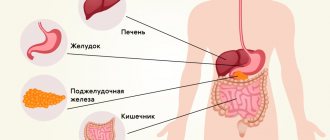
Why you can get food poisoning
Food intoxication is generally understood as a dysfunction of organs and systems caused by the ingestion of toxins or poisons. based on severity : severe, moderate and mild .
The most common pathogens include:
- Clostridium perfringens, enters the body as a result of poor-quality processing of meat, poultry, and fish;
- Stophylococcus aureus actively reproduces at room temperature. The most likely habitats are salads, fermented milk products, cakes, pates, sauces;
- Bacillus cereus, all perishable products that have not been stored at temperatures up to 6 ° C are susceptible.
Particularly dangerous natural and chemical toxins that can cause food poisoning at home are found in poisonous mushrooms and berries, low-quality, expired food products . Poisoning can also be caused by carelessly washed fruits and vegetables that have previously been treated with pesticides used to fertilize plants. Alcohol and surrogates can also be included in this category. Thus, there are known cases of death from methyl alcohol poisoning. Food chemical intoxication occurs when vinegar enters the stomach.
Symptoms of food poisoning:
- Bacterial: vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain and colic, diarrhea.
- Viral: fever, chills, trembling, stomach pain, vomiting, fever.
- Chemical: increased sweating, dizziness, vomiting, diarrhea, salivation, pain in the eye area.
- Botulism: the central nervous system is affected, vomiting, dry mouth, and weakness appear.
If you suspect food poisoning, you should immediately consult a doctor, especially if it concerns children. However, the opportunity to receive medical care is not always available.
In case of acute pathology, it is necessary to take emergency measures, including gastric lavage, taking sorbent drugs and restoring the water-salt balance. Organizing proper dietary nutrition is of great importance. The final stage of treatment is restorative procedures, which include taking multivitamin complexes. As a rule, recovery occurs within 3-5 days.
Prevention
To prevent food poisoning, prevention is very important:
- personal hygiene is mandatory (with soap, at least a couple of minutes in a row before eating, wash your hands; especially after visiting the toilet, communicating with any animals, returning from walks, contact with any frequently used objects - computer, remote controls, etc. )
- keep dishes and all kitchen utensils clean;
- use different cutting boards for each type of product (meat, pork, vegetables)
- wash your hands before preparing food, rinse food thoroughly using soda;
- if there are scratches or wounds on your hands, use rubber gloves;
- regularly change the sponges used for washing dishes;
— it is advisable to use disposable kitchen towels;
- when preparing offal from meat, poultry, fish, maintain a certain temperature;
- control the temperature at which food is stored in the refrigerator and freezer (they should be stored in food containers with lids)
- Never re-freeze any frozen food after thawing;
— expiration dates of products must be checked when purchasing and before preparing and consuming products;
— store waste and garbage in closed containers and out of children’s reach.
source
Clinical picture of food poisoning
The first symptoms of the disease appear during the first 2-6 hours after eating contaminated or low-quality food . In case of severe food poisoning, clinical signs may develop in the first hours.
Please note that in the case of botulism, the first signs of the disease may develop within 1-2 days.
In case of food poisoning, the following symptoms develop:
- nausea followed by vomiting. Vomit may consist of remnants of food, bile, and gastric juice. Vomiting brings temporary relief, but then nausea returns;
- abdominal pain can be localized in the stomach or be like intestinal colic;
- An increase in body temperature is possible with an intestinal infection or with the development of inflammatory complications such as gastritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis. With salmonellosis it can rise to 39.5 degrees;
- diarrhea develops in the first hours of the disease. With salmonellosis, the stool is foamy and greenish, and with dysentery, the stool is watery and streaked with blood. Diarrhea may be accompanied by abdominal cramps. profuse diarrhea leads to a rapid increase in dehydration;
- flatulence and increased discharge of gases are accompanied by pain in the intestinal area;
- general weakness and dizziness accompany intoxication syndrome. The patient becomes lethargic and drowsy;
- tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), hypotension (low blood pressure) are signs of toxic effects on the body of food and fluid loss. Poisoning with certain types of mushrooms may cause an increase in blood pressure. With severe dehydration, the pulse becomes weak and arrhythmic;
- breathing problems develop when the body is intoxicated. The person breathes quickly, shallowly, complains of shortness of breath;
- convulsions throughout the body, similar to an epileptic seizure, are characteristic of damage to the nervous system by toxins. This is possible due to intoxication with mushrooms, fish, alcohol;
- impaired consciousness, deep coma are signs of a serious condition of the patient. They develop in acute poisoning, infectious-toxic shock.
