Symptoms of an umbilical hernia in newborns are a phenomenon that occurs quite often, because it is one of the most common pathologies. Of course, in this state there is little pleasure for both the baby and his parents, however, even if you notice alarming symptoms, you should not panic: an umbilical hernia practically does not threaten the health and life of the baby. However, the sooner you notice problems, the better. So, what are the most common symptoms of umbilical hernia in newborns?
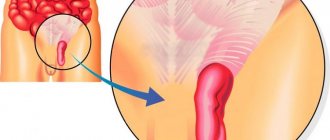
1. Turn the baby into an upright position. Even if the parents are holding the baby in their arms, an unusual protrusion of varying sizes and shapes may be seen in the navel area.
2. If you carefully touch your baby’s tummy with your fingers, you will immediately feel the edges of the umbilical ring, as well as the protruding soft part of the hernia itself, which can easily extend further into the peritoneum.
3. When a child cries or is in a tense state (for example, in the process of defecation), the navel, as well as the areas around it, become somewhat swollen.
4. The diameter of the umbilical ring seems too wide, and even as the child grows, it does not decrease significantly.
Of course, these are not all the symptoms of an umbilical hernia in newborns. Children tend to become restless and may have difficulty sleeping and eating (due to tummy pain). As a rule, parents who have already learned to feel well about their child and notice in time that something is bothering the baby or causing him discomfort, react quickly enough to alarming signs.
Why does an umbilical hernia develop in newborns? The reasons for the occurrence and development of this pathology may be different. Often, a hernia is congenital or hereditary: in this case, problems arise due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the abdominal wall. For example, the muscle umbilical ring may be weakened, sometimes protrusion of the peritoneum occurs due to poor development of connective tissue (this especially often happens in children who were born prematurely).
In addition, an umbilical hernia can be acquired. It occurs due to problems with the gastrointestinal tract, constipation or frequent flatulence. One of the reasons may also be muscle strain.
Now let's talk about how an umbilical hernia in newborns is treated, the symptoms of which cause considerable concern among young parents. General restorative treatment methods include regular exercises and a special massage (it’s best if your pediatrician teaches you how to do it). Exercises in water also have a good effect.
Useful article? Share the link on VKontakte
Massage and other procedures are usually performed after the umbilical hernia has been repaired using a special adhesive plaster. Here, again, it is better for a doctor to do this, but the mother herself can cope with this task by consistently following all the recommendations.
In infancy, an umbilical hernia usually goes away on its own. But older children may sometimes even require surgical intervention. However, doctors resort to such measures only if some complications develop and only after the child reaches 3 years of age.
Now you know what symptoms of umbilical hernia in newborns exist, and how such pathologies are treated.
Umbilical hernia in children 3 years old is common. True, pathology is especially common in the first year of life. However, this phenomenon also occurs in older children.
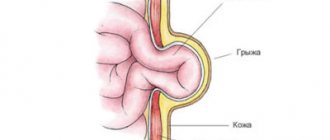
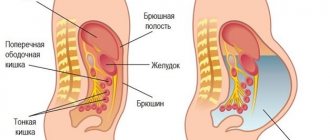
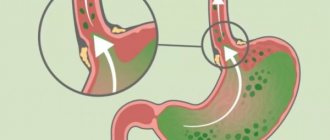
An umbilical hernia is a protrusion of internal organs from the abdominal cavity through the umbilical opening. During pregnancy, the umbilical cord creates a close relationship between the woman and the child, provides him with nutrition, delivers oxygen and all the nutrients necessary for development. When a child is born, his own pulmonary breathing opens, which allows him to take food orally. From this moment on, the child’s biological need for the umbilical cord disappears.
The umbilical cord that is not needed after birth is cut in the delivery room. The umbilical cord remains inside the baby's abdomen, which over time becomes overgrown with connective tissue. This occurs on average by the end of the first month of a child’s life. By the end of the newborn period, the navel should completely heal.
How in practice?
