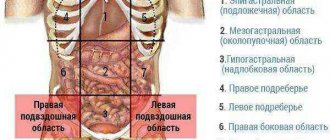
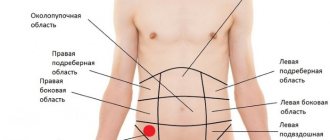
Causes of lumps in the abdominal area
Lumps in the right side of the lower abdomen in women are most often caused by problems with the kidneys and large intestine. The causes of the appearance of formations on the left are called pathologies of the ureter and omentum. Intestinal pathologies are accompanied by lumps in the lower abdomen or in another part of it. Most often, lumps in the right or left side occur due to the following health problems:
- Appendicitis. Inflammation of the appendix is manifested by acute pain on the right side, fever, and nausea. If this condition develops, a person must urgently contact a surgeon to perform an operation.
- Diverticulitis. The disease is accompanied by protrusion of part of the intestinal walls towards the abdominal cavity. This problem can be caused by helminthic infestations, unfavorable heredity or poor nutrition. The pathology is accompanied by indigestion, pain, and possibly increased body temperature.
- Aortic aneurysm located in the peritoneum. A similar problem arises against the background of hypertension, bad habits, and atherosclerosis.
Umbilical cord hernia
One of the obvious signs of an umbilical hernia is a hard lump in the peri-umbilical area, which does not disappear when you press your fingers, but, on the contrary, becomes more noticeable and causes severe pain. In addition, the patient will be bothered by bloating, constipation, vomiting and rapid heartbeat.
An indicator of the appearance of a hernia is a palpable dense area in the abdominal area, which does not disappear when pressure is applied to it. Pressing is accompanied by severe pain, and the hernia becomes even more noticeable.
The following symptoms are also observed:
- bloating;
- bowel dysfunction;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased heart rate.
There are two types of umbilical hernia - strangulated and reducible.
If any of them appear, you should contact a specialist. The first type is eliminated through surgery, and the second type is eliminated by manual reduction of the seal that appears near the navel.
Tumors
Lumps in the stomach area can be caused by cancer - a malignant process that affects men 2 times more often than women. The age period in which the disease manifests itself is about 70 years. But the process begins much earlier; at first they manifest themselves with nonspecific symptoms:
- feeling of fullness in the abdomen, bloating immediately after eating;
- increased salivation;
- nausea, vomiting;
- mild pain in the epigastric region;
- decreased appetite, aversion to meat foods;
- heartburn;
- flatulence.
Signs of tumors
A lump under the skin in the form of a ball on the abdomen can be a tumor - benign or malignant. Most often, women are diagnosed with the following formations:
- Lipoma. A mobile bump on the skin is most often a benign tumor that is filled with fatty tissue.
- Atheroma. The formation looks like a ball that fits tightly to the skin. A dark dot may appear on the surface of the lump in the middle, which indicates a blockage of the sebaceous gland. Such a bulge on the body is accompanied by inflammation, and therefore leads to pain and may be hot to the touch.
- Fibrosarcoma. A malignant tumor with a diameter of 2-15 mm. It looks like a small painful bump on the skin. If left untreated, it becomes crusted or eroded over time.
If a small lump appears on your stomach, this may indicate the development of fibroids. A benign tumor consists of connective tissue. It can appear on the skin, tendons, mucous membranes or on the surface of internal organs.
Benign stomach tumors
Depending on their origin, benign neoplasms of the stomach are divided into epithelial and non-epithelial. Among epithelial tumors there are single or multiple adenomatous and hyperplastic polyps, diffuse polyposis. Polyps are tumor-like epithelial growths in the lumen of the stomach with a stalk or a wide base, spherical and oval in shape, with a smooth or granulating surface, dense or soft consistency.
Gastric polyps most often occur in males aged 40-60 years, usually located in the pyloroantral region. The tissues of the polyp are represented by the overgrown integumentary epithelium of the stomach, glandular elements and connective tissue rich in blood vessels. Adenomatous polyps of the stomach are true benign tumors of the glandular epithelium and consist of papillary and/or tubular structures with pronounced cellular dysplasia and metaplasia.