Please note that in small children the condition worsens faster than in adults. It is very difficult for their body to cope with toxins and loss of fluid and electrolytes.
Why is food poisoning dangerous?
Many people are accustomed to considering food poisoning as a non-dangerous and trivial condition for which there is no need to seek medical help. Indeed, mild poisoning in most cases does not pose a danger to human life, but only a doctor, after examining the patient, can specifically assess the severity of the disease and the patient’s condition.
The following are conditions that often develop against the background of severe food poisoning:
- Infectious-toxic shock is a condition caused by severe intoxication and excessive loss of fluid. Shock is accompanied by disruption of the cardiovascular system, breathing, brain and kidneys.
- Acute gastritis develops with severe stomach poisoning by toxins. The mucous membrane of this organ becomes inflamed. The patient's temperature rises and his condition worsens.
- Acute pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. The patient feels unbearable girdle pain in the abdomen, he experiences uncontrollable vomiting, the level of glucose in the blood may decrease and bruises may appear on the skin near the navel. The temperature rises above 38 degrees. This condition requires urgent surgical intervention.
- Acute renal dysfunction is accompanied by a decrease in the amount of urine, swelling, and lower back pain.
- Gastrointestinal bleeding is a complication of food poisoning, which often occurs in patients with chronic gastritis and peptic ulcers. Black vomiting and stool develop, severe weakness, pale skin, tachycardia.
Cleansing the body
These procedures are necessary, and it is with them that treatment for food poisoning should begin.
The purpose of the manipulation is to help the stomach get rid of food debris that has caused intoxication and harmful toxins. Even if poisoning is accompanied by severe vomiting, this is not enough to completely cleanse the body . It will have to be induced naturally using a special solution.
Washing should take place in the following order:
- Prepare a solution of potassium permanganate (the water should be pale pink). If potassium permanganate is not available, you can use regular baking soda (1 tablespoon per 2 liters of boiled water at room temperature).
- Drink 300-400 ml of solution.
- Induce vomiting artificially by pressing your fingers on the root of the tongue.
- Repeat the procedure several more times. The number of doses of the solution drunk at one time should be at least 500 ml.
During the first vomiting, the bulk of the food will be released, but gastric lavage can be stopped only when the liquid ejected from the stomach becomes absolutely clean and transparent.
The absence of vomiting means that the product that caused the poisoning has moved from the stomach to the intestines . In this case, the washing procedure is no longer effective and pointless.
Diarrhea, like vomiting, is nothing more than the body’s protective reaction to toxins entering the gastrointestinal tract. Some patients make a common mistake - they try to stop this phenomenon with the help of medications, for example, Imodium and its analogues. It should be understood that diarrhea is the fastest and most effective way to get rid of harmful substances. Retention of feces will lead to the fact that the processes of absorption of toxic poisons and their decay will continue, therefore, the patient’s condition will worsen. The question of taking antidiarrheal medications can only be decided by the attending physician.
If the patient does not have diarrhea, it must be induced with laxatives or an enema. But it is better not to use folk remedies that can provoke diarrhea, so as not to aggravate the course of the disease.
Symptoms of the condition
What to drink if poisoned can be decided based on the symptoms that appear. The sooner adequate treatment is applied, the fewer toxic compounds will enter the bloodstream and the patient will feel better.
The main symptoms of food poisoning include the following:
- frequent loose stools;
- general weakness and lethargy;
- temperature;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness.
How many days does a serious condition usually last? In both children and adults, most unpleasant symptoms disappear completely within 3 days.
