Good afternoon, many will be interested in understanding their health and their loved ones, and I will tell you my experience, and we will talk about Chronic indurative pancreatitis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment. Most likely, some details may differ, as was the case with you. Please note that you should always consult with highly specialized specialists and not self-medicate. Naturally, you can quickly find the answer to the simplest questions and diagnose yourself. Write your questions/suggestions in the comments, and together we will improve and supplement the quality of the material provided.
Indurative pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas that is chronic in nature. Unlike other types, the inflammatory process proceeds slowly, and even several years may pass from the moment of an acute attack. However, do not underestimate the danger of indurative pancreatitis. Complications, malignant neoplasms and cysts - this is what awaits patients if they do not consult a specialist in a timely manner and violate doctor’s instructions.
How does indurative pancreatitis manifest?
Symptoms are often muted, which is why the patient simply does not suspect any disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas, attributing the ailments to banal fatigue.
As a rule, after drinking alcohol and eating fatty foods, you feel heaviness in the stomach. Over time, attacks of inflammation of the organ become more frequent, and taking a certain position - bending the body forward - helps relieve discomfort. Some people note that they feel better lying down. Appetite worsens, girdle pain occurs.
Causes
Why does indurative pancreatitis develop? The reasons are poor nutrition. Irregular, unsystematic consumption of food leads to disruptions in the functioning of the pancreas. Most often, the pathology makes itself felt against the background of addiction to fast food, fatty foods, all kinds of smoked meats, and products that contain an abundance of spices and salt.
The progress of chronic indurative pancreatitis is facilitated by the presence of bad habits. We are talking about regular consumption of alcohol along with an abundance of smoked cigarettes. Elements of the breakdown of alcohol inhibit the stable functioning of the pancreas. In combination with tissue saturation with nicotine, local structures are destroyed. Previously healthy areas of the gland are replaced by connective fibers.
Indurative pancreatitis often occurs against the background of a person’s tendency to depression. Prolonged emotional shocks lead to suppressed immunity. The result is the inability of the pancreas to resist inflammation.
What is done to diagnose inflammation?
Diagnostics includes a number of research manipulations.
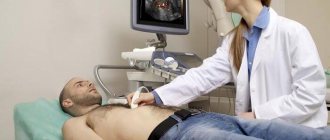
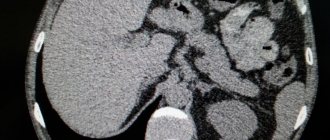
Direct attention is paid to blood and urine parameters. An ultrasound of the organ is mandatory. An increase in the size of the gland and disruption of the structure of the parenchyma are sure signs of repeated inflammation. X-ray clearly demonstrates calcifications in the pancreas, indicating advanced induration of the inflammatory process.
The patency of the ducts is determined using endoscopic pancreatography. In some cases, computed tomography is used to exclude the presence of malignant neoplasms and cysts.
Therapy for pathology
The disease requires urgent hospitalization of a person. In the first days, the patient is advised to fast and drink mineral water without gas. Subsequently, the patient follows a strict diet.
Treatment of recurrent pancreatitis includes the following medications:
- antibacterial agents (“Tetracycline”);
- non-narcotic analgesics for severe pain: “Atropine”, “Baralgin”;
- enzyme agents (“Pancreatin”) if the patient has exocrine insufficiency;
- vitamin therapy: vitamins B and A;
- choleretic drugs.
Since the disease manifests itself in frequent attacks of pain, patients are recommended to take antispasmodics. Following a diet and avoiding alcohol reduces the number and duration of relapses of the disease.
How is indurative pancreatitis treated?
Conventionally, treatment can be divided into conservative and surgical.
The first includes correcting nutrition and taking medications to normalize the functioning of the digestive system:
The emphasis is on plant-based foods that aid digestion and limit protein and fat.
It is recommended to take antispasmodic and enzyme medications: Papaverine, Creon, No-shpa, Festal, etc.
A sanatorium-resort trip, for example, to Essentuki or other health resorts that provide gastroenterological support, will be beneficial.
The protective function is carried out by the drugs Phosphalugel, Almagel, etc.
Surgical intervention is required in case of obstruction of the ducts, cysts or malignant neoplasms, or in the presence of constant severe pain syndromes.
Indurative pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas that is chronic in nature. Unlike other types, the inflammatory process proceeds slowly, and even several years may pass from the moment of an acute attack. However, do not underestimate the danger of indurative pancreatitis. Complications, malignant neoplasms and cysts - this is what awaits patients if they do not consult a specialist in a timely manner and violate doctor’s instructions.
Treatment
Chronic pancreatitis is treated with both conservative and surgical methods. The therapeutic regimen is selected depending on the severity of pathological changes, the frequency of exacerbation, and the presence of complications.
The operation is indicated for suppuration, blockage of the pancreatic ducts, narrowing of the sphincter of Oddi, tissue necrosis, pancreatic pseudocyst.
Replacement therapy
The replacement therapy regimen for pancreatitis includes:
- Enzymes of animal origin (Mezim, Pancreatin, Creon). Reduce the activity of the pancreas, unloading it. Some patients believe that the introduction of artificial enzymes disrupts the functions of the organ, but this is not the case. Taking medications has a positive effect on the further functioning of the gland.
- Secretolytics (Omez, Omeprazole). Reduce the production of gastric juice, increasing the effectiveness of enzyme preparations.
- Antispasmodics (No-shpa, Spazmalgon). Pancreatitis is accompanied by increased pressure in the ducts, which causes a person to feel severe pain. The drugs relax the tissues, eliminating discomfort.
No-spa for pancreatitis relaxes tissues, eliminating discomfort.
Diet
During the period of exacerbation of recurrent pancreatitis, it is recommended to abstain from meals. After the condition improves, diet No. 5 is applied. Sour fruits, marinades, fried and fatty foods, spicy foods, alcoholic and carbonated drinks are excluded from the diet. It is allowed to consume fresh vegetables, dairy products, cereals, and lean meat. Food is steamed, boiled or stewed.
They eat small portions, 5-6 times a day.
