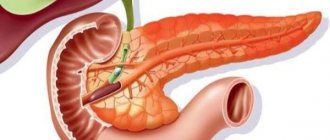
What is parenchyma in the pancreas?
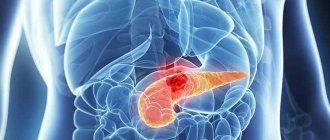
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system that performs important functions. Produces pancreatic juice, insulin and glucagon. The organ is very dense and difficult to diagnose due to its location. In order to determine the condition of the pancreas, an ultrasound is often prescribed.
In medicine, the term parenchyma refers to the internal structure of an organ; in its normal state it is homogeneous.
What is echogenicity of the pancreas?
Ultrasound examination is a common diagnostic method that does not require large financial costs. With its help, you can diagnose many diseases and learn about the condition of internal organs. The method is often used for examinations of the pancreas.
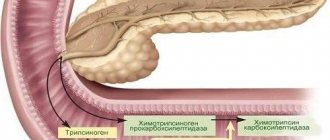
Many people know that the tissues of the human body have different densities, therefore, ultrasound also reflects them differently. The higher the tissue density, the greater the echogenicity, and vice versa - the lower the tissue density, the less echogenicity.
With diffuse changes in the pancreas, the density of the parenchyma increases and its echogenicity increases. The density of the organ decreases in most cases due to various inflammatory changes in the body, leading to swelling of the organ. The liquid has a lower density than the parenchyma itself, so the echo density decreases.
What is organ diffusion?
In fact, structural transformation of tissue is not a diagnosis. This is a kind of syndrome from which this or that pathology begins. If the course of events is unfavorable, they develop into an illness of the internal organ. Thus, DI in the liver can result in hepatitis, and in the pancreas – pancreatitis. In modern medicine, DI of the liver or pancreas parenchyma corresponds to the name - hepatomegaly.
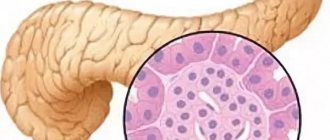
What kind of phenomenon is this – diffuse changes? This is the destruction and replacement of tissue under the influence of an imbalance in the biochemical balance. In other words, healthy cells die, and their place is filled with fatty deposits or connective tissue. That is, the structure and composition of the fabric changes.
These cellular transformations are usually detected by ultrasound. The changed tissue becomes heterogeneous and changes echogenicity:
- a healthy organ is weakly echogenic;
- with the appearance of pathology and its development, the ultrasound examination rate also increases.
But to confirm the suspicion, echographic signs alone are not enough. Biochemical blood and urine tests are also needed.
Causes
The main reasons contributing to the development of diffuse changes include:
- chronic form of inflammation of the pancreas;
- long-term use of toxic medications;
- addiction to alcoholic beverages;
- excessive consumption of fatty foods;
- nicotine addiction;
- previously suffered an acute form of inflammation of the pancreas;
- ailment in the patient’s liver area;
- diabetes;
- infectious diseases;
- disruption of metabolic processes;
- hormonal disorders;
- diseases caused by parasites;
- non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
We also recommend viewing: What is pancreatic lipomatosis and how to deal with it?
Important. According to statistics, the pancreatic parenchyma often becomes denser in elderly patients. Pancreatic enzyme deficiency is more common among children.
Minor compactions of the pancreatic parenchyma occur due to a stressful situation, inflammatory diseases, poor nutrition and depressive diseases. It is very important to find the true cause that led to changes in parenchyma density.
Symptoms and types
Diffuse changes are usually indicated by certain signs:
- constant heaviness in the stomach;
- alternation of dense and liquid stools;
- lack of appetite.
These symptoms are common, but each disease has its characteristic features:
- In acute pancreatitis, the integrity of the gland tissue is disrupted, so the process of removing digestive juices changes, causing general intoxication of the body. The patient feels nauseous, vomiting occurs, acute pain occurs in the left hypochondrium, and sometimes tachycardia increases.