When food poisoning occurs, the intensity of symptoms may vary from person to person. Not the least important role is played by the general condition of the body before poisoning, immunity and the type of product that caused the poisoning.
When food poisoning is accompanied by diarrhea, severe vomiting, darkening of the eyes, low blood pressure, and home remedies do not provide relief, it may be better to call an ambulance. Severe diarrhea can be dangerous.
We recommend: Causative agents of viral diarrhea, symptoms and treatment
Reception of sorbents
The next step in the treatment of food poisoning is the introduction of sorbent drugs into the body. The action of these drugs is aimed at absorbing harmful elements contained in the stomach and removing them as quickly as possible.
The most common sorbent used for intoxication is activated carbon. This medicine in the form of standard black tablets can be found in any home medicine cabinet and is an excellent remedy for poisoning. Coal should be used at the rate of one tablet per 10 kilograms of weight. The medicine can be taken in two ways: chewed and washed down with plenty of liquid or diluted in boiled water.
In case of poisoning, you can also take white activated carbon, available in tablets or powder. It is believed that, unlike black, it removes toxins, but does not affect the beneficial elements found in the body.
Another advantage of the white sorbent is the dosage: 2-3 tablets are enough (depending on the age and individual characteristics of the patient, the degree of poisoning).
Sorbent preparations recommended for use in case of intoxication include:
- smecta;
- enterosgel;
- lactofiltrum;
- attapulgite;
- polysorb;
- polyphepan.
These drugs promote the rapid elimination of toxic substances through adsorption. They should be used between doses of other drugs, during the period without vomiting . Contraindications to taking such drugs include high fever and stomach ulcers. Elderly people and young children should use it with caution, after consulting a doctor.
Medicines
Medicinal effects on the body that has suffered poisoning are not required in all situations: mild food intoxication only involves taking sorbents in order to quickly get rid of the remains of harmful substances. If the patient's condition is severe, stronger symptomatic medications may be needed, but it is advisable to select them with a doctor. Gastroenterologists use the following groups of drugs:
- Adsorbents (Enterosgel, Atoxil) - bind and remove toxins, are used to treat children and adults, but are not prescribed for fever. Be sure to space it out with other medications (for 1-2 hours).
- Rehydrants (Regidron, Acesol) - restore water and electrolyte balance, used for any poisoning. Administration is oral or infusion, depending on the patient’s condition.
- Painkillers (Drotaverine, Duspatalin) are antispasmodics that are taken only for severe acute pain that accompanies attacks of diarrhea.
- Antiemetics (Metoclopramide, Cerucal) - doctors call vomiting a natural defense reaction of the body that helps get rid of toxins, but if the attacks are too intense, it can be blocked with medications.
- Antidiarrheals (Kaopectate, Loperamide) - used only for frequent attacks of diarrhea that cause severe dehydration.
- Antipyretics (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol) are used rarely, mainly in young children and only when the patient knows that the temperature is not caused by an intestinal infection.
- Probiotics (Linex, Bionorm) are used at the final stages of treatment to restore the gastrointestinal microflora.
From poisoning and vomiting
The pharmacological group of antiemetics includes several types of drugs that affect nervous regulation. They mainly block dopamine, serotonin, and histamine receptors, reducing the excitability of the vomiting center, or work as local anesthetics. Cerucal is considered a popular and effective antiemetic drug for poisoning: it works on metoclopramide (10.54 mg per tablet and 5.27 mg per 1 ml of solution), used orally or intravenously. Key points:
- Pharmacological action: central blocker of dopamine (D2) receptors and serotonin, causes inhibition of the trigger zone of the vomiting center.
- Indications: hiccups, nausea, vomiting of any origin, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastric atony, gastric dyskinesia, gastric ulcer.
- Dosage: 1 tablet for adults half an hour before meals, washed down with warm water, up to 4 times a day (for frequent bouts of vomiting). Children over 14 years old should take no more than 3 tablets per day. The intravenous solution is administered slowly up to 3 times a day, 10 ml at a time.
- Contraindications: bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, intestinal obstruction, extrapyramidal disorders, age under 2 years.
