Why are stones formed?
There are many reasons for the formation of stones, ranging from poor nutrition to hereditary predisposition. In addition, experts note that the following factors can affect the appearance of gallstones:
- age, most often the pathology is diagnosed in women after 40-45 years of age who lead a sedentary lifestyle;
- indigestion caused by frequent bloating;
- Crohn's disease;
- overweight or obesity;
- pregnancy;
- long-term course of treatment with certain medications;
- inflammation of the bile ducts or gallbladder walls;
- sudden weight loss;
- cholesterosis or chronic cholecystitis.
You may be interested in: Laser removal of kidney stones
How to know if there are stones in the gallbladder
It is possible to reliably determine the presence of stones in the gall bladder only after a series of diagnostic measures, but suspicions may be justified after a combination of a number of signs:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- digestive disorders (constipation or diarrhea);
- bitter taste in the mouth, especially in the morning, the presence of food does not matter;
- yellowing of the epidermis or eyesore;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- sudden nausea, which often ends with vomiting;
- shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.
Stones in the gall bladder after its removal
If the patient has two or more symptoms at the same time, it is necessary to contact a medical institution for consultation, diagnosis and further treatment. You should never self-medicate; sharp stones can damage the walls of the bladder or ducts, clog the ducts and disrupt the flow of bile, and provoke an inflammatory process that will end in peritonitis.
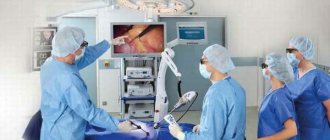
Shock wave lithotripsy of the gallbladder
Lithotripsy is a method of removing gallstones using various types of manipulation of the stone. Lithotripsy can be contact or remote.
During contact lithotripsy, the stone is crushed mechanically using special forceps inserted into the cavity of the gallbladder.
This method is more traumatic, since it is a full-fledged surgical intervention, but with minimal surgical access.
Remote lithotripsy is performed with a special device that delivers shock waves to the place where the stone is located. This method is non-invasive, and in the absence of contraindications, it is easy, safe and absolutely non-traumatic for the patient.
Wave shocks are applied to the stone, crushing it to such an extent that it freely exits through the gallbladder ducts. The number of waves varies depending on the nature of the stone. There is a wide variety of techniques for carrying out this method, through the use of different types of waves: ultrasonic, electromagnetic, piezoelectric.
Gallbladder removal
You may be interested in: Gallbladder removal with surgical laser
If the size of the stone does not exceed 0.3 mm, then it is quite possible that it will pass naturally; for larger stones, surgical treatment is required. Until recently, the gallbladder and its contents were simply excised surgically or by laparoscopy. Currently, they have learned to crush large stones into smaller ones, which makes it possible to avoid surgical intervention.
What is lithotripsy
Extracorporeal lithotripsy is a minimally invasive technique that allows you to crush stones in the gallbladder. Depending on the size of the stone, the three most common techniques are used:
- extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy;
- laser crushing;
- cholecystolithotomy through the skin;
- chemical contact lithotripsy;
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy is based on crushing stones under the influence of high-frequency waves. As a result of manipulations, the existing formations disintegrate into a sand-like state or into small fragments that come out naturally through the intestines. Shock wave lithotripsy is performed only if three main conditions are met: stones - no more than 3 pieces according to X-ray results, the size of the stones is no more than 3 cm, the gallbladder is functioning correctly. Otherwise, shock wave crushing is not acceptable.
How is the operation performed?
Before starting the manipulations, a control examination is performed using ultrasound or radiography. Then the patient is placed on a table equipped with a special lining capable of transmitting waves, stomach down. No anesthesia is required as the procedure is completely painless. The device is placed so that the focus of the waves falls on the gallstone, and the crushing process begins. Usually the session takes about half an hour, but if there are large formations, several procedures may be necessary.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
An undeniable advantage is the absence of incisions and punctures, which require special care and a long period of rehabilitation. Plus, the method is non-contact, which means the likelihood of infection during manipulation is extremely low.
