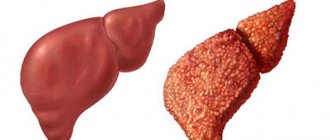
Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis includes a comprehensive examination of liver function: general blood test, biochemical, immunological blood tests, determination of markers of viral infection, hardware diagnostic methods. What is cirrhosis of the liver? This is a dystrophic disease that leads to the death of liver cells. As a result of structural changes in liver tissue, profound disturbances in its functions occur. Without diagnosis and adequate treatment, cirrhosis of the liver can cause death.
How to Diagnose Liver Cirrhosis
In order to promptly identify signs of liver cirrhosis, determine the prognosis of the disease and treatment, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination of liver function.
- The development of liver cirrhosis affects the condition of the entire human body. As the disease progresses, specific changes in the composition of the internal environment occur - blood, lymph, intercellular fluid.
- Blood counts in liver cirrhosis are a valuable diagnostic sign that allows you to determine the depth of the disorders, identify the cause of the pathology, and carry out differential diagnosis with similar liver diseases.
Laboratory diagnosis of liver cirrhosis
The following studies are used as laboratory diagnostics:
- a biochemical blood test that allows you to evaluate the functioning of the liver by the concentration of certain metabolic products, with the determination of: ALT, AST, GGT, protein fractions, lipids, enzymes, amino acids, hormones, TG, GGTP, urea, creatinine, alkaline phosphokinase, cholesterol levels with a lipid profile , glucose; coagulogram.
- general blood test is a standard technique that is carried out to determine the quantitative content of cellular elements and the chemical composition of the blood;
- immunological blood test;
- blood tests to determine markers of viral infection, ELISA, PCR.
- An additional diagnostic method may be a urine test for the content of bilirubin, urobilin, and PTI.
Hardware diagnostic methods
Modern hardware examination methods:
- Fibroscanning of the liver using a Fibroscan machine to determine the structure and density of the liver tissue.
- Dopplerography of the liver, which is performed simultaneously with ultrasound, in order to assess the condition of the hepatic vessels.
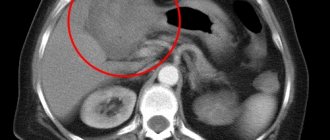
- Other methods of hardware diagnostics: CT, FGDS, radioisotope scanning of the liver, laporoscopy with biopsy, if indicated.
Basic examination methods
The patient usually consults a doctor if he notices yellowing of the skin, weakness, nausea or vomiting. The specialist prescribes laboratory and instrumental studies of the condition of the liver and body. Their results allow us to see the whole picture, to determine not only the pathology, but also the diseases that occur against its background.
Laboratory research
Every patient is curious about what tests show liver cirrhosis, and what needs to be done so that the doctor can make a diagnosis with high accuracy. Modern medicine uses the latest techniques that leave no room for doubt. Almost all of them do not cause discomfort and at the same time are highly effective.
It is important to know! Tests for liver cirrhosis are divided into several types: clinical, liver tests, biochemical, serological methods, coagulogram.
Everyone talks about the stage of the disease, the ongoing processes and helps to choose therapeutic tactics. A general blood test allows you to determine the presence of inflammation in the body, as well as to suspect the process of death of liver cells.
For cirrhosis, the decoding will be as follows:
- Decreased hemoglobin levels. Normally, it should be 120 g/l for women and 130 g/l for men.
- Increased white blood cell count.
- Change in protein composition.
- Decreased platelet count.
- A strong increase in blood clotting coefficient. Normally, in women it is 15 mm/h, in men 10 mm/h.
- Decreased albumin levels.
The condition of the urine is also taken into account. It will contain protein, which indicates serious pathological changes are occurring. Additionally, the patient will have to undergo stool testing to exclude the possibility of echinococcosis and identify undigested proteins, which indicate the development of obstructive jaundice.
