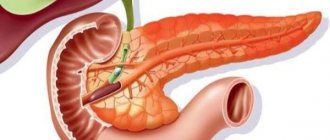
03/29/2019 Alena Masheva Health The gradual transformation of normal pancreatic cells into connective tissue is called fibrosis. This condition is not a separate pathology. It occurs as a result of the progression of other diseases. For example, changes in the parenchyma of an organ often occur due to a chronic inflammatory process (pancreatitis). Pancreatic fibrosis can affect different parts of the pancreas.
Features of the pathology
This disease is diagnosed quite often. It is a consequence of complications of long-term chronic dysfunction of the organ. Replacement of healthy connective tissues with fibrosis of the pancreas negatively affects its activity. There is a gradual inhibition of the production of pancreatic enzymes - substances that take an active part in the digestion process.
This pathology refers to irreversible conditions. However, by following all the doctor’s advice and proper therapy, the patient can slow down the progression of the disease. Ignoring recommendations and irregularly taking medications worsens the situation. Over the past few years, the number of patients suffering from pancreatic fibrosis has increased significantly. This trend is associated with an increase in cases of chronic and acute forms of pancreatitis, which leads to the development of complications.
There have been many medical studies that have shown that individuals who regularly drink alcohol experience problems with this organ after about 15 years. In people prone to alcoholism, healthy tissue is replaced with connective tissue. With an incorrect lifestyle, pathology can lead to death.
Possible complications
With a mild fibrosis-type disease, the pancreas does not change too much. In addition, the pathological process poses absolutely no threat to health, since it only signals the need to begin treatment.
Severe diffuse forms threaten the patient with dangerous complications. That is why you need to regularly take enzyme preparations, as well as undergo a course of therapy in gastroenterology departments. The thing is that the most effective method of therapy does not exist. This means that the pancreas will no longer function normally.
Of particular danger is additional fatty or cystic degeneration against the background of chronic diseases. The result may be necrosis of the pancreatic parenchyma. This condition threatens human life.
Types of disease
There are several types of the disease:
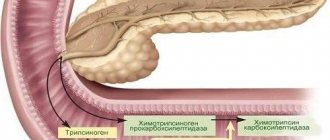
- Cystic fibrosis. Characterized by the formation of a benign tumor in the ducts of the organ. At the first stage, the disease does not have pronounced symptoms. As the pathology develops, a person develops its symptoms. The damaged organ produces thick pancreatic juice containing a huge amount of enzymes. The cyst prevents this secretion from entering the intestines, as a result of which digestion is disrupted.
- With diffuse fibrosis, the pathological process spreads throughout all parts of the organ. In the absence of therapy, the pancreas is completely affected. The disease is accompanied by a decrease in enzyme production. This disease is characterized by a clear clinical picture and is severe.
- Another form of pathology is focal fibrosis of the pancreas. What it is? This term means damage to a limited area of an organ. The lesion does not cover all tissues. Signs of the disease depend on the volume of the lesions. Small areas of fibrosis in the pancreas do not lead to pronounced symptoms.
In addition, there are other types of illness. For example, if there is connective tissue in one area of the organ, fibroma is diagnosed. This tumor is benign. It is not prone to rapid growth and formation of metastases. As a rule, the neoplasm does not worsen the patient’s quality of life (except for those cases when the fibroma becomes large and puts pressure on nearby vessels and organs). In some patients, healthy tissue is replaced by fibrous and fatty tissue. Then specialists make a diagnosis of fibrolipomatosis.
Treatment of pancreatic fibrolipomatosis
After a comprehensive examination, the doctor diagnoses the disease against which fibrolipomatosis developed. There is no specific treatment for this condition; it is impossible to completely get rid of the pathology. Depending on the patient’s condition and the severity of the disease, conservative therapy is prescribed or surgical techniques are used.
Drug therapy
Lipofibrosis usually develops against the background of inflammation of the gland, to relieve the manifestations of which the following is prescribed:
- painkillers;
- antispasmodics;
- digestive enzymes;
- proton pump inhibitors;
- H2-histamine receptor blockers;
- antacids.