- Chronic manifestations of pancreatitis begin with swelling and small hemorrhages due to tissue damage. The pancreas decreases, pain increases during exacerbation.
- Fibrosis can be asymptomatic. Enzyme production decreases, disrupting the digestive process. This pathology can manifest itself as nausea, vomiting, loose stools and weight loss.
- Symptoms of lipomatosis depend on the number of lesions. If he is alone, then the disease is mild or asymptomatic. When pathology spreads throughout the organ, disturbances occur in its functioning, manifested by painful sensations.
- If diffuse changes affect both the pancreas and liver, then this phenomenon is called hepatomegaly. This is not a disease, but a consequence of specific pathological changes. The initial stage of hepatomegaly is often asymptomatic, but after that the liver enlarges, protruding above the ribs. After this, pain occurs, increasing with palpation. The patient suffers from nausea with vomiting, heartburn and an unpleasant taste. Appetite decreases, the skin becomes yellowish, and an itchy rash is possible.
- Heterogeneous diffuse changes may be a sign of a cyst, tumor or sclerosis.
There are also ultrasound signs of such disorders, dividing them into types. The nature of diffuse changes can manifest itself in diagnostics in different ways:
- Decreased echo density (the structure becomes denser), heterogeneity of the echo structure, the size of the gland is moderate, but increased. Such features are characteristic of acute inflammation caused by impaired excretion of digestive enzymes. The parenchyma (special tissue) of the gland undergoes diffuse changes.
- Echogenicity and echodensity are increased, but the size of the organ is normal. Fatty tissue replaces the walls of the gland, and in severe cases overlaps the parenchyma. In this case, lipomatosis is diagnosed.
- Echogenicity and echodensity are increased, the size of the organ is normal or slightly smaller. Iron tissues are replaced by connective structures. These characteristics are characteristic of fibrosis.
- The parenchyma of the gland has changed echoscopically, echodensity is deviated from the norm, some tissues are replaced by a fatty structure. Diagnosis: diabetes mellitus.
- Echodensity and echogenicity are reduced, the size of the gland is normal. The juice outflow passage may be twisted. These are signs of chronic pancreatitis caused by impaired fat metabolism.
Associated symptoms
Depending on the reasons that contributed to the appearance of diffuse changes, there are a number of symptoms that may bother the patient, for example:
- nausea and vomiting;
- blood pressure surges;
- increased body temperature;
- problems with stool;
- bloating;
- feeling of discomfort in the stomach;
- the patient constantly feels tired;
- painful attacks in the pancreas area.
Often, diffuse changes in the pancreas are diagnosed completely unexpectedly, during a routine examination, and are completely asymptomatic. At the same time, the organ fully copes with its functions.
Treatment of pancreatic diffusion
Diffuse changes in the pancreas are not treated separately. Only those disorders that are pathological in nature are subject to treatment. In such cases, therapeutic measures to eliminate diffuse changes are prescribed and performed as part of complex therapy for the underlying disease that caused them. At the same time, diet and traditional medicine recipes are used to improve the condition of the pancreas. The same methods are used for age-related or other non-pathological changes.
Diet
Like the main treatment, the diet for diffuse pancreatic changes is determined by the root cause of their appearance. The highest requirements are placed on the diet if changes develop against the background of diabetes, pancreatitis, and other serious pathologies.
At the same time, the presence of the diffuse changes under consideration also requires compliance with certain nutritional rules:
- Any alcohol-containing drinks are absolutely excluded, since alcohol is as harmful to the pancreas as it is to the liver and can significantly aggravate the situation.
- The diet should be low in calories and based on the consumption of plant foods, grain dishes, lactic acid products, lean fish and meat.
- Prohibited foods include spicy, salty and other aggressive foods, dishes and seasonings, as well as fast carbohydrates - sweets, baked goods, packaged juices, etc.
- Dishes are prepared without frying or using fat.
- The drinking regime should be moderate and even throughout the day.