However, this is a standard course of events, but in practice everything happens differently. Sometimes it happens that the cord does not heal completely because the connective tissue forms too slowly. This is what provokes the development of a hernia in the navel. A hernia can occur due to defects in the development of the peritoneal walls, as well as as a consequence of incorrect actions of obstetricians. According to statistics, every third baby born prematurely suffers from a hernia in the navel. Before school, only 4% of children still have a hernia.
https://youtu.be/CTtSkmuc9l8
What it is?
An umbilical hernia is a partial protrusion of internal organs through the umbilical opening. Pathology occurs quite often in children. Every fifth full-term baby and every third premature baby suffer from this disease. The reasons for the appearance are varied - from congenital malformations to rupture of the umbilical ring, which can be the result of an ineptly tied umbilical cord, strong accumulation of gases in the intestines, constipation, strong and frequent prolonged crying.
The umbilical cord, which provides nutrition and oxygen to the baby during pregnancy, after its birth is no longer needed; normally, after cutting off and tying, the umbilical cord is overgrown with connective tissue about a month after birth. But in some cases, the ring does not heal completely, and this causes an umbilical hernia or increases the risk of its occurrence.
A little later, the baby may develop a hernia due to the fact that the parents brought him to an upright position too early.
Parents often notice a bulge in the navel area at the moments when the baby cries. However, in a calm state, the tummy returns to normal, and the hernia is easily set back. However, the seed of doubt has already been sown, and moms and dads demand that the situation be explained to them.
Evgeniy Komarovsky explains that not every protruding navel is necessarily a hernia. Sometimes a bulging navel is an individual feature of a little person, and there is nothing to worry about.
And in this episode of Dr. Komarovsky, one of the topics covered concerns the umbilical hernia.
A real umbilical hernia can be felt under the navel; only a doctor can determine its size and give a prognosis. In this case, the hernia will significantly increase in size when crying, pushing, or coughing. If the diagnosis has already been made and confirmed by the surgeon, do not panic. Komarovsky assures that this disease can be easily cured in the shortest possible time, without resorting to surgical procedures.
Varieties
Navel hernias are divided into two main types - acquired and congenital. Doctors suggest that in the case of a congenital hernia, the problem began even before the baby was born. Experts believe that the hernia appeared as a consequence of pathology of intrauterine development.
Acquired umbilical hernias in children 3 years old, in turn, are divided into oblique and direct. The latter arise as a consequence of changes in the fascia of the peri-umbilical space. This provokes the release of the hernia through the umbilical ring. In the case of an oblique hernia, the umbilical nodule is formed not in the navel itself, but next to it. The most common location of an indirect hernia is between the thinned peritoneal wall and the transverse fascia, as well as the linea alba. After passing this path, a hernial sac is formed in the umbilical ring.
In addition, hernias can be conditionally divided into those that can be reduced and those that are not amenable to mechanical action. The latter often cause strangulation of the hernial sac and acute pain.
Komarovsky's advice
Evgeniy Komarovsky reminds that massage, gymnastics and tummy tuck do not give instant results, and therefore parents should prepare for a long and systematic course; they do not need to skip classes, then pretty soon they can forget about the umbilical hernia altogether.
A hernia is not always umbilical, sometimes it is inguinal, and this pathology is more common in boys under the age of two than in girls. Or the diagnosis may sound different - “hernia of the white line of the abdomen.” In this case, the doctor determines the treatment depending on the degree of the disease. That is why Komarovsky strongly recommends not making diagnoses on your own, but be sure to seek advice from a specialist.
Komarovsky speaks quite categorically about methods for sealing an umbilical hernia in a child with a plaster. Only a surgeon should carry out the procedure of reducing a protruding hernia and then sealing it; inept actions can harm the child. But even after everything went well, the baby needs to be carefully monitored by specialists, because the hernia may increase in size, and inflammation may begin under the patch.
For relatively mild forms of umbilical hernia, the child can wear a special support bandage; you can buy it at any pharmacy or orthopedic salon.
