What is parenchyma in the pancreas?
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system that performs important functions. Produces pancreatic juice, insulin and glucagon. The organ is very dense and difficult to diagnose due to its location. In order to determine the condition of the pancreas, an ultrasound is often prescribed.
In medicine, the term parenchyma refers to the internal structure of an organ; in its normal state it is homogeneous.
What is echogenicity of the pancreas?
Ultrasound examination is a common diagnostic method that does not require large financial costs. With its help, you can diagnose many diseases and learn about the condition of internal organs. The method is often used for examinations of the pancreas.
Many people know that the tissues of the human body have different densities, therefore, ultrasound also reflects them differently. The higher the tissue density, the greater the echogenicity, and vice versa - the lower the tissue density, the less echogenicity.
With diffuse changes in the pancreas, the density of the parenchyma increases and its echogenicity increases. The density of the organ decreases in most cases due to various inflammatory changes in the body, leading to swelling of the organ. The liquid has a lower density than the parenchyma itself, so the echo density decreases.
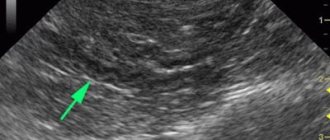
Heterogeneous structure of the pancreas on ultrasound
In adults (especially after 40-45 years), diffuse changes in the organ due to fatty infiltration occur. In this case, the gland will be heterogeneous and the echogenicity will be increased. The dimensions and contours remain normal.
An acute inflammatory process will be indicated not only by the heterogeneity of the echostructure, but also by an increase or sharp decrease in the echogenicity of the organ parenchyma, and an increase in size due to edema. A sharp expansion of the Wirsung duct with thickening of its walls is also possible. In this case, the heterogeneity of the gland will be due to leukocyte or lymphocytic infiltration, expansion of capillaries.
In addition, in acute pancreatitis, the sonologist in the conclusions or in the descriptive part of the protocol may indicate that the pancreas is loose - this means that its contours are unclear, uneven, and its size is significantly increased.
Against the background of chronic pancreatitis, diffuse fibrosis of the pancreas often develops. This is an irreversible process in which normal functionally significant organ tissue is replaced by connective tissue. Fibrous changes in the pancreas give it a “white” appearance. Such an organ has a coarse-grained structure, hyperechoic, and can be reduced in size.
Also, the heterogeneous echostructure of the pancreas may be due to:
- cysts (congenital, post-traumatic, post-inflammatory);
- abscesses, foci of necrosis;
- calcifications, for example, against the background of chronic alcoholic pancreatitis;
- small multiple tumors (insulinomas, apudoms).
Multiple cysts look like small, round, anechoic (black) formations with clear, even contours. Abscesses, on the contrary, have a heterogeneous structure of reduced echogenicity with unclear boundaries, sometimes small hyperechoic inclusions. Calcifications are usually “scattered” throughout the parenchyma of the gland in the form of round or irregularly shaped white formations with a dark track.
Heterogeneous structure in children
In childhood, the pancreas is not an easily visualized organ on ultrasound due to its retroperitoneal location. Its ultrasonic characteristics are also ambiguous.
Thus, in breastfed children during the first year of life it will have reduced echogenicity. If the child is on artificial or mixed nutrition, then the gland is “lighter” and heterogeneous, which is the norm in both cases.
In children, acute pancreatitis occurs much less frequently than in adults, in which the pancreas increases in size due to inflammatory edema and becomes heterogeneous. Its main duct expands in diameter. Over time, hypoechoic areas of necrosis and cysts may appear. This condition requires emergency treatment and diet in a hospital setting.
If a child is diagnosed with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, then ultrasound diagnosis of the pancreas is not very informative. This organ remains unchanged for a long time. Only in some cases do doctors record the heterogeneous echostructure of the organ and its reduced size.
Small cysts are often detected in the area of the head or tail of the gland, which give its structure heterogeneity. As a rule, they are monitored dynamically without any surgical treatment. Radical removal of cysts is prescribed if they reach large sizes and cause complications.
Causes
The main reasons contributing to the development of diffuse changes include:
- chronic form of inflammation of the pancreas;
- long-term use of toxic medications;
- addiction to alcoholic beverages;
- excessive consumption of fatty foods;
- nicotine addiction;
- previously suffered an acute form of inflammation of the pancreas;
- ailment in the patient’s liver area;
- diabetes;
- infectious diseases;
- disruption of metabolic processes;
- hormonal disorders;
- diseases caused by parasites;
- non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
We also recommend viewing: What is pancreatic lipomatosis and how to deal with it?
