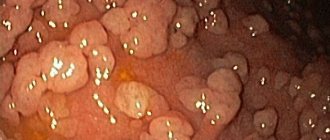
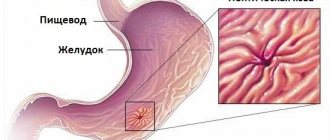
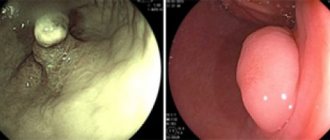
Intestinal metaplasia - what is it?
Intestinal metaplasia is a disease in which tissue from the stomach lining is replaced by intestinal cells. The disease was first described by Professor Kupfer more than 100 years ago.
Elderly people are most often affected. According to statistics, 80% of those infected are diagnosed with chronic gastritis, as well as duodenal ulcer.
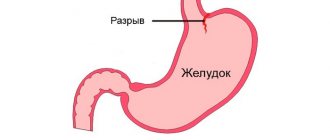
In a healthy state, the tissues that cover the walls of the stomach are constantly renewed. When damaged, cell division increases, which leads to increased migration and restoration of cellular renewal. In patients diagnosed with chronic gastritis, this process is disrupted, resulting in the inability of the gastric glands to perform their functions, which leads to metaplasia.
Features for different parts of the stomach: antrum, pyloric region
Metaplastic changes can occur in any part of the stomach, occupying only part of the mucosa or the entire thickness. The lesions are located in the membrane of the body, fundus or pyloric region, less often in the antrum.
The stomach is a rather complex organ
Important! Pathological changes in the gastric mucosa are considered a precancerous condition, so the disease is classified as dangerous. Studies conducted by many scientists have confirmed the presence of metaplasia in 94% of patients suffering from stomach cancer.
Observations over the past two decades have confirmed that tissue changes in intestinal metaplasia and intestinal type gastric cancer (Lauren classification) are completely identical.
Doctors believe that intestinal cancer occurs under the influence of external carcinogenic factors (substances that cause cancer). Most often occurs in the body of the stomach. Studies have shown that the disease develops in complex epidemiological areas.
Main varieties
Metaplasia also has a gradation according to the types of changes in tissues. It is carried out at the location of the lesions and comes in the following types.
Classification by types of lesions:
- Pyloric metaplasia. In this case, the tubular glands of the stomach are replaced by mucous tissue.
- Ciliated metaplasia. In the tissues of the affected organ, characteristic cells appear that lead to the appearance of cancer.
- Pancreatic metaplasia. A rather rare condition characterized by the appearance of small-grained cells.
Focal and diffuse forms of metaplasia most often occur in the antrum of the stomach.
With focal metaplasia, the pathological process occurs in the antrum of the stomach in a separate part. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, cells stop renewing, atrophy and die. Diffuse metaplasia occurs without tissue death and without affecting the deep layers.
Types of metaplasia of the gastric mucosa
There are two types of disease:
- complete (small intestine, mature);
- incomplete (colon, immature).
Mature metaplasia is characterized by the presence of cells that are found only in the small intestine: border cells, sulfamucines, goblet enterocytes. But the main sign confirming this type of disease is Paneth cells. The tissues of the stomach resemble the small intestine not only in structure, but also in functional properties.
With immature metaplasia, there is a disturbance in the maturation and development of the gastric glands: the upper layers are practically no different from the lower ones. The epithelium mainly consists of cells of the large intestine.
The complete type of intestinal metaplasia is more common, and in most cases is detected in patients with chronic gastritis. It is believed that this is a transitional stage to colonic metaplasia.
Important! According to statistics, an incomplete form of stomach cancer is detected in 94% of cases. Therefore, the disease is considered a precancerous condition, which, if not treated promptly, can lead to death.
According to the type of prevalence of the lesion, they are distinguished:
- weak – localization on 5% of the mucosal surface;
- moderate – up to 20%;
- pronounced – more than 20%.
