Gas formation in the intestines
The human gastrointestinal tract contains approximately 200 ml of gases. Gradually, they accumulate and are eliminated from the body through the intestine (this process is called flatulence or farting). A certain portion of complex carbohydrates remains undigested and begins to decompose and rot. As a result, flatulence develops, which can be accompanied by a very unpleasant odor. Sometimes other manifestations appear that significantly complicate a person’s life.
Why do gases accumulate in the intestines?
The unpleasant smell of gases has its reasons. Gas in the digestive system is either air (from the outside environment) or gases produced by bacteria inside the body. This is completely normal, although people may be embarrassed by belching (gas that passes through the mouth) or flatulence (gas that is forced out through the rectum).
Very strong flatulence
Gas may be disconcerting, but it is part of the digestion process, whether you like it or not. You have a certain degree of control over how much gas you produce, and you can influence it yourself.
Is explosive flatulence a sign of illness?
If there's gas, it's actually fine—it means your digestive system is doing what it's supposed to do: breaking down foods into the vitamins and minerals your body needs.
Unpleasant odor due to gas formation
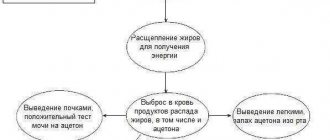
Normally, approximately 0.1-0.5 liters of gases are excreted during the day. For problems with digestion and severe flatulence, this volume increases to 3 liters. The process of involuntary release of gases, accompanied by an unpleasant odor, is called flatus in medical practice. This indicates disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. Intestinal gases are continuously produced and consist of 5 components:
- nitrogen;
- oxygen;
- hydrogen;
- carbon dioxide;
- methane.
Sulfur-containing components give gases a specific odor. They are produced by bacteria living in the intestines. You can cope with flatulence and foul odor if you know the root cause of the problem.
Why do gases come out?
During normal digestion, gases always accumulate in the intestines of a living creature. They subsequently exit the body through the anus. How do gases enter the intestines?
1) Through the mouth while eating (we swallow air).
We put a piece in our mouth. They chewed it and sent it into the stomach. Swallowed, that is. Add the next portion. Let's chew. And at the same time we breathe. Accordingly, air enters the esophagus. When we swallow chewed food, on the way to the stomach it will move the air that has entered the esophagus ahead of it. He can't go back. The cardiac sphincter, the muscular door between the stomach and esophagus, interferes.
2) During the interaction of digestive juices with each other and with water.
In the oral cavity, food is moistened with saliva, which has an alkaline environment. Once in the stomach, the food bolus is exposed to hydrochloric acid. From there, already sour, it goes to the intestines. All these reactions are accompanied by the release of carbon dioxide.
3) As a result of the activity of bacteria in the colon.
About three hundred species of bacteria live in the large intestine. When they feed, ammonia, carbon dioxide, methane, hydrogen and other elements are released.
Now it’s clear why a person farts? This is the result of the digestion process. Quite normal. A person must fart to rid his body of gastrointestinal gases. On average, humans produce 14-16 farts per day.
The process of peristalsis creates high pressure in the intestinal area. As a result, all its contents move down into the low pressure zone. To the anus. And the worm-like shape of the intestines prevents gas bubbles from rising upward. I think we need to thank nature for the fact that gases exit through the anus.
Causes of excessive gas formation
One of the common causes of excessive gas formation with a characteristic foul odor is errors in diet. Eating foods high in coarse fiber and gluten leads to flatulence. Also, this problem is faced by people who abuse dairy products with identified lactose intolerance, or foods that increase fermentation in the intestines. Excessive gas formation can be caused by stress and emotional stress. The nervous system controls the main processes occurring in the body.
If it malfunctions, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract becomes difficult, which leads to the appearance of various disorders, including flatulence. Gases with a specific odor are formed in excess quantities due to dysbacteriosis. In case of long-term therapy with antibiotics, the natural intestinal microflora is disrupted. This leads to unpleasant symptoms such as constipation, diarrhea and even bloating.
Causes of flatulence
It is customary to speak of flatulence if a significant amount of gaseous products accumulates in the intestines. Their exit is accompanied by a specific unpleasant sound. Flatulence can occur in people of all ages.
The most common causes of excess gas formation are:
- consumption of foods that activate fermentation processes in the gastrointestinal tract;
- increased consumption of proteins, sugar;
- lack of enzymes necessary to digest lactose;
- dysbacteriosis;
- infection;
- helminthiasis;
- intestinal obstruction;
- chronic stress.
