should determine the causes of pain and prescribe medications.
Diet to follow if abdominal pain occurs:
- Meat can only be eaten boiled, choosing low-fat varieties.
- It is allowed to drink warm boiled milk.
- You should avoid eating spicy, sour, salty and pickled foods. Even in a completely healthy person, these dishes can irritate the gastric wall, causing it to spasm.
- You can't eat before bed. If it is impossible to cope with the feeling of hunger, then you are allowed to drink a glass of milk, to which you can add a teaspoon of honey.
If the pain is intense, then it can be muffled by eating foods that have a soft consistency. These can be steamed cutlets, pureed soups, boiled porridges, yoghurts.
Since the causes of stomach pain can be quite serious, self-medication is unacceptable. Only a doctor can prescribe therapy, based on the diagnostic results.
When a person knows his diagnosis, and an exacerbation of inflammation or an infectious disease occurs, the following recommendations can be used:
- Follow a strict diet and eat only approved foods.
- Every day drink 0.3 liters of chamomile and mint decoction. The total volume of herbal decoction should be divided into three equal portions.
- Drink 50 ml of blueberry tea 4 times a day. The drink should not be hot.
- When the pain is very intense, you can take a tablespoon of olive oil every half hour. When it is not at hand, you can use any other vegetable oil.
- You can take 3 times a day, 20 drops of calendula tincture in alcohol.
Regardless of the severity of stomach pain, drinking alcohol is unacceptable. After taking it orally, temporary relief is possible, but the pathological process itself will only worsen.
You should definitely visit a doctor if the pain tends to intensify, and also if you need to take more and more medications to relieve it. As a rule, this indicates the development of a serious pathology.
[Video] Dr. Berg - Causes of stomach ulcers, how to get rid of them? What you can eat + diet:
On this topic:
9 healing foods for stomach ulcers