Adenomas are dangerous in terms of malignancy and often lead to the development of stomach cancer. Up to 75% of benign epithelial tumors of the stomach are hyperplastic (tumor-like) polyps that arise as a result of focal hyperplasia of the integumentary epithelium, which have a relatively low risk of malignancy (about 3%). With diffuse gastric polyposis, both hyperplastic and adenomatous polyps are detected.
Rarely occurring non-epithelial benign tumors form inside the gastric wall - in its submucosal, muscular or subserosal layer from various elements (muscle, fat, connective tissue, nerves and blood vessels). These include fibroids, neuromas, fibromas, lipomas, lymphangiomas, hemangiomas, endotheliomas and their mixed variants.
Also in the stomach, dermoids, osteomas, chondromas, hamartomas and heterotopias from the tissues of the pancreas and duodenal glands can be observed. Nonepithelial benign neoplasias occur more often in women and can sometimes reach significant sizes. They have clear contours, usually a round shape, and a smooth surface.
Leiomyomas, the most common benign nonepithelial tumors, can remain in the muscular layer, grow toward the serosa, or grow through the gastric mucosa, leading to ulceration and gastric bleeding. Nonepithelial neoplasms of the stomach are predisposed to malignancy.
Specifics of palpation in children
To perform the procedure on infants, the following requirements must be met:
- the child should lie on his back, the baby’s muscles should be relaxed;
- Before performing the procedure, the doctor needs to warm his hands;
- If pain appears, to which the child reacts by crying, the procedure must be stopped immediately.
The palpation procedure allows you to determine the lower border of the stomach in young children, as well as identify the syndrome of the greater curvature of the stomach. It is necessary to pay attention to the thickness of the child’s skin and muscle elasticity.
Diagnosis in children begins with the stomach area and ends with the navel, where the intestines are palpated. Palpation of the stomach is an important link in the process of diagnosing gastrointestinal diseases. Correct implementation of the procedure allows you to make an accurate diagnosis and promptly begin treatment therapy.
- Why do lumps (painful, round, black, small) appear on the labia majora and labia minora?
- A breast lump is cancer
Causes of lumps around the navel
Pathological seals can occur in the navel area. The main reasons for their development are:
- hernia;
- umbilical ring fistula;
- cyst;
- metastases formed in the presence of stomach cancer.
In the lower abdomen under the navel, the appearance of compactions may indicate the presence of inflammatory bowel pathologies and urolithiasis, rupture of the walls of the diverticulum. Tension and pain also appear with increased gas formation in the large intestine.
Surgery
Conservative methods of dealing with compactions in the stomach area can be effective only at the initial stage of the disease. If the disease is advanced, all doctors are inclined to require surgical intervention.
It can be of three types:
- resection – partial removal of the area of the main digestive organ;
- drainage - removal of liquid or gas from a seal;
- removal of the stomach. This method of surgical intervention is an extreme, undesirable measure. It is practiced only when there is a high probability of death.
From all of the above, a number of conclusions should be drawn:
- firstly, lumps in the stomach area are an extremely rare condition, in most cases having a congenital form;
- secondly, in most cases, compaction is treated with surgical methods;
- thirdly, with timely treatment, the risk of complications of the situation is unlikely.
If symptoms indicate the presence of lumps in the stomach, consult a doctor immediately. This will make it possible to avoid complications and cure the disease at an early stage.
Percussion
The manipulation is carried out by superficial finger strikes, starting from the navel and moving towards the lateral areas of the abdomen. The patient is placed on his back. The method makes it possible to determine Traube's space, that is, the presence of a gas bubble at the bottom of the epigastrium. Palpation of this type is carried out on an empty stomach; if the volume of gas on an empty stomach is insignificant, a preliminary diagnosis of pyloric stenosis is made.
This method also detects the presence of fluid in the stomach. The patient is asked to lie on his back. The doctor also asks the patient to breathe deeply, involving the stomach in the breathing process. The gastroenterologist makes quick, short pushes in the epigastric zone with four half-bent fingers of his right hand. With his left hand, the specialist fixes the abdominal muscles in the lower region of the sternum. If there is liquid in the stomach, a gurgling sound appears. The procedure makes it possible to determine the lower border of the stomach and the tone of the organ.