Causes
According to most experts, children born with an umbilical hernia (ICD-10 code - K42) were exposed to pathogenic intrauterine exposure. The cause of a congenital hernia may be a disturbance in the formation of the peritoneum at the cellular level. A similar reaction can occur during hypoxia, as well as during a number of genetically determined diseases.
Newborn babies are diagnosed when the umbilical ring heals too slowly. Risk factors for newborns are:
1. Loud and frequent crying.
2. Regular constipation.
3. Increased gas formation.
4. Weakness of the umbilical ring is hereditary.
5. Respiratory diseases in acute and chronic form, accompanied by a severe cough.
What does Dr. Komarovsky say about umbilical hernia?
According to the famous pediatrician Dr. Komarovsky, there is no need to treat umbilical hernia in newborns.
The nature of such a defect is physiological and will go away without any help as the baby grows up. As soon as the baby is born, the umbilical ring is weak.
Its protrusion occurs as a result of internal pressure that occurs in the abdominal cavity. Almost every baby has this anatomical feature, and it takes time for it to go away.
If the child constantly screams, then serious complications can arise due to the weakness of the umbilical ring. Then you need to consult your pediatrician or pediatric surgeon. He will make an appointment or recommend therapy methods .
Lifting weights
An umbilical hernia in children 3 years old can form due to heavy lifting and weak abdominal muscles. Quite often, parents independently provoke the appearance of hernias by putting the child on his feet too early and placing children in walkers and jumpers. The child's muscles are not ready for stress in an upright position. He should begin to crawl, thereby strengthening his stomach and back, and then stand up. If the sequence provided by nature is violated, after a year the child develops an umbilical hernia.
Over the age of three years, the appearance of an umbilical hernia (ICD-10 code - K42) can be caused by excess body weight and scars left on the abdomen after surgical operations. A prolonged and intense cough also increases the likelihood of a hernia, regardless of the child's age. Another factor that provokes the appearance of an umbilical hernia is excessive stress after a long break.
Symptoms of umbilical hernia in children
Almost all babies have a belly button that sticks out to one degree or another. However, a strongly protruding or even protruding navel in a baby cannot be called a hernia. An umbilical hernia in 3-year-old children is characterized by a certain set of symptoms and signs; this pathology has its own specific clinical picture, in which a protruding navel is not a key indicator.
Severe pathologies during the development of the peritoneum, when the hernial sacs are large in size, sufficient for the exit of several organs at once, such as the intestines and liver, are diagnosed even during the period of gestation. During a routine ultrasound examination, the specialist should pay attention to such a pathological process. The fetus in this case is considered non-viable and rarely lives more than three days after birth, even under intensive care conditions. Most often, an umbilical hernia in this case is caused by a genetic factor.
What does an umbilical hernia look like? Hernias acquired by a child after birth rarely cause discomfort to the baby. As a rule, the hernial nodule does not exceed 5 centimeters in size and tends to appear when the child strains his abdominal muscles. In a calm and relaxed position, the hernia goes away.
Umbilical hernia in newborns treatment at home Komarovsky
New mothers are always characterized by increased anxiety. They react quite violently to the slightest changes in the condition of their baby, and often sound the alarm for a wide variety of reasons.
Local pediatricians sometimes add their “five cents” when visiting a newborn, reminding that the umbilical wound requires special attention, otherwise “an umbilical hernia will suddenly appear.”
Confused and worried mothers often ask the famous pediatrician of the highest category and TV presenter Evgeniy Komarovsky about her.
What it is?
An umbilical hernia is a partial protrusion of internal organs through the umbilical opening. Pathology occurs quite often in children. Every fifth full-term baby and every third premature baby suffer from this disease.
The reasons for the appearance are varied - from congenital malformations to rupture of the umbilical ring, which can be the result of an ineptly tied umbilical cord, strong accumulation of gases in the intestines, constipation, strong and frequent prolonged crying.
