Causes
The liver is the largest gland in the body. Its weight in an adult is 1.5 kg. The organ performs several important functions - it participates in digestion, blood circulation, and metabolism. The liver neutralizes toxins, secretes enzymes to break down food, and forms bile.
The liver can be affected by:
- Infections;
- Toxic substances;
- Circulatory disorder;
- Metabolic disease;
- Pathologies of the immune system;
- Diseases and disorders of the digestive tract.
Inflammation can be caused by:
- Congenital anomalies;
- Pathologically weak immunity;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Constant nervous shock;
- Alcohol, smoking, drugs;
- Hormonal disbalance;
- Bad ecology;
- Fried, spicy, fatty foods;
- Medicines;
- Endocrine pathologies;
- Obesity;
- Excess weight;
- Taking hormonal drugs;
- Viruses;
- Infection;
- Helminths;
- Injuries;
- Pregnancy;
- Age-related changes;
- Impaired flow of bile;
- Diseases of the pancreas, small intestine, gall bladder.
Conventionally, all unfavorable factors are divided into external and internal. Dealing with internal pathologies is much more difficult; the disease is often recurrent and leads to complications. In most cases, the influence of external factors can be eliminated, after which the liver is restored and fully performs its functions.
Signs of inflammation
The symptoms of acute liver damage are pronounced. A specialist can determine the presence of pathology by examining the patient and palpating. The organ increases in size, pain appears on the right side, yellowing of the skin and eyes is observed. However, the main task is to establish the root cause of hepatitis, for which instrumental and laboratory examination methods are prescribed.
The main symptoms of the acute form:
- Pain under the right rib of varying intensity;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Temperature increase;
- Weakness;
- Headache;
- Dizziness;
- Chills;
- Dark urine;
- Colorless feces;
- Diarrhea or constipation;
- Yellowness of the skin;
- Bitterness in the mouth;
- Itching on the skin as a symptom of impaired bile flow;
- Indigestion.
In the chronic course of the disease, there are no clear symptoms, but a general deterioration in well-being is observed.
- Decreased performance;
- Fast fatiguability;
- Irritability;
- Bad mood;
- Prostration;
- Sleep disturbance;
- Nausea;
- Muscle pain;
- Dryness of the epidermis;
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- Changing the stool.
With prolonged influence of negative factors, the inflammatory process recurs and exacerbations occur. In the absence of qualified assistance, the organ ceases to fully perform its functions, and complications are observed.
Nonspecific symptoms:
- Spider veins;
- Redness of the palms;
- Smooth, crimson-colored tongue without papillae;
- Yellowing of the eyes;
- Hand trembling;
- Flat growths on the upper eyelid;
- Breast enlargement in men;
- Hair growth disorder;
- Swelling of fingers, impaired flexion ability.
In each case, the clinical picture may differ, depending on the cause of inflammation and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Causes of the inflammatory process in the liver and symptoms
The liver is the largest gland in the human body; the weight of the organ in an adult reaches 1500 g. It is multifunctional - it takes part in the digestive process, blood flow, and vitamin metabolism.
The etiology of liver dysfunction is diverse. Factors - pathogenic microorganisms, toxins, circulatory disorders, metabolic processes, immune system ailments, gastrointestinal diseases.
Pathologies of the liver, gallbladder and biliary tract develop for the following reasons:
- Congenital anomalies.
- A sharp decrease in immune status.
- Physical inactivity.
- Nervous tension.
- Hormonal disbalance.
- Poor nutrition.
- Poor environmental conditions.
- Smoking, consumption of alcohol, drugs.
- Excess weight.
- Diabetes mellitus, parasitic diseases.
- Abdominal injuries.
- Use of antibiotics, hormonal drugs.
- Pregnancy.
- Viral infections, etc.
Conventionally, all provoking factors are divided into internal and external. And internal factors pose a greater danger, since they are harder to fight.
Clinical manifestations of inflammation in the gland
Acute liver inflammation has a clear clinical picture. The doctor may suspect an inflammatory process during a physical examination and palpation. Patients are diagnosed with hepatomegaly - the gland increases in size.