- You need to eat fractionally (often and little by little) and in such a way as to prevent overeating or excessive secretion of gastric enzymes.
It is necessary to switch to dietary nutrition immediately after diagnosing diffuse changes in the pancreas, regardless of their cause. After an accurate diagnosis has been established, the diet is adjusted taking into account the restrictions of the underlying disease.
Folk recipes
To normalize the condition in the presence of diffuse pancreatic changes, herbal infusions prepared according to the following recipes are considered very effective:
- From chamomile and immortelle - 1 tbsp. l. each herb to 1 cup of boiling water. Let cool, filter, drink 2 tbsp. l. before every meal. Course - 21 days. You can repeat until the condition improves with a week break.
- From calendula, celandine, yarrow - 1 tbsp. l. collection per 1 cup of boiling water. Let cool, filter, drink according to the previous recipe, but within 30 days.
- From chamomile, mint, plantain, yarrow, St. John's wort, dried wort - 1 tbsp. l. collection per 1 cup of boiling water. Let cool, filter. Drink the resulting infusion 3 times during the day. The duration of admission is not limited.
- From Japanese sophora - 1 tbsp. l. for 1 cup of boiling water, leave in a thermos overnight. Drink 2 tsp. before each meal for 12 days. You can repeat after a week's break.
When choosing medicinal plants for home treatment, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of allergic reactions. With chronic lesions of the pancreas, they develop quite often.
Additional diagnostics
If echo signs of pancreatic pathology are detected, the doctor must prescribe some additional examination methods:
- general blood analysis;
- MRI or CT;
- ultrasound examination of the gastrointestinal tract;
- urine test and so on.
Important. Having carefully studied the medical history and the results of the diagnostics, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis, prescribes individual treatment and a number of related recommendations.
Stages and forms of pancreatic dystrophy
For ease of perception of existing types of diseases, it is better to present the data in a table.
| Stages of dystrophic changes in the pancreas | |
| first | Obesity has occupied up to 30% of the organ, functionality is moderately impaired, and symptoms are not expressed in any way. |
| second | Obesity has occupied up to 60% of the organ, and there are malfunctions in the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract) and pancreas (pancreas). |
| third | Obesity has occupied over 60% of the organ, the clinical picture is pronounced, and in some cases endocrine insufficiency is observed. |
| Forms of dystrophic changes in the pancreas | |
| Diffuse | Muscle lipoma - lipid cells grow together with muscle tissue. The line between normal and pathological tissue is not identified. |
| Knotty | The formation of symmetrically localized nodes, surrounded by a unique capsule, occurs. |
| Mixed | It is a duet of the first two forms with corresponding complications, and the symptoms are often confused with one of the forms. Only a specialist can determine the mixed form. |
We also recommend viewing: Where does the pancreas hurt and how does it hurt: we know more, we get sick less
Types of pathology
- Minor violations. They most often arise due to stressful situations. You need to normalize your diet, and then all the problems will go away.
- Moderate stage of the disease. They appear due to problems in digestion. A mandatory diagnostic procedure is required for this form of the disease.
- Unexpressed diffuse changes. They do not have a negative effect on the functioning of organs and their performance, but in diabetes mellitus they often contribute to an increase in blood sugar levels. The root causes of such changes are cardiovascular diseases, liver diseases, old age, genetic predisposition, and so on.
- Pronounced diffuse changes indicate the presence of inflammatory processes in the organ itself or are a symptom of other diseases. The patient suffers from pain in the abdominal area and digestive problems. The doctor prescribes additional diagnostic examinations and then the necessary therapy.
- The disease is at a chronic stage. Most often there are no obvious symptoms. This form of lipomatosis provokes in the patient.
We also recommend viewing: Possible diseases of the pancreas
What are diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma
The syndrome of diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma is called hepatomegaly in medicine. Dying tissue cells create voids that fill with fluids, fatty deposits or connective tissue.
Such transformations lead to the fact that the liver ceases to be an effective internal “factory” for processing incoming chemical elements. She copes poorly with the task and begins to poison the body.