The umbilical cord, which provides nutrition and oxygen to the baby during pregnancy, after its birth is no longer needed; normally, after cutting off and tying, the umbilical cord is overgrown with connective tissue about a month after birth. But in some cases, the ring does not heal completely, and this causes an umbilical hernia or increases the risk of its occurrence.
A little later, the baby may develop a hernia due to the fact that the parents brought him to an upright position too early.
Parents often notice a bulge in the navel area at the moments when the baby cries. However, in a calm state, the tummy returns to normal, and the hernia is easily set back. However, the seed of doubt has already been sown, and moms and dads demand that the situation be explained to them.
Evgeniy Komarovsky explains that not every protruding navel is necessarily a hernia. Sometimes a protruding navel is an individual feature of a little person, and there is nothing to worry about.
And in this episode of Dr. Komarovsky, one of the topics covered concerns the umbilical hernia.
A real umbilical hernia can be felt under the navel; only a doctor can determine its size and give a prognosis.
In this case, the hernia will significantly increase in size when crying, pushing, or coughing. If the diagnosis has already been made and confirmed by the surgeon, do not panic.
Komarovsky assures that this disease can be easily cured in the shortest possible time, without resorting to surgical procedures.
Treatment
Evgeniy Olegovich begins any conversation about umbilical hernia in newborns by warning parents against unauthorized treatment of the disease with numerous folk remedies, which can harm the baby much more than the hernia itself.
He emphasizes that repairing a hernia yourself and tightening it with elastic bandages is the right path to the surgical table.
And the notorious coin, which is often recommended to be applied to the hernia by grandmothers and even some pediatricians, can cause an inflammatory process in the umbilical space.
So, if a child has a hernia, and doctors confirm this, then only the most complex form of it is surgically eliminated - when the small intestine is pinched between the muscles. Typically, surgery becomes possible when the child turns 5 years old.
Fortunately, such cases are rare rather than the rule. All other types of umbilical hernia can be treated without surgery if parents follow the recommendations. In many children, the disease goes away on its own as the abdominal wall grows and strengthens. Usually, by the age of 1 year, problems with the navel are no longer observed.
After one year, 95% of childhood hernias resolve.
If the baby’s hernia has not gone away on its own before six months, then, according to Komarovsky, it’s time to start treatment. More precisely, parents must take certain actions even before the child turns 6 months old.
Laying on the stomach
One of these techniques, which serves both as an excellent prevention of umbilical hernia and as an effective treatment for existing problems, is placing the baby on his tummy. It is advisable to do this 15-20 minutes before feeding on a flat and hard surface.
During this exercise, the child’s muscles of the abdominal wall, back, neck, and shoulder girdle are strengthened. In addition, lying on your stomach helps remove gases from the intestines and reduce the intensity of colic. The duration of the procedure should begin with 2-3 minutes, and gradually increase to 15 minutes. You can repeat this before each feeding.
Massage
You can start doing it as soon as the umbilical wound has healed and healed.
Komarovsky emphasizes that such treatment will not require any special expenses from the family, because any mother and grandmother, and even father, can master a simple massage technique.
Movements and touches towards the baby should be light and not give the child negative emotions. It is better to massage before meals to avoid regurgitation. It is better not to touch the hernia and the navel at all; all manipulations should be performed around them.
The simplest techniques are stroking the tummy with your fingertips in a clockwise direction in a circular motion, lightly tapping and pinching in a circle around the navel, stroking the tummy with your palms in counter movements. Each reception is done on average 10 times.
This massage not only helps the abdominal wall become stronger, but also helps normalize intestinal function and relieves colic and gas.
Gymnastics
It can be done to children from 1 month. Komarovsky recommends combining exercises with massage sessions. It is useful to practice turning over from tummy to side, from back to side and back.
To do this, you need to let the baby grab onto your fingers, pull the right hand, turn over onto the left side and vice versa. And also bring your legs, bending them with both hands at the knees and connecting them at the hip joint.
Press both legs synchronously to the tummy for a few seconds, and then release, after which bring the legs one at a time, right and left, the movement will resemble the actions of a cyclist.
