2070
0
Every year, approximately 300,000 cases of liver cancer are reported worldwide. The main problem is that cancer progresses quite quickly: the final stage can occur within a few months after the onset of the disease. Therefore, it is important to quickly diagnose the tumor and begin qualified treatment. This allows you to increase the patient’s life expectancy and improve its quality. In this article we will look at how this stage of cancer is characterized, how long people with this disease live, how it is treated and diagnosed.
Causes
A mutation in a tissue cell causes the development of a cancerous area. Scientists have not yet determined why this happens, but they have been able to identify factors that contribute to this.
The main causes of the disease:
- Chronic cirrhosis of the liver is the main cause.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Inflammatory processes caused by hepatitis viruses.
- Steatosis, fatty liver hepatosis.
- Eating carcinogenic substances.
- Exposure to mold fungi - aflatoxins.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Increased use of anabolic steroids.
- Working with hazardous chemicals (varnishes, asbestos).
- Bad ecology.
Symptoms
The first signs of the disease begin to appear in the second stage of the disease, but most people live ignoring them. Stage 4 cancer, unlike the initial stages, progresses more intensively. By this time, the disease affects not only most of the organ, but metastases occur in distant parts of the body.
Clinically, phase 4 of the disease is divided into 2 stages:
- Phase A: both lobes of the organ, the portal vein are severely affected by metastases. Nearby tissues, regional lymph nodes, and neighboring organs are also damaged by cancer spread.
- Phase B: Cancer cells spread through the blood vessels throughout the body. Metastases and tumors begin to appear in distant places and can be found in the lungs, brain, bone tissue, and genitals.
Symptoms become varied, lesions appear in other functional organs.
- The main symptom remains severe pain in the liver area, which can radiate to the back, lower back, or perineum. The pain is growing.
- The beginning of tumor disintegration and the appearance of toxins in the bloodstream provoke the appearance of liver failure.
- Lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, a constant feeling of heaviness, constipation, prolonged diarrhea and other problems with the gastrointestinal tract cause a sharp decrease in weight. Up to extreme exhaustion of the body - cachexia. Dysfunction of the digestive system.
- Fatigue, chronic weakness.
- Obstructive jaundice in cancer occurs due to increased pressure in the bile ducts. Its manifestations include severe itching of the skin, yellowness of the eye sclera, and yellow color of the skin.
Yellowed skin due to hepatic jaundice
- As the disease progresses, anemia is observed, initially partial and progressing to a severe form.
- The concentration of bile in the brain increases and encephalopathy may occur. The functioning of brain processes is disrupted. Depending on the affected area of the brain, various dysfunctions can develop: hearing impairment, loss of vision, loss of movement control, disorientation, difficulty speaking, memory problems, complete destruction of the psyche.
- The development of ascites (dropsy) occurs due to severe pinching of the collar vein by the tumor. A mass of fluid accumulates in the peritoneum. The quantity can reach 20 liters. If the exudate is not pumped out, there is a large load on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Shortness of breath, tachycardia, swelling of the limbs appear, and fatigue becomes even more pronounced. Ascites can lead to death.
- The daily volume of urine decreases. It takes on a dark color.
- Feces, on the contrary, are light in color.
- The severe condition of the body is not able to support the cancerous tumor itself, which causes it to decompose, which leads to heavy bleeding. Coagulation and protein metabolism worsen, and there may be bleeding from the nasal cavity and internal organs.
- If another organ is affected, there may be blood in the stool, pain in another localization, vomiting, cough with blood, and bluish skin.
- Low psycho-emotional state, the patient is in a semi-conscious state, with the absence of an active component of life, loss of ability to work. There are attacks of aggression, sleep disturbances, insomnia is replaced by drowsiness.
- Dehydration begins - this is dry, sagging skin.
- A vascular network and hematomas appear on the skin.
- Body temperature rises to 39 degrees.
The last stage of cancer is extremely difficult for the patient; it is not always possible to successfully fight the pathology, but it is possible to increase life expectancy and improve well-being. All symptoms intensify before death.
Diagnostics
To establish an accurate diagnosis, a complete examination of the patient is required. First, they find out complaints, life history, pay attention to nutrition, bad habits, and concomitant diseases.
The doctor then performs a physical examination of the body. During the examination, if a dense, enlarged, painful liver is detected, he writes a referral for diagnostics in the laboratory.
Laboratory testing includes:
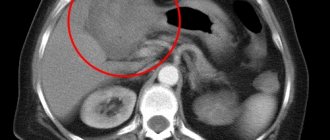
- Ultrasound of the liver. Scanning allows you to quickly identify the affected area with metastases.