Pathological causes
Increased gas formation may be a consequence of pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract. They are usually accompanied by characteristic symptoms in the form of constant rumbling in the stomach, heartburn, belching and severe pain. Similar signs may indicate the following problems:
- cirrhosis;
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- intestinal infection;
- neoplasms, including malignant ones;
- enteritis;
- Crohn's disease;
- gastric atony;
- proctitis;
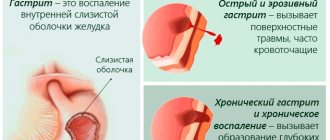
- gastritis;
- helminthiasis
In adults, flatulence, accompanied by a very unpleasant odor, in 40% of cases is caused by pathologies of various parts of the gastrointestinal tract. An excess of gases in the intestines does not depend on how old a person is. Newborn babies may face the problem due to the immaturity of the digestive system. Elderly patients also suffer from it, who often experience age-related changes such as elongated intestines.
Flatulence in women
A woman's body, unlike men, is subject to serious hormonal changes. Therefore, representatives of the fair sex often experience excessive gas formation. For example, during pregnancy. In the early stages, the body begins to immediately rebuild itself. The products consumed by the expectant mother are a source of nutrition for both herself and the fetus.
The digestion process may be disrupted, often resulting in flatulence. In addition, progesterone production increases markedly during pregnancy. This hormone relaxes the intestinal muscles. The food begins to move slowly. Therefore, the processes of rotting and fermentation, which cause increased gas formation with a characteristic odor, cannot be avoided.
During menopause, a woman's body also undergoes some changes. The production of the hormone estrogen decreases. Many ladies begin to gain weight due to a slowdown in metabolism. Therefore, flatulence is a natural continuation of the ongoing processes. Bloating may be accompanied by belching and a feeling of heaviness even after a small meal.
Diet
Increased gas formation is caused by products that contain raffinose, sorbitol, pectins, fructose and starch. Excessive consumption of mushrooms, goose, pork and other foods that are difficult for the stomach also leads to foul-smelling flatulence. They take a very long time to digest in the intestines and begin to rot.
Drinks such as beer and kvass can also cause a foul odor of gas; they enhance fermentation processes. You should exclude or strictly limit the consumption of such products as:
- legumes, cabbage, radishes, onions;
- pears, apples, grapes;
- bread, baked goods;
- pork, goose;
- all cereals except rice;
- milk and dishes containing it;
- carbonated drinks, beer, kvass;
- corn;
- canned food, marinades, pickles;
- sausage;
- mushrooms.
It is recommended to change your diet. The number of meals should be increased to 6 per day. Portions should be small, it is important to avoid overeating. In addition, you need to eat correctly, chewing your food thoroughly, slowly, and without talking. It is also important that the food is warm. It is especially useful to include foods such as:
- kefir, yogurt, cottage cheese, yogurt, sour cream;
- lean meats;
- potatoes, beets, pumpkin, zucchini;
- green tea, rosehip and bird cherry decoction;
- boiled fish;
- omelet, soft-boiled eggs;
- boiled rice porridge;
- greenery.
It is advisable to steam, stew or bake meat dishes without adding oil. At least once a month you should do fasting days, for example, on kefir.
Associated symptoms
Most known gastrointestinal diseases are accompanied by excessive gas formation. Most people are embarrassed by the problem and put off visiting the doctor every time, which is extremely unwise. However, it may also be accompanied by other symptoms:
- cramping pain in the epigastric area;
- bloating;
- belching, rumbling;
- nausea;
- bowel dysfunction in the form of constipation or diarrhea.
A sudden release of gases from the rectum may be accompanied by a loud sound and a specific smell. The clinical picture is sometimes supplemented by rapid heartbeat and arrhythmia. Such symptoms are caused by pinching of the so-called vagus nerve by intestinal loops. Patients may be plagued by constant insomnia due to intoxication of the body. Due to incomplete absorption of nutrients, some patients complain of weakness and a feeling of weakness. All this leaves an imprint on a person’s psycho-emotional mood.
Summary of Gas in the Bowel
Your body must produce gas to break down food. This is an important process, even if it can be frustrating at times. While your body does need to produce gas, there are ways to reduce the amount of gas that is produced with bloating symptoms. Most people don't actually have too much gas, although it may seem that way to some. Some diet and lifestyle changes often help, but if bloating and gas that smells like rotten eggs continue to be uncontrollable, it's best to see a doctor.
Diagnostic methods
A gastroenterologist studies excess gas formation in the intestines, causes and treats the problem. First of all, the specialist must exclude health-threatening pathologies. For this purpose, the patient is prescribed a comprehensive examination of the body.
Usually they start with an x-ray of the peritoneum.
During the procedure, the height of the diaphragm and the volume of gases are assessed. The technology of rapid introduction of argon into the intestines is used. The following diagnostic measures are also used:
- stool culture to identify dysbacteriosis;
- FGDS with simultaneous biopsy;
- colonoscopy;
- coprogram.