The value of percussion in the diagnosis of gastric diseases is small.
Using it, you can determine Traube's space (the area of tympanic sound on the left in the lower part of the chest, caused by the air bubble of the fundus of the stomach). It can be increased when there is a significant increase in the air content in the stomach (aerophagia). Percussion allows you to determine the presence of free and encysted fluid in the abdominal cavity.
With the patient positioned on his back, quiet percussion is performed from the navel towards the lateral abdomen. Above the liquid, the percussion tone becomes dull. When the patient turns on his side, free fluid moves to the lower side, and above the upper side the dull sound changes to tympanic. Encapsulated fluid appears with peritonitis limited by adhesions. Above it, during percussion, a dull percussion tone is determined, which does not change localization when changing position.
Lumps in the lower abdomen
A pathological formation can appear in any part of the abdomen. If a lump is felt in the lower abdomen, then the cause is:
- pinched hernia;
- protrusion of the sigmoid colon;
- rupture of the walls of the diverticulum;
- inflammatory process in the pelvic organs;
- intestinal obstruction in the lower part of the organ;
- increased gas formation;
- tumors in the male genital organs.
Irritable bowel syndrome, an inflammatory process in the intestinal canal, or compression of the nerves can lead to the appearance of a lump in the lower abdomen. A lump often occurs as a stone moves down the ureter.
Gynecological diseases
A slight protrusion in the lower abdomen is observed in the early stages of pregnancy. This phenomenon is especially pronounced in thin women. If pain is felt when pressing on the tubercle or other alarming symptoms are present, the woman should consult a doctor. Other reasons for the appearance of bumps on the stomach include:
- development of adhesive processes in the uterus;
- ovarian torsion;
- the appearance of appendage cysts of significant size.
Often, hard formations appear after childbirth during a cesarean section. They are localized in the suture area and can cause severe discomfort. This phenomenon is caused by the fact that during the healing process, injured areas of the body are covered with dense scar tissue. When using low-quality suture materials against the background of developing autoimmune reactions, ulcers may form under the skin. This phenomenon is accompanied by burning, itching, and the appearance of discharge from the scar.
Factors associated with the occurrence of lumps in the stomach area
Any disease of the gastrointestinal tract entails a lot of problems that cause a decrease in quality of life. As a rule, all gastrointestinal diseases are related to each other, and one can develop into another, for example, gastritis into an ulcer, etc. A cyst, which can arise as a result of the following diseases, is no exception:
- Ménétrier's disease is a systematic disorder of the digestive system associated with the proliferation of the mucous membrane of the main digestive organ. This disease is most often diagnosed in middle-aged men. The causes are not fully understood;
- Zollinger-Elisson syndrome, characterized by excessive production of hormones, which in turn leads to blockage of the glands responsible for the production of digestive juice;
- herpes, which causes damage to gastrointestinal tissue;
- chronic syphilis, which causes damage to the mucous membranes throughout the body, including the stomach;
- pneumatosis, uncontrolled flow, which causes the formation of cysts filled with gas. This condition is typical for people who move little;
Timely treatment of gastrointestinal diseases allows the formation of tumors in the stomach area to be avoided, with the only exception being congenital pathologies. Thus, if you experience symptoms indicating stomach disease, you should consult a doctor.
Nature of the pain syndrome
Let's look at how the pain that accompanies inflammation differs at different stages of gastritis:
- Protracted chronic gastritis, accompanied by an increase or decrease in the level of secretory activity, usually reminds itself of itself by the appearance of aching discomfort of moderate intensity. At the same time, pain is often accompanied by a feeling of fullness in the stomach. Discomfort and heaviness always appear after eating.
- If the sensation is very intense, this is an unfavorable sign. A similar nature of pain with gastritis indicates an exacerbation of the process. If the patient experiences intense pain, it is easy to suspect the development of an erosive or ulcerative process. Perhaps a severe attack became a sign of a concomitant chronic disease - cholecystitis or pancreatitis.
- The acute nature of the sensations, reminiscent of a blow with a dagger, indicates that the patient has a perforation of the stomach ulcer. The disease should be differentiated from acute catarrhal gastritis.
- Hunger pain occurs at night.