The signs of the syndrome are the same as those of incipient hepatitis: pain in the area under the diaphragm, yellowing of the skin and sclera of the eyes, nausea, loss of appetite.
The development of hepatomegaly leads to cirrhosis of the liver, and ultimately (untreated) can cause coma and death. Doctors usually note this scenario in the case of heavy alcoholics. In a person leading a healthy lifestyle, diffuse changes in the parenchyma occur extremely rarely.
Treatment
In the treatment of diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma, general diagnostics and identification of other pathologies are important. Diseases of the body are interconnected. And the destruction of the liver structure can be directly affected by diabetes, pancreatitis or the presence of gallstones in the ducts.
Traditional treatment primarily includes diet therapy. For liver problems, table number 5 and its variations are prescribed (diet number 5p or 5a). The diet excludes harmful drinks and foods of the following plan:
- alcohol, coffee and carbonated sweet drinks;
- fatty meats and fish;
- smoked sausages, dried fish, canned food;
- pickled vegetables or fruits;
- condensed milk, ice cream and rich cream cakes;
- smoked and processed cheeses, very fat homemade sour cream, yogurt or butter (fermented milk products are allowed only in small quantities or with a low fat percentage).
Modern pharmaceuticals have effective means to combat hepatomegaly. There are a number of drugs whose action is aimed at blocking the spread of changes in the parenchyma and even at restoring cells. But they do not work if the patient violates the diet. And they are in vain in already advanced cases, when only surgery can help.
Traditional drug treatment necessarily includes diuretics. In addition to synthetic pharmaceutical drugs, doctors recommend natural ones: special herbal mixtures, boiled beets, rosehip infusion.
Nutrition and diet
- It is recommended to avoid fatty foods.
- You should eat as much fresh and natural food as possible.
- They recommend split meals, up to 5 meals a day.
- In small portions.
- Completely exclude the consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- It is prohibited to consume carbonated drinks and canned food.
- They try to use spices and seasonings as little as possible.
- Limit the consumption of sweets and starchy foods.
- Avoid too cold and hot food.
Principles of treatment
There is no treatment for the diffuse changes themselves. They cannot be eliminated by surgery either, since total removal of the pancreas is carried out in extreme situations.
If diffuse changes occur against the background of complete health, and the examination does not show the presence of any nosological diseases, then following a diet is sufficient for treatment.
Diet and nutrition basics:
- Frequent meals - up to 5-6 times a day in small portions.
- Warm temperature of served food.
- Exclusion from the diet of fatty and fried foods. It is not recommended to include irritating foods: spicy, pickled, salty, spicy, sweet.
- Dishes are steamed or boiled.
- When choosing foods, the main emphasis should be on vegetables, lean meats, and grains.
- Refusal to drink alcoholic beverages and smoke.
If a patient complains of digestive disorders or abdominal pain, then he is subjected to a full range of diagnostic tests. After identifying the underlying disease and establishing a diagnosis, treatment is prescribed, during which diffuse changes are also treated.
In addition to diet, quitting smoking and alcohol, the patient is prescribed symptomatic and remedies and drugs to eliminate the pathology.
Symptomatic medications:
- Enzyme replacement therapy with digestive enzyme preparations: Festal, Pancreatin. They eliminate dyspeptic disorders: heaviness in the abdomen, diarrhea, bloating.
- Analgesics of a number of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Nise, Ketonov, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen. They are drunk during periods of acute abdominal pain.
- Drugs to enhance peristalsis: Metoclopramide, Domperidone, Cerucal.
Pathogenetic therapy to eliminate the underlying disease is selected individually, depending on the nosological group of the pathology.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment often comes down to symptomatic therapy. The doctor prescribes antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
When the body is intoxicated, antibiotics and solutions are used that help remove toxic substances from the patient’s body.
Lipomatosis can be treated with medications or surgery. In this case, all fatty nodes are removed.