Important. According to statistics, the pancreatic parenchyma often becomes denser in elderly patients. Pancreatic enzyme deficiency is more common among children.
Minor compactions of the pancreatic parenchyma occur due to a stressful situation, inflammatory diseases, poor nutrition and depressive diseases. It is very important to find the true cause that led to changes in parenchyma density.
Diseases associated with echogenic, heterogeneous and compacted structure of the pancreas
Heterogeneous structure of the pancreas, what is it? A healthy gland must have a structure with homogeneous areas, only then is it a completely healthy organ that functions correctly.
But there are exceptions when, during long-term diseases, the structure becomes homogeneous, but at the same time echogenicity or compaction increases - this is also a serious deviation from the norm, which requires urgent therapeutic action. We will consider below what diseases are associated with changes in pancreatic tissue.
Pre-acute stage of pancreatitis
It is the condition that foreshadows the imminent onset of a relapse of the disease that is negatively reflected in the diagnostic data of gland density.
With timely diagnosis of this condition, it is possible to restore tissue with the help of drug treatment and avoid worsening the disease. This period does not last long, so it is necessary to contact specialists at the first incomprehensible signs of the disease. Only an echogram and ultrasound will be able to recognize the problem at an early stage.
Chronic form of pancreatitis
With chronic manifestations of inflammation of the pancreas, the disease can only be recognized in the active stage, passing into a state of remission; the disease is not reflected in any way on the gland, and its condition is difficult to determine using an echogram and ultrasound examination.
Cysts
A cyst is a formation on the tissue of the gland, which during diagnosis is visible as small compactions. They can move from time to time, so you need to monitor their development and take measures to eliminate them;
Tumors
Another type of neoplasm that, upon examination, shows uneven structure of the pancreas. Tumors must be treated with special care, because not all of them are benign, and some change from benign to malignant. With an echogram, malignant tumors absorb more sound, so they can be preliminarily recognized at the diagnostic stage.
Associated symptoms
Depending on the reasons that contributed to the appearance of diffuse changes, there are a number of symptoms that may bother the patient, for example:
- nausea and vomiting;
- blood pressure surges;
- increased body temperature;
- problems with stool;
- bloating;
- feeling of discomfort in the stomach;
- the patient constantly feels tired;
- painful attacks in the pancreas area.
Often, diffuse changes in the pancreas are diagnosed completely unexpectedly, during a routine examination, and are completely asymptomatic. At the same time, the organ fully copes with its functions.
Symptoms of the disease
A person may have no appetite and often have problems with bowel movements. Diffuse changes in the pancreas are often caused by pancreatitis. As this disease progresses, pressure is created in the tissues. Improper release of enzymes leads to poisoning.
The pathology provokes abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting.
One of the main signs will be shortness of breath; the pathology also leads to increased blood pressure. Depending on the nature of the clinical manifestations, the patient is prescribed intensive therapy or surgery. If chronic pancreatitis develops, the pancreatic parenchyma becomes damaged and swells. Subsequently, it decreases and the production of digestive enzymes is disrupted. The progression of chronic pancreatitis is accompanied by severe pain in the upper abdomen.
Important information: How to treat and what pills to take for inflammation of the pancreas
Fibrosis and lipomatosis
As a result of diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma, pathology develops under the influence of fibrosis. At first, the disease occurs latently, then the main symptom is inflammation, in which normal tissue is replaced by connective tissue. The pancreas begins to produce less hormones that are needed for metabolism. This pathology can be confused with pancreatitis. If it progresses, pain occurs in the hypochondrium. Lack of enzymes provokes nausea and vomiting. If protein reserves are depleted, insulin production is disrupted and diabetes develops.
Changes in the pancreatic parenchyma can occur as a result of lipomatosis - a pathological reaction in which healthy pancreatic tissue is replaced by pathological ones that are not able to perform vital functions, the body loses substances that are needed for the coordinated functioning of all systems. Symptoms depend on how severe the diffuse changes are. The disease can occur hidden. Later, as it progresses, the parenchyma is compressed by pathological tissue, and pain appears in the upper abdomen.
During ultrasound diagnostics, the doctor can determine the heterogeneity of the structures or increased echogenicity of the organ. If an ultrasound revealed increased or decreased echogenicity, blood tests are required. Subsequently, the suspected pathology is confirmed or refuted.
What else can you see in the picture?
Echo signs can reveal the density and structure of the pancreas. If the organ is functioning well, echogenicity is normal. It increases with pathological reactions associated with pancreatic tissue. Echo signs of diffuse changes often indicate fibrosis, a disease in which scarring occurs. The picture shows that the structure of the fabric is heterogeneous. A common cause of pathology is metabolic disorders.
