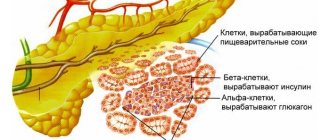
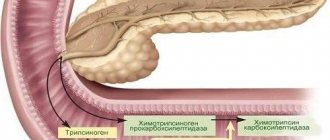
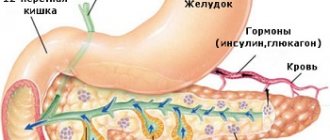
Diagnosis of the disease
At the first symptoms, the patient should seek medical help. After a general examination and tests, further examination will be required. Often in such cases, the study is carried out using ultrasound diagnostics. This is a painless and affordable examination method that allows you to conduct research on the pathology of the pancreas before detecting cancer in the early stages.
In what cases is an ultrasound scan of the pancreas performed?
The procedure is carried out to confirm the diagnosis - the accuracy of the determination of the method is high. Sometimes ultrasonography of the pancreas is performed with such features:
Ultrasound diagnosis of the pancreas
- persistent pain in the form of spasms in the left side of the stomach;
- possible suspicion of jaundice;
- formations discovered during examination (cyst, tumor);
- rapid weight loss without effort;
- stool instability;
- the presence of pain during examination of the source of the malaise;
- when examining other internal organs, detecting possible changes in the pancreas.
Examination of the pancreas using ultrasound is carried out for pancreatitis and possible diseases. If the symptoms coincide, there is a high probability of inaccuracy in diagnosis, resulting in inaccurate treatment.
Preparing for the study
Ultrasound of the pancreas can be performed both routinely and as an emergency in acute conditions. When carrying out a planned procedure, it is necessary to follow some rules and prepare for this procedure. After all, the most problematic thing during ultrasound examination is the presence of air in adjacent hollow organs. It is he who can interfere with a detailed study, distort visualization and expose the patient to an incorrect diagnosis. Doctors recommend undergoing pancreatic diagnostics, preferably in the morning. After all, it is during this half of the day, following all the rules and recommendations, that you can get the most accurate results.
During routine diagnostics, it is necessary to follow a gentle diet three days before the procedure. It is advisable to exclude foods that cause fermentation and bloating in the intestines, and do not consume foods rich in fiber and whole milk. The day before the test, it is recommended to take a laxative to cleanse the stomach and intestines. For twelve hours before the planned ultrasound examination, you must refrain from eating and drinking water, avoid taking medications, and prohibit smoking. Carbonated drinks should not be consumed as they cause excess gas formation. This can specifically affect the results and spoil the ultrasound visualization.
In case of emergency indications for an ultrasound scan of the pancreas, the patient does not need preparation. But this can reduce the information content to approximately 40%.
Preparing for an ultrasound scan for pancreatitis
To carry out the procedure correctly, you should be thoroughly prepared. If we are talking about an emergency operational situation, ultrasound is performed without preparation. The accuracy will be much lower, visible results are not guaranteed. For a routine ultrasound, the patient must be explained how to prepare for the examination. Let's take a closer look at the procedure:
- Ultrasound is often prescribed in the morning, on an empty stomach; at this time, little air has accumulated in the digestive system.
- If time permits, 2 days before the procedure, remove foods that cause gas formation (fruits, vegetables, dairy products, soda) from your diet.
- To reduce flatulence, you can take activated carbon or espumizan.
- The last meal should take place at least 12 hours before the ultrasound, otherwise the result will be distorted.
- It is recommended to do an enema before the study.
- It is undesirable to use medications, alcohol, or smoking before the upcoming process.
A complete picture of the disease will require accurate data. Compliance with the listed preparation rules will allow you to obtain them.
Endoscopic ultrasound examination of the pancreas
With a conventional ultrasound examination it is not always possible to obtain the desired results. Since through the anterior abdominal wall it is not always possible to clearly see small changes in the structure of the pancreas due to its deep location. A new modern technique, endoscopic (or endo) ultrasound helps to get closer to the organ for a more accurate and reliable study. Endoscopic (or endo) ultrasound makes it possible to identify space-occupying formations of the pancreas and its ducts in the early stages, as well as to identify the depth of their growth into surrounding organs, damage to blood vessels, and nearby lymph nodes.