The nature and intensity of the pain syndrome, the duration of the attack depends on the form of the disease and its stage. An experienced doctor, after examining a patient, is able to determine which pain during gastritis indicates the localization of the pathological process in a certain place. Based on the information received, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Characteristic symptoms
Sour belching and heartburn can be a symptom of a stomach cyst.
The disease can be sluggish, the symptoms are mild. Growing to large sizes, it causes characteristic symptoms:
- pain in the stomach, characterized by a sharp tingling sensation;
- fast weight loss;
- decreased appetite;
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- the appearance of swelling on the arms, legs, face;
- sour belching;
- frequent heartburn;
- flatulence.
These are the main symptoms, the detection of which indicates the need for a medical examination.
Urachal cyst
The appearance of a tubercle on the abdomen, accompanied by pain, intestinal and dysuric disorders, may indicate the presence of a urachus cyst. This is an embryonic malformation localized in the urinary system. The cyst contains mucus, residual amniotic fluid, and meconium inside.
The disease may not manifest itself for a long time. The cyst gradually increases in size, this increases the risk of infection with the development of suppuration and sepsis. With such complications, symptoms of intoxication of the body, swelling and pain of the anterior abdominal wall, and hyperemia of the skin appear.
Enlarged abdomen in the epigastric region and abdominal wall
The patient may complain of the appearance of a soft-to-touch protrusion under the skin, which may be a lipoma or an epigastric hernia containing preperitoneal fat.
An epigastric hernia forms in the midline of the abdomen through a white line defect. If pinched, the tumor-like protrusion becomes painful, and redness of the skin around it is noted.
Sometimes the patient complains of a dense bone formation in the upper part of the epigastric region, which turns out to be an ordinary xiphoid process. The patient notices this when deliberately trying to lose weight or rapid loss of body weight due to some disease.
Metastases, for example tumors of the mammary glands or bronchi, can be detected in the form of inactive tumor-like formations in the skin or subcutaneous tissue.
The soft, lobular tumor detected on palpation is most likely a lipoma. This tumor can remain mobile when the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall are tense. A fixed, sometimes painful wen located in the midline of the abdomen suggests the presence of an epigastric hernia. Epigastric hernias in most cases consist of preperitoneal fat, although the contents of the hernial sac may be small intestine. On palpation, you can feel a cough impulse. The tumor-like formation in the case of an epigastric hernia can be reduced.
Solid tumor-like formations in the area of the anterior abdominal wall, having an irregular shape and motionless on palpation, are most likely metastases, especially if the patient has breast cancer or bronchogenic lung cancer.
Treatment measures
Methods are selected exclusively by the attending physician. It is possible to prescribe medications based on the results of diagnostics, other studies, tests, blood and urine tests. So, for example, if a hernia is detected, a correction is required, which means surgical intervention. The main thing is not to give the pathology a chance to develop further.
Additionally, in the case of a hernia in the area of the umbilical ring in infants, it is recommended to massage, place the baby on the tummy more often, and apply a copper coin to the navel.
Reviews from women are such that in some cases the umbilical hernia resolves on its own. The main thing is to start preventive or therapeutic measures in time.
Often in infants a hernia is caused by poor ligation of the umbilical cord or accumulation of gases. It is enough to carry out simple manipulations in a timely manner, which will certainly help to avoid complications and surgery in the future.
Of course, in some diseases, a protrusion at the navel carries a mortal danger:
- peritonitis;
- abdominal aortic aneurysm;
- duodenitis;
- inflammation of the intestine, duodenum.
Conclusion
Immediate assistance from specialists is required. Connivance and lack of reaction to a protrusion in the abdomen on the part of parents can lead to irreversible consequences and death.
If suspicious signs appear in the form of a growth in the navel area, it hurts a lot and increases in size, then you need to consult a doctor immediately.
How to treat?
The doctor determines the treatment of a stomach cyst based on the size, area of tissue damage, and the cause of the formation of the seal:
- The drug method is used if the pathology is detected at an early stage. Immunostimulating, absorbable medications are prescribed and the seal disappears. Practice has shown that the use of medications gives a bad effect even in the early stages.