Diagnostics
An examination by a qualified specialist is not enough to make a diagnosis. In order to make the most accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes the patient such laboratory and instrumental examination methods as:
- A general blood test, which shows an increase in leukocytes and ESR - indicators responsible for the presence of an inflammatory process in the body;
- Biochemical blood test - attention is drawn to increased levels of amylase, bilirubin, glucose;
- General urine analysis - an increase in the normal amylase level is also noted;
- Coprogram - the degree of digestion of food residues is assessed. Steatorrhea and creatorrhea are noted - the presence of undigested fat and protein particles in the stool;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, with special attention paid directly to the pancreas. Ultrasound examination of the pancreas makes it possible to note an increase in its size, as well as a change in the structure of the parenchyma (there is both a fibrous and sclerosing component);
- Endoscopic retrograde pancreatography – the diameter of the main bile duct and the degree of its patency are assessed;
- FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy) is a technique that allows you to evaluate the external secretory function of an organ;
- X-ray examination of the gland, which shows the deposition of calcifications in the organ;
- Cholecystocholangiography – assesses the condition of the gallbladder and its ducts;
- Computed tomography is often used to exclude oncological pathology.
SYMPTOMS OF CHRONIC PANCREATITIS
The first symptoms of pancreatitis appear quite late, when changes in the tissues of the organ are significant and irreversible. The course of the disease is wave-like - exacerbations are replaced by remissions.
- With exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis, the pain syndrome is pronounced. The pain is localized in the epigastric region, left hypochondrium, and may be girdling. Sometimes the left shoulder blade gives way, simulating an attack of angina. The patient takes a forced position lying on his side with his legs brought towards the body.
- Dyspepsia - nausea, vomiting, belching, heartburn. Vomiting can be frequent, debilitating, and not bringing relief.
- Exocrine insufficiency. Due to a decrease in the production of enzymes, digestion processes in the small intestine are disrupted, which contributes to the proliferation of pathogenic microflora, bloating, flatulence, diarrhea, and steatorrhea (the presence of undigested fat in the feces). Long-term digestive disorders lead to weight loss and hypovitaminosis.
- Endocrine insufficiency develops due to a decrease in the production of key enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism - insulin and glucagon, produced by the cells of the islets of Langerhans in the caudal part of the organ. Endocrine insufficiency is observed in approximately a third of patients and is manifested by either hypoglycemic syndrome or signs of diabetes mellitus.
- General symptoms : fever, weakness, loss of appetite and weight, pallor with a sallow tint. Yellowness of the skin and sclera may be observed.
Etiological and predisposing factors
In the development of such a pathology of the digestive system as pancreatitis, the following reasons are of particular importance:
- Frequent episodes of acute pancreatitis;
- The spread of infectious agents from the gastroduodenal zone, as well as the biliary tract, both in acute pancreatitis and in other infectious and inflammatory diseases.
In addition to clearly defined etiological factors, provoking (predisposing) factors such as:
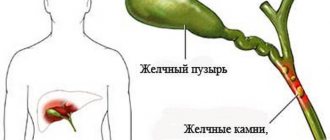
- Cholelithiasis (cholelithiasis) - especially the presence of stones in the common bile duct, as well as the pancreatic duct;
- Liver cirrhosis of any etiology;
- The process of penetration or perforation of an ulcer localized in the stomach or duodenum into the pancreas;
- Frequently occurring stressful situations;
- Atherosclerotic vascular lesions;
- Diabetes mellitus is an insulin-dependent type, in which there is damage to the endocrine areas of the pancreas responsible for the production of insulin;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Improper and unbalanced nutrition: frequent overeating, abuse of fatty, fried, smoked foods.
We recommend reading: Coffee - health benefits and harms, composition and effect on the human body
Causes and risk factors
Indurative pancreatitis most often occurs in elderly people; the following factors lead to the development of the disease in young patients:
- Poor nutrition. Violation of the functions of the pancreas is facilitated by irregular meals, non-compliance with the diet prescribed by the doctor, and consumption of fatty, fried, smoked and salty foods.
- Smoking, drinking alcohol. Alcohol breakdown products adversely affect the condition of glandular tissues, promoting their destruction and replacement with connective tissue fibers.
- Poor circulation in the abdominal cavity.
- The presence of benign or malignant pancreatic tumors.
- Deficiency of vitamins and microelements.
- Advanced forms of acute pancreatitis.
- Diseases of the liver, intestines, stomach, gall bladder (cirrhosis, malignant tumors, ulcerative lesions.
- Depressive disorders, frequent stress. They contribute to a decrease in immunity, against the background of which inflammatory processes begin to develop.
Automune aggression. This pathological condition is characterized by the production of antibodies that destroy healthy cells.
Clinical picture of the disease
This form of pancreatitis in the initial stages of its development does not have specific symptoms that make it possible to make a correct diagnosis only on the basis of clinical symptoms. In the first stage, the pathological process manifests itself quite latently and disturbs the patient extremely rarely, which makes it difficult to diagnose it at an early stage of development due to the patient’s late visit to the doctor.
Indurative pancreatitis, like many other forms of this disease, has the following symptoms:
- Painful sensations in the epigastric region (in the epigastric zone), as well as to the right and left of it (in the right and left hypochondrium). The pain is dull, bursting, aching in nature. Their intensity can increase over time and acquire a high degree. Pain in this disease has a peculiarity: it radiates to the back at the same level as in the abdomen (girdling pain). Initially, the pain can be relieved by taking medications; in later stages, neither oral medication nor intravenous administration helps the patient;
- Feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- Attacks of nausea followed by vomiting or without it;
- Abnormal stool – diarrhea or constipation;
- Decreased appetite, sometimes even to its complete absence;
- Increased general body temperature (usually subfebrile);
- Weight loss;
- General weakness and unexplained malaise;
- In case of compression of the common bile duct by the enlarged head of the gland, jaundice is noted. The degree of yellowness of the skin and visible mucous membranes is determined by the degree of blockage of the ducts.
Causes and clinical manifestations of the disease
The recurrent form of pancreatic pathology is a disease of the modern civilized world. The main reason for the continuous development of this pathology is the negative impact of social factors, such as alcohol-containing drinks and low-quality food products, the consumption of which contributes to the systematic poisoning of the entire human body and an excessive level of activation of the functioning of the pancreas. In combination, all these factors provoke intense release of pancreatic secretion, which does not have time to be completely consumed in the processes of the digestive tract and begins to accumulate in the cavity of the gland, gradually having a destructive effect on the parenchymal organ.