Source: https://dagorthodoxy.ru/pupochnaja-gryzha-u-novorozhdennyh-lechenie-v-domashnih-uslovijah-komarovskij/
First sign
The first sign of an umbilical hernia is swelling in the area of the cavity in which the navel is located. At the initial stage, it is easily reduced with a finger, but later adhesions appear and difficulties arise with reduction. Some parents attribute intestinal colic, poor sleep and constipation to an umbilical hernia, but experts do not confirm this opinion. Sometimes a 3-year-old child’s stomach hurts, and this may indicate the presence of a hernia.
The pathology does not affect the digestive process, so the nausea often attributed to this pathology is most likely caused by other factors, for example, overfeeding the child. It’s a different matter if it comes to pinching the hernial sac. This is an emergency and requires immediate action. Fortunately, strangulation of an umbilical hernia, unlike an inguinal hernia, occurs quite rarely. Symptoms of an umbilical hernia in children should not go unnoticed.
In most cases, acquired pathology in children goes away on their own by the age of one year. This happens by strengthening the abdominal muscles. If a hernia was acquired by a child after three years of age, it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination and choose a treatment method, most often surgical. Over the age of three years, an umbilical hernia is accompanied by mild nausea and constipation. Drug treatment in this case is ineffective, and the result of physiotherapeutic procedures is questionable.
Every parent should know what an umbilical hernia looks like. This will help avoid complications.
Causes of pathology
The navel connects the baby and his mother for all 9 months of his intrauterine life. Through it he eats and breathes. But after birth, this connection is cut off, and the child’s body begins to function independently. After the umbilical cord is cut, the blood vessels supplying it close, and within a month the umbilical ring shrinks completely.
But under some conditions this does not happen, and a gap remains between the navel and the abdominal muscles, into which the small intestine falls out when intra-abdominal pressure increases. This can happen for a number of reasons:
- The muscles around the navel are not strong enough to support the intestines.
- The baby's connective tissues are not yet fully mature. This effect is most often observed in premature babies.
- An umbilical hernia accompanies rickets in children.
- The anterior abdominal wall has some congenital pathologies.
- There is some pathology in the gastrointestinal tract that causes bloating, flatulence, intestinal colic or constipation.
- A strong and prolonged cough can cause so much tension in the peritoneum and increase the pressure in the abdominal cavity so much that an umbilical hernia pops out.
Only the doctor chooses the treatment. It is based on the severity of the disease, the general condition of the little patient and his age. Self-treatment in this case is impossible.
Risk of entrapment
The presence of a hernia in the peri-umbilical or umbilical space is dangerous only in case of infringement of internal organs that fall into the hernial sac. The most common cases of strangulation of the intestinal ring. In young children this probability is quite low, but in an older child the risk of infringement increases.
The main signs that infringement has occurred are:
1. A 3-year-old child often has stomach pain. The pain is characterized as acute and sudden, of high intensity, spreading to the entire abdominal area.
2. Nausea and frequent vomiting.
3. Feeling of abdominal distension, difficult passage of gases or their complete absence.
4. There is an admixture of blood in the stool.
5. The hernial sac becomes inflated, darker and more tense. When in a horizontal position, the hernia does not go away.
The strangulation occurs against the background of a very narrow hernial orifice. If the gate is wide, entrapment is unlikely. The signs listed above cannot be ignored. At the first symptoms of pinching, the child should be placed on his side and an ambulance should be called. With such a pathology, the child is placed in the surgical department.
In newborn children, in most cases, hernias are reduced on their own, but more complex cases cannot be excluded. It is important to visit a pediatric surgeon and monitor the course of the pathology, receive specialist recommendations and follow them. You should not be inactive if your child has an umbilical hernia. It is better to get qualified medical help.
During strangulation, the child should not be given a lot of water, painkillers, or a cold or hot compress. Self-reduction of a hernia is also prohibited. This can lead to peritonitis and necrotic process in the internal organs.