The main symptoms of acute liver inflammation include:
- Pain in the area of the liver projection of varying intensity.
- Nausea, vomiting, disorders of the digestive tract.
- Increase in body temperature.
- Feverish condition.
- Dizziness, headache.
- Changes in the color of urine and stool.
- Yellowing of the skin, whites of the eyes and mucous membranes.
- Bitterness in the mouth.
- Itching of the skin (this is a symptom of a violation of the flow of bile through the ducts).
Chronic inflammation will mean a sluggish process that does not manifest itself with pronounced symptoms, most often associated with a general deterioration in well-being:
- Constant fatigue, decreased performance.
- Unreasonable irritability, emotional instability.
- Periodically there are attacks of nausea.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Excessive dryness of the skin.
- Having an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Changes in stool.
Periodically, chronic liver diseases worsen, which leads to the appearance of clear signs of the disease. If there is no qualified help, the disease progresses, which is fraught with liver dysfunction.
Liver inflammation in some cases manifests itself with specific symptoms:
- Formation of spider veins on the surface of the body.
- Hyperemia of the palms (liver palms).
- Raspberry color of the tongue without visible papillae.
- Tremor of the limbs.
- Formation of flat growths on the upper eyelids.
- In men, breast enlargement occurs.
- Swelling of fingers.
In each picture, the symptoms are different, since they are determined by the etiology of the inflammatory reaction and concomitant pathologies.
Types of inflammation
Hepatitis can be caused by an unhealthy lifestyle, poor diet, as well as complex infections, viruses, and helminths. The symptoms are the same in all cases, but the treatment principle is somewhat different. The main types of liver diseases accompanied by an inflammatory process are as follows:
- Hepatitis;
- Cirrhosis;
- Cancer;
- Tissue infiltration;
- Functional disorders;
- Diseases associated with inflammation of the gallbladder and ducts;
- Pathologies due to disorders of the circulatory system.
Viral hepatitis
There are several types - A, B, C, D, E, G. The incubation period is from 2 weeks to 180 days. Infection with virus A occurs through dirty hands, food, and violation of basic hygiene rules. The rest are transmitted through blood and sexual intercourse. Acute symptoms last for about a week. With hepatitis A, it is possible for the body to self-heal and completely restore the liver. In other cases, the disease becomes chronic. The C virus is considered the most dangerous. Treatment lasts about 2 years, the total cost of the course is about 12 thousand dollars. Complications – cirrhosis, death. In 20% of cases, the virus is neutralized due to the work of the immune system. To prevent the disease, vaccination is carried out, and it is also recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, carefully select a sexual partner, and go for cosmetic procedures in salons with a good reputation.
Inflammation due to intoxication
This includes the effects of alcohol, medications, and household poisons. Most often, hepatitis occurs due to alcohol abuse. Alcoholic drinks gradually destroy liver cells and disrupt the functions of the organ. Poisoning occurs gradually, asymptomatically. The liver does not have pain receptors, so the first painful symptoms appear when the lining of the organ, the gallbladder, is involved in the inflammatory process. Acute tissue inflammation in the absence of qualified therapy and continuation of the usual lifestyle leads to fibrosis, then cirrhosis, and cancer.
Periodic intake of alcohol forms fatty degeneration. Unpleasant sensations arise like a hangover syndrome. Nausea, bitterness, heaviness on the right side, etc. Alcoholic hepatitis is difficult to treat due to the fact that the patient becomes dependent. After some time, he continues to drink alcohol, allowing the disease to progress.
Drug poisoning hepatitis rarely leads to cirrhosis. With the proper approach, liver cells are restored and inflammation stops. About 1000 types of medications can damage organ cells. A high risk of developing hepatitis occurs after long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal drugs, and antibiotics.
Inflammation of the liver in cardiovascular diseases
The main cause is heart failure, arrhythmia. Pathologies cause blood stagnation in the liver, oxygen starvation, cell destruction, and inflammation. As the disease progresses, fibrosis and cirrhosis appear. In the acute form of hepatitis, all the characteristic symptoms appear, as well as chest pain in the heart area, dizziness, changes in blood pressure, and weakening of the pulse.