Liver tests
An important blood test for liver cirrhosis, which is taken by all patients suspected of this pathology or hepatitis, is liver tests. Unlike other methods, this allows not only to identify the disease, but also to determine the cause with high accuracy. The main indicators of the presence of a process of active cell death in an organ are aspartate aminotransferases and alanine aminotransferases. When a person develops cirrhosis of the liver, a blood test will give results with higher values than those in the table.
| Index | Male norm | The norm of a woman |
| ALT (U/l) | ||
| AST(U/l) | ||
| Total bilirubin (µmol/l) | ||
| Protein (g/l) | 64-85 | 64-85 |
| Albumen | 35-55 | 35-55 |
| Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (U/l) | 10-70 | 6-40 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (IU/l) | 40-130 | 35-105 |
Liver tests must be taken on an empty stomach. The results obtained are deciphered by a specialist, who determines deviations from the norm in combination with other manifestations of the disease. ALT is a key blood indicator in liver cirrhosis. It begins to rise long before the first clinical signs develop.
Alkaline phosphatase indicates the development of malignancies or severe bile stagnation. It is assessed only in conjunction with other data, since an increased coefficient on its own is not a basis for making a diagnosis.
Biochemical analysis
Biochemistry for liver cirrhosis is a set of techniques that allows for a complete study of a number of key characteristics of the functional activity of internal organs. It allows you to identify liver problems by increasing basic indicators. It is prescribed along with other methods, as well as if the patient has itchy skin, changes in the shade of the whites of the eyes and skin, and discoloration of stool.
Biochemistry analysis for liver cirrhosis will give the following results:
- Glucose and total protein decrease.
- The levels of AST, ALT, GGT, and alkaline phosphatase are higher than normal.
- Increased bilirubin concentration.
- Decrease in the amount of Na and Ca in the blood.
- Increase in urea and creatinine levels.
At the initial stage, the latter coefficients may not even increase, this is due to the fact that they become higher with the development of complications such as renal failure, ascites, and systemic kidney damage. Normally, the indicators of a biochemical blood test, if there is no cirrhosis of the liver, are within the following limits.
| Index | Lower value | Upper limit |
| Bilirubin (mmol/l) | 8,5 | 20,5 |
| Aminotransferases (IU/l) | 7,0 | 40,0 |
| Gammaglutamyl transpeptidase (U/l) | 10 | 71 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/l) | 80 | 306 |
| Albumin (g/l) | 35,0 | 50,0 |
| Gamma globulins (%) | 12 | 22 |
| Prothrombin time (s) | 11 | 13,3 |
If the indicators increase, the doctor makes a conclusion about the presence of necrotic processes in the liver cells. Biochemistry is one of the most informative laboratory tests that allows you to identify inflammatory processes and diagnose cirrhosis. In addition to this, the patient is prescribed other research methods, the results of which are considered in combination.
Instrumental techniques
After contacting a specialist and undergoing laboratory tests, the doctor recommends that the patient undergo a series of examinations using modern medical technologies.
Such methods are the most informative and allow you to identify disorders even before the first symptoms appear. But they are prescribed only if there are serious reasons, since in the process the person most often receives a dose of radiation.
The most effective diagnostic methods are:
- EGDS. Used to study organs located in the abdominal area. With its help, hidden bleeding that may accompany the development of cirrhosis is determined.
- Ultrasound. A painless method that allows you to check the condition of the liver and the patency of the bile ducts. You can get results 15 minutes after the start of the study.
- Computer tomogram. A progressive technique that allows you to check the functionality of the organ and the operation of all systems. With its help, cirrhosis is detected, as well as regenerative processes in the liver. It is performed with or without contrast.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Biopsy. Allows you to find out what processes are occurring in the organ, identify biliary cirrhosis, and evaluate the dynamics of treatment. Under ultrasound guidance, a needle is inserted through the skin of the abdominal cavity. The technique is accompanied by unpleasant sensations and risks, so it is not always used, depending on the patient’s condition.
In addition to these methods, specialists resort to portomanometry, angiography, and radionuclide scintigraphy to determine the size of the liver, the degree of disturbance of blood flow in it, as well as the development of concomitant diseases.
Immunological studies
Immunological tests can determine the condition of the liver tissue, as well as the development of cytolysis syndrome or mechanical inflammation. They are based on the specific interaction of antibodies and antigens. With their help, hormonal imbalances are determined, as well as the development of tumors and other pathologies in the body.
