Classification
Normally, the liver parenchyma has a homogeneous, slightly dense structure. Its cells (hepatocytes) have a highly specialized, intense metabolism and react painfully to any negative factors. As a result, the gland tissues can swell, increase in size, and undergo dystrophic, sclerotic and other transformations, which causes diffuse changes in the liver. Their severity may vary.
The types of diffuse changes in the organ are as follows:
not pronounced diffuse changes in the liver - a condition in which the liver enlarges slightly. As a rule, the diagnosis is made in young children. If the baby does not have negative symptoms, no special treatment is prescribed. In most cases, this disease disappears on its own over time. If further enlargement of the liver occurs, then treatment is prescribed.- pronounced diffuse changes in the liver - a condition when the organ enlarges by 5 cm or more. Then the entire abdominal cavity is crowned, which catches the eye. The appearance of leukemia and hemoblastosis is possible.
- moderately pronounced diffuse changes in the liver - a condition when the liver exceeds its normal size by 2-2.5 cm. As a rule, negative symptoms do not haunt the patient in this situation. If you follow a certain diet and give up alcohol, the liver can return to normal on its own.
Thus, the severity of parenchymal transformations directly depends on the severity of functional disorders, inflammation or other pathologies that caused diffusion changes in the liver. Therefore, it is very important not only to identify and classify changes, but also to establish the main cause of their occurrence.
Diagnostic methods
The main method for assessing the nature of diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma was and remains ultrasound examination. The signs by which the doctor determines them can be either pronounced or moderate.
To some extent, diagnostics can reveal:
- All serious diseases, previously suffered or occurring at a given time. They leave noticeable marks on the organ, so the doctor will definitely see these pronounced signs of decomposition of certain areas of the liver.
- Moderate signs, as a rule, do not cause such serious damage, but are noticeable on ultrasound, and can be caused by viruses, poor diet, etc.
Using an ultrasound, the doctor determines the size of each lobe of the organ, its echogenicity, as well as the clarity of the contours and uniformity of the structure.
A competent specialist will immediately see diffuse changes in the organ from the echo, these include:
- Fabric of heterogeneous structure.
- Parenchyma with increased echo density.
- The size of the organ is increased.
- The pattern of blood vessels is disturbed.
- In different hepatic lobes, decreased and increased echogenicity is noted.
- Consolidation of periportal tracts.
- Rapid attenuation of ultrasound.
Only a competent specialist with knowledge in the field of physiology and anatomy can diagnose diffuse changes in the structure of the parenchyma of an organ, since this is a complex and labor-intensive process. Thanks to modern advances in the field of ultrasound, the possibilities of differential research have been significantly expanded. But sometimes such diagnostics alone are not enough, since pathological conditions can be quite serious, and morphological changes are not very pronounced.
Causes
The reasons for this situation can be very diverse, namely:
Presence of hepatitis;- Liver cirrhosis;
- Disruptions in the functioning of metabolism;
- Viruses and infections in the body;
- Cardiovascular system disorders;
- Damage to the body by parasites;
- Alcohol and drug abuse;
- Excessive use of certain medications;
- Kidney diseases;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas;
- Oncological diseases;
- Heredity;
- Presence of fatty hepatosis;
- Fibrous changes;
- Development of leukemia;
- Blockage of the bile ducts.
Pathology can occur in both an adult and a very young child. With diffuse changes, the liver becomes lumpy as a result of the proliferation of fibrous tissue. The organ ceases to perform its functions efficiently and enlarges as the disease develops.
Treatment of diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma
If we take into account that there is no change in the liver parenchyma as such a diagnosis, then treatment methods will be aimed at eliminating the disease that caused such a transformation. Once the cause is identified, the hepatologist will determine a therapeutic regimen and prescribe the appropriate medications.
As a rule, standard treatment methods include taking medications according to a specific regimen:
- If the changes were caused by viruses, then antiviral drugs will be prescribed to reduce their toxic effect on the organ. Etitotropic treatment for hepatitis comes down to the prescription of certain medications, depending on its type. It is also necessary to eliminate additional damaging factors, such as alcohol and other toxins. Hepatoprotectors are often prescribed that can “protect” hepatocytes. These can be drugs, both natural and synthetic, and also include amino acids, vitamins and phospholipids.
- Phospholipids are able to normalize the structure of the liver cell membrane, reduce necrosis of hepatocytes, as a result of which biochemical parameters are significantly improved.
- Drugs of natural origin have a stimulating effect on liver cells, due to which hepatocytes are restored; this effect is also achieved due to the choleretic effect of the drugs. The digestion process improves, the influence of harmful substances entering the body with alcohol, medications and food is significantly minimized.
- The action of synthetic drugs is varied and extremely complex; as a rule, they are prescribed for cancer.
- Amino acids help normalize liver function and replenish the deficiency of compounds it needs.