Autoimmune hepatitis
The root causes of the pathology are unknown. The immune system does not perceive liver cells and tries to get rid of them. As a result, the functions of the organ are disrupted and the cells begin to change. The inflammatory process is present almost constantly. The therapy provides temporary relief and slows down the processes of tissue destruction. Hormonal drugs, hepatoprotectors and much more are prescribed.
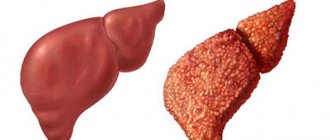
Inflammation as a symptom of cirrhosis
Severe liver damage occurs asymptomatically in the early stages. The inflammatory process is mild. Cell death occurs, tissues are replaced by fibrous compounds. The liver increases in size, ceases to perform functions, and gradually dies. The signs of cirrhosis are no different from acute hepatitis. The enlarged organ can be felt during examination. There is yellowness of the skin and eyes, confusion, dizziness, severe pain under the right rib, and a swollen stomach.
Inflammation of the liver, pancreas
Unique organs work in tandem. Liver pathologies cause pancreatic disorders and vice versa. The disease combines symptoms of diseases of one and another organ. Signs of indigestion are clearly visible:
- Heaviness in the stomach;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Belching bitter;
- Diarrhea or constipation;
- Heaviness after eating;
- Weakness;
- Fever;
- Loss of appetite;
- Rapid weight loss;
- Nervousness.
There is a hormonal imbalance. In women, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, in men, breasts become enlarged, testicular atrophy begins, and impotence appears.
Variants of the inflammatory response in the liver
Inflammation in the liver is detected against the background of hepatitis of viral and infectious origin, fibrosis, cirrhosis and a number of other diseases.
Hepatitis of viral origin
There are several types of hepatitis in medicine - A, B, C, D, E, G. The incubation period varies from 14 to 180 days. Virus A is transmitted through food, dirty hands, failure to comply with basic hygiene rules, and during sex. The remaining species are primarily transmitted through blood-to-blood contact during sexual intercourse.
Hepatitis A has a favorable prognosis, no specific treatment is required, and complications are rare.
When infected with other types of viruses, there is a high probability of a chronic course. The most dangerous virus is considered to be variety C. Treatment with antiviral medications takes about 2 years. In approximately 20% of cases, the human immune system defeats the virus on its own.
Intoxication as a cause of inflammation
Intoxication develops due to the consumption of alcoholic beverages, medications, and the influence of toxic and poisonous substances. The most common diagnosis is alcohol toxic liver disease.
Alcohol gradually destroys hepatocytes; in the early stages, symptoms of the pathological process are not observed. An acute inflammatory reaction against the background of lack of treatment and continuation of the previous lifestyle leads to fibrosis, then to cirrhosis and primary cancer.
Intoxication due to medication leads to toxic hepatitis, after which cirrhosis develops. If complex treatment is started on time - diet, use of hepatoprotectors, the prognosis is favorable.
Inflammation in cardiovascular pathologies
The pathogenesis of inflammation in the liver is caused by heart failure and arrhythmia. These diseases provoke blood stagnation, gland hypoxia, and destructive processes in cells.
Against the background of an acute form of hepatitis in pathologies of the cardiovascular system, all the symptoms are revealed, and there are additional signs - jumps in blood pressure, pain in the sternum, dizziness, and a decrease in pulse rate.
Autoimmune form of hepatitis
The root causes of the disease have not yet been established. The disease develops like this - the immune system perceives liver cells as foreign objects and produces antibodies that attack hepatocytes. All this leads to a transformation of the structure of parenchymal tissues, and severe inflammation develops.
Drug treatment with immunosuppressive drugs gives only a temporary result and inhibits the process of destruction of hepatocytes. The therapy is long-term and requires the use of hormonal drugs, hepatoprotectors and other drugs.