Not all patients require such a study, only if the cause of pain in the right side is differentiated by other methods. In some patients, hepatocytes are destroyed by the body itself, mistaking them for foreign elements. In this case, only immunological tests can determine the cause of the development of cirrhosis.
Advice! Tests check for increased immunoglobulins and the presence of antibodies.
What can a general blood test show?
As a mandatory monitoring, during the initial examination of the patient, a general clinical blood test is performed, even in the absence of complaints. What indicators of a general blood test may be a reason for examination for liver cirrhosis:
- Anisocytosis in a general blood test is a condition of red and white blood cells when they change in size. Indicates that some pathological process is occurring in the body. May indicate liver damage.
- A decrease in the number of blood platelets below the established limit can also occur with cirrhosis of the liver.
- An increase in ESR in a general blood test can occur during inflammatory processes in the body or conditions accompanied by tissue decay, necrosis, and various poisonings. The patient may be developing liver disease.
- Leukopenia in a blood test is a decrease in the level of leukocytes, and is also a reason for examination for liver cirrhosis.
General and immunological blood tests
CBC is not a specific examination method for cirrhosis. However, it helps to identify the inflammatory process occurring in the body. Therefore, any diagnosis begins with a general blood test, including when cirrhosis is suspected. The analysis is done on an empty stomach. Blood is taken from a finger. In this case, the level of:
- Hemoglobin. It is significantly reduced in patients with cirrhosis. If a normal person contains about 120 grams of hemoglobin per liter of blood, then in a patient with cirrhosis this figure decreases several times, depending on the stage of development of the pathology.
- Red blood cells. These are red blood cells, which normally amount to about 4 million per 1 cubic millimeter of blood. If tissue changes occur, there is a significant decrease in the number of red blood cells in the blood.
Cirrhosis according to blood test
- Leukocytes. When a person experiences an inflammatory process, the concentration of leukocytes increases sharply.
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate). The ESR norm for men is 10 million per hour, for women – 15 million per hour. In the presence of inflammation in the liver cells or necrosis in the liver parenchyma, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases significantly.
This is a standard analysis that helps determine the presence of abnormalities in the functioning of the body as a whole. Additionally, a clinical blood test can be performed, which reveals the following indicators of liver dysfunction:
- the presence of antibodies to nuclear antigens indicates autoimmune hepatitis;
- detection of antibodies to the hepatitis virus determines the cause of cirrhosis;
- if ceruloplasmin is detected, the cause of cirrhosis is Wilson-Konovalov genetic disease;
- At the early stage of cirrhosis, in the presence of antimitochondrial antibodies, biliary cirrhosis is diagnosed.
A complete blood count is fundamental. This is where the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis begins. To make a more accurate diagnosis, a specific analysis is used - a biochemical blood test.
In some cases, immunological tests may be required. They help determine the qualitative and quantitative indicators of immunoglobulins – cells that are responsible for the body’s immune defense. In this case, the following immunoglobulins are examined:
- IgA is responsible for protecting the mucous membranes; in cirrhosis, its amount decreases.
- IgG determines the presence of viral liver pathologies.
- IgM, its increase most often indicates cirrhosis.
Biochemical blood test for liver cirrhosis
The initial stage of liver damage may be asymptomatic for a person. But protein components constantly circulate in the blood, formed during the reactions of breakdown and synthesis during the work of hepatocytes - liver cells. And the very first sign of the onset of cirrhosis is a change in the biochemical composition of the blood.
The following biochemical indicators have diagnostic value for signs of liver tissue damage:
- activity of the enzymes aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase (AST and ALT indicators);
- plasma alkaline phosphatase and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) activity;
- content of proteins (especially albumin) and blood clotting factors;
- concentration of bilirubin pigment, its direct and indirect fractions;
- concentration of specific antibodies (antinuclear and antimitochondrial).
- Not only the activity indicators of individual liver tests are taken into account, but also their relationship with each other.