The main disadvantage of the technique is the fact that it eliminates the effect, but does not eradicate the cause that led to the formation of stones. In addition, stone fragments can become stuck in the bile ducts or damage the walls of the bladder.
You may be interested in: Method of crushing (removing) kidney stones using ultrasound
Contraindications to shock wave lithotripsy
This method of exposure is contraindicated when the patient is taking blood-thinning drugs, has a blood clotting disorder, has inflammation in the liver and gastrointestinal tract, or has narrow bile ducts.
Remote techniques
Such techniques are very popular in the early stages of gallstone development, when their size is still small. These crushing methods do not require surgery and are very easy to use. The essence of such lithotripsy is to destroy the stone using either ultrasound or shock waves. The procedure does not require hospitalization and is performed in clinics with appropriate equipment in cases where the patient has no contraindications.
Shock wave lithotripsy produces waves of greater force and is used for stones larger than three millimeters. Ultrasonic crushing is used for smaller stones and is more gentle.
Shock wave technique
This technique is used in cases where surgery is contraindicated for a patient for some reason. The size of the stones should not be more than three centimeters, and their number in the bladder cavity should not be more than three.
The use of shock wave lithotripsy is contraindicated in the following cases:
- the patient has pancreatitis or peptic ulcer;
- in case of blood clotting disorders;
- for chronic cholecystitis;
- if the patient has an installed pacemaker;
- if the patient’s weight is more than 150 kilograms.
Inna Lavrenko
auto RU
If we talk about possible complications when using this method, they are related to the fact that the impact of shock waves is not limited only to crushed stones. They also act on the subcutaneous tissue, the skin itself and the mucous membrane of the organ. The strong vibration created by these waves damages the walls of capillaries and small vessels, which can lead to hemorrhages and bruises. In addition, under the influence of vibration, inflammation may occur on the mucous membrane of the bladder. Also during the procedure there is a risk of blockage of the bile duct and biliary colic.
There are three types of shock wave lithotripsy:
- piezoelectric;
- electrohydraulic;
- electromagnetic;
The piezoelectric technique involves the use of piezoelectric plates made of special ceramics to propagate waves. With its help you can crush stones up to 1 centimeter in diameter. This is a fairly low-noise procedure, but its cost is very high, since the ceramic plates used, which often have to be replaced, are very expensive.
Electromagnetic lithotripsy uses pulses generated by special electromagnetic coils. These pulses are collected into a beam using a biconcave lens. This beam is directed to the crushing object. The membrane through which the pulse is applied to the lens, as well as the coils themselves, require replacement every 10 months.
Read also: Why is palpation of the gallbladder necessary?
The electrohydraulic method involves the use of an electrical impulse and water. Water is first pumped into a special bag, which transmits shock waves to the patient. The wave strength of this method is the highest (compared to the previous two), and this makes it possible to crush even three-centimeter stones.
Laser crushing
The fundamental difference of the technique is that stones are crushed using laser energy introduced into the cavity of the gallbladder.
During the operation, a small incision is made on the patient's skin, through which the device is brought directly to the stone. The manipulation time usually does not exceed 20 minutes; after a couple of hours the patient can go home.
Pros and cons of laser crushing
Thanks to the high efficiency of the laser, the stone is crushed into very small fragments or sand, which easily moves into the intestines. There is no chance that fragments will get stuck in the bile ducts.
The main disadvantage of laser crushing is that with the slightest deviation of the laser beam, severe burns of the gallbladder wall can occur, and if the impact is repeated, then even neighboring organs, up to the formation of ulcers and perforations.
Contraindications for laser crushing
The main contraindication is the patient's overweight (obesity), when the fat layer prevents the insertion of the device into the abdominal cavity. In addition, the operation is not recommended for patients over 60 years of age and people with a complex of concomitant diseases.
Contact techniques
In this article we will briefly review the main existing methods of performing lithotripsy.