Inflammation as a sign of cirrhosis
In the initial stages of the disease, there are no symptoms. Inflammation is sluggish, leading to the death of hepatocytes and replacement with connective non-functional tissues. The patient exhibits hepatomegaly and the functionality of the organ decreases.
Signs of cirrhosis are similar to the clinical picture of acute hepatitis. The enlarged organ is easily palpated, and patients exhibit yellowness of the skin. People complain of pain in the right side, increased gas formation, bloating, and digestive disorders.
Acute hepatitis
The clinic is bright and brings a lot of unpleasant sensations to the patient. Symptoms bother you for about a week, after which the condition returns to normal. And this means that the disease becomes chronic, which can worsen at any time. In case of acute inflammation of the liver in women, the symptoms are pronounced, treatment should be started immediately to prevent serious complications.
Inflammation in acute hepatitis
A clear clinical picture is present at the acute stage. Unpleasant symptoms disturb a person for about a week, after which the condition returns to normal. However, if the effect of negative factors continues, the inflammatory process does not stop completely, the organ continues to deteriorate. Symptoms of chronic inflammation are felt, and a relapse can occur at any time.
Therapy is selected depending on the cause of the disease; antibiotics are often prescribed to eliminate pathogenic microflora, sorbents to remove toxins, and hepatoprotectors. The course of treatment is long and must be combined with a diet and a healthy lifestyle.
How to independently identify the first signs of liver inflammation at home?
It is difficult to diagnose pathology on your own. Often, signs of the disease appear only against the background of intense inflammation, while in the early stages there are no clinical manifestations. Less often, patients pay attention to mild symptoms, but they do not always associate them with inflammation.
Early symptoms include:
- Heaviness and pain in the side.
- Slightly elevated temperature.
- Decreased appetite.
- Mild nausea after eating.
- Vomiting in the morning.
- Weakness.
The described symptoms often occur against the background of other infectious diseases. However, such symptoms suggest an early stage of hepatitis development. In this case, it is advised to visit a doctor to confirm or refute the alleged diagnosis.
This is interesting: Signs, symptoms and treatment of liver inflammation with tablets and folk remedies
Diagnostics
The initial examination is carried out by a therapist. Draws up a clinical picture and palpates the abdomen. If liver inflammation is suspected, he is referred to a gastroenterologist or hepatologist. In small clinics, treatment is carried out by the therapist himself, who gives referrals for tests. Depending on the causes of the disease, consultation with an infectious disease specialist, surgeon, oncologist, or other highly specialized specialists may be required.
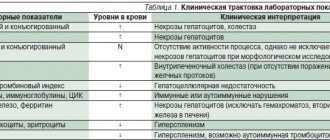
Laboratory diagnostics
It is necessary to take blood, feces, and urine tests. The most revealing is a blood test. As a result of the study, the presence of an inflammatory process, antibodies to viruses, infections, parasites and much more are determined. Full laboratory diagnostics include:
- Study of pigment metabolism;
- Urine bilirubin;
- Determination of the concentration of bile acids in bile;
- Study of protein metabolism;
- Coagulation system;
- Excretory function of the liver;
- Serum enzymes;
- Determination of cholinesterase, liver carbohydrate metabolism.
These studies make it possible to determine the presence of inflammation and pathological processes in the liver, but do not show the degree of damage and do not make it possible to determine the cause. The information obtained is compared with other diagnostic methods.
Instrumental examination
This can be done in several ways.
- Ultrasound. Ultrasound examination is the most informative, accessible, painless method. During the examination, the specialist determines the size of the organ, tissue structure, the presence of neoplasms, congestive processes, and the degree of liver destruction.
- CT. Computed tomography is prescribed to clarify the diagnosis. The technique allows you to see a three-dimensional image, clearly shows the pathological process, the presence of neoplasms, tumors, and tissue deformation.
- MRI. Magnetic resonance imaging is an additional diagnostic method that allows you to clarify details that cannot be traced in other ways. Be sure to prescribe for pathologies of the bile ducts. This is an expensive method, so it is prescribed in special cases.