Biochemical blood test
Indicators of a biochemical blood test for liver cirrhosis are more informative. They help confirm/refute the diagnosis, as well as determine the stage of organ damage. For biochemistry, blood is drawn from the ulnar vein. It is performed in the morning on an empty stomach.
Very specific changes are recorded in the composition of the blood. They relate to the following indicators:
- bilirubin – there is an increase in both fractions;
- transaminases - growth;
- gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase – growth;
- alkaline phosphatase – increases;
- albumins (proteins) – the level decreases;
- globulins – increase;
- prothrombin – decrease occurs;
- urea – decrease in indicator;
- cholesterol – reduction;
- haptoglobin – growth relative to normal;
- liver enzymes – increase.
Particular attention is paid to bilirubin levels, liver enzymes and changes in protein levels.
Bilirubin
When studying the test results, the doctor looks at the level of bilirubin. It is recognized as one of the most important indicators. It is its excess in relation to the norm that indicates inflammation of the liver and bile ducts. It is customary to distinguish direct and indirect bilirubin, as well as total, which is the combined value of both fractions.
The following indicators are the norm for a healthy organ:
- total bilirubin – 8.5–20.5 µmol/l;
- direct – no more than 4.3 µmol/l;
- indirect – not higher than 17.1 µmol/l.
What is bilirubin? This is a special bile pigment formed after the breakdown of hemoglobin and red blood cells. It is the liver that processes and transforms the substance.
In this case, direct (free) bilirubin enters the blood. But it circulates through the bloodstream for a short time. Free bilirubin, being a toxic substance, enters the liver, where it is neutralized.
Under the condition of normal functioning of the organ, free bilirubin in the blood contains a minimal amount that is unable to have a negative effect on the human body. Once in the liver, it binds and is thus rendered harmless.
Indirect bilirubin appears, which practically does not enter the general bloodstream. Then the substance in the bile is transported to the intestines and, together with feces, is excreted naturally.
Increased blood bilirubin is one of the main signs of liver problems.
With cirrhotic damage, the liver is unable to detoxify all direct bilirubin. And the stronger the damage to the organ, the greater the amount of indirect bilirubin detected in the blood. Outwardly, this manifests itself in yellowing of the skin and sclera of the eyes. In addition, the person experiences severe skin itching.
When liver cirrhosis develops, bilirubin fractions may exceed the permissible limits several times.
Specific liver enzymes
With the development of liver cirrhosis, the activity of both specific and nonspecific liver enzymes increases. But if an increase in the value of the latter can also occur in diseases of other organs, then specific liver biocatalysts increase only in the case of damage to liver tissue.
Nonspecific enzymes are considered:
Antibody test for hepatitis C
- AlT – normally does not exceed 40 IU;
- AST – should not exceed 40 IU;
- gamma-GGT - for the female group no more than 36 IU/l, for men - no more than 61 IU/l;
- ALP (alkaline phosphatase) – normally should not exceed 140 IU/l.
Aminotransferases - ALT and AST - are directly involved in the process of producing amino acids. The production of these types of kidney enzymes occurs inside cells, and therefore they are found in minimal quantities in the blood.
But with cirrhotic damage to organ tissue, accompanied by the breakdown of hepatocytes (liver cells), active release of aminotransferases occurs. And after entering the bloodstream, they are determined by performing a biochemical study.
Gamma-GGT is another enzyme necessary for complete amino acid metabolism. It accumulates in the tissues of the pancreas, kidneys and liver. During the breakdown of hepatocytes, it is also released in significant quantities into the general bloodstream.
With cirrhosis of the liver, deviations from the norm of both specific and nonspecific enzymes are observed
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is necessary to separate phosphates from molecules. The enzyme accumulates in liver cells and in cirrhosis, accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the organ cells, is released into the blood. There is a significant excess of indicators.
The list of specific liver enzymes includes arginase, nucleotidase and others. Deviation from the norm also occurs as a result of the active breakdown of hepatocytes.
Tests, ALT, AST, interpretation, normal
Enzymes found in the plasma of hepatocytes - alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase - can be released into the bloodstream in large quantities when cells are destroyed.