- Side effects: urticaria, stool disorders, dry mouth, tachycardia, fluid retention, drowsiness (with frequent use).
An important advantage of Cerucal and other drugs containing metoclopramide (Metamol, Metoclopramide, Reglan) is the rapid effect on nausea and vomiting of any etiology, excluding vestibular - after half an hour the condition returns to normal. Less commonly, doctors prescribe Osetron, which uses ondansetron, as an antiemetic drug. Unlike metoclopramide, this substance does not cause an increase in prolactin levels, but its mechanism of action on vomiting is not fully understood. Instructions for use:
- Indications: nausea and vomiting of postoperative origin or caused by taking cystostatic drugs, radiation therapy.
- Dosage: daily dose – 8-32 mg for adults, it is advisable to take no more than 8 mg at a time.
- Contraindications: pregnancy, age up to 2 years (tablets) and up to 12 years (large dosages), lactation.
- Side effects: headache, arrhythmia, constipation.
Medicines for poisoning and diarrhea
In order to relieve diarrhea, attacks of which occur more often than 2-3 times a day, you can use decoctions of astringent herbs or drugs with antidiarrheal properties, which are based on loperamide, attapulgite, racecadotril, smectite. Some of them are also sorbents. Mostly in case of poisoning, gastroenterologists advise taking medications based on attapulgitis, which include Neointestopan (630 mg per 1 tablet):
- Pharmacological action: adsorption of liquid and pathogenic microorganisms with the toxins they produce in the intestines, a general reduction in intoxication, normalization of intestinal flora, thickening of liquid contents.
- Indications: acute diarrhea due to food poisoning, imbalance of intestinal microflora.
- Dosage: initial dose – 4 pcs. after defecation, then 2 pieces, washed down with warm water. The daily dose does not exceed 14 pcs. for adults. In children 6-12 years old, dosages are reduced by 2 times.
- Contraindications: fever, intestinal obstruction, parasitic diarrhea, children under 3 years of age.
- Side effects: constipation.
Kaopectate is similar in pharmacological action to Neointestopan, since it is also based on attapulgite, but 1 tablet contains 750 mg of the active substance, which makes this drug more effective (in terms of speed of action). Unlike Neointestopan, Kaopectate is also available in the form of a suspension, where the same concentration of the active ingredient (750 mg) is achieved when taking 15 ml. Indications and contraindications are identical to those described above; you only need to pay attention to the dosage:
- Adults: 2 tbsp. l. suspensions or 2 tablets up to 6 times a day, after each bowel movement.
- Children 6-12 years old: 1 tbsp. l. suspensions or 1 tablet up to 6 times a day.
- Children under 6 years old: no more than 1 tsp. suspensions up to 6 times/day.
Painkiller
If the acute stage of intoxication is accompanied by severe pain, causing suffering during the urge to defecate and between them, doctors allow the use of antispasmodic drugs. The most famous remedy of this type is No-shpa (analogs are Drotaverine, Spasmol). It works on drotaverine, is a myotropic antispasmodic, relaxes the intestinal muscles, is allowed in case of intolerance to M-anticholinergics. Features of use:
- Indications: spasms of smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract and urinary tract.
- Dosage: 1-2 tablets no more than 3 times a day.
- Contraindications: hypotension, lactation, pregnancy, renal, heart and liver failure.
- Side effects: decreased blood pressure, dizziness, arrhythmia, skin reactions.
- How to remove fat from the sides quickly, exercises and diet. How to remove fat on the sides at home, video
- Mackerel baked in the oven, stuffed. Detailed recipes with photos
- Self-massage of the prostate
Less well known are antispasmodics containing mebeverine (Duspatalin, Sparex), prescribed only for abdominal pain. They also have a myotropic effect, but do not cause a drop in blood pressure or affect normal intestinal motility. In addition to them, the anticholinergic Platifillin, used for spasms of smooth muscles of the abdominal organs and vascular spasms, or the combined drug Spazmalgon (containing metamizole sodium, pitofenone hydrochloride and fenpiverinium bromide) can be used as painkillers for poisoning:
- Pharmacological action: analgesic, antispasmodic.