Doctors distinguish intestinal metaplasia according to the type of pathology:
- pyloric - the tubular glands in the body of the stomach are replaced by mucous. They are called "Sterck's pyloric glands." Found, as a rule, with atrophic gastritis;
- ciliated - characterized by the appearance in the digestive tract of ciliated cells, which are absent in a healthy person. Doctors believe that their formation is associated with the development of metaplasia. In addition, the pathology occurs with a malignant tumor - adenocarcinoma. However, this type of disease does not always lead to stomach cancer;
- pancreatic – quite rare. It is classified by the appearance of fine-grained texture cells in the mucosal tissues.
Focal and diffuse forms
Additionally, focal and diffuse forms of development of the anomaly are distinguished in pyloric metaplasia.
With the focal type, replacement of some tubular glands occurs against the background of inflammation and damage to the cellular renewal of the gastrointestinal tract. Diffuse pathology is characterized by damage to the gastric mucosa without disruption of the structure and death of cells.
Degrees and classification
Two types of disease have been identified:
- Small intestinal (complete) metaplasia. It provokes gastritis, most often the mature form is observed. It is determined by the presence of acidophilic cells, which should be located in parts of the small intestine.
- Colonic (incomplete) metaplasia. This is an immature, more dangerous form. It is characterized by the presence of colon cells on the epithelium of the stomach. Most often it is diagnosed as a precancerous form (only 5 out of 100 people have a benign course). It is for this reason that it ends in death in 95% of cases.
Severity of the disease:
- Low prevalence, when changes cover about 5% of the epithelium.
- Moderate – about 20%.
- Complete – more than 20% of the cellular epithelium is affected.
By the nature of the lesion:
- Pyloric. Focal metaplasia is observed, in which only some glands are affected. This occurs when cell renewal is disrupted.
- Ciliated. Ciliated cells are formed, which are absent in a healthy person. In 60% of cases, the formation of carcinoma is provoked.
- Pancreatic is the rarest form. It is characterized by the formation of a fine-grained texture on the epithelium.
Degeneration of the gastric mucosa can damage part or all of its thickness. Localization of lesions can be observed on the membrane, fundus, pylorus or antrum.
Causes
The main reasons for the development of the disease include:
- inflammation of the gastric mucosa caused by various factors;
- gastrointestinal irritation;
- chronic esophagitis - inflammation of the tissues of the esophagus;
- long-term gastritis - especially with increased stomach acidity. In most cases, the development of metaplasia is associated with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. The microorganism affects the immune system and adapts to its changes, causing damage to the gastric epithelium of varying severity;
- frequent stressful situations;
- chronic reflux - esophagitis - exposure to irritating factors on the mucous membrane of the esophageal walls for more than six months. Inflammation occurs when gastric juice leaks or leaks into the esophagus;
- hormonal disorders.
Symptoms of the disease
Intestinal metaplasia itself does not manifest itself. All symptoms relate to ailments that preceded its development. Doctors identify the main signs of the disease:
- nausea;
- aching pain in the epigastric region;
- loss of appetite.
The epigastric region is part of the abdomen in the upper, middle region just below the ribs.
With increased acidity of the stomach, heartburn and “hunger” pains are observed, which intensify at night. If the disease is accompanied by reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus, vomiting and a feeling of bitterness in the mouth may occur.
Main symptoms
One of the main threats of this disease is its almost asymptomatic course. In the early stages, when treatment is particularly successful, the disease manifests itself as minor discomfort, which usually no one pays attention to.
The situation is worsened by the fact that metaplasia usually develops against the background of chronic gastritis or ulcers, so patients mistake the signs for symptoms of existing diseases.
The main signs of gastric metaplasia:
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Burning feeling in the stomach.
- Feelings of hunger appear in the evening and at night.
- Heartburn and bitterness in the mouth.
- Periodic pain in the side.
- Loss of appetite.
- Weight loss.
In most patients, symptoms appeared irregularly and without great intensity. This significantly complicates the diagnostic task and also leads to significant progress of the disease.
