Causes
There are many reasons for bloating and gas formation, and they are not always pathological. Negative provoking factors can be:
- Products that stimulate gas formation:
- desserts, sweets;
- legumes;
- potatoes, mushrooms;
- radish, radish;
- cabbage, apples;
- dairy products;
- kvass, beer, carbonated drinks;
- flour, rye bread;
- products that are incompatible in a particular case (individual sensations).
- The concentration of enzymes involved in the process of breaking down food. The lack of substances is acutely felt with excessive consumption of protein foods. Excess protein and lack of enzymes are the cause of not only bloating, but also kidney pathology and intestinal flatulence. A feeling of heaviness, bloating, or distension after eating fatty foods also indicates a lack of enzymes.
- Physiological processes in a woman’s body can affect the state of the digestive system and cause bloating. High levels of hormones during menstruation, during menopause, lead to bloating. Moreover, stool disturbance occurs and constipation appears.
- Psycho-emotional shocks and stress lead to intestinal spasms followed by obstruction of accumulated gases.
- If the cause of impaired intestinal motility is dysfunction of the blood circulation, then exercise and diet can alleviate the symptoms and eliminate them completely.
- Chronic pathologies:
- pancreatitis;
- colitis;
- cirrhosis.
- Helminthic diseases.
- Imbalance of intestinal microflora.
Bloating and gas accumulation in the digestive system can cause everyday bad habits:
- conversations while eating;
- chewing gum;
- snacks on the go;
- violation of dental prosthetics technique;
- smoking.
Do not exclude the possibility of gas formation due to intolerance to lactose and milk sugar. You can get rid of flatulence and discomfort by eliminating the negative factor.
Bloating after eating
Most often, the cause of flatulence is poor nutrition. A person without signs of pathology swallows too much air along with food or supplies an abundance of gases along with the consumed soda. Discomfort may well be caused by poorly digested foods. The accumulation of food residues leads to the processes of rotting and fermentation. It is worth noting that when consuming coarse fiber along with sunflower seeds, vegetables, nuts and oats, the products must be chewed more thoroughly.
Causes and treatment of bloating in adults
Patients who suffer from this condition are concerned about the following question: what causes bloating?
There are many reasons for the condition in which, as people say, “swelling”. Here are the main ones:
Swallowing air or aerophagia
Excessive swallowing of air, both during and outside of meals, can occur when:
- hasty absorption of food, slurping, talking and laughing during the meal
- difficulty breathing through the nose
- sore throat with pain when swallowing
- diaphragmatic hernia
- hysteria, psycho-emotional shocks
- excessive salivation and swallowing (smoking, sucking on lollipops)
The main symptom of excessive air intake in this way will be belching, loud and sonorous. It can also bother you outside of meals.
Eating foods that cause bloating, often and in large quantities
Products that pollute the gastrointestinal tract include:
- legumes
- carbonated drinks, including alcoholic drinks
- milk
- baked goods and brown bread
- fresh fruits and vegetables
- mushrooms
- as well as any food to which there is an individual intolerance
When consuming the above products, fermentation processes actively occur inside the digestive tract.
For comparison, you can imagine a bottle of young home-made grape wine with a glove on the neck. What happens to the glove during active fermentation? She's bloated. The intestinal loops are also swollen from excessively produced gases.
Stressful situations
Banal stress can provoke flatulence. The increased release of hormones has a slowing effect on peristalsis, which is why the evacuation of air can slow down and its excess accumulate.
Dysbacteriosis
“Beneficial inhabitants” of the intestines - bifidobacteria and lactobacilli are responsible for order in the gastrointestinal tract and ensure that the “harmful inhabitants” do not actively reproduce. This maintains microflora balance and ensures good digestion.
But as a result of a decrease in the body’s immune forces, long-term use of antibacterial drugs, chronic infections, a shift in the balance occurs: the number of pathogenic microbes can increase sharply, and the number of beneficial ones can decrease.
The result of dysbiosis can be bloating, and not only that. Symptoms include stool disorders, nausea, pain, unpleasant taste in the mouth, and the appearance of pieces of undigested food in the stool.
Lactose intolerance
The enzyme lactase works to break down milk sugar or lactose into smaller subunits - monosaccharides. Only they are able to be absorbed into the blood and go to the needs of the body. Lactose itself is not able to penetrate the intestinal capillaries and the bloodstream.