- Radioisotropic scanning. It is carried out using x-ray irradiation, produces a two-dimensional image, and is less informative than other methods. Used if there are contraindications to other diagnostic methods.
- Biopsy. Using a special needle, material is taken directly from the liver for analysis. The method is necessary if viral hepatitis or oncology is suspected.
Additionally, gastroscopy may be prescribed to examine the digestive tract.
Drug treatment
Medicines are selected after confirming the diagnosis and establishing the cause of inflammation. In the case of viral hepatitis, drugs are prescribed to remove toxins from the body, drugs to improve digestion, and antiviral drugs. If helminths are present, the patient initially undergoes a course of antiparasitic drugs, then the function of the organ is restored. In case of violation of the secretory function of the liver, stagnant processes, choleretic agents are prescribed. Hepatoprotectors are recommended for any type of inflammation. The products restore cells, restore functions, remove toxins, and increase the body’s protective properties.
- Plant hepatoprotectors. Made from medicinal plants. They have a wide spectrum of action - they stop inflammation, restore cells, remove toxins, increase immunity, improve digestion, and normalize the flow of bile. Hepatoprotector plants – milk thistle, artichoke, chicory, demyanka, yarrow. Based on them, dietary supplements are made to treat the liver.
- Hepatoprotectors of animal origin. Produced in the form of capsules and powders. Stimulators of hepatocyte regeneration are obtained from the healthy liver of pigs and cows. The drugs are taken under the supervision of specialists; an allergic reaction is possible. Take with extreme caution in case of alcoholic hepatitis, viral hepatitis, liver failure.
- Essential phospholipids. The main building component of liver cells. Phospholipids compensate for the lack of their own enzymes and normalize the functioning of the organ. After a while, the liver itself will begin to reproduce all the necessary substances for proper functioning.
- Glycyrrhizic acid. Derived from licorice roots. The product has anti-inflammatory, regenerating, antibacterial, antioxidant, and antifibrotic properties.
- Amino acids. The drugs are effective in preventing inflammation and are also prescribed for the treatment of various diseases. The medicine is indicated for toxic damage, chronic processes, metabolic disorders.
Effective drugs:
- Alfarona. Antiviral, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory agent. Often recommended for viral hepatitis.
- Ademetionine. A drug for restoring the liver during alcohol intoxication.
- Viferon. Antiviral drug with a wide spectrum of action. Strengthens the immune system, helps the liver recover.
- Heptor. A drug from the group of antibiotics. Prescribed in the presence of infectious processes.
- Pegasis. Modern antiviral drug. Often included in complex treatment of viral hepatitis.
- Rabavin. A drug for the treatment of the most complex form of hepatitis C. It supports organ functions, restores cells, and eliminates the inflammatory process.
- Trivorin. An antiviral drug with an immunomodulatory effect.
- Euvax B. Hepatitis B vaccine.
- Phosphogliv. The combined agent includes glycyrrhizic acid and phospholipids. Prescribed for inflammation of various etymologies. Produced in the form of capsules, 50 pieces in a package, price 450 rubles. Contraindications include childhood, pregnancy, and individual intolerance.
- Rezalut Pro. Hepatoprotector with phospholipids, vitamin C. Especially indicated for fatty hepatosis and metabolic disorders. Side effects include diarrhea and an allergic skin reaction. Price for 50 capsules 800 rub.
- Essliver Forte . Contains phospholipids, a complex of vitamins. Supports the functioning of the diseased organ, increases protective functions, stimulates cell restoration.
- Hepatosan. A drug based on animal enzymes. Made from pig liver. Produced in capsule form.
- Karsil. The active substance is silymarin, which is obtained from milk thistle. Tablets should not be taken in case of acute intoxication. The course of therapy is about 3 months.
- Heptral. It is an antidepressant with hepatoprotective properties. Calms the nervous system, normalizes metabolic processes, accelerates cell restoration, and removes toxins.
- Ursofalk. A remedy for dissolving gallstones. Prescribed in the presence of liver pathologies in parallel with cholelithiasis. The course of therapy is long – up to 2 years.