- In biochemical tests, this is expressed by an increase in the activity of ALT and AST. Indicators of the norm of aminotransferase enzymes:
- AlT – 5-33 IU/l
- AST – 7-40 IU/l
During the cirrhotic process, these indicators can increase several times, and the degree of their increase is proportional to the intensity of necrotic processes (excluding the terminal stage).
- A sharp decrease in enzyme levels with already established cirrhosis is an extremely unfavorable prognostic sign: this is how massive necrosis in the terminal stage of the disease affects blood biochemistry.
Biochemistry and death of hepatocytes
Biochemical screening for cirrhotic processes is more informative when compared with OAC. It helps to confirm or refute the doctor’s preliminary diagnosis and determine the stage of gland damage with an accuracy of 95%.
Blood is taken from a vein and must be donated in the morning, on an empty stomach. The analysis is done on a doctor’s referral at a public clinic, or in a private laboratory for a fee. The price of a minimum biochemistry profile is within 3,500, and the cost of an extended one is about 5,500 rubles.
In liver cirrhosis, the following indicators are determined: the level of bilirubin, GGT, alkaline phosphatase, albumin, globulins, prothrombin index, urea, total cholesterol content, liver enzymes, etc. Importance is given to changes in the concentration of bilirubin, protein substances and liver parameters.
Bilirubin
The dominant indicator, which indicates the functionality of the organ. Bilirubin increases in liver cirrhosis, which indicates an inflammatory reaction in the gland and bile ducts. There are direct and indirect fractions of the substance, as well as total bilirubin - it is represented by the sum of two fractions.
Normal bile pigment:
- The sum of the two fractions is 8.5-20 µmol/l.
- Direct fraction – up to 4.3 µmol/l.
- Indirect fraction – up to 17.1 µmol/l.
Bilirubin is formed in the human body after the destruction of red blood cells and iron-containing protein, and the liver is responsible for the breakdown process.
The free fraction enters the human blood, but does not stay there for long, because soon, due to its toxicity, it ends up in the liver, where it is neutralized. When the liver is functioning fully, there is practically no free form of bilirubin in the blood, and the trace amount that is present does not have a harmful effect.
Against the background of cirrhosis, indirect bilirubin is determined in the blood; normally, it should be absent from the circulatory system or present only in minute concentrations.
If the liver is malfunctioning, it cannot cope with the neutralization of free bilirubin, and its content increases. And the worse the gland functions, the higher the amount in the blood. So, in advanced cases, when there are complications (ascites, portal hypertension), bilirubin can be 400 µmol/l.
Enzymes of specific and nonspecific types
In liver cirrhosis, the activity of liver enzymes of specific and nonspecific types increases.
But if an increase in the latter type also develops with other ailments, then the former increase only with damage to parenchymal tissues.
Nonspecific enzymes include:
- ALS – the normal value is 40 IU.
- AST – up to 40 IU.
- GGT – for women 36 IU per liter, and for men up to 61.
- ALP – up to 140 IU per liter.
Indicators, ALT, AST are above normal
- A moderate increase in concentration (1.5-2 times) is characterized by fatty liver infiltration and chronic viral hepatitis.
- Liver cirrhosis is accompanied by a significant increase in enzyme levels, especially ALT, which is a symptom of liver tissue destruction.
- The average degree of increase in the indicator is considered to be an excess of 2-19 times compared to the norm, expressed by 20 or more.
- Comparison of the concentrations of ALT and AST is also of diagnostic importance; for example, a ratio of 1:2 indicates liver damage due to alcohol intoxication.
- To obtain reliable results, you must donate blood early in the morning on an empty stomach.
Changes in total protein levels in blood tests
Laboratory assistants, blood tests
- An absolute increase in the concentration of total protein in the blood serum, not associated with an imbalance of water balance, may indicate active chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver.
- An absolute decrease in the concentration of total protein in the blood serum occurs when there is insufficient intake or synthesis of protein in the body. And it can talk about hepatitis, liver cirrhosis or poisoning.
Bilirubin levels in a blood test
When hemoglobin breaks down, the pigment bilirubin is formed, a toxic compound that can easily penetrate cells and disrupt the course of fundamental chemical processes.