- The folk method is used for the first time when making a diagnosis. It consists of using herbal infusions from beneficial plants. It has been noted that using an infusion of pine needles has a good effect. 2 tablespoons of pine needles are poured into 0.5 liters of boiling water and left to brew for a short time. You need to drink the tincture a day and prepare a new one. The juice of burdock leaves is often used. Take 2 tablespoons of juice half an hour before meals 3 times a day. The duration of treatment is at least a month. It must be remembered that treatment with folk remedies must be carried out under the strict supervision of a specialist. Self-medication can lead to exacerbation of the disease. Contraindications must be taken into account when taking folk remedies in order to avoid unpleasant consequences.
If the conservative method of treatment is ineffective, an operative method through surgery is used. It is divided into 3 types:
- Resection is partial removal of the stomach followed by reconstruction of the digestive system. Depends on the size of the affected area. Relapse after such an operation is extremely rare.
- Drainage of a gastric cyst is the removal of internal contents using special medical equipment. Indicated for a single cyst. It is characterized by low invasiveness. It has a fairly large percentage of reoccurrence – relapse.
- During a gastrectomy, the stomach is completely removed. To fully restore digestion, surgeons connect the esophagus to the rectum. The difficult rehabilitation period after illness and the risk of complications in the area of damage to the gastrointestinal system leads to the fact that the method is rarely used and only in extreme cases, if any other methods are not effective. In the case of complete removal (gastrectomy) of the stomach, a difficult stage of rehabilitation follows. The patient is given injections of B vitamins.
Alarming symptoms
If you notice bumps on your stomach, you should not wait for them to disappear. The fact of their presence is the first alarming symptom. The formations may be accompanied by redness of the skin, pain, high fever, and general malaise. They are able to roll like a ball, be motionless, have clear contours or blurred boundaries. In each case, the tumor may be dangerous and require special treatment.
If lumps are detected in the abdominal area, a woman should visit a general practitioner. He will examine the patient and, if necessary, provide a referral to other specialized specialists. This could be a gynecologist, dermatologist, gastroenterologist, surgeon, or oncologist.
Symptoms of stomach carcinoma
The appearance of a palpable tumor is a very late symptom of gastric carcinoma, which they try to recognize based on the patient’s complaints and laboratory data:
- long-term pain;
- lack of appetite;
- weight loss, nausea;
- achlorhydria;
- hidden bleeding;
- positive reaction to lactic acid;
- X-ray data.
Carcinoma of the anterior wall of the stomach becomes usually palpable, but the posterior wall is not palpable. Carcinoma of the pylorus of the stomach is palpated in the navel area, slightly to the right of it. Very vague consolidation may occur with diffuse infiltration of the gastric wall.
Diagnostics
When a lump is detected on the abdomen, the patient is offered a number of studies to determine an accurate diagnosis:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs;
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- endoscopic examination of the digestive organs and others.
In severe cases, a woman may be prescribed a CT or MRI, this allows a more accurate determination of the causes of the development of the pathology. If tumors are present, a puncture is prescribed, followed by a cytological examination of the resulting biomaterial.
Enlargement of the abdomen in the epigastric region and retroperitoneal space
The patient's complaints of pain in the lumbar region or a pulsating tumor-like formation in the epigastric region may indicate the presence of an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
Pain in the lumbar region can be observed with lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes) of the retroperitoneal space.
Upon palpation of the abdominal cavity, a pulsating tumor-like formation can be detected. Palpate the pulsation of the arteries of the lower extremities (acute occlusion of the artery as a result of embolism is accompanied by the development of limb ischemia). Metastases to the retroperitoneal lymph nodes in testicular cancer can manifest as a large retroperitoneal tumor. Palpate to rule out testicular tumor. Palpate all areas of possible lymph node enlargement (especially the left supraclavicular node). Lymphoma may be the cause of enlarged lymph nodes. Rule out enlarged lymph nodes in all accessible areas and splenomegaly. Detection of a dense, uneven and mobile tumor-like formation upon palpation, especially if the patient has ascites, allows us to suspect a secondary lesion of the omentum (ovarian cancer, stomach cancer - check the Virchow node, i.e. the node in the left supraclavicular region).
