What is cirrhosis of the liver?
In cirrhosis, normal parenchymal liver tissue is replaced by pathological stroma, or fibrous connective tissue. The surface of the organ becomes lumpy and very dense. Often the liver increases significantly in size, but there are cases of its reduction.
People over 40 years of age who abuse alcohol are most susceptible to liver cirrhosis . The disease occurs in all corners of the world, about 300 thousand people die from it every year, and this figure is growing rapidly.
Many people who drink alcohol in large quantities have no symptoms.
Causes of the disease
Here is a list of the main causes of liver cirrhosis:
- Excessive alcohol consumption. People who regularly drink alcoholic beverages for 10 years or more are 80% susceptible to developing this disease.
- Hepatitis forms B, C and D, with form C often called the “gentle killer” because in the early stages a person does not experience any symptoms, but the risk of developing cirrhosis is 97%.
- Immune system disorders: autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis.
- Stagnation of venous blood in the liver, or Budd-Chiari syndrome.
- Toxic poisoning with poisons, chemicals and other substances.
- Diseases of the gallbladder and its ducts (impaired patency of the ducts, formation of stones, etc.).
- Genetic diseases, for example, Wilson-Konovalov disease (with this disease, copper accumulates in the liver due to metabolic disorders).
Often doctors cannot determine the exact cause of the development of this disease. In this case, it is given the name “cryptogenic cirrhosis.”
How to increase life expectancy with liver cirrhosis
Therapy for cirrhosis, as we have already noted, is mainly aimed at slowing down the scarring of liver tissue and preserving its function. To do this, the patient needs to radically reconsider his lifestyle. Regardless of the cause of the disease, all patients need to stop drinking alcohol, remove all harmful fats and carcinogens from their diet, and reduce the amount of protein. This is necessary in order to relieve as much stress as possible from the liver.
Treating the cause of cirrhosis is also critical. For hepatitis C, antiviral drugs are used: their effectiveness is now 96-98%. Ursodeoxycholic acid is used in complex therapy of hepatitis. It helps protect and restore liver cells and improve organ function. UDCA is also indicated for other diseases that cause cirrhosis: fatty hepatosis, cystic fibrosis, alcoholic liver disease, disorders of the gallbladder and biliary tract.
Symptomatic treatment of cirrhosis includes the following drugs:
- diuretics – to reduce the amount of excess fluid
- lactulose – to remove ammonia and normalize intestinal flora
- nitrates, β-blockers, ACE inhibitors, glycosaminoglycans - to control portal hypertension
- hemostatic drugs
People with cirrhosis should visit their doctor regularly and get tests to monitor the progression of the disease. And in order to prevent the development of cirrhosis, you need to take care of your liver and follow these simple rules.
Symptoms of liver cirrhosis
As a rule, symptoms do not appear at the initial stage of the disease, although it is at this moment that there is a chance of complete recovery. The first signs of cirrhosis include: bleeding gums, an increase in the size of the abdomen, and some changes in behavior.
As the disease progresses, the person becomes more tired. Patients rapidly lose weight, constantly want to sleep, and become absent-minded.
Cirrhosis is often accompanied by loss of appetite and discomfort in the abdominal cavity . Liver damage is also reflected in the color of the skin: it becomes icteric.
With cirrhosis, feces become lighter, and urine darkens. Patients develop ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity), which causes the volume of the abdomen to increase. The legs may also swell. Various bleeding (nasal, intestinal, subcutaneous) is another clear sign of liver cirrhosis.
People suffering from this disease constantly suffer from colds. There may be a decrease in libido, and in men the mammary glands often increase in size.
In addition to the above, patients may experience the following accompanying symptoms:
- increase or decrease in liver size;
- the spleen increases in size;
- pain in the liver area (aching or dull);
- “stars” appear on the skin;
- palms and tongue turn red.