Diagnosis of the problem
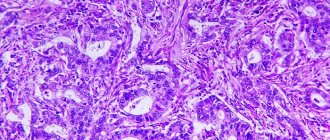
The diagnostic standard is considered to be histological examination, which reveals the form of the disease. During the procedure, small pieces of tissue taken from the human body are examined. The method of collecting cells or epithelium is called a biopsy. This is a mandatory way to confirm the diagnosis if the formation of malignant tumors is suspected.
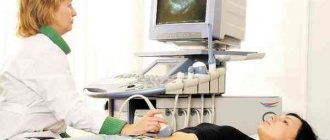
To determine the extent of damage, an additional examination of the gastrointestinal tract is carried out using endoscopic equipment with cell staining. Suspected pathological tissues are tinted with a special paint - methylene blue, which is absolutely safe for human health. Damaged cells acquire a special color and become visible under a microscope.
A combination of methods allows you to diagnose the disease more accurately. In addition, the degree of identification of the bacterium that causes chronic gastritis is increasing, and the need to identify it in intestinal metaplasia in order to prevent a precancerous condition is increasing.
Practical recommendations
Treatment of metaplasia should begin as early as possible, and all recommendations must be strictly followed
Treatment of metaplasia should begin as early as possible, and all recommendations must be strictly followed. It is necessary to establish a daily routine and wakefulness. Sleep duration should be 7-8 hours. Proper nutrition is important. You need to eat in small portions 4-5 times a day, avoiding long breaks. It is worth excluding fried, spicy, and salty milk from your diet. Coffee, strongly brewed teas, carbonated drinks, and alcohol are excluded. The diet should contain a sufficient amount of fruits and vegetables. Different types of cereals are useful. The last meal should be at least 2 hours before bedtime
Following this diet is extremely important. As with any other intestinal pathology, it makes up a significant part of the treatment.
The main thing is to treat the underlying disease. In the case of chronic gastritis and detection of carriage of the Helicobacter bacterium, eradication therapy is necessary with mandatory monitoring of cure. For this purpose, established first- or second-line treatment regimens are used.
For gastroesophageal reflux disease, drugs are used to correct gastric secretion:
- antacid drugs (phosphalugel, magnagel, maalox);
- H2-histamine blockers (ranitidine, cimetidine, famotidine);
- proton pump inhibitors (omeprozole, rabeprozole).
Prokinetics (domperidone) and reparants (sucralfate, solcoseryl) are used. Nonspecific anti-inflammatory drugs are also used. But their effect has not been fully studied.
Usually, with proper treatment and compliance with all recommendations, the process of metaplasia slows down. The question of a complete cure is now being debated. It is believed that atrophy of stomach tissue can be completely cured, but areas of metaplasia are not completely cured, but only stop developing. Therefore, all patients should constantly monitor the condition of the gastric mucosa.
All those who are found to have gastric metaplasia are registered at the dispensary. Usually observation is carried out by a gastroenterologist at the place of residence. In his absence, this is done by a general practitioner. Once every 1-2 years, it is necessary to conduct a diagnostic fibroesogastroduodenoscopy to control the disease and prevent the development of cancer.
https://fitsmed.ru/atrophic-hyperplastic-gastritis-with-intestinal-metaplasia-intestinal-metaplasia-of-the-stomach-is-a-common-severe-disease/
https://gastritinform.ru/yazva.bezgastritov.ru/yazva/ochagovaya-kishechnaya-metaplaziya-zheludka-vylechivaetsya-li/
Post Views: 13,540
Features of treatment
Therapy depends entirely on the degree of damage to the mucosa. If metaplasia is detected, the patient is registered with a gastroenterologist.
Drug therapy
Treatment with medications is primarily aimed at:
- elimination of gastroesophageal reflux disease - a disease in which the acidic contents of the stomach are regularly thrown into the esophagus. Under the influence of acid, damage to the mucous membrane occurs;
- suppression of gastric secretion;
- destruction of the bacteria H. pylori;
- prevention of benign neoplasms.