The doctor is preparing to perform egdosonography of the pancreas
An endoscopic (endo) ultrasound involves inserting a special long tube with a video camera and a small ultrasound probe at the end through the nose or mouth into the stomach and duodenum. Endoscopic (endo) ultrasound is performed under the supervision of an experienced physician. The patient needs to prepare for such a study in the same way as for an ultrasound scan through the abdomen. It is performed strictly on an empty stomach with preliminary medicinal preparation of the patient to reduce his anxiety before the procedure.
Healthy pancreas results
During the examination, ultrasound will show the overall picture using medical indicators that are unclear to the patient. The main numbers by which it is possible to guess the existence of pathology are the parameters of the pancreas - shape and size. The information is available for comparison to any patient. Then ultrasound reveals other points characteristic of the diagnosis of pancreatitis.
When the pancreas is scanned with the machine, the components of the organ are clearly visible: the body, tail and head. For an adult, the following sizes are considered normal:
- body up to 21 mm;
- tail up to 35 mm;
- head up to 32 mm;
- The width of the duct is no more than 2 mm, the walls are smooth.
The silhouette of the pancreas itself is outlined with a clear line, the structure is uniform. An important indicator is the echogenicity of the organ, which determines the ability of the gland to increase or absorb the signal from the device’s sensor. The screen is identified by image parameters, brightness and clarity. The normal value coincides with the data for the liver and spleen.
Let's take a closer look at the indicators determined for pancreatitis. For different types of pancreatitis, an individual picture is displayed on the screen.
What should a healthy organ look like?
Normal pancreas levels are the same for both women and men.
During an ultrasound examination of this organ, the uzologist evaluates many parameters.
- The shape of the pancreas: in the normal state, it looks like an English letter; any change indicates an isolated defect or other pathologies that have a negative effect on the pancreas.
- Organ dimensions. The length of the pancreas in an adult varies from 14 to 22 cm, and the weight ranges from 70 to 80 g. Since the organ is anatomically divided into 3 parts, the parameters of each of these segments have their own standards. So, the natural length of the head should not be less than 25 mm and more than 30 mm. Body sizes range from 15 to 17 mm, and the tail reaches a length of 20 mm.
- Diameter of Wirsung's duct. This section of the pancreas is designed to transport pancreatic juice into the digestive tract. 2 mm is exactly the value that is typical for this channel in the absence of pathologies. With inflammation, the indicator most often increases (up to 3 mm), but narrowing indicates that the duct from the outside is being compressed by something, for example, a stone, cyst or tumor.
- Smooth and clear contours of not only the pancreas as a whole, but also all its parts separately.
- The average density of the organ, which should approximately correspond to the density of the liver or spleen - this parameter is determined by uniform echogenicity, allowing for small inclusions.
- Granular structure of the parenchyma.
The given indicators may vary slightly, which is not a deviation from the norm. In this case, the values determined by the upper limits are taken into account.
What does acute pancreatitis look like?
A number of forms of acute pancreatitis are known; pathology implies mild and severe course of the disease. In the first case, the organ is slightly damaged; when the symptom is first removed, it becomes difficult to identify the seriousness of the situation. The severe form manifests itself in the form of certain indicators.
Indicators of acute pancreatitis
The general picture of signs of acute pancreatitis on ultrasound comes down to the following:
- the overall size of the organ is increased;
- the boundaries of the pancreas have an unclear contour, with curvatures;
- increased echogenicity in sources of inflammation;
- the structure is heterogeneous;
- the duct is much wider than normal;
- liquid conditions are detected in the organ area, changes in neighboring organs;
- in severe cases, cysts, areas of decay, and other uncharacteristic changes may be detected.
Changes in the abdominal cavity indicate acute pancreatitis. Along with laboratory tests, analyzing each symptom along with an ultrasound examination, confirmation of the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis will be reliable.