If the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis is confirmed, then, in addition to the above medications, anabolic steroid hormones are necessarily prescribed to normalize body weight. In the mixed form, mucolytics and expectorants are prescribed.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is indicated when nodular growths, large cysts and tumors are detected that compress the vessels and ducts of the gland. In some cases, the head of the gland can reach large sizes, squeezing the loops of the small intestine. This condition requires urgent surgery, otherwise bleeding, necrosis and intestinal obstruction may occur.
Folk remedies
In addition to the main treatment, with the permission of the attending physician, you can use infusions and decoctions prepared according to traditional recipes at home. A drink based on rosehip has proven itself well, which has a gentle effect and is allowed even with exacerbation of pancreatitis. Astringent jelly made from oatmeal is widely used.
Reasons contributing to the development of pathology
This disease usually does not occur against the background of complete health. It is preceded by a long process of chronic inflammation or acute pancreatitis, leading to tissue necrosis. This condition can develop due to the following factors:
- Presence of obesity.
- Smoking.
- Drinking large amounts of alcohol.
- Diseases of the biliary tract, which are accompanied by increased pressure in the ducts.
- Infectious processes.
- Intoxication.
- Prolonged and uncontrolled use of medications.
- Cystic fibrosis.
- Mechanical damage to the organ.
- Psychological stress.
Causes
The main factors for the progression of pathology include:
- constant abuse of alcoholic beverages;
- smoking;
- the use of surrogates for alcohol and low-quality alcoholic beverages, chemicals;
- deposition of stones in the bile ducts;
- inflammation of the duodenum;
- poor quality nutrition with consumption of significant amounts of unhealthy food;
- infections;
- weight gain;
- stress;
- long-term use of certain medications;
- cystic fibrosis (a hereditary disease that causes cystic fibrosis);
- increased activity of the thyroid gland.
Main signs of the disease
Even in the presence of large areas of damage and replacement of healthy tissue with connective tissue, the patient has no symptoms of pancreatic fibrosis. There are no specific manifestations of this pathology. However, the likelihood of its development is indicated by signs of an inflammatory process, for example:
- Frequent attacks of belching air.
- Fever.
- Feeling nauseous.
- Attacks of vomiting and hiccups.
- Flatulence.
- Discomfort in the peritoneal area, which has no clear localization.
- Feeling of dryness in the mouth.
- Loss of appetite and severe weight loss.
- Frequent, watery stools up to eight times a day. When carrying out laboratory analyzes of stool, a significant amount of undigested lipids is found in them.
Main symptoms
Changes in the pancreas such as fibrosis do not become noticeable immediately. The first complaints appear only when there are serious violations of the structure of this organ. Much depends on the severity of the pathological process. Among the main symptoms, the following should be highlighted:
- pain in the left hypochondrium or in the upper abdomen;
- belching;
- feeling of heaviness after eating;
- diarrhea;
- bloating;
- loss of appetite;
- nausea;
- weight loss;
- the presence of undigested food residues in the stool.
If the growth of connective tissue is focal in nature, then after some time it can develop into fibroma. The presence of complaints in this case will depend on the size of the tumor. A large tumor puts pressure on nearby organs and, in addition to pain, can cause nausea or even jaundice.
Diagnostic measures
If you suspect the presence of an illness, the patient should consult a specialist - a gastroenterologist. First, the patient is examined. Symptoms of pancreatic fibrosis that can be replaced externally are severe body weight deficiency, dry surface of the tongue and skin, a red tint to the face, and bluish spots in the peritoneum. In addition, the doctor palpates the organ and performs laboratory tests of biological material. The presence of the disease is indicated by a decrease in enzyme activity and insufficient protein content in the blood. An ultrasound examination is also necessary.
In the process of such diagnostics, increased echogenicity of the organ, enlargement of the Wirsung duct, heterogeneity of tissue structure, and a decrease in their volume are detected. If it is possible to notice signs of pancreatic fibrosis on ultrasound, computed tomography is recommended to confirm the diagnosis. There are cases when this technique does not provide the specialist with the necessary information. Then the doctor performs a biopsy of the organ.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
Fibrofatty degeneration of the pancreas cannot be determined with the naked eye during a routine objective examination of the patient. Diagnosis is especially difficult at an early stage, when there are no symptoms of the disease. That is why it is necessary to conduct a whole range of studies and analyzes in order to promptly identify the process while the treatment is still effective.