Chemical contact lithotripsy
This method of grinding stones is considered the safest among other contact methods. Before the operation, the patient must be examined to determine if he has an allergy to the substance used to crush the stones. Under anesthesia, a laparoscopic intervention is performed, during which a catheter is inserted through a special hollow tube (trocar), through which a special chemical solution is supplied into the organ cavity, which will dissolve the stones. After this, the cavity of the gallbladder is washed in order to remove the remaining particles from it along with the solution. Chemical contact lithotripsy is used in cases where the bile ducts are too narrow, and other methods of grinding stones are not applicable.
Mechanical contact lithotripsy
This technique involves a full-fledged surgical intervention. After the patient is prepared for surgery and anesthesia is administered, an incision is made in the abdomen through which a lithotripter (a special device used for crushing) is inserted. It looks like a basket equipped with cables to capture the crushed formation. The basket contains a mechanism for exerting strong pressure on the stone, under the influence of which it is crushed. If it is possible to crush the formation into very small particles, then they are washed out of the gallbladder cavity with a special solution.
It is worth saying that the use of this technique can lead to complications (both during the operation and after its completion). During surgery, the doctor may have problems introducing the lithotripter through the lumen of the bile duct, in which it can simply get stuck and injure its walls. In addition, it is also not always possible to grab a stone with a lithotripter, which makes crushing it impossible. Additional difficulties during such an operation are created by diseases such as jaundice and cholangitis.
Read also: Methods for treating an enlarged gallbladder
Contact lithotripsy is prescribed:
- patients with single gallstones larger than 1 centimeter;
- in case of the presence of several stones that are located close to each other;
- if the stones fill almost the entire cavity of the bladder;
- if a calculus has formed in the common bile duct (choledochus) and caused inflammation and jaundice;
- for young patients, in order to preserve the functionality of the sphincter of this organ.
Lithotripsy procedure
This crushing method cannot be used in the following cases:
- very strong stones against the background of jaundice and cholangitis;
- if the patient is in serious condition;
- if the stones are located in the intrahepatic bile ducts;
- if the bile ducts are greatly dilated.
Laser contact lithotripsy
It is important to know!
78% of people with gallbladder disease suffer from liver problems! Doctors strongly recommend that patients with gallbladder diseases undergo liver cleansing at least once every six months... Read more...
This modern technique has recently been used more and more widely. Using a laser, it is possible to crush stones not only of cholesterol, but also of other nature. This method is often used for patients over 60 years of age, since they begin to develop all sorts of complications of gallstone disease. In addition, people at this age may simply not be able to withstand general anesthesia and not undergo the operation itself due to the presence of pathologies of the cardiovascular and/or respiratory system.
Laser lithotripsy is performed under local anesthesia. This technique can be used in cases where the size of the stone does not exceed 2.5 centimeters.
The intervention itself is minimally invasive. Through a small incision in the peritoneal wall, a tube on which the laser device is located is inserted into the cavity of the gallbladder. With the help of a laser, almost any type of stone can be crushed into dust. This lithotripsy is very effective against stones whose density is very high. After the destruction of the calculus, its remains are sucked out through the same tube using saline solution.
The main disadvantage of laser crushing is that the procedure requires very high precision. The slightest deviation of the beam from the stone can lead to severe burns of the mucous membrane of the organ.
Read also: How are polyps in the gallbladder treated in a child?
Percutaneous cholecystolithotomy
The essence of the technique is to insert a rigid cytoscope into the gallbladder, with the help of which stones are removed. First, a small incision is made in the patient's abdominal wall. The entire operation is performed under anesthesia, and monitoring is carried out using an ultrasound machine. If the stones are too large, they are first crushed using a laser or electro-hydraulic device.
After the stones are removed, a special drainage is inserted into the gallbladder, which can remain in the patient’s body for up to 10 days.
Advantages and disadvantages of the technique
With cholecystolithotomy, there is no chance that sharp fragments will remain in the bladder that could get stuck in the bile ducts or damage their walls; the rehabilitation period is no more than two weeks, after which the patient can return to normal life and activities.