- Ursosan. Made from rose hips. It has a pronounced choleretic property. Eliminates stagnant processes, improves the functions of the liver, gall bladder, and normalizes the functioning of the digestive tract.
- Berlition. A tool for improving metabolic processes. Prevents the accumulation of glucose in blood vessels, improves blood circulation. Stimulates the production of antioxidant substances. Prescribed for liver diseases of varying severity.
Drug treatment is carried out in parallel with dietary nutrition and a healthy lifestyle.
Treatment of liver inflammation
For viral hepatitis, treatment at home is impossible. Inflammation of toxic or autoimmune origin in mild forms is treated on an outpatient basis. For severe lesions, bed rest and treatment in a hospital are indicated. During therapy, complex measures are used: medications that eliminate the harmful factor, drugs to restore liver cells, as well as a special diet.
Diet and lifestyle
The liver is part of the digestive system, so diet affects its condition and the course of recovery. A diet for liver inflammation includes avoiding alcohol, spicy foods, marinades and sauces, fatty and fried foods, as well as coffee and other energy drinks.
All you can eat are low-fat soups, cereals, and some fruits and vegetables. Drinks allowed are weak tea, vegetable and fruit juices, and still mineral water. If you have chronic inflammation of the liver, you will need to stick to this diet for the rest of your life. If the inflammation is acute, it will be possible to return to your favorite junk food only a few months after complete recovery.
Physical activity is contraindicated during illness and rehabilitation. During the recovery process, you will need to perform special gymnastics under the supervision of a specialist, but this is the only permitted type of exercise.
Drug therapy
When treating hepatitis, doctors prescribe:
- Drugs to eliminate the cause of inflammation. These are antiviral, antiparasitic agents, and for toxic lesions - antidotes and sorbents.
- Hepatoprotectors – Phosphogliv, Essentiale, Heptral. These medications protect liver cells from toxic effects and accelerate the elimination of harmful substances.
- B vitamins. In severe cases, they are prescribed in the form of droppers, and in mild forms of inflammation, you can take tablets.
You cannot exceed the dosage of the drug and replace it with analogues yourself, because drugs have side effects and contraindications. After selecting a therapeutic regimen, you must continue to take medications until complete recovery.
Traditional and other alternative methods
There is no effective way to relieve liver inflammation at home. Among the folk methods, the use of decoctions of artichoke and milk thistle roots has a mild effect. To prepare them, you will need to pour a tablespoon of raw material with a glass of boiling water and let it brew for half an hour. Take half a glass of decoction before meals. To better cleanse the liver, you can drink 100 ml of carrot or pumpkin juice before each meal.
These methods do not replace full treatment. To eliminate the risk of side effects from such measures, you should consult your doctor before using them.
Traditional methods of treatment
To treat liver inflammation, medicinal herbs, seeds, and some foods are used.
- Corn silk
Efficiency is clinically proven. For treatment, decoctions and tinctures are used. The classic cooking recipe is 1 teaspoon. Pour a glass of boiling water over a spoon of raw materials, cook over low heat for 15 minutes, and let it brew for at least 30 minutes. Strain. Take a tablespoon every 4 hours. The folk medicine has choleretic properties, lowers cholesterol levels, normalizes blood circulation, improves the functioning of the digestive tract, and eliminates congestion in the liver.
- Turmeric
Natural hepatoprotector with anti-inflammatory effect. Stops the inflammatory process, helps liver cells recover, improves the functioning of the organ. A simple, effective recipe - 0.5 tsp. Mix spoons of turmeric with a spoonful of honey, throw into a glass of warm water. Wait 5 minutes, drink in one go. Repeat the procedure three times a day.