Diagnosis of late cirrhosis and its complications
How to diagnose liver cirrhosis in the later stages of the disease in order to avoid complications of cirrhosis? In later stages, signs of the disease may appear:
- The abdomen increases in size, fluid accumulates in the abdomen in a volume of more than 15 liters. This complication of cirrhosis is called ascites. The anterior abdominal wall is tense, the navel turns outward, there may be ruptures of the navel;
- Difficulty breathing, it becomes rapid and superficial due to the restriction of the movement of the diaphragm and the occurrence of one of the complications - ascites in liver cirrhosis;
- Dilation of the veins on the skin of the abdomen in the form of a peculiar pattern of the head of a jellyfish, dilation of the veins in the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach, from where life-threatening bleeding can begin. This complication is called portal hypertension and appears in the later stages of liver cirrhosis.
And if liver cirrhosis is detected, you need to be aware of the signs of complications of the disease, which are very dangerous and can result in death if left untreated. These complications manifest themselves:
- Low pressure. Arterial systolic (upper) pressure is below 100 mmHg; when a person moves to a vertical position, it sharply decreases by 20 mmHg. The pulse is increased. Vomiting of blood, coffee grounds, and black stool may occur. These symptoms indicate the development of a formidable complication - bleeding from dilated veins of the gastric and esophageal mucosa;
- A decrease in the amount of daily urine can be determined as a sign of hepatorenal syndrome;
- Hepatic coma or confusion may present as a complication of cirrhosis such as hepatic encephalopathy;
- An increase in body temperature, abdominal pain of varying intensity, constipation, diarrhea, and vomiting are symptoms of bacterial peritonitis.
In order to detect cirrhosis in a timely manner, in addition to identifying clinical signs, it is necessary to use physical examination methods and a survey:
- body weight measurement. Patients with liver cirrhosis lose body weight;
- measuring the volume of the abdomen. A sharp increase in abdominal volume indicates the development of ascites (a complication of cirrhosis, the accumulation of a large amount of fluid in the abdomen);
Using a survey, the patient is identified:
- alcohol consumption: drinking alcohol for over 12 years, 40–80 ml of pure ethanol per day, allows one to suspect the development of liver cirrhosis;
- also, the fact of infection with viral hepatitis B, C, D should be alarming due to the likelihood of developing liver cirrhosis;
- diseases occurring with blockage of the biliary tract: obstruction of nearby organs by a tumor, gallstones or adhesions of the bile duct;
- history of autoimmune diseases;
- storage diseases: hemochromatosis and Wilson–Konovalov disease;
All these signs make it possible to identify patients with liver cirrhosis and then examine them in detail.
If these symptoms are detected, you must consult a doctor to determine further diagnostic and treatment tactics, which is the key to health and longevity.
The next stage in recognizing this disease is diagnosis using research methods: laboratory and instrumental.
What laboratory tests and instrumental research methods are used to check the liver for cirrhosis? There is no single test for cirrhosis. In order to reliably identify the disease, it is necessary to be fully examined, that is, take a set of tests and undergo research.
First of all, this:
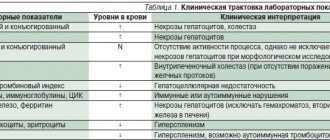
- General detailed blood test: determines hemoglobin, red and white blood cells, platelets and lymphocytes, erythrocyte sedimentation rate. In liver cirrhosis, changes are characterized by an acceleration of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, a decrease in the number of platelets, and the number of lymphocytes serves as an indicator of the degree of exhaustion of the patient’s body;
- biochemical analysis: increased activity of liver enzymes: alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, increased amount of bilirubin, both total and its fractions, decreased amount of total protein, increased concentration of gamma globulins;
They also determine glucose in the blood serum, the amount of sodium, potassium, creatinine and urea (increases with the development of a complication - hepatorenal syndrome).
In order to identify the cause of liver cirrhosis, the following studies are necessary:
- Determination of hepatitis viruses (RNA and DNA fragments in human blood) and antibodies to these viruses;
- If autoimmune liver damage is suspected, it is necessary to be tested for the detection of antinuclear, antimitochondrial, etc. antibodies;
- Study of cerulloplasmin (Wilson-Konovalov disease);
- Study of the amount of ferritin, transferrin for a presumptive diagnosis: hemochromatosis;
- Study of the hemostasis system: blood clotting time, prothrombin index, etc.;
- Analysis of urinary sediment and general urine analysis;
- Stool analysis.