Analysis of results
The ultrasound conclusion contains the most important information for a specialist: based on the information received, the doctor has the opportunity to confirm or refute the initially assumed diagnosis. If a patient has pancreatitis, as evidenced by the procedure performed, the doctor determines the severity of the disease, as well as its degree. If the picture is not entirely clear or provides incomplete data, the patient is referred for further examination (CT or MRI). Especially more accurate and extensive diagnostics are necessary when identifying neoplasms in the pancreas.
Normal indicators
The patient should not worry at all about the health of his pancreas if his report contains the following entries:
- The size of the pancreas is from 14 to 22 cm (any indicator that is included in this limitation);
- Well-visualized segments: organ head, body, tail;
- The size of the head is no more than 30 mm, the body is no more than 17 mm, the tail is up to 20 mm;
- Homogeneous granular structure of the parenchyma;
- Smooth and clear edges of the walls of the pancreas;
- Wirsung's duct is not dilated, its diameter is 2 mm;
- Absence of anechoic inclusions;
- Uniform echogenicity and average organ density.
However, even this ultrasound result must be shown to a specialist. If there are no obvious changes in the pancreas, and pain still bothers the patient, then the examination must be continued. Most likely, the reason lies in some other pathology, which is highly not recommended, because untimely treatment is sometimes fraught with the most disastrous consequences.
Deviations from the norm
The nature of any violations primarily depends on the severity of the disease. And if at the initial stage of the pathological process these changes may be insignificant or mildly expressed, then the picture that is visualized in severe pancreatitis is replete with a whole set of deviations. In addition, it is easier for an uzist to determine the acute course of the disease than the chronic one, since during an exacerbation the parameters of the pancreas are changed quite strongly.
In general, such violations include:
- Significant increase in the size of the pancreas, swelling;
- Unclear boundaries of the walls, unclear contours of the organ;
- Heterogeneity of the pancreas structure;
- Seals, which are signaled by increased echogenicity;
- Dilatation of the Wirsung duct up to 3 mm;
- Presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- Complications: cyst, pseudocyst, necrotic foci, tumor;
- Enlargement of nearby organs.
The chronic form of the disease is characterized by slightly different signs:
- The size of the pancreas, on the contrary, decreases - this is due to fibrosis and atrophic changes in tissue, which occurs as a result of a long course of the disease;
- Heterogeneous structure of the parenchyma - this is indicated by numerous hyperechoic inclusions, which are foci of fibrosis;
- Changes in the contours of the pancreas due to retraction of external areas;
- Dilation of the Wirsung duct (over 2 mm), which does not narrow further - as a rule, this is evidenced by subsequent ultrasound results.
Indicators of chronic pancreatitis
The ultrasound screen shows individual changes characteristic of chronic pancreatitis. Features of manifestation:
- constant expansion of the duct over 2 mm;
- the boundaries of the organ reveal a jagged membrane, sometimes with small tubercles;
- in addition to increased size, echogenicity will be less;
- sometimes pseudocysts are found in advanced disease, in such a case the echogenicity will be higher;
- as the disease progresses, the monitor screen shows how visually the pancreas becomes smaller compared to the enlarged duct, due to atrophy;
- if there is a suspicion of stone formation in an organ, you will see a circle-shaped spot with an echogenic trace;
- the structure of the organ is heterogeneous, with diffuse errors.
If moments are found when the signs of chronic pancreatitis are distorted or do not provide a complete description of the situation on ultrasound, the examination continues in other ways using MRI or CT (magnetic resonance or computed tomography).
Pancreatic cysts on ultrasound
Single small simple cysts occur as incidental findings in the healthy pancreas. In chronic pancreatitis, small simple cysts are quite common. If a cyst is suspected, note the enhancement of the contour of the far wall and the effect of signal enhancement in the tissue behind. Simple cysts are isolated from the parenchyma by a smooth thin wall. There should be no partitions or wall irregularities inside; the contents of the cyst are anechoic. Simple cysts are always benign. But, if the cyst is not obviously “simple”, further investigation is required.
| Photo. Simple pancreatic cysts on ultrasound. A, B — Single simple cysts in the area of the body (A) and neck (B) of the pancreas with a thin smooth wall and anechoic contents. B - Classic signs of chronic pancreatitis: the main pancreatic duct is dilated against the background of parenchymal atrophy, the contour of the gland is uneven with notches, there is calcification and small cysts in the parenchyma. | ||
Important!!! Simple pancreatic cysts are common, but don't forget about cystic tumors. Cancer is the most dangerous disease of the pancreas.