- Indications: gastroenteritis, colitis, unspecified pain in the abdominal area.
- Dosage: up to 6 tablets per day, 1-2 per dose. After eating, drink water.
- Contraindications: heart, liver, kidney diseases, pregnancy, lactation, age under 6 years.
- Side effects: headache, tachycardia, urticaria.
Sorbents
The most important part of the treatment of poisoning is taking adsorbent drugs, which help remove toxins from the body, but they are drunk only in the absence of intense vomiting. Other medications can be taken no earlier than 2 hours later, since otherwise, in addition to toxins, beneficial substances will also be captured. The safest and most accessible adsorbent is white or black activated carbon (and drugs based on it: Carbactin, Sorbex), but more often gastroenterologists recommend Polysorb MP, on silicon dioxide:
- Pharmacological action: sorption and detoxification, binding and removal of exogenous and endogenous toxins, pathogenic bacteria, food allergens, heavy metal salts.
- Indications: acute and chronic intoxication of any etiology, intestinal infections, poisoning with toxic substances.
- Dosage: calculated individually, 0.1-0.2 g of powder per kg of weight with a frequency of up to 4 times a day, prepare the suspension exactly before use. Take the medicine 1 hour before meals.
- Contraindications: exacerbation of peptic ulcer, intestinal atony, bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Side effects: allergic reactions.
The disadvantage of Polysorb is the powder format, which requires dilution (the required amount is dissolved in 50-100 ml of water). Similar actions should be performed with the drugs Smecta and Neosmectin, which work on smectite and, in addition to adsorption, perform an antidiarrheal function. Paste-like Enterosgel (based on polymethylsiloxane polyhydrate) is more convenient to use:
- Pharmacological action: sorbs and removes medium molecular toxins, has a detoxification effect.
- Indications: acute and chronic intoxication of any etiology, intestinal infections, poisoning with toxic substances.
- Dosage: 22.5 g (1.5 tbsp.) with a frequency of 3 times/day. Daily dose – 67.5 g. Drink by stirring in warm water.
- Contraindications: intestinal atony.
- Side effects: nausea, constipation.
Restoring water-salt balance
Vomiting and diarrhea, being a natural reaction of the body to toxins, nevertheless contribute to the excretion of beneficial substances and fluids. Its volume should be replenished. During illness, the patient should drink a lot to maintain fluid balance .
Mineral water without gas is best suited for this purpose. To maintain electrolyte balance, it is recommended to drink water with a small addition of table salt (not sea salt). The solution is prepared from 1 liter of water and 1 tsp. salt. You should drink at least 2-2.5 liters of salted water per day. In this case, you need to follow a certain rule: a glass of water an hour before a meal, and after a meal you cannot drink for an hour. In this way, the stomach will be prepared for the next meal and will begin to secrete gastric juice correctly.
To restore the mineral balance, the use of the drugs rehydron and oralite (contain microelements, glucose and salts) is indicated.
In case of poisoning, you can also drink weak, sweet black or green tea, a decoction of chamomile or rose hips.
Drug treatment for poisoning
After cleansing the body, restorative therapy with probiotics is indicated to restore the intestinal microflora. The normal intestinal biocenosis after intoxication is almost always disrupted, therefore, after recovery, it is recommended to take medications containing beneficial bacteria .
These include “Hilak Forte”, “Linex”, “Bionorm”, “Bioflor”. If food poisoning is accompanied by fever, you should take antipyretic drugs (ibuprofen, paracetamol).
Self-medication is dangerous! Antibiotics, painkillers, as well as specific drugs (antiemetics and antidiarrheals, etc.) are prescribed by a doctor!
Therapeutic diet
During the period of acute intoxication, the patient, as a rule, does not feel the desire to eat. However, this does not mean that he should refuse to eat. A weakened body needs strength to fight the disease. In addition, the stomach and intestines cannot fully restore the epithelium ; without food this is problematic. Of course, neither an adult nor a child who does not want to eat should be forced, but hunger is not practiced specifically for medicinal purposes.
During poisoning, you should adhere to a strict diet, since the gastrointestinal tract does not work properly and cannot cope with large volumes of food.