Laboratory
Each patient who consults a gastroenterologist must undergo a mandatory list of laboratory tests, namely:
- clinical blood test;
- blood glucose level;
- biochemical analysis with determination of the levels of enzymes, bilirubin and total protein fractions;
- coprogram for detecting free fat in feces.
This minimum range of tests must be done 2-3 times a year. To monitor cystic fibrosis, you should take a stool test once every 2 months.
Blood tests
Functional
The most accessible and safe diagnostic method is ultrasound. The structure of the pancreas changes diffusely and, if fibrosis predominates, has increased echogenicity. If adipose tissue grows to a greater extent in the gland, then the echogenicity of the reflected ultrasound signal is reduced, which is characteristic of lipomatosis. Fibrous nodes and cysts of the pancreatic glands are clearly visualized on the ultrasound screen.
Ultrasound of the abdomen
With cystic fibrosis, the doctor can record an increase in the size of the gland, dilated and cystic changes in the excretory ducts. With a total change in the gland, it can all be filled with liquid round formations. At the same time, the liver is examined; as a rule, it increases in size.
Important! If multiple cysts are detected, the specialist will prescribe a sweat test to determine sodium and chlorine ions in sweat. An increase in the level of these microelements in sweat reliably indicates cystic fibrosis.
To exclude gastritis or ulcerative lesions of the gastric and duodenal mucosa, esophagofibrogastroduodenoscopy is performed.
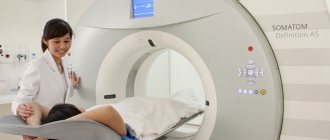
If the gland cannot be clearly visualized on ultrasound, then an MRI is performed. This is an expensive but highly informative method that provides comprehensive information regarding the location and structure of the pancreas and surrounding tissues. Magnetic resonance imaging is contraindicated during pregnancy, the presence of heart rate drivers, metal bodies or implants in the body.
CT allows you to obtain layer-by-layer sections of any organ. In this case, the patient is exposed to x-ray radiation, so the study must be carried out strictly according to indications.
As a differential diagnosis with oncological neoplasms, a biopsy of the gland is performed under the control of an ultrasound sensor. The results of histological examination play a key role in choosing treatment tactics.
Drug therapy
Patients with fibrosis of pancreatic tissue are prescribed the following groups of drugs:
- Medicines that eliminate spasms (“Drotaverine”).
- Medicines that stop gagging (Metoclopramide).
- Non-steroidal drugs with anti-inflammatory effects (Diclofenac).
- Enzymes to improve the digestion process (Creon, Pangrol).
Of course, all of these medications should be used only as prescribed by a specialist.
This disease usually does not require surgical intervention. In exceptional cases (when tissue affected by fibrosis transforms into a tumor), the doctor regularly monitors the patient, and if the tumor begins to grow rapidly, it is removed.
Signs of diffuse fibrous replacement of the pancreas
Replacement of pancreatic tissue is accompanied by symptoms of enzyme deficiency. These symptoms include:
- Dyspeptic disorders: belching, bloating, loss of appetite, heaviness in the epigastrium, frequent loose stools. Feces with pancreatic juice insufficiency are liquid or mushy, with a large admixture of undigested fats and lipids.
- Pain in the upper abdomen (in the epigastric region, in the subcostal areas). Pain occurs 40-60 minutes after eating. The pain is especially typical after eating a rich, fatty meal. During exacerbations of chronic diseases, pain can be acute; during periods of remission, it can be nagging, aching, subacute in nature.
- Some patients lose weight due to insufficient digestion of fats, which are the main energy substrate for the body.
- Nausea and vomiting after a large fatty meal.
Important to remember! In most patients, the process of degeneration (especially local) is asymptomatic and is discovered randomly during a routine diagnostic examination. Severe symptoms are accompanied predominantly by diffuse connective tissue replacement of the parenchyma.
Dietary recommendations
Diet is an important condition for maintaining the well-being of a person with pancreatic fibrosis. With chronic inflammation of an organ, its functions are impaired. Disruptions occur during the digestion process. Eating heavy, fatty foods causes discomfort in the peritoneum, nausea, vomiting, belching and gas formation. The patient should change his diet. It is necessary to avoid foods containing large amounts of lipids, dishes that stimulate the secretion of pancreatic juice (pickles, marinades and seasonings, meat broth, smoked meats, fried foods). The patient is recommended to eat up to 5 times a day, in small portions, to reduce the load on the affected organ.