With a deficiency or complete absence of lactose, milk sugar transits to the lower intestinal sections, where it becomes food for the microorganisms that inhabit them. Colon bacteria eat sugar and trigger active fermentation mechanisms.
Manifestations of this pathology, in addition to flatulence and rumbling in the abdomen, include loose, foamy stools, pain, nausea, and weight loss.
There is a congenital form, which manifests itself from early childhood, and an acquired form, which affects adults after infectious diseases, or with developing age-related enzyme deficiency
Celiac disease
A genetic enzyme defect that causes intolerance to the gluten protein found in cereals.
The clinical picture can be very bright, progressing after eating gluten-containing foods: frequent profuse loose stools, with an admixture of fat and mucus in the stool, sharp pain, rumbling, heaviness.
The disease can occur in a latent form, when excess air accumulation is the only clinical symptom.
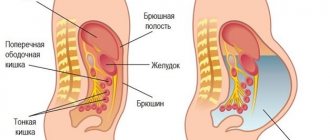
Chronic gastrointestinal diseases
The digestive tube cannot function separately from its sections and organs involved in digestion. Problems in the stomach will undoubtedly affect the functioning of the colon.
Chronic pathologies - gastritis, enteritis, liver and pancreatic lesions, intestinal colitis, infectious processes disrupt both motor and enzymatic activity, accompanied by excessive gas production and impaired gas removal.
IBS
The variant of irritable bowel syndrome with flatulence is one of several in the classification of this exclusion diagnosis. This disease is so named because it can be diagnosed only after a thorough examination and the absence of convincing evidence for organic disorders in the digestive system.
Stressful situations, poor diet, endocrine disorders, and physical inactivity can provoke the development of IBS.
Under the influence of provoking factors, an imbalance in the activity of the vegetative system, an imbalance of hormones produced by the digestive system is disrupted, and the processes of absorption and evacuation of the contents of the gastrointestinal tract are disrupted.
The clinical picture is dominated by bloating, pain, bowel dysfunction, neurosis-like manifestations (headache, feeling of lack of air, mood lability, irritability)
In case of IBS, pathological changes in laboratory tests, as well as signs of organic pathology, are not detected during instrumental examination.
Tumors
Formations of the gastrointestinal tract and nearby organs can mechanically prevent the passage of food gruel and gases. Impaired evacuation leads to symptoms and pain.
Symptoms
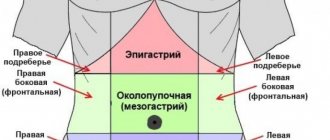
Subjective signs of bloating are part of the complex of symptoms of flatulence syndrome and are accompanied by the following disorders:
- bursting pain in the abdomen;
- increased volume of the peritoneum, severe bloating;
- belching – release of gases through the mouth;
- flatulence – uncontrolled release of foul-smelling gases;
- bloating and rumbling in the stomach;
- pain;
- a seething sound in different directions, either in the side or in the lower abdomen;
- a sharp deterioration in health after eating;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- pain in the heart due to displacement of the diaphragm;
- The stomach is very swollen.
It is worth noting that if the stomach is swollen and hurts, then this is usually a short-term phenomenon, indicating flatulence. An annoying sensation occurs when accumulated gas migrates through the intestines and releases in different places.
If the pain syndrome is persistent for a long time, this is a signal from the body about a disease not related to gases.
As a result of these symptoms, notice:
- psychoemotional disorder;
- feelings of guilt and shame;
- anxiety, anxiety, phobias;
- depressive state.
With the persistent nature of the disease, symptoms negatively affect the quality of life. A person becomes more tense, less sociable, and strives to change his lifestyle. This condition destroys family and social relationships. Constant bloating, bad breath, spontaneous belching and release of gases do not contribute to a full-fledged existence.
Bloating and nausea can be a sign not only of diseases of the digestive system; therefore, it is worth excluding physiological causes.
What diseases cause flatulence?
Flatulence can annoy an absolutely healthy person who regularly violates their diet. Hasty and insufficient chewing, talking while eating and overeating can cause an increased amount of gas in the intestines.
A feeling of heaviness in the abdomen is caused by excessive consumption of raw vegetables and fruits, bread and carbonated drinks.
However, such a condition may indicate the development of certain diseases:
- colitis;
- pancreatitis;
- dysbacteriosis;
- Crohn's disease;
- cholecystitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- neoplasms in the intestines;
- adhesions indicating inflammatory processes in the pelvic area.