- Garlic
Natural antibiotic. Destroys pathogenic microflora, strengthens the body's protective functions, stimulates bile secretion, and increases cholesterol release. Garlic activates the movement of bile, which prevents the deposition of fats in liver cells. You need to take the medicine in doses, since excessive use leads to a decrease in blood pressure. A couple of cloves of garlic are cut into circles, placed in a glass, and filled with cold water. Let it brew for 12 hours. I drink it in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Oats
Cleanses the body of toxins and harmful substances, cleanses the blood, normalizes digestion, improves metabolic processes, increases energy potential, and saturates the liver with beneficial enzymes. Oatmeal, flakes, and oat grains have beneficial properties. The porridge cooks very quickly and the dish turns out delicious. Boil a liter of milk or water, add salt, a couple of tablespoons of sugar, a glass of cereal. Cook after boiling for 5 minutes, let it brew a little. Before serving, add butter.
Oatmeal decoction has the maximum therapeutic effect. Pour 150 g of oat grains into 1.5 liters of boiled water and cook over low heat for 20 minutes. Leave to infuse in a warm place for 3 hours. Drain the liquid and drink the entire portion throughout the day. The grains are used to prepare healthy dishes.
- Beets + carrots
Beetroot contains betaine, a fat solvent. Vegetables and tops are used for medicinal purposes. The products eliminate congestion, normalize blood circulation, and restore liver cells. In combination with carrots, beets remove toxins, nourish, cleanse cholesterol, and improve bile flow. Mix beet and carrot juice in a ratio of 1:10 or 3:10. Add a pinch of salt. Be sure to let it sit for 15 minutes. During this time, oxidative processes occur and some substances that are difficult for the digestive system are neutralized. For chronic stomach diseases with high acidity, the juice is diluted half with water. Treatment for diarrhea is prohibited.
- Pumpkin
Cleanses the liver, removes toxins, restores cells, stops the inflammatory process. In addition, pumpkin improves digestion, normalizes acidity, has a beneficial effect on pancreas function, accelerates the movement of bile, prevents obesity, and reduces cholesterol. Drink 0.5 cups of fresh pumpkin juice on an empty stomach. Drinking the drink daily will help you avoid problems with the liver, gall bladder, stomach, pancreas, and intestines. It is useful to crack pumpkin seeds and eat porridge from the pulp. Raw seed gruel with the addition of vegetable oil helps get rid of helminths.
- Honey with cinnamon
It has anti-inflammatory, healing, regenerating, and disinfecting properties. Improves blood circulation, eliminates pain, normalizes the functions of the digestive tract and liver. Add 2 tbsp to 0.5 liters of fresh honey. Spoons of cinnamon. Stir thoroughly. Eat 2 tbsp. Spoons four times a day before meals or 2 hours after meals.
STAGE 2: Fibrosis – beginning of liver scarring
Fibrosis is a condition in which healthy liver tissue is gradually replaced by scar tissue. Scarring leads to a decrease in liver function - the whole body suffers from this. The worse the liver cleanses the blood of toxins, the more they accumulate. A patient may have an allergic reaction out of the blue: people, not realizing fibrosis, go to a dermatologist with itchy skin, but what they need is a gastroenterologist.
This is because fibrosis is also not always obvious. It manifests itself through poor appetite, causeless rapid weight loss, and weakness. We wrote more about liver fibrosis and its symptoms .
At this stage, the liver can still be restored without loss of health. Enough changes in lifestyle (switching to a therapeutic diet Table No. 5 , increasing physical activity) and taking hepatoprotectors - medications to restore and protect the liver.
Essential phospholipids, milk thistle, UDCA. What do doctors think? There are several hundred hepatoprotectors on the Russian pharmaceutical market. Plant origin, animal origin, based on essential phospholipids and UDCA. Which ones are effective and which ones are not? Let's try to figure it out.
Diet food
During an exacerbation of hepatitis, you need to adhere to a strict diet; in the chronic course of the disease, you need to constantly follow the principles of a healthy diet. It is forbidden to eat fatty, spicy foods, a lot of sweets, and alcoholic drinks. They eat often, but in small portions; overeating and prolonged fasting should not be allowed. They prepare dishes by steaming, baking, boiling, stewing.