According to statistics, a recurrent form of pathology often develops in males of mature and old age. Women are exposed to this pathology only after an attack of an acute attack of pancreatic gland disease.
A child in adolescence or younger may also be susceptible to the development of this pathology due to a hereditary predisposition.
The presence of the following factors can have a provoking effect on the development of the disease:
- progressive stage of gallstone pathology,
- trauma to the abdominal cavity,
- intoxication of the body,
- development of a chronic infectious disease,
- stressful influences.
Clinical signs of pathology first of all begin to manifest themselves in the form of the development of steatorrhea, or the presence of fatty compounds in the stool, which have a fetid odor, a greasy sheen and an increased level of stickiness.
Disruption of the processes of bile outflow in the patient's body against the background of the development of pathology often leads to the formation of yellowness of the skin. After which, painful sensations begin to appear, having a radiating nature with a gradual return to the back, shoulder blades and epigastric zone. Also observed:
- worsening of the patient’s general well-being,
- development of diarrhea, constipation and flatulence,
- regular feeling of nausea and vomiting,
- systematic weight loss,
- increased level of salivation.
It is worth noting that a relapse of chronic pathology of the pancreas can be caused by emotional overstrain, and attacks of pain can accompany a person, both for 3-5 hours and for 5-6 days.
Consequences
In the absence of proper treatment or with a late diagnosed disease, the following complications of indurative pancreatitis may develop:
- The appearance and growth of pancreatic cysts;
- The appearance of benign or malignant neoplasms of the organ;
- Complications of a purulent nature: gland abscesses, peritonitis, sepsis;
- Cholestasis is a violation of the outflow of bile;
- Intestinal obstruction;
- Thrombosis of the splenic vein, etc.
An examination by a qualified specialist is not enough to make a diagnosis. In order to make the most accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes the patient such laboratory and instrumental examination methods as:
Indurative pancreatitis of acute and chronic nature
Regular exposure to stressful situations on the human body in combination with an unbalanced diet, excessive consumption of alcohol-containing products, smoking and irresponsible attitude towards health often cause the development of many pathological processes affecting the organs of the digestive tract.
One of the many types of such pathologies is indurative pancreatitis. In the materials of this article, we will consider in more detail how chronic indurative pancreatitis manifests itself and what kind of pathology it is, its causes of development, treatment methods, as well as possible consequences and preventive measures aimed at preventing complications.
What is indurative pancreatitis?
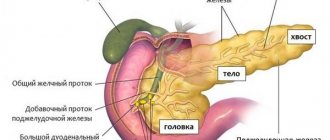
Chronic indurative pancreatitis, which has a code according to ICD 10 K86.0, is a consequence of repeated acute attacks of pancreatic damage to the pancreas, characterized by calcification of the tissue structures of the pancreas, or the development of tissue fibrosis and obstruction of patency in the cavity of the pancreatic ducts.
This type of pathology has a rather slow development and can manifest itself several years later, after an “attack” on the pancreas, with an acute pancreatic attack.
The progressive stage of the disease has a high level of danger; untimely treatment has unfavorable prognosis for its further course and can become the root cause of the formation of cystic lesions of the mucous surfaces of the gland, as well as the development of a tumor-like neoplasm.
Causes of the disease and predisposing factors
The reason for the development of this type of pathological process affecting a parenchymal organ may be the presence of the following predisposing factors:
- unbalanced and chaotic nutrition,
- frequent preparation of dishes with a high percentage of fat and salt,
- attack of an acute pancreatic attack in the gland cavity,
- alcohol abuse,
- progressive stage of gallstone disease,
- diseases of the stomach and duodenum.
Moreover, the cause of the onset and progression of the indurative form of pancreatic organ damage may be chronic depression, as well as a sharp decrease in immunity, against which inflammatory pathology may begin to develop.
Such a department of medical sciences as pathomorphology has not yet fully studied the mechanisms of influence of psychosomatic factors in the development of the indurative form of pancreatic gland disease, so they are not worth considering in detail.
Symptoms and manifestations of pathology
Acute indurative pancreatitis, as well as its chronic type of developing lesion, have similar symptoms to the morphology of the acute form of the usual inflammatory process in the pancreatic cavity and manifest themselves as follows:
- periodic feeling of nausea, causing profuse vomiting, which ultimately does not bring any relief in general well-being,
- the appearance of constipation, diarrhea, general disturbances in stool and gas formation,
- yellowing of the skin,
- acute feeling of pain in the epigastric zone with gradual irradiation to the back and stomach,
- elevated body temperature to subfebrile levels,
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach area,
- weight loss and loss of appetite.
With the development of indurated pancreatic disease, patients experience low performance, a feeling of lethargy and pain after eating. The risk of developing pathologies such as diabetes increases.
It often happens that against the background of general symptomatic manifestations, the attending physician can diagnose acute pancreatitis. Therefore, to make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to complete the entire course of diagnostic procedures and pass all the necessary tests. An advanced form of indurative pancreatitis can lead to the formation of pseudotumor lesions of the gland.
Diagnostic procedures
To most accurately identify the general condition of a parenchymal organ and make a correct diagnosis, the following types of diagnostic procedures are prescribed:
- Ultrasound diagnostics is necessary to visualize the structural features of the parenchyma, as well as to identify the development of possible compactions.
- A CT scan is performed if the development of a pancreatic tumor-like neoplasm is suspected.
- If severe complications of the pathology develop, an x-ray examination of the abdominal cavity is prescribed, which makes it possible to identify all the problems of the affected organ and detect the presence of calcifications in the cavity of the gland.
- Endoscopic examination is necessary to assess the degree of blockage of the pancreatic ducts, detect stones and cystic lesions of the organ, as well as to determine the size of developing compactions.
A comprehensive type of examination is considered the most informative, allowing the doctor to assess the condition of the affected organ from different angles and correctly determine the type of pathology.
Treatment
Treatment of the indurative form of pancreatic lesions of the pancreas can be carried out using two methods:
- with the help of medicinal macropreparations and micropreparations,
- by surgical intervention.