Diagnostics
Before prescribing an adequate treatment method, the doctor must examine the patient’s medical history, clarify the presence of concomitant pathologies, and refer the patient for a series of laboratory tests. Only after determining what caused the bloating can we talk about therapeutic regimens.
For diagnostics use:
- general blood test for sugar, cholesterol, Helicobacter pylori;
- general urine analysis;
- laboratory examination of stool;
- X-ray;
- Ultrasound;
- colonoscopy;
- CT (computed tomography) of the peritoneum.
Treatment
Therapeutic regimens should be drawn up by the attending physician - a gastroenterologist. Initial therapeutic actions are carried out with enterosorbents. They tend to collect excess gases, absorb them and remove them from the body. One of the available remedies is activated carbon (1 tablet three times a day).
You should not use drugs of this effect for a long time, as they eliminate not only air bubbles, but also useful substances.
Medications
After determining the cause and establishing a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes medications for bloating:
| Group of drugs | Name of drugs |
| Enterosorbents | "White coal"; "Polysorb"; "Lactofiltrum"; "Polyphepan"; "Enterosgel". |
| Defoamers | "Espumizan"; "Simicol"; "Pepsan - R". |
| Enzymatic preparations | “Mezim – forte”; "Creon"; "Pancreatin"; "Micrazim". |
| Probiotics | “Hilak fotre”; "Bifidumbacterin"; "Linex"; "Normoflorin"; "Bifiform". |
| Herbal remedies | Dill water; Fennel tea |
- It should be noted that defoamers do not absorb gases, but promote their rapid removal. They do not cause intoxication of the body and are absolutely harmless even to children.
- Enzymatic drugs are prescribed for pancreatic dysfunction.
- Probiotics include a high concentration of beneficial bacteria. Through the drug, the barrier functions of the body are strengthened, the processes of decay and gas formation are stopped.
- Herbal medicines are plant-based medicines.
Drug treatment should be combined with physical activity and dietary nutrition. This way you can improve your metabolism and eliminate the possibility of gas accumulation. The feeling of bursting in the lower abdomen goes away after the air leaves the intestines, in any way possible.
Traditional treatment
Alternative therapeutic methods are an excellent means of prevention. When the disease worsens, when the stomach swells after eating, such measures are not very effective.
Important! Before self-medication, you should consult a doctor.
Helps with bloating:
- Carrot seeds (1 tbsp), pour boiled water (1000 ml) and leave for 12 hours without access to light. Consume before meals - 5 times a day (100 ml).
- Dill seeds (2 tsp), pour boiled water (400 ml), leave for 10 minutes. in a sealed container. Take three times, half an hour before meals.
- Caraway seeds (2 tsp), pour boiled water (200 ml), leave for up to 2 hours, strain. Drink three times a day, 50 ml (a quarter of an hour before meals).
Cumin seeds
Self-prepared medicines according to traditional medicine recipes also require caution. It is necessary to understand that medicinal preparations can be a source of allergic reactions. They are able to suppress or enhance the effect of the active substance of medications. When treating bloating, it is possible to aggravate the course of parallel pathologies.
Baking soda is an excellent remedy for bloating and gas, but it is not a panacea, but a temporary relief. In the future, the symptom becomes more pronounced.
Treatment for bloating
Abdominal bloating requires complex treatment, since it is necessary to eliminate not only the annoying symptom, but also the cause, otherwise the situation will repeat itself.
Any appointments must be made by a specialist - a gastroenterologist or therapist. As a rule, the standard regimen always includes taking enterosorbents, which allow the gases accumulated in it to be removed from the body as soon as possible. Since these drugs cannot independently distinguish harmful compounds from beneficial ones, they cannot be taken for a long time.
Depending on the patient’s medical history and the causes of bloating in the abdomen and intestines, non-toxic defoamers, used even at a very young age, enzymatic agents, and probiotics that restore damaged intestinal microflora may be prescribed. The specialist will also definitely recommend sticking to a diet for some time that does not burden the gastrointestinal tract.
It is very important to find the cause as quickly as possible in order to quickly alleviate the patient’s condition. Therefore, it is necessary to contact only experienced therapists and gastroenterologists. These are exactly the kind you will meet within the walls of JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) - a multifunctional medical center located in the very center of Moscow. The building is located at 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya Lane, building 10, next to the Mayakovskaya metro station.
Here they will quickly select a medicine for bloating that will specifically solve your cause, since the main principle of this clinic is an attentive and individual approach to each patient.