Using instrumental research methods, you can learn about the extent of liver damage, the condition of the body and the stage of the disease.
These include:
- Ultrasound examination of the liver and nearby organs. Using this research method, the size of the liver, the echogenicity of the liver (high echogenicity indicates the detection of fibrosis), the size of the spleen (an increase indicates the development of a complication - portal hypertension), the state of the biliary system, the presence or absence of ascites are determined.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy. With the help of this study, a complication of liver cirrhosis - varicose veins of the gastric and esophageal mucosa - can be determined. If this complication is not detected, then it is recommended to repeat fibrogastroduodenoscopy every three years for preventive purposes.
- A biopsy helps determine whether a patient actually has cirrhosis of the liver. This test allows you to check the liver for cirrhosis with almost 100% accuracy. The resulting material is examined under a microscope, the degree of fibrosis and the histological activity of the process are revealed. This study is carried out in the absence of hemorrhages and bleeding and under ultrasound control.
- Study of ascitic fluid. The cellular composition of this fluid is determined to exclude tumor ascites; biochemical analysis - determination of protein content, primarily albumin. If the concentration of blood albumin is more than 1.1 g/l higher than the amount of albumin in ascitic fluid, then we can talk about portal hypertension and cirrhosis of the liver as the cause of ascites. They also determine the number of neutrophils (leukocytes - cells that are directly involved in inflammation): if the number of these cells exceeds 250/mm3, then peritonitis of a bacterial nature is diagnosed.
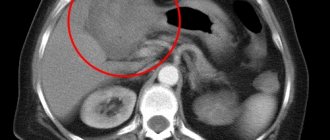
- To clarify the diagnosis, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography of the kidneys, liver, spleen, biliary tract, and pancreas are used.
Diagnostics
The first examination that is prescribed for suspected cirrhosis is an ultrasound of the liver. With its help, the doctor will determine the size of the organ, and during Doppler sonography, he will examine the condition of the blood vessels.
The second step is taking a biochemical blood test for the following indicators: ALT, GGT, AST, protein fractions, bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase. Additionally, the rate of blood clotting is studied.
Currently, there is an effective way to determine the extent of the disease: using the Fibrotes, FibroMax or Fibroscan apparatus, the liver is examined. Based on the results, the doctor will determine the degree of development of the disease from 0 to 4, where 0 is normal, and 4 is cirrhosis. Also, to determine the cause, the patient is prescribed a test for the presence of hepatitis.
The first signs of approaching death from cirrhosis of the liver
An accurate way to determine the severity of processes is through testing. A sign of an approaching coma is a decrease in the level of albumin, against the background of which there is an increase in the content of bilirubin in the blood. At the same time, an increased level of ammonia is recorded in the blood. External signs include progressive ascites, changes in consciousness, and disorientation in space.
How a person dies with cirrhosis depends on the medical measures provided. In case of irreversibility of death, it is possible to relieve pain and provide psychological support to the patient. Cirrhosis is an incurable disease, so every person with this diagnosis and their loved ones need to be prepared for a possible death.
Treatment options
As a rule, it is almost impossible to completely cure cirrhosis of the liver. Treatment is aimed at maintaining a normal quality of life and strengthening the immune system. Patients with liver cirrhosis should adhere to diet No. 5. Fatty, smoked and other unhealthy foods are completely excluded from the diet, and the amount of protein consumed is limited (up to 30 grams per day). You should definitely stop drinking any type of alcohol.
Taking medications
For liver cirrhosis, the following medications are prescribed:
- antiviral drugs (in the presence of hepatitis);
- hepatoprotectors: Silymarin, Ademethionine, Ursosan and others (support the work of liver cells);
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- cytostatics (reduce the growth of scar tissue in the damaged organ);
- choleretic drugs;
- immunomodulators (help strengthen the immune system and stimulate it);
- for ascites - diuretics (help remove excess fluid from the body);
- antioxidants (remove toxic substances from the body).
As an addition to the main treatment, the patient is prescribed vitamins (ascorbic, folic, lipoic acid) for two months. To support digestion, enzyme preparations that do not contain bile are prescribed.
Surgical method of treatment
If drug treatment does not bring results, the patient may be prescribed a liver transplant. The organ is removed from a deceased donor who signed consent for this during his lifetime.