Medications
The basis of drug therapy is the use of the following medications:
- antispasmodic agents, such as papaverine and no-spa,
- enzymatic preparations, in the form of Creon, Pancreatin, Festal and Methionine,
- if the acidity of the gastric juice is elevated, antacid treatments such as phosphalugel and almagel are prescribed,
- histamine H receptor blockers in the form of ranitidine, cimetidine and famotidine,
- vitamin complexes, especially group B.
An important role is played by adherence to a special dietary diet and treatment in sanatoriums with a gastroentorological focus.
Diet for illness
Compliance with the correct dietary intake will be the key to successful drug treatment, therefore, it is recommended to completely eliminate from the daily diet the consumption of foods that contribute to irritating the mucous surfaces of parenchymal organs and provoking inflammatory processes. Among these foods, the following have a particular level of negative impact:
- semi-smoked and smoked food products,
- fried foods,
- foods with high levels of spice and salt,
- carbonated water and alcoholic drinks,
- canned foods.
The use of infusions and decoctions based on medicinal herbs: violet, chamomile, St. John's wort, immortelle and rose hips will help prevent the recurrence of pathology.
But it is worth noting that the use of folk remedies must be previously agreed with the attending physician.
Consequences and prevention of complications
With inappropriate treatment or its absence, indurative pancreatitis can become the root cause of the development and progression of the following types of complications:
- formation of cysts on the walls of a parenchymal organ,
- formation of a benign or malignant tumor,
- development of peritonitis, abscess or sepsis,
- a pathological disorder of the processes of bile outflow, called cholestasis,
- intestinal obstruction,
- formation of thrombosis of the splenic veins, etc.
An advanced medical history, characterized by the maximum level of damage to the gland, can cause the patient's disability.
In the form of preventive measures aimed at preventing the development of the above complications, it is necessary to follow the prescribed diet with table No. 5, give up bad habits and lead a healthy lifestyle with the maximum exclusion of stressful situations.
Source: https://mfarma.ru/pankcreatin/indurativnaya-hronicheskaya-forma-pankreatita
Treatment of chronic inflammation
If the diagnosis of pancreatitis has revealed a chronic form of the disease, then patients can be prescribed various medications: enzyme preparations based on pancreatin (Mezim, Festal, Creon), antibiotics (Abaktal, Amoxiclav, Sumamed) etc. In some cases (for example, with a formed pseudocyst), minimally invasive (percutaneous) drainage or surgical intervention is required.
Nutrition plays an important role. If the disease worsens on the 1st or 2nd day, patients are prohibited from eating anything. You can only drink liquid (1-1.5 liters per day): weak tea, alkaline mineral water without carbon, rosehip decoction (1-2 glasses). On the 2-3rd day you are allowed to eat. Slimy soups, liquid pureed milk koshes, vegetable purees, and fruit juice jelly are allowed.
During periods of remission, you should adhere to the following tips:
- Steam, puree or bake food in the oven. Eliminate pure fats from the diet and limit table salt to 6 g per day.
- Eat small meals 5-6 times a day. The recommended temperature for hot dishes is no higher than 57-62 degrees, cold food - no less than 15-17 degrees.
- Exclude from the diet sour, spicy, spicy and canned foods, peas and beans, mushrooms, carbonated and alcoholic drinks, kvass, sour fruit juices, and baked goods. Cream and sour cream are allowed in small quantities in dishes.
Diet for chronic indurative pancreatitis
Proper nutrition can significantly slow down the progression of pathology. Strict adherence to a special diet allows you to normalize the functioning of the digestive organs and reduce the concentration of glucose in the blood structure. A prerequisite for a fruitful fight against the development of the disease is the exclusion from the diet of sweet foods, various kinds of smoked foods, sour vegetables and fruits, carbonated drinks, and canned food.
Diet for pancreatitis of the pancreas, sample menu:
- Breakfast - porridge, omelette cooked in a steam bath, unsweetened tea, a small slice of cheese.
- Lunch – lean vegetable soup, boiled poultry fillet, moderately sweet fruit jelly.
- Afternoon snack – low-fat cottage cheese or yogurt, unsweetened biscuit.
- Dinner - mashed potatoes or zucchini, stewed fish fillet, steamed cutlets, fruit compote.
Elderly people are offered a slightly different diet for pancreatitis of the pancreas. A sample menu includes a chicken fillet-based lean soup for breakfast. For lunch, lazy dumplings with low-fat cottage cheese, baked apples or pears, and carrot soufflé are served. In the evening, it is recommended to consume vegetable puree soups. Compliance with such a diet is associated with slow metabolism in the body of older people and a tendency to constipation.
Signs of acute inflammation
Pain in the epigastric region is a symptom indicating acute pancreatitis. Differential diagnosis in the presence of this sign is carried out immediately, because the pain is often so strong that people cannot lie or sit quietly. Only after diagnostics and an accurate diagnosis can specialists take any measures to alleviate the condition of patients.
Another common sign of acute inflammation of the pancreas is vomiting, which in most cases is repeated. It does not bring relief to sick people. Their condition only worsens due to vomiting. Other symptoms of acute pancreatitis include:
- pallor of the skin, acrocyanosis (the skin acquires a bluish color);
- bloating;
- retention of gases, stool;
- severe weakness.
Diagnosis of pathology
The recurrent form of pancreatic pathology is diagnosed quite simply and almost always with accurate results and the correct diagnosis. Basic diagnostic procedures:
- Ultrasound, which helps visualize the heterogeneity of the structural structure of the gland by detecting calcifications and its increase in size.
- Carrying out fibrogastroscopy to assess the condition of the stomach and duodenum.
- CT diagnostics, which makes it possible to identify pathological changes in the area of the parenchyma of the gland, as well as their intensity of development and the extent of damage to the parenchymal organ.
- Using MRI diagnostics, the condition of the pancreatic ducts is assessed.
Blood tests for biochemical testing and stool tests for scatological testing are also prescribed.
The danger of reactive pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis leads to diabetes mellitus.
An inflamed pancreas cannot fully perform its functions. The organ produces and conducts digestive enzymes, which are responsible for metabolism and metabolism.
If a malfunction occurs, then the entire gastrointestinal tract is not able to break down incoming foods into fats, proteins and carbohydrates.