Important information: What is the echogenicity of the pancreas and why is it increased?
Pancreatitis changes the density of the parenchyma, resulting in increased echogenicity. The pancreas interacts with the liver. If any changes occur in the liver, this affects the functioning of the pancreas. Increased echogenicity occurs in diseases associated with metabolism or pathologies in which normal tissue is replaced with dysfunctional tissue.
The cause may be cardiovascular diseases, pathologies associated with circulatory disorders. The structure of the pancreatic parenchyma changes if an infectious disease or illness associated with metabolic disorders progresses.
Diffuse changes are observed in patients who have suffered acute pancreatitis; even after recovery, they may experience pain in the hypochondrium.
Internal organs and systems are interconnected, reactive changes may indicate pathology of the liver or stomach. Such diseases occur in people who overeat or consume a lot of fatty and spicy foods. Pathological processes are also observed with drug overdose.
Diagnostic measures and stages
To establish the exact cause of diffuse changes, it is necessary to conduct an examination. The doctor examines the patient and collects anamnesis.
Diffuse changes in the parenchyma are divided into 4 stages:
- Tissue density is reduced, echogenicity is reduced, and the structure of the organ is enlarged. This picture is observed with pancreatitis.
- Reduced echogenicity.
- The organ is of normal size. The cause is lipomatosis. The disease can develop against the background of diabetes mellitus.
- The echogenicity increases and the density increases, the structure is heterogeneous. The pancreas is large or of normal size, this is due to fibrosis, in which healthy tissue is replaced by dysfunctional tissue.
Moderate diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma appear with the development of gastrointestinal disease. The pancreas swells if preconditions for pancreatitis appear. As the disease progresses, compactions can be seen in the image. If a person eats a lot of fatty foods, normal pancreatic tissue is replaced by pathological tissue.
Important information: What are the spots on the skin in diseases of the pancreas?
Additional diagnostics
If echo signs of pancreatic pathology are detected, the doctor must prescribe some additional examination methods:
- general blood analysis;
- MRI or CT;
- ultrasound examination of the gastrointestinal tract;
- urine test and so on.
Important. Having carefully studied the medical history and the results of the diagnostics, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis, prescribes individual treatment and a number of related recommendations.
Types of pathology
- Minor violations. They most often arise due to stressful situations. You need to normalize your diet, and then all the problems will go away.
- Moderate stage of the disease. They appear due to problems in digestion. A mandatory diagnostic procedure is required for this form of the disease.
- Unexpressed diffuse changes. They do not have a negative effect on the functioning of organs and their performance, but in diabetes mellitus they often contribute to an increase in blood sugar levels. The root causes of such changes are cardiovascular diseases, liver diseases, old age, genetic predisposition, and so on.
- Pronounced diffuse changes indicate the presence of inflammatory processes in the organ itself or are a symptom of other diseases. The patient suffers from pain in the abdominal area and digestive problems. The doctor prescribes additional diagnostic examinations and then the necessary therapy.
- The disease is at a chronic stage. Most often there are no obvious symptoms. This form of lipomatosis provokes in the patient.
We also recommend viewing: Possible diseases of the pancreas
Nutrition and diet
- It is recommended to avoid fatty foods.
- You should eat as much fresh and natural food as possible.
- They recommend split meals, up to 5 meals a day.
- In small portions.
- Completely exclude the consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- It is prohibited to consume carbonated drinks and canned food.
- They try to use spices and seasonings as little as possible.
- Limit the consumption of sweets and starchy foods.
- Avoid too cold and hot food.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment often comes down to symptomatic therapy. The doctor prescribes antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
When the body is intoxicated, antibiotics and solutions are used that help remove toxic substances from the patient’s body.
Lipomatosis can be treated with medications or surgery. In this case, all fatty nodes are removed.
For diabetes mellitus, medications are prescribed to help reduce the amount of glucose in the blood, and in some cases insulin injections are necessary.
Treatment of pancreatitis, including diffuse, lasts quite a long time. It is important to start a therapeutic course on time so that the disease does not become chronic. In addition to a special diet, patients are prescribed a number of medications that promote the production of pancreatic juice, relieve pain symptoms, and relieve spasms. Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a doctor and is accompanied by regular tests, in particular lipase and amylase.
We also recommend viewing: How to clean the pancreas without harm?
What do diffusely heterogeneous structural changes in the pancreas mean in ultrasound results?
The tissue of any parenchymal organ, including the pancreas, has a homogeneous structure when examined. Diffuse are disturbances in the structure of an organ that are evenly distributed throughout. They are sometimes discovered accidentally during sonography for another reason. This is an objective symptom that confirms the pathology, in this case, thickening of the gland tissue.