In addition, a person suffering from this pathology should exclude:
- Fatty dairy products (sour cream, cream, condensed milk).
- Canned food, processed foods and fast food.
- Lipids of animal origin (lard, bacon).
- Baked goods, desserts (cakes, cakes, chocolate, pies, ice cream).
- Alcoholic drinks.
- Strongly brewed tea, coffee, sparkling water, cocoa.
- Berries and fruits with a sour taste.
- Garlic, onion.
A diet for pancreatic fibrosis should include the following foods:
- Vegetables (pumpkin, eggplant, turnips, carrots, cucumbers, potatoes, cauliflower).
- Fruits (strawberries, kiwi, sweet apples, mangoes, melons and watermelons).
- Rice, buckwheat and semolina, oatmeal.
- Lean varieties of meat (rabbit, beef, chicken, turkey).
- Skinny fish.
- Non-acidic dairy products with low lipid content.
- Vegetable oil and butter (in small quantities, for cooking).
- Juices from sweet fruits and berries, rosehip decoction, weakly brewed tea, jelly, dried fruit compote, still mineral water.
Patients are not recommended to eat too hot or too cold foods. It is better to bake food, steam it, boil it, or grind it using a blender. Sweets are allowed in minimal quantities once a day.
Therapeutic measures
There is no cure for pancreatic fibrosis. In modern medicine, there are no drugs yet that can transform the connective epithelium back into functional tissue. All therapeutic measures are aimed at relieving symptoms and alleviating the patient’s condition.
First of all, the patient is prescribed a strict diet. This measure allows you to stop the inflammatory process and relieve the pancreas. Spicy, fatty, smoked, salty, fried and rough foods are excluded from the patient's diet. In addition, it is necessary to avoid products that increase the secretion of gastric juice (seasonings, sauces, marinades). Meals should be small, and the patient should consume large amounts of fluid. Alcohol for fibrosis (even in small quantities) is strictly prohibited.
Important information: Instructions for use of Gordox for pancreatitis
An important factor in treating the disease is controlling enzyme levels. Also, depending on the cause that provoked the inflammation, the gastroenterologist may prescribe the following groups of drugs:
- antispasmodics;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- interferons;
- antibiotics;
- analgesics;
- antiemetics;
- digestive enzymes.
If fibrosis is treated in the right way, the patient’s digestion will normalize and weight loss will stop. But there are a number of cases in which surgical or endoscopic intervention may be required. For example, when:
- constant pain syndrome that cannot be relieved by analgesics;
- compression of the pancreatic flow;
- degeneration of tissue into a tumor;
- development of a postnecrotic cyst in the gland;
- obstructive jaundice.
A favorable prognosis for fibrosis depends on how extensively the gland is affected. If you follow the diet and all medical prescriptions, give up alcohol and smoking, the disease may not develop for a long time.
Unconventional methods of therapy
For pancreatic fibrosis, treatment with folk remedies involves the use of the following medicinal plants:
- Elecampane roots.
- Oats.
- Fennel.
- Peppermint.
- Centaury.
- Rosehip (roots).
- Purple sedum.
- Dill.
- Violet tricolor.
- St. John's wort.
- Cottonweed.
- Coriander.
Folk remedies should not be used as the main method of therapy. Before using them, you should consult a specialist.
Causes
The causes of pancreatic fibrosis can be very different. Basically, the pathology occurs due to inflammation of the mucous membrane of this organ. It also develops with acute or chronic disorders of pancreatic function. In addition, provoking factors include the following:
- alcohol abuse;
- obesity;
- smoking;
- dysfunction of the biliary tract;
- poor nutrition;
- intoxication of the body;
- severe stress;
- infectious processes;
- long-term use of strong medications;
- hereditary factor.
It is very important to know what it is - pancreatic fibrosis, for what reasons it occurs, and what signs it has. Symptoms of pathology at the initial stage are very difficult to detect, since they are mild.
How to prevent the development of pathology?
The main way to prevent pancreatic fibrosis is regular monitoring of the condition of the organ. In addition, it is necessary to exclude factors that could lead to a deterioration in its functions. This includes smoking, drinking alcohol and eating foods containing large amounts of lipids. The inflammatory process in the pancreas is known to occur due to addictions. In addition, it is necessary to carry out timely and competent therapy for pathologies that can provoke the development of fibrosis (for example, disorders of the gallbladder).