When enzymes stop flowing, the duodenum begins to gradually digest its soft tissues, which lead to complete destruction (destruction) and the appearance of ulcers. With reactive pancreatitis, the functionality of the liver and kidneys decreases.
Chronic disease often leads to diabetes mellitus, and then to atherosclerosis and vascular diseases. If reactive pancreatitis is not diagnosed in time, there is a risk of complications of the disease.
The acute form of pancreatitis can develop into infected and purulent pancreatic necrosis (decomposition of soft tissues and cells of the pancreas, as well as their necrosis and necrosis).
Treatment of pathology
Depending on the course and severity, the disease may be subject to the following types of treatment:
Chronic indurative pancreatitis is practically incurable. Therefore, the main goal of treatment is to improve the patient’s general condition and prevent exacerbation of the disease. the most important point that attention is first paid to is the correction of nutrition and the development of a diet. You need to add fruits and vegetables to the menu, which help improve the excretory function of the gastrointestinal tract.
Medicines are used to relieve pain. Antispasmodics and painkillers are usually used. To restore the pancreas, enzymatic agents are successfully used, with the help of which not only the digestion of food is improved and the pancreas is unloaded, but also the positive effect on the overall functioning of its glandular elements is enhanced.
Surgical treatment is indicated for complications such as:
- Impaired flow of bile through the main bile duct;
- The presence of tumor-like formations, actively growing cysts;
- Severe pain syndrome that is not relieved by pharmaceutical drugs;
- Ineffectiveness of conservative therapy.
In the absence of proper treatment or with a late diagnosed disease, the following complications may develop:
- The appearance of a pancreatic cyst;
- The appearance of benign or malignant neoplasms that lead to disability;
- Complications of a purulent nature: abscesses, peritonitis, sepsis;
- Cholestasis is a violation of the outflow of bile;
- Intestinal obstruction;
- Thrombosis of the splenic vein.
Chronic pancreatitis: ICD 10 classification
This classification is modern and the most widely used today. According to this classification, the World Health Organization adds new diseases to the list every ten years, which also includes chronic pancreatitis. The modern classification gives each disease its own code, so even if the doctor does not understand a foreign language, using this code, he will be able to understand what kind of disease we are talking about.
We recommend reading: TSH after menopause
So, according to this classification, chronic pancreatitis has two forms:
- form of alcoholic origin;
- other forms of this pathology.
After providing first aid, you must immediately call a doctor. The person must be hospitalized in a hospital. The hospital immediately performs an ultrasound diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. After an accurate diagnosis has been established, analgesics (Baralgin, Analgin) are prescribed to suppress pain.
Consequences and prevention of complications
With inappropriate treatment or its absence, indurative pancreatitis can become the root cause of the development and progression of the following types of complications:
- formation of cysts on the walls of a parenchymal organ,
- formation of a benign or malignant tumor,
- development of peritonitis, abscess or sepsis,
- a pathological disorder of the processes of bile outflow, called cholestasis,
- intestinal obstruction,
- formation of thrombosis of the splenic veins, etc.
An advanced medical history, characterized by the maximum level of damage to the gland, can cause the patient's disability.
In the form of preventive measures aimed at preventing the development of the above complications, it is necessary to follow the prescribed diet with table No. 5, give up bad habits and lead a healthy lifestyle with the maximum exclusion of stressful situations.
- Maev I.V., Kazyulin A.N., Kucheryavyi Yu.A. Chronic pancreatitis. M. "Medicine Publishing House", 2005, p. 504.
- Minushkin O.N. Chronic pancreatitis: some aspects of pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. Consilium medicum. 2002 No. 1, pp. 23–26.
- Maev I.V., Kucheryavyi Yu.A., Andreev D.N., Dicheva D.T., Gurtovenko I.Yu., Baeva T.A. Chronic pancreatitis: new approaches to diagnosis and treatment. Educational and methodological manual for doctors. Moscow: FKUZ "GKG MIA of Russia", 2014.
- Maev I.V., Kucheryavyi Yu.A., Andreev D.N., Dicheva D.T., Gurtovenko I.Yu., Baeva T.A. Chronic pancreatitis: new approaches to diagnosis and treatment. Educational and methodological manual for doctors. Moscow: FKUZ "GKG MIA of Russia", 2014.
- Khazanov A.I., Vasiliev A.P., Spesivtseva V.N. et al. Chronic pancreatitis, its course and outcomes. M.: Medicine, 2008.
source
How is the disease treated?
Enlargement of the gland and changes in the structure of the parenchyma are determined using ultrasound. The results of computed tomography will help differentiate chronic pancreatitis from a tumor and determine the diagnosis of pancreatic cysts.
The patient may be prescribed an X-ray examination, which can reveal the presence of calcifications (stones). If stones are found, this means that indurative pancreatitis is in an advanced stage. Using endoscopic pancreatography, a specialist examines the diameter of the main pancreatic duct and its patency, eliminating the formation of cysts and tumors.
Treatment may be as follows:
If there are problems with the digestive system, then the attending physician additionally prescribes medications that improve digestion - Almagel, Phosphalugel. Conservative treatment involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition. You need to eat low-calorie foods and give up alcohol.
If the attending physician makes such a decision, then painkillers are used in therapy, the effect of which is aimed at relieving spasm. Such medications improve the production of enzymes, since disruption of the gland makes this process difficult. If all methods and means of conservative treatment do not bring the expected positive effect, then the attending physician is forced to perform surgical intervention. Its main goal is to achieve patency in the main duct of the gland.
The question of surgical intervention most often cannot be resolved unambiguously.
Surgery is necessary if conservative treatment for several years does not produce positive results.
First of all, it is necessary to determine the etiology factor of the disease, the stage and changes in the systems of the affected organ. Surgical intervention is prescribed for advanced forms of the disease, which are manifested by jaundice, cyst formation, as well as for diseases developing against the background of peptic ulcer, colitis and gastritis.
Contraindications to surgery are diabetes mellitus, metabolic disorders, as well as decompensated adaptation mechanisms in older people. When surgical treatment is prescribed, one should remember its limited capabilities. It is necessary to take into account the risk of surgery and the danger of disease. Before performing surgery, it is necessary to identify the individual characteristics of the patient.