- There is a natural mechanism for its neutralization by converting it into an inactive form, during which bilirubin enters the liver tissue and binds to glucuronic acid on the surface of hepatocytes. The (direct) bilirubin bound in this way is excreted from the body.
- In a healthy person, the concentration of direct bilirubin does not exceed 4.6 µmol/l,
- indirect (unbound) – 17 µmol/l,
- total – 8.4 – 21.6 µmol/l.
Jaundice in liver cirrhosis, causes
Jaundice in liver cirrhosis
In the cirrhotic process, blood bilirubin levels can be significantly higher, due to the following reasons:
- inability to capture pigment by hepatocytes due to a violation of their integrity;
- violation of conjugation due to the necrotic process;
- disruption of the flow of conjugated bilirubin into the bile, resulting in it being sent back into the bloodstream.
- A significant increase in the concentration of bilirubin in cirrhosis is accompanied by the appearance of a jaundiced tint of the skin, and itching often develops.
- In severe (decompensated) disease, bilirubin levels may be above 100 µmol/l, which requires immediate medical attention!
Types of cirrhosis
Looking at blood counts in liver cirrhosis, or more precisely, at the content of bilirubin, prothrombin, albumin and others, one can judge the severity of the pathology. In general, it is determined according to the Child-Pugh scale, taking into account all indicators. The disease can be in an active or inactive stage as symptoms develop.
Liver cirrhosis occurs:
- Compensated. To treat this pathology, during which the protein-synthetic function of the organ is disrupted, it is worth identifying the cause and limiting physical and mental stress.
- Alcoholic. It develops against the background of alcohol abuse and is treated with hepatoprotectors and complete cessation of the bad habit. The prognosis is not always positive.
- Non-alcoholic fatty. It can occur against the background of hormonal disorders and can be treated with medications and a certain diet. The prognosis is mostly positive.
- Decompensated. It can cause severe complications (bleeding, ascites) and can be treated both conservatively and surgically.
Causes of liver cirrhosis
The most common causes of liver cirrhosis are:
- alcohol intoxication,
- harmful production,
- obesity,
- hepatitis of various etiologies. Viral hepatitis is especially dangerous.
During biochemical analysis, the activity and concentration of enzymes, antibodies, pigments, and whey protein fractions are examined. By the degree of increase in enzyme activity, one can judge the cause of cirrhotic changes.
- The appearance of specific antibodies in the blood indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the liver, which is always accompanied by an immune response.
- Blood biochemistry first of all makes it possible to assess the cause, intensity of pathological processes and their prevalence.
What tests help determine cirrhosis?
Many people ask what tests should be taken for liver cirrhosis. Most often, blood is tested, but for different indicators. A blood biochemistry test shows how, in general, the liver performs its functions, whether it copes with the job or not. An enzyme test shows whether an inflammatory process is present. It is inflammation that lasts for a long time that can lead to cirrhosis.
To clarify the diagnosis, elastometry (elastography) of the liver may be additionally prescribed. After the diagnosis, the doctor determines the degree or severity of the pathology on a scale from 0 to 4 points.
Urinalysis for liver cirrhosis
Determination of liver function by urine analysis
Biochemical and organoleptic indicators of urine also help in diagnosing liver pathology.
- The content of erythrocytes and leukocytes, protein molecules, and excreted bilirubin are examined.
- Normally, bilirubin in urine is not detected or is detected in small quantities.
- Its content, depending on the intensity of pathological processes, can range from 9 to 50 µmol/l. This condition is called bilirubinuria and is accompanied by severe darkening of the urine.
- The results of a urine test are evaluated along with a breakdown of biochemical blood parameters.