Diffusion means interaction, interpenetration. Diffusion changes involve the penetration or proliferation of cells from one tissue into another. In the parenchyma of the pancreas, normally functioning cells of the organ are replaced by others - fatty, connective tissue. These cells cannot provide pancreatic function because they are not adapted for these purposes. Next to the healthy cells of the gland, cells with a different structure that are unusual for its tissue are located, provoking the further development of the pathological process and creating structural heterogeneity.
The examination reveals a change in the echostructure of the pancreas: during ultrasound, evenly alternating areas with increased and decreased echogenicity are visualized against a generally normal background of parenchyma.
Causes of diffuse heterogeneity of the pancreas
There are many reasons for diffuse heterogeneous changes. These include those that can be corrected, but there are also those that cannot be treated, as well as physiological ones that begin to act over time:
- age-related changes,
- genetic disorders
- metabolic disorders leading to dystrophy,
- pancreatitis in the initial stage of an acute or early exacerbation of a chronic process,
- decreased blood supply to the pancreas due to vascular diseases,
- biliary tract dysfunction,
- unhealthy diet
- stress,
- bad habits,
- uncontrolled use of medications,
- diabetes.
Pathologies causing changes in structure
Under the influence of external negative factors, the main structural units of pancreatic tissue can be affected:
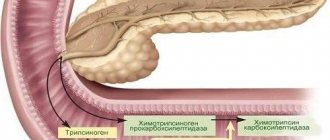
- acini, consisting of glandular cells that secrete enzymes,
- islets of Langerhans, the cells of which produce all the main hormones that control basic metabolic processes, including carbohydrate metabolism.
As a result, it develops:
- pancreatitis - inflammation of pancreatic tissue, in which necrosis of glandular cells occurs and their replacement with connective tissue,
- diabetes mellitus - as a result of the death of beta cells, the production of the main pancreatic hormone - insulin - sharply decreases.
These disorders lead to changes in the structure of the tissues of the pancreas and neighboring organs (liver) and can significantly increase the echogenicity of the gland. When performing sonography, heterogeneous hyperechoic structural changes are visualized, which over time continue to increase the size of the organ itself to significant values.
Eating fatty and fried foods leads to the development of pancreatitis. This is a high risk factor for the development of pancreatitis and changes in the structure of the pancreas. Junk food, like alcohol, has a selective effect on the body. In some people this does not cause any changes, but in a child or patient with existing problems in the digestive system, even a small amount of prohibited foods or a few sips of alcohol can cause moderate or moderate pathological disorders in the pancreas. In the future, the number of pathologically altered cells will increase, and the organ will gradually lose its functions.
Chronic stress also negatively affects the pancreas: they cause hormonal disruption in the body, which leads to heterogeneity in the structure of the pancreas.
Preventive measures
As a preventive measure it is recommended:
- Watch your diet - avoid fatty and sweet foods, as well as pastries and carbonated drinks. They eat fresh vegetables and fruits. They try to steam it.
- Forget about cigarettes and under no circumstances drink alcoholic beverages.
- Strengthen the immune system: consume vitamin complexes.
- Take frequent walks in the air and engage in physical activity regularly.
- Once a year after reaching 35 years of age, undergo an ultrasound examination of the internal organs located in the abdominal cavity.
- Treat infectious and inflammatory diseases, in particular those related to the digestive system, in a timely manner.
It is important at any age to closely monitor your own health and the health of your children. If strange symptoms appear, seek professional help from a doctor. Self-medication is not recommended.
Symptoms
The doctor finds out any manifestations of pancreatic pathology by interviewing the patient, examining them, and comparing them with the results of blood, urine, feces, and biochemical tests.
Ultrasound results are a valuable diagnostic tool. However, they are not associated with specific symptoms and complaints of the patient.
In acute pancreatitis, severe pain of a girdling nature with nausea, vomiting, and signs of shock (pallor, tachycardia, drop in blood pressure) comes first. The patient needs intensive therapy to prevent necrosis (death) of the parenchyma and diffuse peritonitis caused by the release of enzymes into the abdominal cavity.
In a chronic course, pain occurs only during exacerbation or violation of the diet. More worrying is loss of appetite, weight loss, frequent diarrhea, bloating. Digestion is disrupted as tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue and requires increasing compensation with medications.
Fibrosis of the parenchyma in a chronic process necessarily affects the endocrine part of the gland and suppresses insulin production. Diabetes mellitus in such a patient is difficult because it depends on an irreversible process. Symptoms include: vomiting, weight loss, thirst, diarrhea.