A huge disadvantage is that the technique is highly traumatic compared to the two methods described above.
Contraindications for surgery
Percutaneous cholecystolithotomy is not performed in the presence of cholestatic syndrome, large stones, or the accumulation of a large number of stones. Simply put, the technique is appropriate when there are single moving stones, the size of which does not exceed 3 cm.
Shock wave lithotripsy of the gallbladder price
Gallstone disease is a disease characterized by the formation of stones in the cavity of the bladder or its ducts. The formation of stones is associated with the deposition of bile pigments, cholesterol fragments, protein and calcium ions, as well as products caused by impaired metabolic processes of fatty acids.
Indications for lithotripsy for cholelithiasis
Among the conditions for which lithotripsy of gallstones is prescribed are:
- detection in its cavity of no more than three stones, the size of which does not exceed 3 cm;
- stones of various structures with a predominance of lime inclusions;
- intolerance to drugs intended to destroy these formations;
- lack of effect from the therapy for cholelithiasis;
- detection of preserved contractile activity of the bladder against the background of stones in the cavity.
The choice of indications is decided by a specialist on an individual basis based on the clinical picture, the dynamics of the pathological process and the use of medications.
Types of lithotripsy of gallstones
In clinical practice, several techniques are used to remove stones. Shock wave and laser lithotripsy are widely used. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, which are taken into account when selecting treatment.
Shock wave
The technique refers to procedures prescribed in the presence of contraindications to surgical intervention. The size and number of identified stones are preliminarily determined.
There should be no more than 3 of them, and the size of each should not be more than 2 cm. Ultrasound scanning, radiography or computed tomography are used as diagnostics.
One of the additional conditions for the procedure is that the patient’s weight does not exceed 150 kg.
Currently, there are several types of shock wave lithotripsy, these include:
- Piezoelectric lithotripsy is based on the propagation of waves from a piezoelectric plate, which is made of a special ceramic material. As a result, the stone is crushed to 1 cm in diameter. There is no high-frequency noise produced during the procedure. The cost of the procedure is explained by the need to frequently replace the plates.
- Electrohydraulic therapy is based on the use of impulses simultaneously with water. It must first be pumped into a special bag capable of transmitting impulses to the patient. Due to the high force of the wave, stones up to 3 cm in size are quickly crushed.
- Electromagnetic lithotripsy is based on the formation of pulses emanating from an electromagnetic coil. Using a biconcave lens, a beam of waves is created that is directed towards the crushing area. The procedure can also be expensive due to the need to replace equipment components once a year.
Shock wave lithotripsy, despite its pronounced therapeutic effect, has disadvantages associated with the principle of its effect on the body. The wave acting on the gallstone is not selective, that is, when passing through the tissues of the body, it also affects other areas.
In particular, strong vibration leads to damage to capillaries and small vessels, which leads to the formation of hematomas and inflammation of the bladder walls.
Laser
This type of lithotripsy is classified as an invasive technique. It is performed during ERCP (Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography). Together with the conductor, a light guide is inserted into the common bile duct; a radiation source will subsequently come from it. In order to achieve maximum effect, it is necessary to connect the light guide to the stone.
Due to the supply of energy, it is destroyed into many parts. Removal of broken remains is carried out using special forceps. To clean the cavity, it is washed with saline solution. These procedures reduce the risk of complications and relapses due to the preservation of small stones.
The advantages of the technique include:
- the possibility of dissolving large stones;
- use against the background of developed obstructive jaundice;
- performed without anesthesia with percutaneous transhepatic puncture.
The disadvantages of laser lithotripsy include an increased risk of bleeding or wall burns, as well as possible wall perforation.
Treatment of the gallbladder with lithotripsy
This is a collective concept that implies methods for removing stones. Currently, there are two main methods - remote procedure and contact. The first includes shock wave and ultrasonic techniques.
Contact crushing methods include:
- chemical;
- mechanical;
- laser lithotripsy.