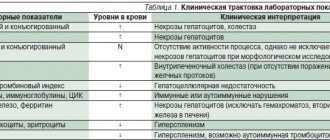
- General and biochemical blood test.
- Alpha-fetoprotein tumor marker tests.
- A diagnosis of increased bleeding is carried out - a coagulogram.
- Biochemical analysis of increased levels of transaminases, decreased protein, and the amount of bilirubin.
- For thorough visualization, tomography, magnetic resonance or computed tomography is performed. Thanks to this, the size, structure and location of the tumor are known.
- Biopsy. Under ultrasound control, a puncture of the affected tissue is performed for histological analysis.
- To resolve the issue of the possibility of surgical treatment, diagnostic laparoscopy is performed. With multiple magnification, the doctor assesses the spread of the malignant process.
- It is possible to prescribe radiography, fluorography, and scintigraphy to detect individual metastases.
Lifespan
Stage 4 liver cancer is a very serious disease, and no doctor would dare answer the question of how long people live with it. We can only cite statistics that say that less than six percent of all patients survive five years. But this is by no means a verdict in each specific case. Here, much depends on the patient’s age, the body’s ability to respond to therapeutic measures, and finally, on the patient’s mental status.
In addition, serious medical literature describes several cases when the oncological process was suspended and remission began. Therefore, when a diagnosis of “stage 4 liver cancer” has been established, it is very difficult to answer the question of what the life expectancy of patients is - everything is decided by the individual characteristics of each individual person.
Unfortunately, there are currently no guaranteed ways to cure stage 4 hepatocellular liver cancer, but there is a possibility of reducing the rate of tumor growth, and therefore extending the life of patients.
Treatment
The fourth degree of malignancy is incurable. However, a lot of drugs have been created to alleviate the condition and prolong the life of the patient. The oncologist in most cases offers palliative treatment.
Transplantation or surgery have low effectiveness, since the presence of metastases and secondary tumors in certain areas of the body worsens the picture of recovery. Surgery is used only to remove the main lesion. To reduce the growth of the tumor, embolization of the vessels feeding it can be carried out.
Palliative therapy does not provide a complete cure, but involves containing the progression of the disease. The goal is to reduce pain and the manifestation of secondary symptoms, as well as increase the functioning of important human organs. Great attention is paid to the functioning of the heart, kidneys and brain. They try to treat the remaining metastases with chemicals.
Therapy includes:
- Prescription of narcotic analgesics. Reducing pain is the main goal.
- Maintenance nutrient solutions.
- Albumin if hypoproteinemia is observed.
- Blood transfusion to control anemia.
- Antiemetics.
- Plasmapheresis to combat intoxication and cleanse the blood.
- Ultrahemofiltration.
- Hemosorption.
- Drugs to reduce blood clotting.
- Medicines to prevent heart attacks and strokes.
- Chemotherapy, if the body is able to withstand it.
Traditional methods for cancer are ineffective and useless; relying on medicinal herbs at stage 4 is pointless. Folk remedies help to slightly improve the condition and slightly delay death.
Chemotherapy treatment should be described separately. The introduction of drugs into the blood gives positive results. The effect spreads to most of the body, entering every molecule with the blood. Chemotherapy is an effective treatment measure in the final stages of this cancer. The downside is intoxication, which is why it is not actively used by oncologists. Due to illness, a patient cannot always withstand the load of chemical intoxication, because he is already severely weakened, exhausted and dehydrated. Doctors can use it in small doses, but the potential result will then be greatly affected.
Treatment of stage 4 liver cancer
Carcinoma with metastases is not operated on; the main treatment is chemotherapy. The first of several drugs is sorafenib, which can increase life expectancy. The drug is taken for a long time - as long as there is benefit from it and complications of treatment allow it. In some cases, it is possible to reduce the dose - reduction. It is still not clear under what characteristics of the tumor one can hope for a good result, and when chemotherapy should not be prescribed.
If the disease progresses on sorafenib, regorafenib is recommended, which also added several months to the life of clinical trial participants.
Other cytostatics, alone or in combination, manage to help only every fifth patient, so they are used when the disease progresses or cancer cells are resistant to the first two drugs, and only when the patient is in good health.
At stage 4 “local spread” and without distant metastases, at the first stage the possibility of surgery is considered, primarily resection, or removal of the liver with transplantation of a donor organ.
While waiting for transplantation, chemotherapy with sorafenib and local techniques are offered: chemoembolization (TACE), radiofrequency ablation (RFA), injection of ethanol into the tumor, cryodestruction. It is possible to combine several local methods in different sequences and repeatedly.
If it is impossible to remove the liver due to the growth of a cancerous conglomerate into large vessels or the diaphragm, intimate adhesion to vital organs, and concomitant complications of cirrhosis, only symptomatic therapy is possible.