The treatment regimen is developed only by the attending physician, taking into account the results of the examinations. Therapy begins with the appointment:
- Proton pump inhibitors are modern medications that reduce the acidity of gastric juice. These include: rabeprozole, omeprozole, pantoprazole;
- antacids (Maalox, phosphalugel) - agents that neutralize hydrochloric acid;
- H2 – histamine blockers (cimetidine, ranitidine) – antisecretory drugs;
- gastroprotectors - in case of increased acidity of the stomach, they prevent the destruction of the mucous membrane.
Pregnancy and childhood are restrictions for taking certain medications.
To enhance the effect, first-line antibacterial agents (amoxicillin, clarithromycin) are additionally prescribed. The course of treatment is 7–10 days. In case of ineffectiveness of therapy, as well as low sensitivity of the infection to these drugs, second-line antibiotics (tetracycline, metronidazole) are prescribed.
The use of inhibitors increases the pH of the stomach, reduces the viscosity of gastric mucus, and prevents the destructive effect of antibacterial drugs. It is necessary to take into account that at the same time you should take medications that strengthen the immune system and prevent the development of dysbacteriosis.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is recommended if there is no positive effect on conservative treatment. In order to minimize the area of intervention in the body and the degree of injury, operations are performed using special endoscopic equipment. This type of surgery is called minimally invasive surgery. It is characterized by a limited depth of damage to the mucous membrane. If necessary, the damaged area is completely removed. As a result of the procedure, the risk of carcinogenic formations is significantly reduced.
What treatment is prescribed
Therapy is carried out comprehensively, based on how severely the epithelium is affected. In addition, the patient is registered with a gastroenterologist.
Drugs
Treatment trends are as follows:
- Eliminate the problem of backflow of stomach contents into the esophagus. This prevents the inflammatory process in the latter.
- Elimination of infection caused by Helicobacter.
- Prevention of cancer tumor formation.
After studying all the tests, the gastroenterologist determines an individual treatment regimen. To normalize the microflora, the drug “Linex” or its analogue is prescribed. Additionally, synthetic and natural immunomodulators and herbal treatment are often prescribed.
The most commonly used medications are:
- Inhibitors. Restores acid levels in gastric juice. These are Omeprazole, Rabeprazole, Pantoprazole and others.
- Antacids. Neutralize hydrochloric acid. This is Phosphalugel, Maalox.
- H2 blockers, which neutralize the activity of secretions. These include Ranitidine, Cimetidine.
- Gastroprotectors. They normalize acid levels and block the process of cell replacement.
- Micropreparations for chronic gastritis, erosion of the gastric mucosa, ulcers, adenocarcinoma.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is prescribed only in extreme cases when other treatment methods are ineffective. The procedure is performed with special endoscopic equipment. This is the so-called minimally invasive surgery.
In more advanced cases, complete removal of the changed zone is required. Carrying out such manipulation minimizes the risk of the formation of carcinogenic formations.
Home methods
The disease cannot be cured using folk remedies alone. They are used as additional ones to eliminate inflammation and reduce symptoms.
- Flax decoction: pour 25 grams of seeds into 200 ml of boiling water, simmer in a water bath for 60 minutes, cool, strain. Take 2 tbsp. spoons before meals.
- Take 5 grams of chamomile, yarrow and marshmallow, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water, leave for 60 minutes. Drink every time before meals.
Nutrition for illness
For more effective therapy, it is necessary to follow a healthy diet. A special diet has been developed for this:
- Remove dairy and fermented milk products from the menu.
- Avoid spicy, salty, fried foods, as they irritate the gastric mucosa.
- During treatment, avoid drinking alcohol, coffee and soda.
- Eat small portions, but at least 6 times a day.
- Do not eat 2 hours before bedtime.
- Increase your consumption of vegetables and fruits.
- Be sure to include various cereals in the menu.
- Avoid eating too hot or too cold foods and drinks.
Diet
Treatment will not be complete without proper nutrition. Patients are recommended:
- exclude dairy products from the menu, as well as those that irritate the gastric mucosa (fried, spicy, salty);
- do not drink alcohol, coffee, carbonated drinks;
- meals should be fractional, at least 5–6 rubles/day;
- last meal – 2–3 hours before bedtime;
- The diet must include fresh vegetables and fruits.