A transplant is performed if the patient has life-threatening symptoms: extensive bleeding, ascites that cannot be treated, low albumin levels.
In addition to the indications, there may also be contraindications to transplantation : various infections, serious disorders of the lungs and heart, cancer with metastases, patient age (more than 60 and less than 2 years), brain damage.
The duration of the operation is 8 hours. Surgeons remove the damaged liver and transplant a healthy organ or part of it.
In some cases, the following complications may occur: the formation of blood clots in the hepatic artery, rejection of a foreign organ, etc., but in general the prognosis is quite favorable.
Treatment with folk remedies
Treatment of liver cirrhosis with folk remedies is very common. Here are some popular and effective recipes:
- Vegetable juice from Norman Walker. Each recipe requires a juicer. First recipe: mix beets, fresh cucumbers and carrots in a ratio of 3:3:10, make juice. Second recipe: mix spinach and carrots in a ratio of 6:10, make juice. Third recipe: pour a couple of tablespoons of black radish juice into the prepared carrot juice.
- Milk thistle tea. Mix a small spoonful of seeds and crushed leaves of the specified plant and pour a glass of boiling water. After 15 minutes, the infusion can be strained. This remedy is taken three times a day, one mug. It is worth noting that peppermint added to the infusion enhances the effect of milk thistle.
- Turmeric infusion. Take a glass of water (preferably warm or hot) and add a spoonful of crushed turmeric. You can add a little honey to improve the taste. The mixture is drunk twice a day, half a glass.
- Garlic. Add chopped or pressed clove of garlic to kefir (about 50 grams). This mixture is drunk daily in the morning. There is another way: add a couple of crushed cloves of garlic to a glass of boiling water, after a day the infusion is ready for use.
- Herbal infusions. To treat cirrhosis, many people take infusions of medicinal herbs internally. Such preparations can be purchased at a pharmacy and prepared according to the instructions.
Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
As a preventive measure, along with following a balanced diet rich in omega-3, doctors necessarily recommend regular physical activity to patients.
The relationship between physical activity (PA) and indicators such as:
- tissue sensitivity to insulin;
- level of lipids in the blood, including triglycerides, a high level of which may be a marker of high cholesterol;
- normalization of blood pressure.
In addition, physical activity helps reduce body mass index, which is one of the factors in calculating cardiovascular risk (CVR).
Types of liver cirrhosis and methods of its treatment
Most often, cirrhosis is the result of a long course of various liver diseases. Therefore, before starting treatment for cirrhosis, it is necessary to establish the causes of its occurrence.
There are the following main types of disease:
– Alcoholic: the disease becomes a consequence of progressive alcoholic liver disease caused by excessive drinking.
– Metabolic: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which develops when glucose and lipid metabolism are impaired.
– Infectious: cirrhosis develops against the background of viral hepatitis.
– Autoimmune: as a result of malfunctions of the immune system, which begins to attack the body’s own cells.
– Others: toxic, cryptogenic.
Practice shows that cirrhosis of the liver in 50% of all cases is caused by several reasons. However, chronic alcoholism is almost always a catalyst for the disease.
Treatment of liver cirrhosis: methods and their effectiveness
Treatment methods for cirrhosis include: treatment of the underlying disease that led to the development of cirrhosis (complete abstinence from alcohol in the case of an alcoholic cause, treatment of viral hepatitis, weight loss in the case of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) and surgery. Additional medications can also be used for symptomatic therapy.
The basis of treatment for liver cirrhosis is drug therapy. And although a complete cure is possible only through transplantation, modern drugs and techniques significantly improve the quality and life expectancy of the patient if prescribed in a timely manner and carried out in full. Remember: at an early stage, you can stop the destruction of cells, and with an advanced disease, complications are inevitable.
How long can you live with cirrhosis of the liver?
In case of timely diagnosis of cirrhosis and its systematic treatment, the patient can live fully for 10 years or more. However, in each specific case, this figure may change.
The patient's life expectancy depends on:
– Causes of the disease: alcohol, viruses, intoxication, heredity. The most dangerous are viral and alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver.