Prohibited products:
- Fatty pork;
- Duck;
- Goose;
- Eggs;
- Spices;
- Mutton;
- Mayonnaise;
- Ketchup;
- Cakes;
- Hot sauces;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Fried, salted fish;
- Smoked meats, sausages;
- Coffee;
- Chocolate;
- Cocoa;
- Candies;
- Cakes.
Allowed:
- Milk;
- Homemade yogurt;
- Sour cream;
- Cottage cheese;
- Kefir;
- Hard cheese;
- Rice;
- Semolina;
- Oatmeal;
- Still mineral water;
- Vegetable stew;
- Buckwheat;
- Vegetable and fruit juices;
- Berries;
- Pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds;
- Dried fruits;
- Nuts;
- Cracker cookies, shortbread;
- Stale bread;
- Butter, vegetable oil, olive oil;
- Chicken, lean pork, turkey;
- Stewed fish.
The daily diet should include first courses - soup, borscht, porridge, vegetables, fermented milk products, decoctions of medicinal herbs.
Diet
Liver restoration as a whole includes drug treatment, traditional medicine and the basics of proper nutrition. The diet for liver inflammation was created back in Soviet times. And it is used today in hospital treatment conditions. It is called “Table No. 5”.
Treatment must be supplemented with diet in order to support the liver and to prevent its diseases. In addition, it does not place additional stress on the organ.
In the diet of the acute period of the disease, porridges and soups with low fat content are prescribed. At this time you can eat:
- Gray bread.
- Low fat dairy products.
- Vegetables and fruits that have neutral acidity.
- The fish is strictly boiled.
- Boiled lean meat (turkey, rabbit, chicken).
- Buckwheat, oatmeal.
If you have liver disease, you should absolutely not eat fried foods, marinades, spicy foods, and mushrooms. Alcohol should also be avoided.
There are a few tips to follow to keep your liver healthy. Do not abuse alcoholic drinks and medications. Maintain good hygiene and never have unprotected sex. Get checked periodically, as the disease can be asymptomatic for a long time.
Prevention
The main preventive recommendations are to maintain a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, and discriminating sexual relations.
- Give up bad habits - alcohol, smoking, drugs;
- Do physical exercise, walk more;
- Follow the diet;
- Do not overeat, do not allow long periods of fasting;
- Strengthen the immune system in every possible way;
- Monitor hormonal levels;
- Do not abuse medications;
- Take vitamin complexes, natural hepatoprotectors;
- Maintain normal weight;
- Carefully select a sexual partner and lead a healthy sex life;
- Adhere to basic hygiene rules.
Seek help from specialists in a timely manner.
Prevention and diet
If doctors managed to eliminate liver inflammation, this does not mean that you can forget about the disease forever. To avoid relapse, the patient must adhere to the following rules of prevention:
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis on time.
- Get rid of bad habits.
- Do not use other people's personal hygiene products; this may result in hepatitis infection.
- Undergo routine examinations and tests annually.
- Play sports, take walks outdoors.
- Sex should be protected, especially if it is casual.
- If the symptoms of liver inflammation return, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Diet No. 5
The diet of a person with liver inflammation is special, this is diet No. 5. Such a table completely excludes the consumption of certain types of food. Thus, the following are prohibited:
- alcohol and soda;
- flour products;
- salt;
- canned food;
- meat and fish of fatty varieties;
- smoked meats;
- black tea and coffee;
- sausages of all types;
- semi-finished products;
- animal fats, strong broths;
- sour fruits and juices from them.
Some patients do not even understand what they should eat if a ban is imposed on almost all products. If you make an effort and imagination, then such patients can eat tasty and varied food.
Basic diet:
- Porridge.
- Fermented milk products with low fat content, cottage cheese.
- Vegetables and soups made from them.
- Fruits.
- Dried fruits.
- Nuts.
- Meat and fish are lean.
You cannot fry food; it is better to steam, boil or bake it. Food should be consumed warm and pureed. First courses and soups should be present in the diet every day. You can't overeat. You need to drink a lot of liquid, about two liters, these can be drinks in the form of herbal teas, fruit drinks, birch sap.