For diabetes mellitus, medications are prescribed to help reduce the amount of glucose in the blood, and in some cases insulin injections are necessary.
Treatment of pancreatitis, including diffuse, lasts quite a long time. It is important to start a therapeutic course on time so that the disease does not become chronic. In addition to a special diet, patients are prescribed a number of medications that promote the production of pancreatic juice, relieve pain symptoms, and relieve spasms. Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a doctor and is accompanied by regular tests, in particular lipase and amylase.
We also recommend viewing: How to clean the pancreas without harm?
How to treat diffuse changes in the pancreas?
The need for and extent of treatment is determined by the attending physician. When there are no symptoms that are characteristic of gland diseases, therapy is not required, but research must be continued for the presence of a cyst or neoplasm.
Treatment of diffuse changes in the pancreas is carried out only if there are complaints characteristic of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and after confirmation of the diagnosis. Therapy in this situation is aimed at correcting the main disease.
Treatment of acute pancreatitis
- During the period of acute pancreatitis, the gland should be allowed to rest.
- For these purposes, food is reduced or completely canceled for a certain period of time.
- Until inflammation decreases, ordinary nutrition is replaced with intravenous nutrition. In such a situation, the symptoms of malfunctions in the functioning of the gland should decrease.
To remove the causes of the disease, in certain cases, surgery is used to remove stones that block the bile duct connecting the gland, gallbladder and duodenum.
Treatment of chronic pancreatitis
During chronic manifestations of pancreatitis, in the absence of exacerbations, the patient may experience dull pain, constipation, nausea, poor digestion of fats, and intense stool may appear. In chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic tissue is destroyed over a long period of time.
A complete cure does not occur and the main task of specialists is to prevent further destruction of the gland:
- Diet plays an important role in inflammation of the pancreas.
- It is necessary to exclude caffeine and alcoholic drinks,
- eat light foods with low fat concentrations,
- take enzymes and vitamins,
- treat diabetes, if present.
Treatment of spasmodic smooth muscles of the gland ducts
To relax the spasmodic smooth muscles of the gland tract, antispasmodics (no-spa, platifilin) are prescribed. This helps improve the outflow of pancreatic juice, which contains enzymes, into the intestine.
To reduce the production of digestive enzymes, atropine is used, local therapy such as cold on the gland area. Black elderberry is characterized by a slight choleretic and antipyretic effect, and reduces muscle spasms. Elderberry inflorescences are included in many collections.
Treatment of sclerosis of the pancreatic parenchyma
Moderate diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma may indicate replacement of glandular tissue with scars or fat cells.
When sclerosis of the parenchyma progresses and is associated with severe enzyme deficiency:
- Protein is administered intravenously.
- Amino acid nutrition is introduced.
- Prescribe vitamins and hormones that improve anabolism.
- Drug therapy is used only in the fight against pathology.
- Enzymes are prescribed. These medications are taken with food. In this way, the patient somewhat compensates for the inability of the gland to produce the required number of its digestive enzymes.
Treatment of pancreatic fibrosis
It is necessary to treat fibrosis of the gland in order to compensate for intra- and exocrine insufficiency:
- Diet No. 5p is prescribed, which includes stimulating the secretion of enzymes and foods with a high concentration of proteins.
- Limit carbohydrates.
- When cachexia is severe, parenteral meals are taken.
- Etiotropic therapy is to eliminate the causes of the pathology (exclude the use of alcoholic beverages, cholecystectomy during cholelithiasis, surgery for papillostenosis).
To replace exocrine insufficiency, enzymes are prescribed: pancreatin, Creon, lipase and others. When the deficiency is absolute, such drugs are used regularly in the highest doses. The criterion for the effectiveness of such treatment is considered to be stopping weight loss, reducing dyspepsia, and eliminating diarrhea.
Correction of carbohydrate metabolism failures is carried out:
- Using oral hypoglycemic agents;
- Insulin treatment is rarely needed.