During the period of poisoning, the following are prohibited:
- fatty, salty, heavy foods;
- fermented milk products, including milk;
- instant products, semi-finished products;
- alcohol;
- sauces, ketchup, mayonnaise;
- raw fruits, vegetables, berries;
- sweet.
You need to eat 5 times a day, in small portions. Food must be boiled or steamed. Fried foods are excluded.
The patient's diet should consist of:
- mashed potatoes with water, without oil;
- boiled rice;
- oatmeal, semolina porridge (with water);
- chicken meat;
- crackers, biscuits;
- low-fat broths.
It is allowed to eat bananas, as fruits enriched with nutrients, and watermelons, which have a diuretic effect.
What to do after intoxication
What to do after poisoning? When the symptoms of intoxication have already passed, it is important to restore the health of the body. First of all, it is necessary to restore the intestinal microflora, which can be done with Linex and Bifidumbacterin.
Nutrition and a properly composed diet are important. Fatty and fried foods, spicy foods, canned food, marinades, fast food, coffee, carbonated drinks and alcohol should be excluded from the menu. Preference should be given to low-fat broths, porridges and cereals, vegetables and fruits; vegetables can be stewed or baked. You are allowed to eat lean meat and fish. Fermented milk products will help restore intestinal microflora.
It is necessary to observe the drinking regime, drink a sufficient amount of clean water, you can also drink decoctions, jelly, and fruit drinks.
The next stage of recovery is to improve the condition of the whole body; during this period it is recommended to increase immunity, take a lot of vitamins, and do physical exercise. Sport improves blood circulation throughout the body, including the gastrointestinal tract, which improves the quality of digestive function.
In what cases is hospitalization necessary?
Food poisoning can be successfully treated at home, but in some cases qualified medical assistance is necessary. Hospitalization is indicated for children under three years of age. In children, treatment of intoxication should be carried out only under the supervision of medical personnel , since diarrhea and vomiting will very quickly lead to dehydration. It is almost impossible to force a small child to drink, and in the hospital he will be given intravenous rehydration solutions. Pregnant women and elderly people are also hospitalized.
Treatment in a hospital setting is indicated for:
- intoxication caused by poisonous plants and mushrooms;
- severe form of poisoning;
- diarrhea (more than 10-12 times a day);
- high temperature;
- diarrhea with blood;
- persistent vomiting;
- increasing symptoms of the disease;
- bloating;
- loss of consciousness;
- excessive weakness.
If any of these signs occur, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Rehabilitation period after poisoning
Any poisoning is stressful for all organs and systems. It is important to know what to do after poisoning. When discharged from the hospital, the doctor will give you recommendations on proper nutrition and outpatient treatment.
In the first 2 weeks, the patient should adhere to a diet, stop smoking, drinking alcohol, fried, smoked, fatty and spicy foods.
To restore the intestinal microflora, probiotics are prescribed - preparations that contain beneficial bacteria. If complications develop (gastritis, cholecystitis), they are treated.
Traditional methods of treating food poisoning
Nobody has canceled folk methods of combating intoxication, but they should be resorted to after consulting a doctor and only in cases of mild poisoning .
Cinnamon infusion
Cinnamon is a natural antispasmodic and natural absorbent. Cinnamon infusion is prepared as follows: pour a pinch of dried and crushed bark into 250 ml of hot water, let it brew for 15-20 minutes. Drink the strained broth in small doses throughout the day. Recommended volume is 1.5 liters.
Decoction of yarrow and wormwood
Brew 1 tablespoon of medicinal plants that effectively cleanse the stomach of toxins and pour a liter of boiling water. Let it brew for 15 minutes, strain. Divide the decoction into 5 equal parts and drink throughout the day.
Marshmallow infusion
You can use all types of plants - roots, flowers, leaves, as they contribute to a speedy recovery. Marshmallow (1 teaspoon of roots or 2 tablespoons of flowers and leaves) pour a glass of boiling water and leave for 4 hours. Drink 3 times a day. You can add half a teaspoon of honey.