You can make an appointment for consultation, diagnosis and treatment by calling 24/7 +7 (495) 775-73-60 or using the feedback form on the medical center website.
Proper nutrition and diet
If you are prone to increased accumulation of gases in the hollow organs, if your stomach is very bloated, you should review your diet in detail. All products that stimulate foaming must be excluded. If they have nutritional value, it is worth choosing alternative, but less harmful ones. The menu for bloating should include the following products:
- meat of lean, dietary varieties;
- low fat fish;
- pumpkin, carrots and beets;
- warm drinks;
- lactic acid products;
- dried bread;
- dried fruits;
- soups, porridges (buckwheat, rice);
- greenery.
There should be at least five meals a day. Oversaturation in pathology is unacceptable. Doctors recommend keeping a food diary and eating strictly on time, following a diet for bloating. If you get sick, you should control the amount of water consumed - it should be at least 1.5 liters. Foods that cause bloating are completely excluded from the usual diet.
Bloating in the stomach
In adults, bloating is common and is mainly caused by poor diet, gastrointestinal dysfunction, or abuse of bad habits.
It also often causes a bloated stomach in women during pregnancy, especially in the later stages, which is caused by increased pressure on the digestive organs and disruption of their functioning.
If your stomach is constantly bloated and you are experiencing acute pain, you should visit a doctor to find out the causes of flatulence and, if necessary, begin treatment.
What are the causes of gas formation?
Constant bloating, discomfort and heaviness in the stomach often indicate serious problems in the functioning of the digestive system. Therefore, it is dangerous to ignore such symptoms or try to treat them with improvised means. The main causes of stomach bloating are:
- poor nutrition;
- swallowing air while eating;
- the predominance of hard-to-digest foods in the diet;
- disruption of the body’s secretion of an enzyme that is responsible for the complete digestion of milk protein;
- progression of gastrointestinal pathologies such as ulcers, gastritis, pancreatitis, cirrhosis, Crohn's disease;
- stress and chronic neuroses;
- some groups of medications that affect the level of stomach acidity and cause gas formation.
To successfully get rid of the problem, it is important to determine why your stomach is blowing. When the irritating factor is eliminated, bloating and stomach pain will disappear on their own.
Associated symptoms
With flatulence caused by indigestion, a person may experience nausea after eating.
Gastric flatulence, caused by a functional disorder of the digestive organs, is often accompanied by other uncomfortable conditions.
After eating, a bursting, painful sensation appears in the stomach area; a person is bothered by a burning sensation in the esophagus, nausea, and sometimes vomiting. If liver damage is observed, in addition to the stomach swelling, the patient is bothered by bitterness in the mouth, weakness, and the skin becomes gray-yellow. During menopause, a bloated belly indicates a hormonal imbalance.
An increase or decrease in estrogen levels causes fluid retention in the body and increased gas production.
In pregnant women, stomach discomfort and bloating are often observed after eating. In addition to the fact that a woman becomes bloated, she may experience an upset stomach or, conversely, constipation. In this situation, no special treatment is required. It is important to eat properly and avoid foods that cause excessive gas in the intestines.
Diagnostic methods
If a person has a very swollen stomach in the upper part, poor intestinal function and constant swelling, it is urgent to find out the causes of the discomfort and immediately begin to eliminate them.
The problem will be treated by a gastroenterologist; it is with him that you should initially make an appointment.
At the initial examination, the doctor will try to find out why the stomach is so swollen, and after that he will give a direction for a number of diagnostic tests, such as:
Gastroscopy is an effective diagnostic examination of the digestive organs.
- Ultrasound;
- gastroscopy;
- colonoscopy;
- radiography;
- biopsy;
- blood, stool, urine tests;
- a test that will show low or high acidity in the stomach.
Drugs
Once it is possible to find out what is causing the bloating and the discomfort, the doctor will prescribe a treatment regimen that will help relieve unpleasant symptoms and normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
If the stomach is swollen due to inflammatory processes in the stomach, antibiotics must be prescribed.
If there is a malfunction of the digestive organs, medications are prescribed that reduce or increase the production of hydrochloric acid, as well as those aimed at curing a particular pathology.
The following tablets are prescribed against bloating:
It is important to keep in mind that these drugs can only eliminate the accompanying symptoms, but they are not able to affect the cause of the bloated stomach. Therefore, comprehensive treatment under the supervision of a doctor is mandatory. It is possible to remove harmful substances and toxins from the body with the help of drugs such as:
Espumisan will help rid the body of toxins and harmful substances.