Surgical treatment is aimed at achieving the following goals:
- identification and subsequent elimination of the root cause of the disease;
- elimination of pain syndrome;
- normalization of the outflow of pancreatic juice and bile into the intestines.
Surgical treatment of indurative pancreatitis is prescribed when the patency of the pancreatic duct is impaired, when calcification and cysts appear in the pancreas, and when pancreatitis with severe pain syndrome, which leads to decreased performance. Correction is necessary when identifying pathologies of the gallbladder.
Diagnostics and complex therapy for recurrent conditions
In addition to the standard diagnostic examination, which includes ultrasound scanning of the abdominal organs and computed tomography, it is necessary to determine the functional state of the exocrine system of the digestive organ. A laboratory analysis of excrement (coprogram) is required - a microscopic examination to identify undigested food. The assessed state of the exocrine pancreatic system allows us to determine further actions on the effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapy and select the appropriate program of comprehensive medical treatment.
Treatment of chronic recurrent pancreatitis requires an individual approach to each patient, since the age, gender and physiological characteristics of the patient should be taken into account. The general scheme of complex treatment includes therapeutic fasting in the first 2-4 days of hospital treatment and a strict diet in subsequent days. The most common and rational is dietary nutrition according to the method of M. I. Pevzner (diet No. 5). The diet was developed by the author in the middle of the 20th century and is popular today.
Important! Dietary table No. 5 is the optimal amount of organic components (proteins, fats and carbohydrates) that a person needs according to his physiological needs for diseases of the digestive system, liver, gallbladder and bile ducts at any stage of exacerbation.
The daily energy value of consumed foods should not exceed 2000-2500 kcal. The daily intake of organic substances is considered to be:
- carbohydrates – 250-350 g;
- fats – 70-80 g;
- proteins – 90-100 g.
Proper nutrition is the key to successful treatment of pancreatitis.
All food products must be thermally processed, that is, baked in the oven or boiled. The recommended daily number of meals should be at least 5-6 times. The traditional drug treatment regimen is diagnostic standard No. 125 dated April 17, 1998, developed by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, which provides for the use of pharmacological drugs. The therapeutic tactics are as follows:
- In the case of a chronic or acute course of the disease, urgent and continuous aspiration of pancreatic juice is necessary, as well as intravenous administration of pharmacological drugs that provide a secretory decrease in gastric contents. These include Ranitidine, Famotidine and other pharmacological combinations.
- If necessary, a certain amount of insulin is administered to the patient to avoid hypovolemic shock.
- To suppress gastric and pancreatic secretion and to relieve pain, inhibitors are administered: Rabeprazole, Omeprazole, Esomeprazole and other pharmacological drugs.
- Enzyme toxemia, which determines the severity of the disease, is eliminated by boosting doses of diuretics: Mannitol, Lasix and other drugs.
In addition, it is necessary to ensure a decrease in blood pressure in the bile duct system of the pancreas. This is achieved with the help of myotropic antispasmodics (Mebeverine, Drotaverine, etc.) and anticholinergic blockers (Platifillin, Gastrocepin, etc.). All further actions for drug treatment should be aimed at restoring pancreatic secretions and ensuring high-quality outflow in the bile ducts. Antibacterial therapy is used if necessary. The indication for surgical intervention is the failure of pharmacological correction of the digestive organ.
For recurrent pancreatitis, it is necessary to take a complex of medications
Provoking factors
Moreover, not only the factors listed above contribute to the appearance of pathology. Pancreatic fibrosis can be caused by:
- cholelithiasis;
- liver cirrhosis at any stage of development;
- penetration or perforation of an ulcer of the duodenum or stomach;
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus;
- smoking and drinking alcohol;
- improper (unbalanced) nutrition.
In addition, frequent and intense stress can cause indurative pancreatitis.
Having been admitted to the hospital with a preliminary diagnosis of acute inflammatory process in the pancreas, it is discovered that the disease has long been chronic.
Indurative pancreatitis: causes, symptoms, treatment, diet
Indurative pancreatitis occurs due to inflammatory processes that affect the tissue of the pancreas. The disease is chronic. The development of pathology occurs slowly.
The time period between individual attacks of the disease can be several years.
Despite the predominantly sluggish nature of the pathology, disruption of the pancreas hides an increased health hazard.
Causes
Why does indurative pancreatitis develop? The reasons are poor nutrition. Irregular, unsystematic consumption of food leads to disruptions in the functioning of the pancreas. Most often, the pathology makes itself felt against the background of addiction to fast food, fatty foods, all kinds of smoked meats, and products that contain an abundance of spices and salt.
The progress of chronic indurative pancreatitis is facilitated by the presence of bad habits. We are talking about regular consumption of alcohol along with an abundance of smoked cigarettes.
Elements of the breakdown of alcohol inhibit the stable functioning of the pancreas. In combination with tissue saturation with nicotine, local structures are destroyed.
Previously healthy areas of the gland are replaced by connective fibers.
Indurative pancreatitis often occurs against the background of a person’s tendency to depression. Prolonged emotional shocks lead to suppressed immunity. The result is the inability of the pancreas to resist inflammation.
Symptoms
Symptoms of indurative pancreatitis are similar to signs of the development of acute inflammatory processes in the structure of the liver. As clinical statistics show, diabetes mellitus develops in half of cases against the background of the disease. The trouble is observed due to the inhibition of tissues that perform endocrine functions, in particular those responsible for the synthesis of insulin.
The clinical picture of the disease indurative pancreatitis is as follows:
- Regular attacks of nausea, which cause an abundance of vomit. Emptying the stomach of poorly digested food does not bring relief. Poor health is observed throughout the day.
- Development of constipation, diarrhea. A general stool disorder makes itself felt. The patient has to suffer from increased gas formation.
- Dull girdle pain in the pancreas area. The discomfort gradually moves to the hypochondrium area, under the shoulder blade, and radiates to the back. There is a feeling of heaviness in the stomach.
- There is a noticeable loss of body weight. The problem arises against the background of conscious refusal of food. The action is due to the fear of the formation of new attacks of unbearable pain.
- After eating, a person often feels general weakness, suffers from sluggish tone, and increased temperature. Troubles are reflected in a decrease in performance.