To exclude oncological processes in the intestines, an endoscopic examination is prescribed. If lactase deficiency is suspected, special lactose tolerance tests are used. Additionally, the doctor studies the patient’s diet.
Principles of treatment
Treatment for excessive gas formation with an unpleasant odor is complex. Usually it includes a combination of etiotropic and pathogenetic therapy. At the same time, the patient must understand that if a disease is the cause of the pathology, treatment should begin with the root cause. Symptomatic therapy involves eliminating the disorders associated with increased gas formation. For this, painkillers and antispasmodics (No-shpa, Drotaverine) are prescribed.
When the cause of flatulence is aerophagia, measures are taken to stop swallowing large quantities of air during meals.
An important component of complex treatment is a strict diet.
To relieve discomfort, you must avoid fatty foods. This will allow nutrients to be absorbed much faster and gases to leave the intestines. As a supplement, recipes from traditional healers can be used.
What to do if foul gas forms
When gas with an odor appears, you need to immediately reconsider your diet. Diet is always the basis for the treatment of flatulence and any gastrointestinal diseases. A properly designed menu helps improve digestion and reduce the release of smelly gases. It is also a good idea to seek advice from a gastroenterologist. If frequent gases with an unpleasant odor appear, an examination is prescribed. Can be assigned:
- colonoscopy;
- blood biochemistry;
- Ultrasound of the peritoneum;
- general blood, urine and stool tests;
- coprogram;
- fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy.
If the examination reveals pathologies, then treatment will initially be aimed at eliminating the disease. In other cases, it is enough to simply reconsider your diet.
Drug therapy
In some cases, when there is strong gas production with an unpleasant odor, drug therapy is necessary. It includes carminatives, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. Agents that restore microflora are also prescribed. If following a diet does not help, medications that reduce flatulence are indicated:
Drug therapy
Drug therapy consists of pathogenetic and etiotropic treatment. In the first case, tablets are used that directly combat excessive gas formation. The details of the drugs used are presented in the table below.
| Drug group | Mechanism of action | Examples |
| Sorbents | Binds and quickly removes toxic components. Not recommended for long-term use due to the risk of side effects. | Enterosgel, Phosphalugel |
| Enzymatic medicines | Improves the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract in a comprehensive manner. | Mezim, Pancreatin |
| Defoamers | They destroy foam, in the form of which gases continuously accumulate in the intestines, and improve its absorption ability. They have a pronounced carminative effect. | Dimethicone, Simethicone |
The goal of etiotropic therapy is to eliminate the immediate causes of excessive gas formation. In case of dynamic flatulence, Cerucal is used. This drug enhances intestinal motility. To normalize its functioning and reduce dysbiosis, probiotics (Enterol, Linex) are used. They contain live bacteria.
If flatulence is caused by mechanical causes (for example, neoplasms of various origins in the intestines or constipation), its treatment will be determined by the specific disease. Prolonged constipation is eliminated with fast-acting laxatives. For tumors, surgery is recommended.
Help from traditional medicine
Traditional recipes are often used for excessive gas formation in the intestines. Your doctor should tell you how to get rid of this problem. Most often, various decoctions and infusions based on medicinal herbs are used. The most popular and at the same time cheapest remedy is Fennel. The plant is characterized by a mild carminative effect.
Therefore, decoctions based on it can be given to children and women during pregnancy. An infusion of caraway seeds and anise has a similar effect. To prepare it, you will need to pour a teaspoon of the ingredients into a glass of boiling water and leave for no more than 15 minutes. Take the medicine one third of a glass before meals.
Peppermint tea is beneficial for excess flatulence.
To prepare it, you can take different varieties of plants: pepper, spike or cat. Pour a glass of boiling water over a teaspoon of pre-crushed leaves and simmer over low heat for 5 minutes. The finished product is consumed as regular tea.
To combat constipation, you can make a mixture of senna herb and dried fruits. 400 g of dried apricots and prunes should be poured with warm water and left overnight. In the morning, pass the mixture through a meat grinder, add 200 g of honey and a tablespoon of senna herb. Take 2 teaspoons of the mixture before bed.
Diet
First of all, you need to exclude foods that increase gas formation from your usual diet. For some patients, these include flour products, and for others, meat and fatty foods. Particular attention should be paid to foods high in fiber (cabbage, various fruits, brown bread, tomatoes, berries, legumes). It is better not to eat vegetables raw, but try to bake or stew them. There is no need to completely exclude them from the diet.
Doctors advise stopping eating ice cream and whole milk for 2 weeks. If, after this time, intestinal motility returns to normal, then the cause of the dysfunction is lactose intolerance. If there are no changes, it is useful to eat kefir and cottage cheese every day.