– The degree of organ damage before the start of medication.
– Age and gender of the patient. Cirrhosis is more difficult for women and older people.
– Concomitant diseases complicating the course of the disease.
– Strict adherence to the doctor’s instructions.
– Opportunities to completely eliminate negative factors.
According to the degree of liver damage, cirrhosis is divided into:
– Compensated
Most liver cells are still fully functional, but the process of replacing healthy tissue with fibrous tissue has already begun. With proper treatment at this stage, the progression of the disease can be stopped.
– Subcompensated
If liver cirrhosis is not detected at the previous stage and progresses, the first symptoms of the disease appear due to a decrease in the number of healthy hepatocytes (liver cells).
– Decompensated
With uncompensated cirrhosis, the liver can no longer perform its functions. Most often, liver transplantation is no longer possible.
Treatment
Cirrhosis can and should be treated regardless of the stage of the disease. In this case, treatment includes not only liver support, but also the prevention of complications (internal bleeding, abdominal ascites, hepatic encephalopathy).
Depending on the cause of cirrhosis, you can improve your condition:
1. Completely giving up alcohol.
2. By starting to take antiviral drugs prescribed by your doctor in case of viral cirrhosis of the liver.
3. Adhering to a strict diet recommended for all liver diseases.
Remember: cirrhosis of the liver is not a death sentence. Drug and surgical treatment can alleviate the disease. You just need to identify it in a timely manner and strictly follow all the instructions of specialists in order to improve your quality of life.
Bibliography
1. Belousov Yu. B., Khanina N. Yu. Approaches to choosing the dose of drugs in patients with liver cirrhosis // Farmateka. — 2006. No. 1 (116). — P. 76-84.
2. Schiff, Yu. R. Liver diseases according to Schiff. Alcohol, drug, genetic and metabolic diseases / Eugene R. Schiff, Michael F. Sorrell, Willis S. Maddray; lane from English edited by N. A. Mukhina [and others]. – Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2011. – 476 p.
3. Ivashkin V. T., Bueverov A. O. The present and future of clinical hepatology // Diseases of the digestive organs (for specialists and general practitioners): Breast Cancer Library. 2002. - T. 4, No. 1. - pp. 13-15.
4. Loginov A. S., Blok Yu. E. Chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver. M.: Medicine, 1986. - 256 p.
Prevention of liver cirrhosis
The development of cirrhosis can be avoided if the following preventive measures are observed:
do not abuse alcohol;- give up unhealthy (fatty, spicy, smoked) foods;
- do not take medications without first consulting your doctor;
- Have your gastrointestinal tract examined every year;
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis regularly;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- in the spring-autumn season, take complex preparations with vitamins and minerals.
Forecast
Liver cirrhosis cannot be cured completely , but if you start treating the disease in time, you can significantly prolong life. According to statistics, patients with compensated cirrhosis (the liver is still able to perform its function) can live more than 7 years if they consult a doctor in a timely manner.
With decompensated cirrhosis (the liver practically does not function), only 12-30% of patients remain alive 3 years after diagnosis, and with ascites this number decreases by 4 times. It is worth noting that with a successful liver transplant, 75% of patients live 5 or more years, and 40% of them can live with a transplanted organ for more than 15 years.
Video on the topic: Basic methods of treatment and diagnosis of cirrhosis
Liver cirrhosis is a dangerous disease that develops over many years. Do not abuse alcohol, monitor your health and at the first signs of illness, immediately seek help from a specialist. Remember: with timely treatment there is a chance to significantly prolong your life!
Prognosis for Hepatitis and liver cirrhosis
Hepatitis C is a “gentle” killer, the development of which in the body can be asymptomatic. According to statistics, approximately five hundred million people in the world are carriers of this virus. The mortality rate ranges from three to seven percent. If the virus damages the liver, the mortality rate is approximately fifty-seven percent.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to determine exactly how long a person with hepatitis C and such a liver diagnosis can live.
Life expectancy in this case depends on the following factors:
- Immunity status;
- Age;
- Addiction to bad habits.
Timely treatment is also an important factor. And one more thing: if treatment is started in a timely manner, a person leads a healthy lifestyle, then there is a chance to live up to eighty years.