Forms of the disease
Doctors distinguish several types of indurative pancreatitis.
The mild form of the disease is characterized by subtle disruptions in the functioning of the pancreas. A person practically does not feel discomfort in the area of the digestive organs. Exacerbations, accompanied by prolonged attacks of pain and stomach upsets, occur several times a year.
The development of the moderate form of indurative pancreatitis is accompanied by a higher frequency of exacerbations. You experience suffering a couple of times during each season. The pain is severe and long-lasting.
Severe pathology is accompanied by continuous relapses. Each time the pain becomes more acute. There are serious disruptions in the functioning of the pancreas, which has the most negative impact on the well-being and condition of the entire body.
Diet for chronic indurative pancreatitis
Proper nutrition can significantly slow down the progression of pathology.
Strict adherence to a special diet allows you to normalize the functioning of the digestive organs and reduce the concentration of glucose in the blood structure.
A prerequisite for a fruitful fight against the development of the disease is the exclusion from the diet of sweet foods, various kinds of smoked foods, sour vegetables and fruits, carbonated drinks, and canned food.
Diet for pancreatitis of the pancreas, sample menu:
- Breakfast - porridge, omelette cooked in a steam bath, unsweetened tea, a small slice of cheese.
- Lunch – lean vegetable soup, boiled poultry fillet, moderately sweet fruit jelly.
- Afternoon snack – low-fat cottage cheese or yogurt, unsweetened biscuit.
- Dinner - mashed potatoes or zucchini, stewed fish fillet, steamed cutlets, fruit compote.
Elderly people are offered a slightly different diet for pancreatitis of the pancreas. A sample menu includes a chicken fillet-based lean soup for breakfast.
For lunch, lazy dumplings with low-fat cottage cheese, baked apples or pears, and carrot soufflé are served. In the evening, it is recommended to consume vegetable puree soups.
Compliance with such a diet is associated with slow metabolism in the body of older people and a tendency to constipation.
Diagnostics
An effective method for making a correct diagnosis is ultrasound. As a result of the event, doctors have the opportunity to detect pathological changes in the structure of pancreatic tissue.
During the examination, the patient is often prescribed an x-ray. This diagnosis allows you to notice areas of tissue where calcium concentration occurs. The sign is evidence of endocrine disruption and speaks of the prerequisites for the formation of pathology.
Drug therapy
In order to treat indurative pancreatitis, doctors prescribe the following pharmacological agents:
- “No-Shpa”, “Papaverine” - have an antispasmodic effect on pancreatic tissue.
- “Almagel”, “Phosphalugel” - biologically active substances in the composition of the products reduce the level of acidity of gastric secretions.
- “Festal”, “Creon”, “Methionine”, “Pancreatin” - the components of the drugs are sources of essential enzymes that are required for the normal functioning of the pancreas.
- Vitamin complexes – contribute to the overall strengthening of the body and the maintenance of immunity.
Traditional methods of treatment
The use of the following remedy allows you to avoid relapses of attacks of indurative pancreatitis.
Take a tablespoon of crushed dried St. John's wort, dandelion, knotweed, violet flowers and corn silk. The ingredients are poured into a liter of boiling water. The composition is boiled over low heat for half an hour.
The medicine is allowed to brew for 10-15 minutes. The liquid is decanted and consumed warm in a glass before each meal.
To get rid of the characteristic discomfort during the development of the disease, it is possible to take tincture of golden mustache. They use the large root of a medicinal plant.
The raw materials are finely chopped, placed in a glass jar and filled with strong alcohol in an amount of 200-250 ml. The product is sealed with a lid, after which it is sent to infuse in a dark place for 2 weeks.
The finished medicine is taken 10 drops after meals.
Surgical intervention
If drug therapy and alternative treatment of the disease do not produce results, doctors resort to surgical methods to eliminate the problem. The following techniques are used:
- Stenting – a mesh frame is introduced into the structure of the pancreas, which improves the patency of local ducts.
- Resection – necrotic tissue areas are amputated, calcium accumulations are removed, and malignant neoplasms are excised.
- Cholecystectomy – the gallbladder is partially removed if there is a complete blockage of the organ’s ducts.
Prevention
The disease belongs to the category of chronic pathologies, which are accompanied by periodic exacerbations. In case of an individual tendency to develop pancreatitis, a number of preventive measures are required.
Regular, balanced nutrition along with leading a healthy lifestyle makes it possible to avoid the occurrence of unpleasant symptoms.
To find out about products that can provoke the onset of illness, consult an experienced doctor.
You need to understand that indurative pancreatitis is a serious disease that cannot be completely cured. Therefore, it is extremely important for people with high acidity of digestive juices and a weak pancreas to lead a healthy lifestyle, eliminating the maximum number of risk factors.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/427723/indurativnyiy-pankreatit-prichinyi-simptomyi-lechenie-dieta
Classification of acute pancreatitis
Clinicians share the classification of acute pancreatitis according to certain characteristics.
According to the severity of the disease:
- Easy.
- Average.
- Severe form.
With a mild course of the disease , short exacerbations may occur 1-2 times a year. Painful symptoms can be relieved with painkillers.
With moderate severity, exacerbations can occur 3 to 4 times a year. Note that signs of exacerbation can occur with a typical long-term pain syndrome. In a patient with moderate severity, pancreatic hyperfermentemia, creatorrhoea, amenorrhea, and steatorrhea are noted.
We recommend reading: Ovulation on day 11 of the cycle, is this normal?
In severe cases , signs of exacerbation often occur, which are characterized by a long course. The pain syndrome has a pronounced course, the patient experiences diarrhea, a sharp loss of body weight, and disturbances in the exocrine function of the pancreas occur.
Clinicians share the classification of acute pancreatitis according to certain characteristics
If you do not provide assistance to the patient in a timely manner, there is a risk of serious complications. For example: partial stenosis of the duodenum occurs due to an enlargement of the head of the pancreas, obstruction of the common bile duct is noted, and pseudocysts are formed.
Recommendations from Elena Malysheva in the special issue “Live Healthy!” on how to overcome pacreatitis using the healing effects of natural remedies.
Additionally, acute pancreatitis is divided by scale, as well as by the nature of the lesion. 5 types in total :
- Edema acute.