- "Smecta";
- "Espumizan";
- "Atoxil".
You can improve intestinal motility using the following means:
The following will help normalize the digestion process:
- "Pancreatin";
- "Mezim";
- "Creon."
Folk remedies
If your stomach is very swollen, and for some reason you cannot immediately visit a doctor, it is recommended to use useful, unconventional recipes, among which the most effective are considered:
- Dill water. Pour 250 ml boiling water 1 tbsp. l. plant seeds and leave in a warm place for 15-20 minutes. Drink this infusion throughout the day like tea, and your bloated belly will gradually return to its normal state.
- Cinnamon drink. If your stomach is very swollen and hurts, it is recommended to prepare a healthy cocktail from a glass of warm milk and a spoon of cinnamon, which is consumed on an empty stomach in the mornings and evenings. This spice is also added to tea, yogurt or fermented baked milk.
- Baking soda and apple cider vinegar. To prepare the drink, take ½ tsp. each ingredient and mix thoroughly in a glass of water. The drink is recommended to be consumed after 30 minutes. after the main meal.
It is important to keep in mind that using folk remedies as the main method of treatment is contraindicated. Only a doctor knows what needs to be done in case of bloating, and it is with him that the scheme of drug and auxiliary therapy is agreed upon.
Nutritional Features
In case of flatulence, it is necessary to exclude rich pastries from the diet.
If a person has a constantly bloated stomach, then, in addition to drug therapy, a therapeutic diet is necessarily prescribed, in which foods that promote fermentation and increased gas formation are excluded from the diet. The following foods cause flatulence:
- fresh bread and sweet pastries;
- pasta;
- legumes, corn;
- potato;
- raw vegetables and fruits;
- milk and fatty fermented milk products;
- carbonated drinks, beer;
- protein foods - meat, fish, meat broths;
- food containing soy;
- smoked meats, spicy, fatty and salty dishes.
Instead of these dishes, it is recommended to enrich the diet with such foods and dishes as:
- boiled or baked meat and lean fish;
- beets, carrots, pumpkin;
- cereals, except millet and pearl barley;
- dried fruits;
- vegetable soups;
- fresh juices;
- smoothies made from bananas, strawberries, wild strawberries;
- steamed scrambled eggs and omelet;
- herbal teas.
To normalize digestion, it is useful to drink at least one and a half liters of still water per day.
Regular drinking water, which is necessarily included in the treatment regimen, will help normalize digestion and the secretion of gastric juice. It is useful to drink at least 1.5 liters of clean water per day, or mineral water without gases. If the bloating is severe, you can sit on the water itself for 1 day, excluding all other food. It is acceptable to drink 3-4 cups of herbal decoction or infusion of chamomile, St. John's wort or mint.
Prevention
To prevent increased gas formation in the stomach, it is first of all important to improve your diet and get rid of bad habits such as alcohol and smoking.
Prevention of flatulence is considered to be timely treatment of gastrointestinal diseases and prevention of their progression to the chronic stage.
It will be possible to normalize digestion with the help of water, the daily amount of which should not be less than 1.5 liters per day.
Source: https://EtoZheludok.ru/ventri/simptomy/vzdutie-zheludka.html
How to quickly get rid of bloating
If your stomach is swollen and such cases recur from time to time, you should immediately contact a gastroenterologist. If the symptom manifests itself unexpectedly, you should resort to emergency medications and clearly understand how to quickly get rid of bloating.
Algorithm of actions when the stomach is very swollen:
- defoamers - drugs with a carminative effect that disperse accumulations of foam in the intestines;
- in acute cases, it is necessary to take sorbents to remove toxic compounds from the body;
- enzymes - drugs that stimulate the digestive system and eliminate the formation of gases;
- exclude products that have coarse fiber in their structure (radish, black bread, corn, legumes, apples, cabbage);
- a warm bath or heating pad on the stomach to relieve muscle spasms;
- abdominal massage - intense kneading in a clockwise direction;
- swimming, cycling, exercises to activate bowel function.
When performing physical activity, you should monitor proper breathing. It should be done through the nose. Exhale through the mouth. This way, excess air is not trapped. If bloating does not go away, you need to be examined by a gastroenterologist.
How to cure bloating and intestinal pain
The treatment tactics for this symptom will depend on many factors that the doctor pays attention to:
- patient age
- cause of clinical symptoms
- its duration
If pain and bloating appeared recently and bothered you for a short time, decreased or completely disappeared after the passage of gas and bowel movements, the patient can associate them with errors in nutrition - there is no good reason for concern.