Nutrition and care
A person with liver cancer at the last stage has a depleted body and obvious liver dysfunction. The gland cannot cope with cleansing the body of toxins and harmful substances. Therefore, the diet is organized in such a way that there is enough strength to fight and maintain vital functions. And the heart, kidneys and brain could function as long as possible.
Proper diet therapy is of great importance; easily digestible foods are selected that promote the absorption of toxins and the excretion of bile.
Particular attention is paid to caring for the sick, since at this stage a person cannot care for himself. At this moment, the help and support of those around you is important.
Let's describe the components of care and nutrition:
- The food should be light. In frequent, small portions, in a liquid porridge-like consistency. More than seven times a day. This will reduce the load on the digestive tract.
- The diet should be enriched with microelements to improve immunity. Wheat is suitable for these purposes, even in sprouted form.
- Increase your consumption of greens, vegetables and fruits. This rule does not apply to tomatoes. It is advisable to first remove the peel from the products.
- Stimulation of digestion is required. You should eat raw vegetables before meals.
- Rice, buckwheat, and oatmeal will provide fiber to a fading body.
- Light broths and soups are welcome in the diet.
- Using fish for cooking.
- Omelette is allowed, but not more than 10 times a month. Helps fight weight loss.
- Dishes are prepared by steaming; boiling, stewing, and steaming are allowed.
- You are allowed to drink herbal teas, compotes, and fruit drinks. Drinking carrot juice on a daily basis helps cleanse liver cells. Sour milk fights the elimination of toxins.
- It is better to replace sugar-containing products. A substitute can be honey, jam or marshmallow.
Strictly prohibited:
- chocolate;
- coffee;
- black strong tea;
- cakes;
- spicy seasonings;
- fried foods;
- semi-finished products;
- fats;
- nuts;
- legumes;
- smoked meats;
- drinks with a lot of sugar;
- do not consume products containing dyes, food additives, antioxidants, preservatives. All harmful substances enter the liver, destroying the gland even more. Naturally, alcohol-containing drinks are prohibited.
The patient needs regular support for body cleanliness, breathing exercises and communication. The support of relatives is important at such moments.
Most often in the latter form the person is lying down, so you should turn over on the bed more often, stretch your body and limbs, and wash them to avoid the development of bedsores. If red spots appear, then use talc, camphor oil or the drug Desitin. Raise the headboard and pillows to improve breathing. Frequent drinking is required; if the patient refuses, wet his lips with water.
Nutrition for a terminal patient
Malignant tumor growth significantly affects many biochemical processes in the body. First of all, this applies to the digestive system. Therefore, it is so important to choose the right diet and menu for the patient. Food itself does not affect the course of the disease or the rate of tumor growth, but it can improve your well-being.
A big problem can be the patient's reluctance to eat. Liver cancer is characterized by a sharp decrease in appetite, and the last stage is its complete absence. It is not recommended to artificially induce the desire to eat using special preparations: firstly, they are useless, and secondly, they can cause irritation of the oral mucosa. Therefore, whenever possible, the patient’s dietary preferences must be taken into account.
It is important to know! Adequate nutrition for stage 4 liver cancer is difficult, since the patient must be provided with all the necessary substances and calories with a significantly limited list of permitted products.
The patient should eat not much, but often, and only easily digestible foods should be included in the diet. Food must be served warm. The menu is designed so that it contains enough carbohydrates, and the amount of proteins and fats in the terminal stage is reduced. It is important to remember about vitamin-containing foods. Food should be boiled or steamed.
Forecast
At this phase of the disease, the prognosis for life is unfavorable. There have been cases where people with this diagnosis lived for five years, but this is 5% of the number of patients. Most patients die within two years. If the progression is fleeting, the patient has six months to live.
The life expectancy of a cancer patient depends on the composition of the tumor, age, care, and treatment method. Also, a lot depends on the stage at which treatment began, so it is recommended to undergo medical examinations more often, monitor your diet and get rid of bad habits. These methods will help prolong your life.
Features of patient care
Caring for a seriously ill patient requires great patience and accuracy. It should be remembered that the majority of the patient’s painful symptoms are caused by intoxication. Toxic products are eliminated through the skin and mucous membranes, so they must be kept clean. If the patient’s condition allows, then it is necessary to take baths every day, but if this is not possible, then daily wet wiping of the body is necessary. Bed linen, like underwear, should also be changed every day. It is important to monitor not only nutrition, but also bowel movements. If there is no stool, enemas are given.
Advice! Considering the length of stay on bed rest, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the skin of the bedridden patient. When foci of necrosis appear, the affected areas are treated with a concentrated solution of potassium permanganate.