Deep sliding
The examination is scheduled after a visual examination. The procedure is carried out with the fingers slightly bent along the middle phalanx, which are placed parallel to the stomach. As the patient exhales, the hand slowly plunges into the abdominal cavity, the doctor’s fingertips slide along the back wall of the stomach, which helps to establish mobility, pain and structure of the organ.
You need to exhale 2 to 4 times per press from the doctor. Deep palpation of the stomach is carried out starting from the intestine and ending with the pylorus. When pain appears, their nature and location are determined. During the procedure, the position of the organs relative to each other, their sizes and the possibility of displacement, the nature of the sounds, the presence of seals or tumors are also recorded by determining the lower border of the stomach.
The procedure can also be performed while the patient is standing. In the vertical state, it is possible to feel the lesser curvature and highly located neoplasms of the pylorus.
Examination of patients
If a painful or painless formation in the stomach area is detected, you should consult a doctor. If there are indications to exclude stomach cancer, the following diagnostic measures will be prescribed:
- endoscopy of the upper gastrointestinal tract with biopsy, subsequent histological examination of the material taken during the biopsy;
- X-ray examination with barium, computed tomography with contrast;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, retroperitoneum, pelvis, cervical, supraclavicular areas;
- X-ray of the chest organs;
- examination by a proctologist, women by a gynecologist, men by a urologist;
- clinical, biochemical blood and urine tests;
- tumor markers;
- colonoscopy;
- PET-CT;
- scintigraphy.
It is necessary to remember that ulceration of the stomach walls is detected during gastroscopy, that this is such a dangerous precancerous disease as a callous ulcer.
Therapy methods
Treatment of lumps in the abdominal area occurs both conservatively and surgically. In the presence of benign or malignant tumors, their removal is indicated. In the latter case, after surgery the patient is prescribed chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
In the presence of inflammatory diseases, antibiotics and other drugs may be prescribed to stabilize the condition. Treatment often includes the use of modern methods of physiotherapy (laser, magnetic), diet, exercise and sports.
Medicinal and traditional methods of treatment
Lumps in the stomach area should be treated under medical supervision. It is he who prescribes therapy, based on the data obtained during the diagnosis of the compaction. Most often, a cyst is treated in two ways: medication and folk remedies. We should talk about them in more detail.
The drug method is practiced if the cyst is detected at an early stage. The patient is prescribed immunity-stimulating drugs and absorbent drugs. It is worth noting that the drug method is ineffective.
The traditional method of treatment is to take infusions from various medicinal plants. Doctors note that the use of pine needle infusion has a good effect. It is prepared as follows:
- you need to take 2 large spoons of spruce or pine needles and pour 500 milliliters of water at a temperature of 90-95 degrees;
- leave to infuse for half an hour;
- You need to take the medicine throughout the day, in small doses.
It should be noted that the infusion is suitable for use only for 24 hours.
In addition to the infusion of pine needles, you can treat yourself with the juice of burdock leaves, taking 2 large spoons of it 30 minutes before meals for a month, 3 times a day. Despite the fact that the methods are traditional, treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Uncontrolled self-medication can cause the situation to worsen.
Why does pain occur?
Patients often associate the onset of an attack of pain with eating. In the epigastric region, pain begins 20 minutes after eating. A likely and common cause of pain is dietary disturbances. If the dish the patient consumed the day before turned out to be prepared in violation of the diet rules or from prohibited foods, the pain persists for several hours.
In selected cases, pain in the stomach bothers the patient after suffering psycho-emotional stress. Another common cause of stomach pain with gastritis is smoking a cigarette or drinking a cup of black strong coffee. The reaction occurs especially quickly if coffee and cigarettes are taken on an empty stomach.
Symptoms characteristic of the appearance of seals in the stomach
As a rule, this type of pathology develops sluggishly without pronounced symptoms.
Most often, a cyst is diagnosed only after it has grown to a large size and causes significant discomfort. The main symptoms of its presence are:
- tingling pain in the stomach area;
- rapid weight loss;
- lack of appetite;
- nausea turning into vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- swelling in the arms, legs and face;
- heartburn and flatulence.
One of the above symptoms is not a reason to panic, but if they are combined and appear regularly, you should immediately consult a doctor.