Dill decoction with honey
Honey helps retain potassium, which is excreted during diarrhea and vomiting . Dill reduces abdominal pain, facilitates vomiting, and promotes the rapid elimination of toxins. Brew a teaspoon of dill seeds with 1.5 cups of boiling water, boil for 3 minutes. Cool, strain, add a teaspoon of beekeeping product to the warm broth. In case of food poisoning at home, the infusion should be taken at least 1 liter per day.
Vitamin complexes
Multivitamin complexes serve as excellent support for the body during treatment of poisoning at home. Can be used by both children and adults. Such complexes contain vitamins and minerals that are necessary for normal metabolic processes. When food poisoning occurs, the body is weakened and needs support. Detoxification mechanisms can be helped by taking such support vitamins. Common complexes:
Vitrum vitamins contain a complex of vitamins necessary for daily nutrition of the body. Made in the USA. Another complex, Alphabet, also contains all the necessary vitamins and minerals, but is produced in Russia and will cost less. The Doppelhertz series of multivitamins offers different complexes to support the body; you can choose the general one “from A to Zinc”, aimed at strengthening the body.
How to Avoid Food Poisoning
Preventive measures to prevent intoxication come down to observing the necessary hygienic procedures, eating only high-quality products, and their correct shelf life.
Expert recommendations:
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Process vegetables and fruits thoroughly.
- Do not buy products with damaged sealed packaging.
- Do not eat expired food.
- Do not hesitate to throw away cloudy drinks with sediment, foods with an unpleasant odor or taste, or ready-made meals that have been sitting in the refrigerator for more than three days.
- Eat only those mushrooms and berries that you are confident in.
- When preparing food, follow the rules of heat treatment.
- Boil homemade milk first.
- Drink boiled water.
- Eliminate cockroaches, flies, and rodents in your home - they are carriers of bacteria.
- Store raw and cooked meats on separate shelves in the refrigerator.
Follow these simple precautions and you will never experience food poisoning.
Reasons for the development of poisoning
Treatment will directly depend on the reasons that caused the unpleasant condition. In case of poisoning and diarrhea, assistance measures must be quick, clear and correct. Not everything depends only on the pills you take.
There can be many toxic factors. Most often, assistance must be provided due to poisoning:
- mushrooms;
- mercury;
- alcohol;
- paint.
If a person is poisoned, this can also be caused by uncontrolled use of pills or even the most ordinary foods. A poisoned person might not even think about how great the impact of expired food is, or how important it is to quickly put cooked dishes in the refrigerator. This rule especially applies to meat and dressed salads.
All vegetables and fruits can also cause food poisoning. To avoid this, you need to wash them thoroughly after purchasing, and pour boiling water over the greens. Since plant food is located close to the ground during the ripening process, it can become a source of infection by various helminths.
Poisoning and subsequent intoxication can be caused by improperly prepared meat and fish. Pathogenic microorganisms die only with complete heat treatment. Therefore, there is always a high risk of being poisoned by undercooked meat products or sushi.
What to look for?
Inedible or poisonous mushrooms can cause very severe poisoning. You should never try mushrooms raw or collect unknown or questionable types of product. The same rule applies to wild berries. Some can be poisonous, causing severe poisoning.
Symptoms of mushroom poisoning are usually pronounced, and in addition to the usual symptoms, hallucinations may appear. In this case, you should call an emergency ambulance and get medical advice.
What to do if poisoning occurs due to mercury entering the body? First aid for the victim is the same as for ordinary food poisoning. Before you start taking any medication, it is important to consult with your doctor.
In case of alcohol poisoning, it is also better to seek help from a hospital. Some types of alcohol toxins can cause death in large quantities. Timely medical assistance can save a person’s life and maintain health.
In case of paint poisoning, a person should be taken out into fresh air, given plenty of fluids and, if necessary, call an ambulance and get advice on what to do in such a situation.
We recommend: How to treat diarrhea if it occurs simultaneously with heartburn?
The same remedy for poisoning and diarrhea may be effective for treating one person and completely unsuitable for another. How to treat diarrhea after poisoning, taking into account the reasons that caused the condition? It is important to understand what first aid is needed for a person affected by toxic substances.