Contact interventions are carried out using chemicals or lithotripters (devices designed for crushing), as well as precisely directed laser beams. The procedure requires general anesthesia or local anesthesia. Most often, the latter is used for elderly patients.
External lithotripsy of formed gallstones is the most common technique. This is largely due to the lack of intervention in the body and the need to stay in a hospital. Unlike contact methods, manipulation is possible only with small formations.
Contraindications and complications
Before carrying out the procedure, you must carefully study the presence of contraindications. These include:
- bleeding disorders with ambiguous effects of drugs on the hemostatic system;
- signs of pancreatitis, cholecystitis or stomach ulcers;
- aneurysm of a vessel or the presence of cystic formations in the area affected by the shock wave;
- symptoms of shutdown of the functional activity of the gallbladder;
- manifestations of obstruction of the bile ducts;
- stones in the non-inflamed gallbladder in the amount of more than three, with the simultaneous identification of the diameter of any stone more than 2 cm;
- built-in pacemaker for heart failure;
- pregnancy at any stage. In this case, the exact effect on the fetus has not been identified; the technique is not used due to insufficient information.
When performing lithotripsy of gallstones against the background of these contraindications, the risk of complications increases.
The main complications include:
- inflammation of the gallbladder and development of hepatic colic;
- an increase in the concentration of liver enzymes in the blood serum, as well as bilirubin;
- choledocholithiasis;
- gross hematuria that occurs after the procedure;
- hematoma in the liver tissue, as well as surrounding tissues;
- cholangitis;
- sepsis.
The appearance of these complications requires urgent medical care to alleviate well-being and improve the prognosis. Despite the ease of use and rapid recovery of the body after the procedures, it is necessary to regularly visit a specialist in order to prevent relapse.
Removing stones from the gallbladder with a laser is one of the progressive techniques that allows you to crush gallstones and remove them from the body without resorting to traumatic abdominal surgery. In case of cholelithiasis, doctors try to preserve the organ and its functions as much as possible, and the use of laser successfully solves this problem.
Source: https://mybabic.com/info/udarno-volnovaja-litotripsija-zhelchnogo-puzyrja/
Chemical (drug) contact lithotripsy
Chemical contact lithotripsy is considered one of the most gentle methods, which consists of injecting directly into the gallbladder a special substance that can dissolve stones. Before starting the procedure, a test is carried out to determine the patient’s tolerance to this medication. The medicine is administered through a laparoscopic incision in the abdominal cavity. After the stones are dissolved, the gallbladder cavity is washed with a special solution to remove the smallest particles from the organ. Chemical contact lithotripsy is indicated for extremely narrow bile ducts when the use of other non-invasive techniques is contraindicated. The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
The advantage of the technique is that all stones can be removed in one session, the disadvantages are that intolerance to the chemical substance occurs in approximately 15-20% of patients.
You may be interested in: Laser tonsil removal, tonsillectomy
Contraindications to chemical contact lithotripsy
One of the main contraindications is pathological blood diseases; in addition, the doctor pays attention to the age, weight and general condition of the patient.
Mechanical biliary lithotripsy
The essence of the technique comes down to crushing, capturing and removing stones and fragments using a lithotripter. After removing the stones, the bladder is washed and repeated cholangiography is performed. If stones or fragments are found in the image, the manipulation is repeated. The entire operation lasts about two hours under general anesthesia.
Advantages of the method
Mechanical biliary lithotripsy is appropriate for developed obstructive jaundice (stones entering the bile ducts), stones of any size are crushed, the cost of the operation is relatively low.
Disadvantages of the technique
The operation is technically complex and with the slightest inaccuracy the bladder and ducts can be damaged. There is often a situation where small fragments are implanted into the inflamed wall of the bladder and remain unnoticed; often the operation takes place with great blood loss for the patient.
Contraindications to mechanical biliary lithotripsy
Dense, immobile stones are difficult to remove, especially those located inside the hepatic ducts. The general serious condition of the patient for whom long-term surgical intervention is contraindicated.