Determining the severity of the disease
To determine the stage of cirrhosis, the patient’s condition, and the choice of treatment tactics, the Child-Pugh scale is used. Thanks to it, you can make a life expectancy forecast. Conduct an assessment using the table.
| Index | 1 point | 2 points | 3 points |
| Encephalopathy | 0 | 1-2 | 3-4 |
| Ascites | — | Not pronounced | Tense, difficult to treat |
| Bilirubin (µmol/l) | Less than 34 | 34-51 | >51 |
| Albumen | >35 | 28-35 | |
| Prothrombin time | >60 (1-3) | 40-60 (4-6) |
Each of these indicators is assessed in points, after which they are all added together into one sum. If the obtained value is 5-6, then class A (compressed) is assigned; if the indicator is within 7-9, then class B (subcompressed); if the number is 10-15 points, then class C (decompressed).
If the patient is assigned class A, then his life expectancy will be approximately 15-20 years. Class C is considered the most severe, since the patient will live no more than 1-3 years. Mortality at this stage is 80%, at the initial stage 10%. By analyzing the condition, the feasibility of radical methods is determined.
Various tests and instrumental techniques allow the doctor to determine the degree of development of cirrhosis, concomitant diseases, and choose the appropriate treatment tactics. They are used not only for diagnostic purposes, but also to track the dynamics of therapy. If a tumor or complications are suspected, a comprehensive examination and biopsy may be prescribed.
Hardware methods for studying liver function
In addition to laboratory methods for studying liver function, instrumental methods are an important informative assessment of the degree of liver damage:
- Fibroscanning of the liver, or elastography, elastometry, is performed on a fibroscan machine and helps determine the structure of the liver tissue and its density.
- Dopplerography of the liver, which is performed simultaneously with ultrasound. This method allows you to assess the condition of the hepatic vessels and determine the degree of vascular changes, which often complicates cirrhosis.
- CT - computed tomography, radiography using a contrast agent.
These are accessible and non-invasive techniques that are highly informative regarding the stage of cirrhosis and other liver diseases and the prognosis of the disease.
What tests are performed?
Cirrhosis is a serious disease that results in destruction of the organ leading to death. The main causes of liver pathology include alcohol dependence, viral hepatitis, parasitic diseases, autoimmune disorders, and the use of drugs and substances of hepatotoxic properties.
If suspected, the doctor prescribes tests, especially the determination of blood counts when the patient complains of pain or discomfort in the right side, discoloration of the stool, darkening of the urine, and an unreasonable increase in temperature to the level of low-grade fever.
Blood tests for liver cirrhosis are divided into the following groups:
- Biochemical screening. It is important to determine the value of AST, ALT, bilirubin. They deviate from the norm even against the background of the early stage of cirrhotic processes.
- Enzyme research. It helps to identify the inflammatory reaction in the gland.
- Additional examinations (fibroscanning, ultrasound, etc.).
The diagnosis of cirrhosis is made based on a combination of test results and instrumental diagnostic methods. It is important to establish the degree of liver damage, the stage of the disease (initial or late), to differentiate the type of pathology - primary biliary, alcoholic, viral, etc.
Complications of liver cirrhosis
Ascites in liver cirrhosis
- A serious complication of liver cirrhosis is ascites, when the patient needs urgent help. Ascites is the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. A characteristic symptom of ascites is a pronounced network of venous vessels in the abdomen, which is called the “head of the jellyfish”,
- With modern medical technologies, ascites is treated without an incision, using stenting. A special stent is inserted into the vein, then it enters the portal vein, opens in the right place, and hepatic blood flow is normalized. The stent remains in place for life.
- Liver cirrhosis can be complicated by bleeding.
- Asthenic syndrome may appear.
- Hydrothorex is also one of the complications of liver cirrhosis.
- Encephalopathy due to liver damage. Conservative supportive treatment of liver cirrhosis can stop the clinical picture of encephalopathy.
Clinical signs of cirrhosis
Liver cirrhosis is one of those diseases that does not occur suddenly. Therefore, if you come to the clinic and tell the doctor that you need to get blood tests because you suddenly suspect cirrhosis of the liver, he will just shrug his shoulders.
Cirrhosis is not a sexually transmitted infection. In the case of sluggish chlamydia, a person may not feel anything, but blood tests can accurately identify a “bad” infection if the patient accidentally acquired it a few days ago.
