What is hepatic steatosis?
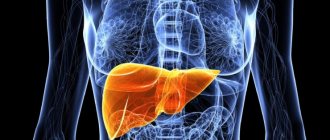
The liver is the second largest organ of the human body and has the function of processing and filtering all toxic substances resulting from the digestion of food so that they do not enter the bloodstream.
Normally the liver produces new liver cells that replace damaged ones. However, some health problems can permanently damage these cells, creating a problem for the rest of your life.
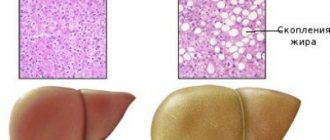
Liver steatosis (synonyms: fatty hepatosis, fatty liver) is a disease characterized by the accumulation of triglycerides and other types of fats in liver cells. It is normal for the liver to have a certain amount of fat, but to be considered healthy, the liver should generally have a maximum of 10% fat mass of its own weight.
When fat enters the liver in excess, a gradual accumulation of fat occurs, which can cause liver cell inflammation and increase liver volume.
Foreign studies show that in Americans alone, 10%-20% of the population suffers from excess fat in the liver, fortunately without damage or inflammation.
The diagnosis of the disease is usually made late and mainly in people aged 40 to 60 years. The amount of fat accumulated in the liver can be assessed using several tests, including ultrasound (ultrasound).
Diet for steatosis
For fatty hepatosis, diet No. 5 is prescribed. It provides a complete diet to the patient, helps stabilize liver function and the secretion of bile.
Recommended Products:
| Group | Name |
| Bakery products | Pastries made from soft dough, rye bread, crackers, biscuits |
| Soups | Dairy, vegetable broth, with cereals, beetroot |
| Meat fish | Beef, chicken, rabbit, lean fish, boiled or baked |
| Fats | Refined and butter |
| Dairy | Low-fat cottage cheese, kefir, milk, sour cream, mild cheese |
| Eggs | Steam protein omelet, soft-boiled eggs no more than 1 piece per day |
| Cereals | Oatmeal, buckwheat, rice |
| Vegetables | Boiled, baked, raw |
| Beverages | Black or green tea, juice, coffee with milk, chamomile or rose hip decoction |
Such nutrition allows you to weaken the disease, eliminate exacerbations, lose weight, and improve overall well-being.
It is advisable to adhere to these recommendations after therapy, since eating fatty, smoked or spicy foods will minimize the results of treatment and the course will have to be repeated.
Classification
There are mainly two types of liver steatosis : alcoholic liver steatosis and non-alcoholic (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease). The first type is directly related to excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages. The second type is associated with overweight, obesity and poor nutrition. In this case, patients may also experience high cholesterol levels as well as cases of diabetes.
Steatosis can be diagnosed and defined to varying degrees depending on the progression of the disease. Mild hepatic steatosis , also called grade 1 hepatic steatosis, occurs when there is a small accumulation of fat in the liver and is usually asymptomatic and more difficult to diagnose.
Causes of liver steatosis
The causes of this disease are not yet fully understood and studied, but it is believed that this accumulation of fat occurs as a result of the liver's reaction to aggression and poor functioning of the body. Here are some of the possible causes of the disease:
– Liver diseases.
Several liver diseases are manifestations of hepatic steatosis, including hepatitis B and C, Wilson's disease, cholestatic diseases and alcoholic liver disease. Most patients who abuse alcohol are diagnosed with hepatic steatosis.
– Secondary causes.
When the causes are secondary, the picture of the disease may change. There are several factors that can cause the disease, such as hypothyroidism, chemical exposure, drug abuse, including anabolic agents, cortisone, cancer medications, cardiac arrhythmia medications, etc.
– Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
This is the main cause of this disease, accounting for about 70% of cases. It is directly linked to diabetes, obesity, high cholesterol and triglyceride levels, and several metabolic changes in the body.
Main symptoms and complications
Stage 1 liver steatosis has no obvious symptoms , as this is the beginning of the disease. For this reason, diagnosis is often made using other types of imaging tests (abdominal ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging), and it is common to encounter patients with already advanced disease who are misdiagnosed at diagnosis.
When symptoms are obvious , such as in mild to diffuse steatosis , a person may experience vomiting, nausea, bloating, localized pain, yellowing of the skin and eyes, fatigue, weight loss, loss of appetite, weakness, difficulty concentrating, and dark spots on the skin. and so on..