Prevention of pathology
The sooner you start prevention, the less likely the disease is to develop. This rule especially applies to people suffering from pancreatitis. In order to reduce the risk of developing fibrosis or stop its progression, you must:
- exclude alcohol;
- stop smoking;
- control the amount of food consumed.
You also need to monitor the quality of food you eat and drink enough water during the day. Any chronic diseases should be treated in a timely manner, especially pancreatic pathologies. A healthy lifestyle and lack of stress significantly reduces the risk of fibrosis.
Forecast
Unfortunately, there are no treatment methods that can completely restore a damaged organ. Medications and traditional methods of therapy do not transform connective tissue into parenchyma. This process is not possible. Patients often ask specialists about the prospects for a disease such as pancreatic fibrosis and prognosis. How long do people live with this pathology? It is impossible to answer unequivocally in this case. The prognosis is determined by factors such as the functioning of the damaged organ, the spread of lesions, and the individual characteristics of the patient (for example, the presence or absence of addictions). Strict adherence to all doctor’s recommendations gives the patient a chance for a normal and long life.
To avoid relapse of chronic inflammation in the pancreas (pancreatitis), you should completely eliminate smoking and consumption of alcohol-containing products. In case of exacerbations of the disease, it is necessary to take medications prescribed by the doctor (medicines to eliminate spasms, drugs to improve the digestion process, and so on).
Changes in the structure of the organ themselves do not lead to death. However, to avoid complications, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations, ultrasound diagnostics of the pancreas, and follow the recommendations of gastroenterologists.
Source: fb.ru
What is fibrosis and fibrolipomatosis of the pancreas?
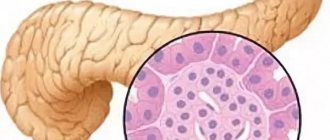
Fibrosis and lipomatosis themselves are not a separate disease; they are a consequence of serious disturbances of homeostasis and the inflammatory process in the gland. Against this background, adequate blood supply is disrupted. Tissues cannot function normally in conditions of insufficient oxygen and nutrients, so normal gland cells gradually die, and connective tissue cords form in their place. Diffuse changes in the pancreas similar to fibrolipomatosis occur.
In people with lipid metabolism disorders or those suffering from diabetes mellitus, gland obesity may occur when adipose tissue actively grows in its place.
The doctor can detect changes in the structure of the organ during an ultrasound examination. And although, when making a final diagnosis, one cannot rely only on the sign of an increase or decrease in echogenicity, it should force one to pay attention to the state of the digestive organs and take appropriate measures.
general information
Due to its anatomy and location, the gland is very sensitive to negative effects. It quickly reacts with the development of an inflammatory process, up to necrosis, as well as the formation of stones in the ducts and tumors.
In addition to replacing healthy pancreatic cells, cystic protrusions with liquid contents can form due to blockage of the ducts. This process is called cystic fibrosis of the pancreas. This often indicates a serious hereditary disease called cystic fibrosis. The gene mutation is transmitted according to a recessive type of inheritance and manifests itself in damage to the respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract, or a mixed form, including symptoms of dysfunction of both systems.
Usually, changes develop gradually, unnoticed by the patient himself due to the absence of clear clinical manifestations. Characteristic symptoms appear when the structure of the pancreatic parenchyma has almost completely and irreversibly changed.
Interesting to know! Pancreatic nodes arise in places of the most intense growth of connective tissue. They are usually detected incidentally on abdominal ultrasound.
When making a final diagnosis, the doctor must determine the extent of organ damage. Classification includes 3 stages:
- first – the structure of 1/3 of the organ has been changed;
- second – up to 60% of the entire gland is affected;
- third - fibrous degeneration affects more than 60% of healthy tissues.
In addition, it is customary to distinguish between diffuse and local lipofibrosis. In the first case, adipose and connective tissue grow evenly in the parenchyma of the organ. This is usually how any sluggish chronic diseases in the pancreas end. In the second case, a focus of intense growth occurs in a separate area of the gland. This option most often occurs with pathologies of the liver and biliary tract, as well as against the background of severe psycho-emotional shocks.