Nutritionists advise introducing a variety of cereals into your diet. It is recommended to eat food only warm.
Too hot food irritates the gastric mucosa, while cold food takes a long time to digest and provokes the release of hydrochloric acid.
Photo gallery: foods you can eat
You can eat steamed meat. It retains many beneficial substances for the body, which are so necessary during illness.
The absorbent properties of rice porridge are successfully used to effectively remove toxins and waste.
Fresh fruits are a source of fiber and vitamins
Fresh and steamed vegetables will not harm the stomach and will be an excellent addition to the diet
Treatment
Therapy includes medication and surgery, diet, and traditional medicine.
The treatment regimen is developed by the doctor, taking into account the clinical picture, the diagnostic results obtained, the individual characteristics of the patient’s body and his age.
Drug treatment
Doctors usually prescribe:
- antibiotics to destroy pathogenic microflora;
- at the same time, probiotics are prescribed to restore the normal bacterial flora of the stomach - Linex, Bifiform;
- for increased acidity of gastric juice - Omeprazole;
- for heartburn - Phosphalugel, Maalox;
- to reduce secretory activity - Ranitidine;
- gastroprotectors - to protect the mucous membrane from destruction.
If no positive dynamics are observed during repeated examinations, surgical intervention is recommended.
Surgery
Abdominal surgery – used for extensive lesions. In this case, the areas of the stomach affected by metaplasia are completely removed.
Laparoscopy is a gentle method. In practice it is used more often.
Diet
The key to successful treatment is diet. Meals should be fractional. It is ideal if the food is fresh and prepared in a home kitchen from good quality ingredients. You should exclude all fast foods and semi-finished products from your diet. Food is served warm; hot and cold dishes are prohibited.
The following should be excluded or limited:
- all fried, fatty, salted, smoked, marinated, peppered, spicy foods and dishes made from them;
- from drinks, a complete abstinence from alcohol, soda, strong black tea and coffee, and store-bought juices is required;
- Smoking is prohibited - tobacco smoke, entering the stomach, is irritating to the mucous membrane.
Authorized products:
- dietary meats (chicken fillet, turkey, rabbit) or fish prepared by boiling, steaming or baking - can be consumed as independent dishes or together with broth;
- porridge from any cereals;
- nuts, herbs, fruits, vegetables, fresh and thermally processed;
- mineral water, green tea, jelly, compote, decoctions.
The daily menu should be prepared in accordance with the doctor's recommendations. After consuming foods and drinks, the patient should analyze his internal feelings and give preference to those that do not cause discomfort.
ethnoscience
Among traditional medicine there are time-tested recipes that are effective for gastritis, peptic ulcers and other pathologies:
- Herbs infused for half an hour in boiling water (1 teaspoon per 200 ml of water) - yarrow, chamomile, St. John's wort. Take 30 ml half an hour before meals. You can brew the herbs separately or mix them and make a collection.
- If there are no contraindications to the use of honey, you can prepare a mixture of honey and aloe leaves. To do this, cut aloe leaves are kept in the refrigerator, then the thorns are removed from them and crushed in a blender or meat grinder, combined in equal proportions with honey. The mixture is kept in a cool, dark place for 2 weeks, then taken on an empty stomach, one tablespoon at a time.
- Instead of decoctions, you can use alcoholic tinctures of herbs or propolis. They are dosed in drops and diluted in water.
The use of folk remedies
Traditional medicine offers no less effective methods of combating the disease. Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs and herbs reduce signs of inflammation and relieve pain.
- Herbal mixture of chamomile, calendula, yarrow and marshmallow root. Take 1 tsp. each herb, mix and steam 0.5 liters of boiling water. Leave in a thermal container for about an hour. Filter and take 3-4 times a day for 30 minutes. before meals, 20 ml.
- Pour boiling water over flax seeds (1 tbsp) and boil for 5 minutes. Leave for 1-2 hours, take 30 ml before each meal.
- St. John's wort. Grind 15 gr. dried herbs, steam 200–250 ml of boiling water. Leave to infuse in a thermos for 12 hours, preferably overnight. Filter the mixture and bring the volume to 250 ml. Take 30 minutes before. before meals, 50 ml of infusion. The course of treatment is 14 days, then take a week break.