- Vitamins B and E are hepaprotectors and are often prescribed as part of a general liver treatment regimen.
In addition to following the treatment regimen, almost any liver disease that causes diffuse changes requires following a certain diet. The diet will need to be adjusted in a special way, as the doctor will correctly advise you on how to do this, but the main recommendations boil down to the following: exclusion of salt, seasonings, spicy, fatty, fried foods. Introduce fiber and potassium-rich foods into the diet. Naturally, depending on the nature of the disease, recommendations will vary in favor of certain products. But alcohol is strictly contraindicated in liver treatment, since in some cases it can not only reduce the effectiveness of the prescribed regimen, but also, in combination with certain drugs, lead to death.
If changes in the organ parenchyma are caused only by poor nutrition and alcohol consumption, then doctors recommend dietary table No. 5 according to the Pevzner classification, where fortified and protein foods predominate, as well as fermented milk products. Depending on the condition of the body, with diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma, immunomodulators and some liver preparations are also prescribed.
On the subject: List of the best hepatoprotectors for liver restoration
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of the disease can also be different and depend primarily on the causes of its occurrence.
One of the main signs that both the patient and the doctor can independently detect during examination is an increased size of the liver upon palpation. It is also possible to feel pain when pressing on the organ.
Additional signs:
the appearance of edema;- enlarged kidneys;
- attacks of nausea or vomiting;
- excessive fatigue;
- periodic diarrhea or, on the contrary, constipation;
- distortion of taste buds;
- intolerance to certain foods;
- heartburn;
- yellowish skin color;
- dark spots;
- discomfort in the stomach;
- the appearance of itching.
At the first symptoms of the disease, you should immediately consult your doctor.
Signs of the disease
Symptoms of reactive transformations of organ tissue are directly dependent on the reasons that led to their appearance. However, a large number of pathologies have similar symptoms. These include:
- Digestion problems. Patients experience heartburn and nausea, complain of a frequent urge to defecate and a change in the color of stool.
- Deterioration of the condition of the skin. Diffuse changes in the structure of the liver cause changes in skin color (yellowing), acne, lumps and papillomas. Often the pathology is accompanied by severe itching, allergic reactions, swelling of the skin in some areas and peeling.
- Formation of unpleasant plaque and cracks on the plane of the tongue.
- Various pains and discomfort are also a sign of the presence of changes in liver tissue. If the diffuse changes in the left lobe are small, then the pain is mild. Severe intense pain occurs when there is purulent inflammation, malignant neoplasms or injury in the cells of the organ.
- Increased sweating. In liver pathologies, the sweat produced has a pungent and unpleasant odor.
- Feeling of bitterness in the mouth. Usually appears in the morning, as well as after eating spicy or fatty foods.
- Increased fatigue, decreased performance and general weakness of the body also indicate problems with the liver. Patients report severe fatigue even after minor physical exertion.
- Frequent mood changes, severe irritability, headaches.
- Increased body temperature.
- Loss of strength in the walls of blood vessels, which leads to frequent bleeding.
Diagnostics
As we have already noted, diffuse changes in the liver can be detected during an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs - the gland will look heterogeneous, enlarged, have an uneven pattern of blood vessels and other characteristic signs. But to identify the cause of parenchymal transformations and make a final diagnosis, ultrasound alone is not enough. Therefore, diagnostics are carried out comprehensively, which involves the use of the following laboratory and instrumental methods.
General and biochemical analysis of blood and urine.- Liver tests.
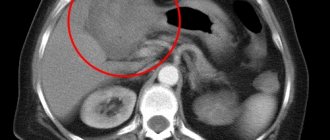
- MRI.
- CT scan.
- X-ray examination of the peritoneum.
Much attention is paid to collecting the patient's medical history. After all, information about the presence of diseases, lifestyle, and diet can help identify the root cause of transformations and accurately diagnose diffuse liver enlargement, which will greatly facilitate the choice of treatment methods.
Features of diagnosis and treatment
Typically, an ultrasound diagnostic doctor, describing the ultrasound results, notes the severity of hepatitis with a subjective assessment as a moderately expressed process, mildly expressed, moderately expressed. However, such an assessment cannot give an idea of the true condition of the liver .
To clarify the degree of liver damage, it is necessary to conduct an examination using the Fibroscan device. It allows you to determine the density of the liver tissue, which increases if there are any factors in the liver that destroy it.
Causes of diffuse changes
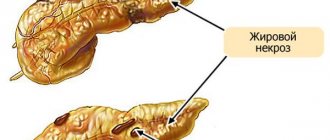
The most common causes of liver damage are hepatitis B and C viruses, as well as fatty liver disease (steatosis). In the case of viral hepatitis, the destruction of liver tissue occurs with its replacement by connective tissue and fibrosis is formed with subsequent progression of the process to cirrhosis. With fatty hepatosis, liver tissue is replaced by fatty tissue, which does not function like a healthy liver and can also lead to cirrhosis.