The situation is completely different with regularly recurring, long-term disturbing symptoms.
Prevention
To exclude severe flatulence, you should know the causes and prevent their influence on the digestive system. First of all, it is recommended to periodically undergo routine examinations with a gastroenterologist, avoid stressful situations, and pay attention to the diet and diet. With a little attention to prevention, anti-bloating pills may not be necessary.
The following measures must be taken to prevent abdominal distension in the future:
- exclude foods containing coarse fiber;
- eat steamed, stewed, baked vegetables;
- eat food correctly, do not rush, do not combine eating with reading and other activities, do not swallow air with food;
- eat on time, at least 5 times a day;
- the interval between the last meal and sleep should not be less than 2 hours, thus eliminating bloating at night;
- include sports and walks in your usual lifestyle;
- refuse fast food.
It is important to listen to your body and if you experience frequent bloating or disturbances in the digestive process, you should consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Reasons for appearance
To successfully solve any problem, you need to know about the prerequisites for its occurrence. Having studied the causes of increased gas formation in the intestines, the following influencing factors can be noted:
- Flatulence is noted in patients with lactose intolerance. The phenomenon is especially pronounced when eating dairy products, even in minimal quantities.
- Unbalanced diet. Those patients who have composed their diet in such a way that it is dominated by the names of products that cause flatulence are tormented by gases. For example, dishes from legumes, white cabbage, potatoes, black bread. The same list can include fruits such as apples and grapes, pears. Lemonade and similar drinks promote gas release.
- Regular consumption of drinks that contribute to the occurrence of fermentation processes in the body: beer, kvass, kombucha.
- Often the causes of systematic gas formation in the small and large intestines are pathologies of the digestive system.
Let's look at some of the listed points in more detail.
Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and other organs
The causes of gas formation in this case are identified by examination by specialists in the field of gastroenterology. Often, flatulence is just one of the symptoms of more serious diseases and pathologies of the digestive organs.
Such diseases and conditions may be:
- Colitis.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Dysbacteriosis of intestinal microflora.
- Chronic pancreatitis.
- Enteritis.
- Acute intestinal infections.
- Gastrointestinal diseases of an inflammatory nature.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Postoperative intestinal motility disorders.
- Infection with intestinal parasites.
Gases in the human intestines indicate problems in the gastrointestinal tract, but the reasons may be related not only to the digestive organs. For example, constant stressful situations and nervous system disorders contribute to the appearance of malaise.
Sometimes gas in the stomach appears due to excessive haste in the process of absorbing food. In this case, a person involuntarily swallows air, which can cause discomfort in the intestines.
Incorrectly composed diet
The following reasons associated with improper eating habits cause the process of gas formation:
- Carbohydrate foods.
- Products high in starch.
- Foods enriched with dietary fiber.
- Soda and drinks that cause fermentation processes.
If everything is very clear with the last point, then with the previous names the question often arises as to why gases are formed. After all, all of the listed products are included in the diet of every person, and it is impossible to completely exclude them. The point is actually how much the product provokes strong gases in the stomach and its quantity.
Among carbohydrates, the most pronounced provocateurs are:
- Lactose found in dairy products.
- Sorbitol, which is part of almost all vegetables and sweet fruits. This substance is often used as a sweetener for dietary products, sugar-free chewing gum and sweets.
- Raffinose. The record holders for its content are legumes, cabbage, and asparagus. Slightly less of it is found in pumpkin, Brussels sprouts, artichokes and broccoli.
- Fructose. It also comes from most vegetables and fruits. The substance is widely used in the production of soft drinks.
Interesting! Increased gas formation in the stomach: causes and treatment
The benefits of dietary fiber for the digestive system have been well studied today. However, you need to choose the right type, some of them can affect the process of severe gas formation in the intestines.
Dietary fiber is found in all foods; they are divided into soluble and insoluble. The latter do not contribute to flatulence, and soluble ones (pectins) turn into a helium mass, the breakdown of which produces strong gases in the intestines.
The vast majority of starchy foods (corn, potatoes, beans and others), with the exception of rice, lead to the formation of gases in the human intestines.
Important! A sensitive attitude to your health, a proper diet in combination with the doctor’s recommendations (see below for treatment of systematic gas formation in the intestines) will help overcome unpleasant symptoms.