- When there are no exacerbations of the disease, treatment in sanatoriums or resorts is recommended.
- Surgery. When pain is severe, conservative treatment is ineffective, weight is rapidly lost, and pancreatitis constantly recurs.
Treatment of lipomatosis
Most often, attempts are made to treat glandular lipomatosis using conservative methods.
These include:
- Review and adjustment of nutrition.
- Counteracting excess weight.
- Elimination of bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol.
- Active lifestyle.
In addition to the above, additional treatment is prescribed aimed at normalizing digestion and restoring the lack of hormones.
Conservative therapy refers to the treatment of associated diseases:
- Hepatitis.
- Thyroid disease.
- Therapy during diabetes mellitus.
When conservative therapy does not give the desired effect, areas of lipomatosis are eliminated by surgical intervention.
Preventive measures
As a preventive measure it is recommended:
- Watch your diet - avoid fatty and sweet foods, as well as pastries and carbonated drinks. They eat fresh vegetables and fruits. They try to steam it.
- Forget about cigarettes and under no circumstances drink alcoholic beverages.
- Strengthen the immune system: consume vitamin complexes.
- Take frequent walks in the air and engage in physical activity regularly.
- Once a year after reaching 35 years of age, undergo an ultrasound examination of the internal organs located in the abdominal cavity.
- Treat infectious and inflammatory diseases, in particular those related to the digestive system, in a timely manner.
It is important at any age to closely monitor your own health and the health of your children. If strange symptoms appear, seek professional help from a doctor. Self-medication is not recommended.
Authorized Products
The diet for diffuse changes in the pancreas includes:
- Soups made from vegetable broths with ground and well-cooked permitted cereals, seasoned with butter, sour cream, and cream.
- Cereals (buckwheat, semolina, oatmeal, rice), cooked in water and brought to a semi-viscous consistency.
- Boiled/mashed zucchini, carrots, potatoes, pumpkin, cauliflower, green peas, beets. Later - raw carrots/pumpkin and grated cucumbers, peeled tomatoes.
- Low-fat fish (carp, pike perch, hake, cod, perch, pike, pollock), steamed/boiled in pieces or in the form of cutlets.
- Lean red meat (beef, veal), rabbit meat, chicken in the form of chopped products (meatballs, cutlets, souffle, meatballs), steamed. Boiled chicken/rabbit can be cooked in pieces.
- Low fat fermented milk products. Milk is only allowed to be added to dishes. Sour cream - as a seasoning for dishes, mild cheese in grated form.
- White omelettes (1 egg per day).
- Stale wheat bread, biscuits.
- Homemade sauces based on vegetable broth with the addition of sour cream/milk.
- Fruits - in the acute period, baked sweet apples. Mashed dried fruits. Later - jelly, mousse, marshmallow. During the remission stage, limited amounts of pureed raw fruits/berries are allowed.
- After an exacerbation, fats are introduced very carefully, first - butter, and later - refined sunflower oil.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Fruits | ||||
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| dried apricots | 5,0 | 0,4 | 50,6 | 213 |
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Bakery products | ||||
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir 1.5% | 3,3 | 1,5 | 3,6 | 41 |
| curdled milk 1% | 3,0 | 1,0 | 4,1 | 40 |
| acidophilus 1% | 3,0 | 1,0 | 4,0 | 40 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 1% | 16,3 | 1,0 | 1,3 | 79 |
| cottage cheese 1.8% (low-fat) | 18,0 | 1,8 | 3,3 | 101 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken breast | 29,8 | 1,8 | 0,5 | 137 |
| boiled turkey fillet | 25,0 | 1,0 | — | 130 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| flounder | 16,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 83 |
| pollock | 15,9 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 72 |
| blue whiting | 16,1 | 0,9 | — | 72 |
| cod | 17,7 | 0,7 | — | 78 |
| hake | 16,6 | 2,2 | 0,0 | 86 |
| pike | 18,4 | 0,8 | — | 82 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| peach juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,5 | 40 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||