Diagnostics using the Fibroscan device (elastometry)
Unlike ultrasound diagnostics, which gives only a qualitative assessment of liver damage, the results obtained with the Fibroscan device describe the exact degree of fibrosis from 0 to 4 (4 - cirrhosis), and the exact degree of steatosis from 0 to 3 (3 - requires treatment, since it is threat of cirrhosis formation).
Liver elastometry - examination prices:
- Degree of fibrosis
3,500 rubles
- Degree of fatty hepatosis
2,500 rubles
- Consultation on results
for free!
on PROMOTION! (Moscow, Park Kultury metro station)
You can get tested:
- from 9:00 to 17:30 on weekdays
- from 9:00 to 15:00 on Saturday
Sign up by phone
+7
Seven days a week from 9:00 to 21:00
Request a call back
Treatment
Is it possible to cure diffuse liver changes? Let's start with the fact that it is not the changes themselves that will have to be treated, but the underlying disease that caused the pathology. Subject to successful treatment, the absence of complications, and compliance with recommendations regarding lifestyle and nutrition, minor and moderate transformations of the parenchyma are completely reversible. And in case of serious complications, organ transplantation is possible.
So, how are diffuse liver changes treated? Firstly, the cause of their appearance is eliminated. At the same time (or after this), restoration of the functions and parenchyma of the gland begins. Thus, treatment is carried out comprehensively.
Drug therapy to eliminate the root cause - taking antibiotics, antiviral and other drugs.- Hepatoprotective therapy is the use of natural remedies to protect and restore the liver.
- General strengthening therapy is a complex of natural remedies for cleansing and normalizing microflora, the body and the liver.
Symptoms
Diffuse damage to an organ of the hepatobiliary system is characterized by the absence of specific clinical signs that would accurately indicate the course of a specific disease. The symptoms of the disorder are pronounced and cannot be ignored.
Main symptoms of the disease:
- pain syndrome of varying degrees of intensity - pain is localized in the area under the right ribs;
- an increase in the size of the liver - hepatomegaly, which is easily detected by palpation of the abdomen;
- the appearance of a bitter taste in the mouth;
- loss of appetite and complete aversion to fatty foods;
- the appearance of a white, yellow or gray coating on the tongue;
- weakness and weakness;
- increased fatigue and decreased ability to work;
- emotional instability;
- attacks of headaches;
- nausea - present on an ongoing basis and practically does not cause vomiting;
- increase in abdominal size;
- release of large amounts of gases;
- discoloration of feces and dark urine;
- yellowness of the skin, sclera and mucous membranes;
- severe skin itching;
- rashes resembling hives;
- tendency to swelling;
- menstrual irregularities in women;
- decreased libido in men;
- fluctuations in blood tone values;
- unnatural shine and stench of feces;
- frequent exposure to colds and infectious diseases as a result of a weakened immune system;
- slight increase in temperature;
- exhaustion of the body.
Symptoms in adults or children are often supplemented by external manifestations of the underlying disease, which has caused diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma.
Diet
After the final diagnosis is made, the patient is recommended to adhere to a diet - as a rule, this is table No. 5. His diet includes a reduction in the amount of fatty foods and a rational ratio of proteins and carbohydrates. The following dishes may be included.
Lean meats.- Vegetables.
- Fruits low in sugar and acids.
- Low-fat fermented milk products.
- Lenten broths, soups.
- Whole grain porridge.
To quench your thirst, green tea or rosehip decoction without sugar, mineral water without carbon, decoctions of medicinal herbs with honey - chamomile, mint, calendula - are suitable.
Diffuse changes in the liver require increased attention. You need to be prepared for the fact that you will need to give up “snacks when and how you have to.” You will need to eat frequently, in small portions - up to 6 times a day. Food should be at room temperature or slightly warm. The preferred methods of cooking food are steaming, baking or boiling.
It is important to know! Fried, smoked, canned and spicy foods are not allowed. It is necessary to exclude from the diet all products with food “chemicals” - dyes, thickeners, stabilizers, preservatives, etc. Coffee, chocolate and especially alcoholic drinks are prohibited.
General symptoms
The problem is that the condition in question in the vast majority of cases occurs without any symptoms.
The following symptoms are very rarely observed:
- minor pain in the right side of the body under the ribs;
- you can feel the heaviness there;
- the skin around the eyes and their mucous membranes turn yellow.
Sometimes the pain radiates to the right forearm.
Diabetes mellitus is often the culprit of diffuse changes. In this case, the liver enlarges in all lobes, and the echogram also reveals:
- heterogeneity of structure;
- smoothness of blood vessels;
- increased echogenicity of tissues with noticeable attenuation deep in the organ.