Liver cirrhosis has been persistently presenting itself for a number of years. Long before the first signs appear, the patient has been treating various chronic disorders of the liver tissue for many years. They arise as a result of alcohol abuse, chronic viral hepatitis B and C, and autoimmune pathology. The patient has been treating the underlying disease for many years, and cirrhosis is its natural outcome. A person feels specific symptoms, malaise, and sees the reflection of his face in the mirror. There are symptoms that allow one to unmistakably suspect this pathology in most cases without any blood indicators in liver cirrhosis.
What are the symptoms of cirrhosis? The patient experiences the following symptoms:
- nausea, loss of appetite, rare vomiting, heaviness in the stomach, belching, bloating and intolerance to fatty foods are signs of dyspeptic syndrome;
- gradual but steady emaciation of the patient, up to cachexia;
- asthenovegetative symptoms, such as irritability and weakness, depression and insomnia, decreased activity and headache - as a manifestation of liver failure;
- endocrine disorders, such as decreased libido and potency, disruption of the monthly cycle up to complete amenorrhea;
- pain and discomfort in the right hypochondrium, which occurs when the enlarged liver capsule is stretched. They bother you in the initial stages, and then, when the liver decreases in volume during cirrhosis, this feeling of heaviness and pressure disappears;
- in the active stage of hepatic cirrhosis, there may be an increase in body temperature, even with chills and sweats;
- in case of liver cirrhosis, the patient is often diagnosed with jaundice syndrome, sometimes the sclera and oral mucosa are stained yellow, jaundice is especially pronounced in biliary cirrhosis, which is accompanied by stagnation of bile;
- patients with cirrhosis are usually pale, this is due to anemia, as a symptom of liver failure (with protein deficiency, there is nothing to build red blood cells from). Pallor is especially pronounced in advanced stages of cirrhosis, when bleeding from varicose veins of the esophagus develops;
- A characteristic symptom of cirrhosis is the appearance of spider veins - telangiectasia on the skin. Their sizes range from a millimeter to 1-2 cm. The pulsation of the stars can be determined by eye, and if the telangiectasia is small, then you can slightly pull the skin or press on it, and this pulsation will be detected;
- palmar erythema, or hepatic palms. This is the name given to the bright red, symmetrical color of the soles and palms;
- skin itching can accompany the course of cirrhosis, especially persistent, painful and at night;
- bleeding, increased bruising, nosebleeds, hemorrhagic syndrome;
- in advanced stages, the patient develops a hepatic odor from the mouth, which has a characteristic sweetish aroma that is felt by others. This is a violation of the metabolism of aromatic acids;
- significant enlargement of the abdomen with accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity, or ascites;
- finally, expansion of the veins in the anterior abdominal wall in different directions from the navel, which are called the “head of the jellyfish” symptom.
Patients with various forms of cirrhosis may also occasionally experience gynecomastia, testicular atrophy and hair loss, as a result of a complete “collapse” of the synthesis of steroid hormones, a bright red color of the tongue with a smooth and varnished surface (vitamin metabolism disorder) and other symptoms.
As a result, everything ends in psychoneurological disorders - hepatic encephalopathy, which is manifested by drowsiness, inappropriate behavior, disorientation of the patient in space, time and self, and these disorders are harbingers of the inevitable hepatic coma with subsequent death. The reason for this is the inability to utilize ammonia accumulating in the liver as the final product of protein metabolism. In cirrhosis, there are fewer and fewer full-fledged liver cells, the ornithine cycle, which converts ammonia into urea, which is excreted by the kidneys, begins to stop, and the brain is poisoned by toxic nitrogenous substances.
From this brief overview it is clear that the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis is based primarily on clinical symptoms, the patient’s medical history, and on instrumental and imaging studies, and liver tissue biopsy. But all symptoms are caused either by high resistance of liver tissue to portal blood flow, or by disruption of numerous liver functions.
We also suggest taking a short Liver Health Test, with only 12 questions.
Tests for cirrhosis show a very large number of various disorders, since the liver is, as mentioned above, the main chemical factory of the body. And yet, if the above symptoms are not enough, then how to determine liver cirrhosis by tests, or, more precisely, confirm all processes in the laboratory? Of course, the most informative is a biochemical blood test.