There are two types of pancreatic cystic tumors: benign microcystic adenoma and malignant macrocystic adenoma. Microcystic adenoma consists of many small cysts and appears as a dense formation on ultrasound. Macrocystic adenoma usually includes fewer than five cysts larger than 20 mm. Sometimes polypoid formations can be seen in such cysts.
| Photo. A, B - Benign microcystic adenoma of the pancreas: a large cystic formation in the head of the pancreas. B - Pancreatic adenoma with macro- and microcystic components. | ||
With pancreatitis, pancreatic secretions digest surrounding tissue and pseudocysts form. Pseudocysts from the abdominal cavity can extend into the chest and mediastinum. Pseudocysts are often found in patients who have suffered acute pancreatitis (see below).
As a result of pronounced dilation of the pancreatic duct, retention pseudocysts may form distal to the site of obstruction.
The effectiveness of ultrasound in pancreatitis
Using ultrasound, they examine the general visual picture of the condition of the organ, regarding the size, shape, and silhouette of the object. When changes occur, there is a reason to concentrate attention on this point. The use of ultrasonography is considered a mandatory method for diagnosing pancreatitis in any form of manifestation. The use of an examination method helps in making a diagnosis, prescribing the correct treatment for a complex disease, and allows for periodic analysis of the condition of internal organs.
Thanks to ultrasound, the initial stage of the disease is detected, and it is easy to monitor organs. For the doctor and the patient, it is easier to prevent an impending threat than to fight it later.
Ultrasound of the pancreas for various pathologies
For pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas and can be easily detected using an ultrasound scan. After all, it is the acute onset of this disease that greatly affects the structure, size, and structure of the gland tissues. The disease occurs in several stages and each stage, of course, will have its own characteristics.
Pancreatitis can be total, focal, segmental. They can be distinguished from each other by determining the echogenicity of the organ. A change in echogenicity can occur both in the entire gland and only in a certain part of it.
Initially, the pancreas will actively increase in size, the contours will be distorted, and the central duct will expand. As the gland enlarges, compression of large vessels will occur and the nutrition of neighboring organs will be disrupted, with an increase in echogenicity in them. The liver and gall bladder will also enlarge.
In the last stages of this serious disease, an experienced doctor will be able to consider when the necrotic stage will progress, organ tissue will disintegrate, and there may be the presence of pseudocysts or foci with abscesses in the area of the walls of the abdominal cavity.
Prevention of pancreatitis
Whatever one may say, a healthy lifestyle after an attack is the right decision, thanks to which good health can be maintained for many years. It is necessary to maintain good physical shape and eat small and often . After winter, when the body especially needs vitamins, you need to eat more natural foods, vegetables, and take vitamin complexes.
Smoking and drinking alcohol damage the human body at all levels, including contributing to the development of pathological processes in the pancreas. If it is not possible to eliminate alcohol completely, then it is necessary to reduce its dose and reduce the frequency of use.
Pancreatitis can be asymptomatic, and when symptoms do appear, it will be impossible to return the pancreas to its previous full state. It is easier to prevent pathology by avoiding all sorts of excesses than to later try to save the organ with the help of medicine.
A few final tips
The recommendations will be useful to people who care about the priceless gift of health and would never want to face a terrible disease.
- The longer food is subjected to heat treatment, the less valuable substances it contains for the body.
- Dishes heated one, two or more times are harmful.
- The number of dishes on the table is 2-3. If there are more of them, then in the stomach they turn into an indigestible mass and cause digestive disorders. The pancreas also suffers.
- The brown crust that forms on fried foods is a source of carcinogens. It is not absorbed by the body and is harmful in all respects.
- Drinks are not consumed during meals. You can drink 1 hour before sitting at the dinner table, and after eating, 1 hour later.
- Instead of coffee and black tea, it is better to give preference to decoctions of healthy and aromatic herbs.