For a while, it is necessary to exclude carbonated drinks and beer, because they cause fermentation. Chewing gum is also prohibited. During the chewing process, a person swallows excess air.
To get rid of constipation, you need to include indigestible fiber in your diet. It is found in large quantities in wheat bran. Exotic dishes can also pose a danger. Therefore, you need to give up Asian or Chinese cuisine for a while.
Diet for gas with a smelly odor
To prevent the foul smell of gas, a certain diet is necessary. You should exclude from your diet foods that contain:
Goose, pork, mushrooms and other foods that are difficult for the digestive tract lead to the formation of foul-smelling gases. They are not completely processed, the remains begin to rot. Some drinks, such as kvass and alcohol, can also give a gas stench. They significantly enhance fermentation. The following must be excluded from the menu:
- onion;
- grape;
- pears;
- radish;
- canned food;
- baked goods;
- apples;
- bread products;
- cereals (except rice);
- corn;
- pickles;
- legumes;
- sausage;
- cabbage;
- milk and products containing it;
- marinades.
We recommend watching the video: Why do we fart with and without smell?
It is also recommended to change your diet. You need to eat in small portions 5-6 times a day, avoid overeating. After 19.00 it is better to get by with kefir or other drinks. You need to chew food very carefully, do not swallow large pieces, and do not snack on the go. It is not recommended to talk while eating. Dishes should be eaten warm; too hot and cold should not be eaten. It is recommended to include in the menu:
- boiled fish;
- greenery;
- potato;
- kefir;
- eggs (soft-boiled and in the form of an omelet);
- zucchini;
- overcooked rice;
- beets;
- dietary meat (chicken, turkey);
- cottage cheese;
- sour cream;
- pumpkin;
- yogurt;
- curdled milk.
Carbonated drinks and coffee are excluded from the diet. They can be replaced with a decoction of bird cherry and rose hips, or green tea. It is necessary to exclude everything fried, spicy and smoked. It is preferable to stew, boil or steam products without oil. Fasting days are needed a couple of times a month. For example, apple, kefir.
The causes of putrid odor do not always lie in disease. This is often caused by food or unchewed pieces that end up in the stomach. If the unpleasant odor is only a temporary phenomenon, it is enough to change the menu. Otherwise, you should consult a doctor.
People don't like to discuss this sensitive topic. However, in some cases it is necessary, otherwise it may be too late. How do you know when your flatulence is harmless and when it is not?
All people fart, less often or more often. Intestinal gases are an integral part of the digestive process, and they are always present, in greater or lesser quantities. Most often, it is simply air that gets into the stomach while eating along with food. Many foods, when digested, release large amounts of gases. First of all, these are foods with a high combination of fiber and protein (for example, legumes), followed by carbonated drinks.
Moderate gas formation is completely normal: on average, a person emits up to 2 liters of gas per day. But if you have excessive flatulence or unusual symptoms, you need the help of a gastroenterologist. In each case, we are talking not about a one-time attack, but about repeated ones.
Here's what you should be concerned about:
GASES TOO STINKY
You will be surprised, but our gases normally do not smell. Only 1% of all farts have the smell of hydrogen sulfide, and we simply don’t smell them. If each of your farts starts to smell, and it is not associated with odorous foods like garlic, curry
Doctors' opinion
Excessive accumulation of gases in the intestines is not considered a dangerous problem. If it is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms such as constant heartburn, abdominal pain or constipation, you should visit a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination to exclude serious pathologies. Intestinal dysfunction in the absence of diseases is easily treated by changing the usual diet and symptomatic medications. Otherwise, serious therapy will be required, for which medications are selected individually.
Share with your friends
Do something useful, it won't take much time
Severe flatulence
We all know that the accumulation of small amounts of gas in the intestines is a completely natural manifestation of the functioning of the body. It is normal until a person begins to experience severe discomfort, manifested not only in loud rumbling, but also in sufficiently severe pain that prevents the person from working, for example.
Gases are formed due to the active activity of bacteria that are located in our intestines. As a rule, the appearance of such gases indicates the need for bowel movements.
Gases are formed due to the active activity of bacteria that are located in our intestines.
Severe flatulence: forms
- Nutritional. Occurs if you eat starchy foods.
- Enzymatic. Occurs due to disruption of food digestion processes.
- Mechanical. If there are mechanical obstacles to the movement of food (tumor).
- Dynamic. Occurs due to gastrointestinal motility disorders (various infections).
- Circulatory. If blood circulation in the intestinal veins is impaired.
- Psychogenic. Occurs, for example, with various forms of hysteria.