Complications
All patients with excess fat in the liver, even if they have not yet been diagnosed with hepatic steatosis, are at increased risk of developing other diseases over the years, including diabetes and cardiovascular diseases such as coronary heart disease, stroke and heart attack.
Diagnostics
Since liver steatosis symptoms begin to appear only in the second stage, this disease is often diagnosed by chance. The main methods of instrumental diagnostics are:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. In this case, the doctor can see an enlargement of the liver and spleen, determine the echogenicity of the liver and see if there are fatty cysts.
- MRI and CT. These are modern methods that allow you to visualize the liver and see it in section.
- Laparoscopic examination. This is a minimally invasive procedure in which the doctor can use an optical device inserted into the abdominal cavity to assess the condition of the organ.
- Liver biopsy. In this case, biological material is examined, that is, a fragment of the liver. The doctor will be able to understand how affected the organ is and what percentage of fat is in it.
Among laboratory tests, it is advisable to conduct a blood test for biochemistry and liver tests. Thanks to these tests, you can determine the level of cholesterol, proteins, enzymes, and bilirubin. And these are very important indicators for this pathology.
Treatment
Depending on the stage of the disease and the degree of its development, grade 1 liver steatosis and grade 2 liver steatosis can be reversible. First, it is necessary to identify the possible cause of the disease so that more appropriate treatment can be determined.
Treatment usually includes both medical intervention and nutritional advice, as well as follow-up with some health care professionals to create a physical activity plan.
Most patients experience a steady regression of the liver, which can be stopped throughout treatment until the metabolic problem is completely cured or at least there is improvement. Hepatic steatosis, which occurs when fat accumulates in the liver, can progress to steatohepatitis, which is characterized by inflammation, and finally can progress to cirrhosis and can no longer be reversible.
Diet and nutrition tips for patients
Patients with a disease caused by secondary causes must receive adequate treatment and lifestyle modifications, which are the main cause of the problem. Initially, treatment is aimed at changing the patient's living habits and can be carried out in combination with the use of medications.
It is important to be very careful about the type of food you eat, eating foods rich in nutrients, containing fiber, as well as low-calorie foods, low in unhealthy fats and rich in healthy fats, such as polyunsaturated fatty acids (omega 3).
Here are some foods that are recommended and can be used in meals prepared during the treatment of patients with hepatic steatosis:
- extra virgin olive oil;
- vegetable oils such as corn, rice, canola, soybean and other oils;
- oat bran;
- flax seeds;
- lean beef and chicken;
- skimmed milk;
- low-fat cheeses such as mina fresco cheese, ricotta and cottage cheese;
- fruits and vegetables;
- foods rich in fiber and whole grains, such as whole wheat bread and brown rice;
Hepatoprotectors
Steatosis is one of the types of hepatosis caused by the replacement of hepatocytes with adipose tissue cells. Hepatoprotectors are used to reduce lipid content in the organ and stimulate metabolism. They prevent the destruction of parenchyma by accelerating recovery processes in hepatocytes. Treatment with medications has a positive effect on digestion and prevents complications of steatosis (fibrosis, cirrhosis).
Treatment for fatty liver includes:
- Carsil is a silymarin-based product that protects liver cells from destruction. Used to treat steatosis, cirrhosis and toxic damage to the parenchyma. Has lipotropic and antioxidant properties. Take 1 tablet 2 times a day for no more than 3 weeks.
- Essliver Forte - capsules with phospholipids that restore hepatocytes when the liver is damaged by alcohol, viral infections, and medications. Prescribe 2 capsules with meals 3 times a day.
- Hepatosan is a tablet based on pig liver cells that has antitoxic and hepatoprotective activity. Drink 2 tablets three times a day 20 minutes before meals.
- Gepabene is a herbal preparation with milk thistle and fume extract. It has a choleretic and restorative effect on the organs of the hepatobiliary system (liver, gall bladder, bile ducts). The maximum daily dose of the drug is 6 capsules per day.
- Ursohol - tablets with ursodeoxycholic acid, have a fat-burning and regenerating effect on the parenchyma. Stimulate lipid oxidation, reducing the degree of liver steatosis. For steatosis, take 1 tablet up to 3 times a day.
Treatment with hepatoprotectors is carried out for all forms of liver steatosis. They not only restore the functions of the organ, but also protect it from the toxic effects of other pharmaceuticals.