Photo gallery: popular folk remedies in the treatment of gastric metaplasia
St. John's wort has astringent properties, prevents the appearance of malignant neoplasms
A decoction of flax seeds protects the mucous membrane from the harmful effects of gastric juice
Chamomile, yarrow, calendula, calamus root have an anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effect
Complications
In a healthy person, epithelial cells are constantly renewed. Under the influence of harmful factors (alcohol, long-term use of medications, poor diet), the mucous membrane gradually changes. If treatment is not started in time, the inflammatory process becomes chronic.
Gastric metaplasia develops against the background of concomitant diseases and successive changes.
Chronic gastritis caused by the Helicobacter bacteria leads to complications such as:
- glandular atrophy – pathological changes in the mucous membrane;
- dysplasia – a violation of the epithelium and its functional properties;
- Neoplasia of the gastric mucosa is the first sign of cancer.
Some scientists have scientifically proven that chronic gastritis, the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, intestinal metaplasia, atrophy and stomach cancer are links in one chain in which a microorganism becomes a provocateur. As a result of infection, chronic inflammation is formed in the mucous membrane, and tissue degeneration occurs, provoking the development of intestinal-type stomach cancer.
Against the background of atrophic chronic gastritis, in which the irreversible disappearance of the gastric glands occurs with their replacement by altered tissues, gastrointestinal cancer develops in 75% of cases.
In addition to the bacterium H. pylori, other types of microorganisms appear that produce carcinogenic and mutagenic substances that accelerate the risk of tumors.
In addition, atrophic hCG leads to impaired secretion of internal factor and a decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid. As a result, the normal absorption of vitamin B12 is disrupted, which leads to anemia and neurological disorders.
The gastric mucosa is replaced by metaplastic epithelium, which leads to irreversible processes and the development of cancer
Features of the disease
What is gastric metaplasia? Gastric metaplasia is indicated by a pathological process in which special cells of the gastric epithelium are significantly damaged due to exposure to unfavorable factors. After a certain period of time, cells are formed at this site that are specific to another organ of the gastrointestinal tract. This leads to the fact that the stomach cannot cope with its functions, since the detected cells perform new functions.
Intestinal metaplasia of the stomach is the process of degeneration of the glandular epithelium of the stomach into the intestine. The parietal cells responsible for acidity lose their established functions, as a result of which a reduced level of gastric acid acidity is observed and food digestion is disrupted.
The gastrointestinal tract is undergoing dramatic transformations that can reduce its functioning, so urgent treatment and diet are required. With intestinal metaplasia, metabolism is disrupted. There is a low level of stomach activity, as a result of which the person is in a dangerous but treatable condition. When colon cells begin to multiply, the condition can be called precancerous. You should not self-prescribe symptomatic medications. If signs of illness are detected, you should consult a qualified doctor.
It should be understood that this disease can be cured. However, it is necessary to start therapy in the early stages of the disease, before complications begin.
Metaplasia is not an independent disease. As a rule, it accompanies the course of another illness. When the human body is affected by unfavorable factors for a long time (poor nutrition, smoking, medications, alcoholic drinks), changes can be detected in the gastric mucosa. First, the inflammatory process appears in the stomach. If proper treatment is not started in a timely manner, the process will become chronic. Once the cells lose all their functions, they atrophy. If pathology is not detected in time, the phenomenon can develop into dysplasia and cancer.
The reasons for the development of the inflammatory process can be very different. Basically, this is a peptic ulcer of the duodenum and stomach, gastritis, provoked by a special bacterium - Helicobacter pylori. The frequency of outbreaks of the disease is quite high, which is associated with the negligence of most patients, as well as untimely contact with a doctor.
The second most common cause of the disease is reflux disease, in which the contents of the stomach are thrown into the esophagus, or bile enters the stomach because the pylorus does not function properly. The third cause of inflammation is regular irritation, negative effects on the gastric mucosa, various diseases, and hormonal imbalances.