- Sterile pencreatic necrosis.
- Infected course of the disease.
- Formation of pancreatogenic abscess.
- Formation of pseudocysts in acute pancreatitis.
The classification of the acute course of the disease is extensive. Therefore, doctors further divide into causal classification . For example:
- Nutritional reason.
- Biliary.
- Gastrogenic and also ischemic.
- Infectious or toxic-allergic cause of acute pancreatitis.
- Traumatic.
- Congenital.
As for the clinical form of acute pancreatitis, it is distinguished into interstitial, in which swelling of the pancreas occurs, and the tissue often swells. The second clinical form is necrotic, the disease occurs with severe inflammation, and complications often occur.
In medical practice, there are types of pancreatitis, a certain classification of pancreatitis, which the doctor later uses in order to correctly diagnose, determine the severity and form of the disease.
Features of the course of the disease
The two main provoking factors of the disease are alcohol abuse and poor diet. The following pathologies are often the cause of the disease:
- abdominal trauma;
- stress;
- gallstones;
- poisoning;
- intoxication of the body in a chronic form;
- smoking.
Diagnostics reveals the disease in 60% of cases. It is divided into acute and chronic forms. If symptoms of the disease occur in the first six months after the onset of its course, then an acute form is diagnosed. A disease that appears after 6 months from the moment its first signs appear is classified as chronic.
Chronic recurrent pancreatitis is associated with frequent periods of remission and exacerbations in the patient. In this case, the symptoms are expressed in the form of cholestasis, in which the flow of bile into the duodenum is significantly reduced.
Exacerbations of the disease last differently depending on the characteristics of an individual person. The general dynamics of the occurrence of symptoms of pathology is expressed as follows:
- at the initial stage, attacks occur three or four times a year;
- after a year after the onset of the disease, the frequency of attacks increases to 4 per month;
- the duration of attacks in the first stages is half an hour;
- If the disease lasts for a long time in a person, attacks can last about 5 days.
Main clinical manifestations
Often recurrent pancreatitis begins to manifest itself in the form of steatorrhea. With it, a person’s feces become excessively oily, which is expressed in a non-specific shine. The patient also develops signs of obstructive jaundice. Human skin acquires a yellow tint.
Subsequently, the exacerbation increases, and the patient begins to be bothered by girdle pain. They can radiate to various parts of the body. Most often, pain is felt in the shoulder blade, stomach, left side of the back, under the ribs.
The patient may also feel a lump in the navel area, which may indicate the development of a cancerous tumor in the pancreas. In some cases, the symptoms of the pathology resemble a condition in which the patient’s bile ducts are compressed. Such clinical manifestations may also indicate a tumor of the head of the organ.
We recommend that you find out what nutrition should be like for pain in the intestines.
Read what esophageal leukoplakia is and why it is dangerous.
Among the characteristic additional signs of the disease are also:
- nausea with vomiting;
- profuse drooling;
- flatulence;
- diarrhea;
- weight loss;
- fever accompanied by chills.
In some cases, the patient does not have diarrhea, but constipation appears.
Features of diarrhea in the disease
The course of recurrent pancreatitis is associated with systematic digestive disorders in humans. There is a failure in the secretory function of the organ. The breakdown of incoming food occurs insufficiently. As a result, food is poorly absorbed into the intestines. For this reason, the patient is bothered by frequent diarrhea. Diarrhea is accompanied by the release of feces containing incompletely digested food fragments.
The number of urges to go to the toilet in a person during an exacerbation of the disease reaches 5 times in one day.
The patient's condition worsens in the following days. Against this background, he is experiencing severe weight loss and dehydration.
Another feature of the disease is the patient’s frequent feeling of hunger. All this is accompanied by excessive production of saliva. After eating, a person begins to experience pain in the left half of the abdomen. The pain is paroxysmal in nature and is poorly relieved by taking analgesics. Against this background, the patient subsequently begins to experience an aversion to food, which also affects his rapid weight loss.
Find out how and why to drink No-shpa for pancreatitis.
Read: how gastric papillitis manifests itself.
We advise you to find out how liver adenoma is treated.
Specific signs of the disease
During an exacerbation of the disease, blood and urine tests detect the presence of pancreatic enzymes in them, which is not noted at the stage of remission. With chronic pancreatitis, signs of an acute form of pathology may appear. In this case, the course of the disease is accompanied not only by gastrointestinal disorders, but also by the development of polyneuropathies.
They affect the peripheral nerves of a person, which is expressed in the form of paralysis and loss of sensitivity in the limbs.
Gastritis of the stomach is another reason when chronic recurrent pancreatitis is most often observed. The disease can occur hidden. Its detection is possible only by diagnostic methods. Latent pancreatitis develops symptoms similar to other diseases. The patient is also bothered by severe pain in the abdominal area, which radiates to the back, under the shoulder blade and ribs.
Classification of the disease according to V.T Ivashkin
The disease can occur due to various reasons, so the scientist believes that the classification according to the type of pathology is outdated. Therefore, the doctor proposed a new classification of the disease, which will accurately help to recognize the degree and form of all types of pancreatitis.
Much attention is paid to algorithms for examining patients with various nosological forms.
The basis of the classification remains the same, pay attention to the photo above.
Types of pathology that are associated with complications:
- The patient has a disturbance in the outflow of bile.
- Portal hypertension occurs.
- Additional infectious diseases that aggravate the course of the underlying disease.
As complications of pancreatitis, inflammatory disorders, as well as various endocrine pathologies, can occur.
Diet for illness
Compliance with the correct dietary intake will be the key to successful drug treatment, therefore, it is recommended to completely eliminate from the daily diet the consumption of foods that contribute to irritating the mucous surfaces of parenchymal organs and provoking inflammatory processes. Among these foods, the following have a particular level of negative impact:
- semi-smoked and smoked food products,
- fried foods,
- foods with high levels of spice and salt,
- carbonated water and alcoholic drinks,
- canned foods.
The use of infusions and decoctions based on medicinal herbs: violet, chamomile, St. John's wort, immortelle and rose hips will help prevent the recurrence of pathology.
But it is worth noting that the use of folk remedies must be previously agreed with the attending physician.