The choice of method for crushing gallstones remains with the attending physician after a thorough study of the entire clinical picture. It is worth noting that a single lithotripsy does not guarantee the absence of stones in the foreseeable future, since each of the above methods eliminates the effect, leaving the cause unattended. According to statistics, about 30% of people who have undergone lithotripsy, stones appear again, and all the efforts spent on their elimination are in vain.
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy of the gallbladder
This article was edited by gastroenterologist Daniela Sergeevna Purgina.
In this article, we will talk about a method of treating cholelithiasis, such as lithotripsy, that is, crushing stones.
What is lithotripsy
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy - destruction of stones using shock waves induced by a generator. This technique was first used in 1985. It is practiced strictly according to indications as independent therapy or in combination with oral administration of litholytic (dissolving) drugs, which gives the best result.
This type of treatment for gallstone disease is conceived as an alternative to cholecystectomy: in order to avoid removing the gallbladder. However, in practice, stone crushing is rarely used. This is explained by three reasons:
- High risk of serious complications (eg acute pancreatitis).
- Presence of contraindications.
- Limited indications.
Is it effective to crush gallstones?
The effect is considered effective if there is no relapse within a year, and ultrasound 6 and 12 months after the procedure shows that the gallbladder is free of stones. If the patient, after crushing the stones, takes ursodeoxycholic acid, which has a litholytic effect, then the effectiveness can reach 80%, at least 45%.
At its core, this method is symptomatic, and not etiotropic (eliminating the cause of the disease) treatment. Therefore, it does not prevent the reappearance of stones.
Most often it is used to break up stones stuck in the duct after removal of the bladder.
But only if for some reason it is impossible to perform endoscopic lithoextraction: for example, there are contraindications or other obstacles to the operation.
In what cases is stone crushing carried out?
Lithotripsy is in principle only possible under the following conditions:
- cholelithiasis with an uncomplicated course;
- the ability of the gallbladder to contract is preserved by 60% or more;
- cholesterol stones or partially (only at the edges) calcified, i.e. transparent to x-rays;
- number of inclusions from 1 to 3, no more;
- the size of the stones is no more than 3 cm and no less than 1 cm;
- stones occupy no more than half the volume of the gallbladder.
The most important condition: the gallbladder must have sufficient motility, and the ducts must have normal lumen for the evacuation of fragments.
Crushing gallstones without surgery is possible, but it is usually not worth it. View in full size
When the procedure is prohibited
We list the absolute contraindications to crushing stones:
- calculi are calcium in composition;
- too many inclusions: 3 or more;
- the stones are too large: their total diameter is 3 cm or more;
- blood clotting is impaired;
- there are cysts or vascular aneurysms in the path of the shock wave;
- cholecystitis;
- duodenal ulcer;
- pancreatitis;
- obstruction of the ducts;
- use of pacemakers;
- pregnancy.
What complications are there?
After crushing there can be very serious, deadly complications:
- in 30–50% of cases - biliary colic;
- 3–5% - hematuria;
- 2–4% - cholangitis and biliary sepsis;
- 2–3% - acute pancreatitis and cholecystitis;
- 1–2% - increased bilirubin and transaminases in the blood;
- lower back pain;
- obstructive jaundice;
- hematomas in the liver, right kidney.
How is lithotripsy performed?
Shock wave generators are:
- electrohydraulic;
- magnetically restrictive;
- piezoelectric.
Laser crushing
Cutting stones using a laser is also called percutaneous cholecystotomy, and this highly effective treatment is prescribed in cases where surgery cannot be performed.
This method prevents bacteria and viruses from entering the wound. The body recovers as quickly as possible after such exposure. During a 20-minute session, the stones are broken into fine sand and removed painlessly.
Laser crushing refers to laparoscopic operations. A laser tube is inserted into the stone through a small incision in the abdomen. Manipulations are carried out under ultrasound supervision. After the session, the hole is drained for a week.