Diagnostics
If a child has an umbilical hernia, what to do? This question is often asked by parents of children. A pediatric surgeon can determine the presence of pathology. If parents suspect an umbilical hernia, it is worth starting with this specialist. The surgeon will conduct a visual examination and palpation of the child’s abdomen, review the medical history, and also ask several questions about the course of pregnancy and childbirth. The surgeon will also be interested in the healing process of the umbilical wound.
Sometimes the doctor asks the child to cough (if age allows). This is part of the initial examination of the child for the presence of an umbilical hernia. A qualified specialist will determine a hernia even on the basis of palpation, however, to clarify the diagnosis, a number of additional examinations will be necessary.
Research methods
The list includes an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, which allows you to confirm the presence of a hernia, its size and exact location. In addition, radiography and irrigoscopy may be needed. The last study is carried out after the injection of a contrast agent into the intestine. This method allows you to visualize all parts of the intestine and identify the presence of adhesions, defects and perforations. In some cases, the child is prescribed an endoscopy. The examination also includes taking blood and urine for a general examination.
How to treat an umbilical hernia will be described below.
Treatment
The main and most effective method of treating umbilical hernia today is surgical intervention. However, in childhood this causes certain difficulties. As a rule, surgery in newborns is performed only in emergency cases, since the hernia tends to regress. An emergency case is considered to be a strangulated umbilical hernia. Therefore, doctors most often prescribe a wait-and-see approach. If the hernia does not go away on its own by the age of five, a planned operation is performed.
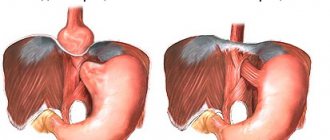
Indications for surgical removal of an umbilical hernia in children are age over five years, and the size of the bulge is more than 1.5 cm. The decision to perform an operation is made if the hernia formation is prone to growth, as well as in the presence of a narrow hernial orifice. The official name of the operation is hernioplasty. During the manipulation, the hernial sac is excised, which is replaced with its own tissue or a special mesh implant, which takes the entire load on itself and does not allow the hernia to recur.
Your doctor should tell you how to treat an umbilical hernia. In childhood, it is considered optimal to use the tension-free hernioplasty method when an implant is used. Excision of the hernia is not performed in every case. Sometimes it is possible to straighten the formation and fix it in such a way as to prevent further protrusion, that is, in fact, there is no need to remove it.
A mesh implant is placed both directly above and below the umbilical ring. It depends on how wide the hernial orifice is. At the final stage of the operation, the hernial space is sutured to prevent relapse. Modern medicine makes it possible to perform surgery on an uncomplicated hernia using the laparoscopic method. This is a minimally invasive intervention with minimal traumatic effect and a quick recovery period. In addition, reduction and excision of hernial sacs is carried out using more modern methods, for example, using a laser.
Surgery is performed under any type of anesthesia, which is important for the treatment of young patients. However, not all surgical hospitals perform such operations in childhood. Quite a few specialists adhere to the tension method when removing a hernia. The question of the method of performing the operation is discussed at the preparatory stage with the surgeon.
A modern development that helps cope with umbilical hernia is the Porofix umbilical patch. The medical device is also recommended for use as a prevention of pathology.
Methods for treating the disease in girls
Treatment of umbilical hernia in girls is practically no different from the methods used for boys.
In children, elimination of such a defect is carried out surgically, even if the child does not experience any discomfort .
An effective method is to apply a patch specifically designed for this disease. This is done by a doctor. The application technique is as follows:
- The specialist presses the hernia into the abdomen;
- The abdominal muscles on both sides are stacked one on top of the other;
- A patch is placed over the navel. It cannot be touched for ten days.
In most cases, one sealing will completely eliminate the problem. If there is no positive result, this method can be used two more times in a row. If the defect still persists, the patching technique is considered ineffective. Then other treatment methods are used.
If symptoms of a strangulated hernia appear, or it becomes inflamed or increased in volume, you should immediately consult a doctor. Surgery will probably be scheduled.