Due to the fact that the procedure does not affect the metabolism in any way, every second patient experiences a relapse - and the stones grow again.
Contraindications to laser crushing:
- inability to bring the laser tube to the stone;
- blood diseases;
- viral infection;
- pregnancy;
- the patient's weight is more than 120 kg;
- oncological diseases.
Shock wave crushing
The shock wave (or ultrasonic) method, unlike the laser method, does not require any incisions at all. The stones are destroyed by ultrasonic pulses that pass unhindered through the body tissues. The shock wave is generated under water, and is focally applied to the patient’s body through a bag of water, which is placed on the skin lubricated with gel.
After processing, the stones break down into smaller pieces and then come out. However, if they are hard, they may not break even after several sessions. The easiest to crush are urate and oxalate formations up to 25 millimeters in size.
Contraindications to ultrasonic crushing:
- the patient's weight is more than 120 kg;
- height more than 2 meters;
- diseases of the heart, blood, blood vessels;
- pregnancy;
- acute viral diseases.
Before the session, blood-thinning medications and antibiotic therapy are prescribed several days before the session in case of identified infections.
The duration of the session is no more than 1 hour, it is performed under general or local anesthesia. Pain can be observed both during the manipulation and over the next 2 weeks, when stone fragments come off. These pieces are quite large and have sharp edges. Therefore, they can injure the mucous membranes, cause severe colic or completely block the duct.
Contact chemical cholelitholysis
This technique has appeared recently, it is more experimental than practical. Necessary conditions for its implementation:
- cholesterol formations;
- the organ is fully functional and not inflamed;
- the ducts are completely passable.
The essence of the method: a catheter is inserted into the gallbladder through a peritoneal puncture, and through it a potent substance is supplied to the calculus, which dissolves the stone-forming substance. After some time, the “cocktail” is sucked out with a syringe and another portion of the solvent is supplied. The session lasts 4–16 hours.
For solidified cholesterol, methyl tert-boryl ether is used as a solvent. This substance does not irritate the mucous membrane, but is not able to completely dissolve the solid formation. New layers quickly grow on the remaining fragments. Therefore, the technique is not self-sufficient; it can only be used as an addition to traditional therapy.
What are the advantages of lithotripsy
The biggest advantage of stone crushing is the ability to avoid surgery for patients for whom it is contraindicated.
During cholecystectomy operations, a 10–15 cm long incision is made. Considering that most patients with cholelithiasis are obese, such wounds heal poorly due to the thick layer of subcutaneous fat. And this is fraught with many complications, including sepsis.
Cons of the procedure
Gastroenterology clinics, where they were the first to practice lithotripsy, quickly became disillusioned with this method of treatment. Expensive equipment is practically idle. And there are two main reasons for this:
- Firstly, it turned out that after shock wave exposure, the wall of the gallbladder loses the ability to contract normally. In fact, it turns into a stone collection bag, which must be removed surgically. As practice has shown, most patients who have undergone lithotripsy sooner or later have their organ removed.
- Secondly, evacuation of fragments in half of the cases occurs with severe colic. The high risk of its occurrence lasts 2 weeks, and at this time the patient is already at home or at work. The patient's condition in this case requires emergency medical care. If the duct is completely blocked by a large fragment, then urgent surgical intervention is required within 3 hours after the onset of colic. Otherwise, death is possible due to rupture of the gallbladder or due to painful shock.
Sharp-edged fragments injure mucous membranes along the way. These microtraumas take time to heal. Also, scratches can become a gateway to infection and provoke various inflammatory processes in the digestive tract.
Therefore, most gastroenterologists have practically abandoned such therapy, preferring to solve the problem immediately radically: by removing the gallbladder on the operating table. Thus, cholelithiasis became a surgical pathology.
Alternatives to lithotripsy
There are only two ways to remove the gallbladder:
Both options are done under general anesthesia. However, the first method is less traumatic and does not require a stay in intensive care. Patients are discharged home after 2 days, and can begin work after a month.