Esophageal polyp is a disease manifested by the formation of benign tumors on the mucous membrane, ICD-10 code - K22. Polyps can be single or multiple, and are more common in men. There are several assumptions about what causes polyps. The main symptoms are difficulty swallowing and discomfort when food passes through the esophagus. Treatment is carried out surgically, the process of removing tumors is called polypectomy.
What is it - esophageal polyp
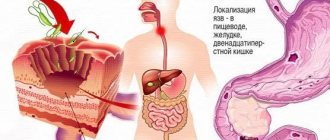
A polyp is a benign growth of certain areas of the mucous membrane of hollow organs, including the esophagus. They can form throughout its entire length. If several such growths have formed, the condition is called polyposis. The sizes of the formations vary from several millimeters to tens of centimeters.
Table. Classification of polyps
| Sign | Kinds |
| By location | Localization of the esophageal polyp:
Polyps of the cardiac region (the junction of the esophagus and the stomach) are isolated separately. |
| According to morphological characteristics | Hyperplastic - formed due to increased proliferation of epithelial cells of the mucous membrane. They grow slowly and rarely become malignant. Adenomatous - formed from gland cells that secrete mucus. Glandular polyp of the esophagus is a high risk of malignancy |
| According to the form of attachment | On a broad base - a polypous growth sits tightly on the mucous membrane, has a spread-out shape. On a stalk - the polyp is round, attached to the mucous membrane with the help of a thin stalk |
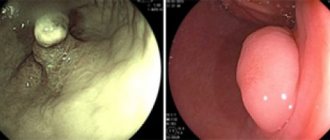
The appearance of polypous formations, their location and size are determined using endoscopic examination. To find out the morphological nature of the tumor, it is necessary to cut off a piece of it (up to about 1 cm) and send it for a study called cytology.
Possible complications
Growths that form on the mucous membrane of internal organs are not as safe as they seem. They are injured when solid foods pass through the esophagus, and the leg grows. It becomes difficult for a person to swallow drinks and eat food.
A polyp, which is located near the larynx, sometimes falls into it, causing pain and a feeling of the presence of a lump.
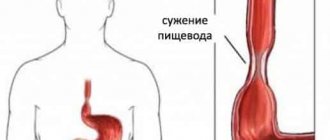
The growths that form where the esophagus meets the stomach often become pinched, closing the lumen in it. They bleed and increase in size to 10–20 cm in diameter.
Due to compression of the respiratory tract by the polyp that has formed near the larynx, the person begins to experience a lack of oxygen and suffocation develops.
Polyp in the esophagus - is it dangerous?
How dangerous an esophageal polyp is depends on its characteristics:
- glandular formations are more likely to cause cancer;
- if the polyp is located in the cardiac region and has a long stalk, it can be pinched by the pyloric sphincter, causing a sharp pain attack;
- A long-pedunculated tumor located near the larynx can block it, causing suffocation.
Therefore, any polyp must be treated immediately after its discovery by surgical removal.
Prevention
Knowing the causes of the disease, you can do everything necessary to prevent it. This rule works, but not always. Some people become hostage to the situation, having a genetic predisposition to the disease. Even if you follow all preventive measures, you cannot be sure that the disease will never appear. But following the doctor’s recommendations significantly reduces the likelihood of polyps.
What you need to do to prevent esophageal polyps:
- follow the principles of healthy eating, refuse aggressive dishes, after which you may feel heartburn and discomfort;
- give up bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol, because they increase the likelihood of polyps appearing and their degeneration into cancer;
- contact a gastroenterologist if symptoms appear in the gastrointestinal tract;
- undergo treatment for gastritis and peptic ulcers, taking medications prescribed by your doctor and following a diet.
To prevent esophageal polyps, you need to follow the principles of a healthy diet.
These are simple rules that will help maintain the condition of the digestive organs. When polyps have already been diagnosed, the operation cannot be delayed for long, because this can result in much more serious illnesses.
Esophageal polyp and causes
There is no specific reason for the formation of polypous growths in the esophagus. Gastroenterologists identify several factors that cause esophageal polyps:
- chronic inflammatory process in the mucous membrane – esophagitis;
- frequent injuries to the mucous membrane - rough and irritating food, alcoholic drinks, foreign bodies;
- reverse reflux of acidic gastric juice;
- frequent vomiting;
- hereditary factor.
Polyp in the stomach - what to do and how to treat
Frequent stress, poor nutrition, and poor environment increase the risk of developing polypous formations.
Diagnostics
Examination of a patient for suspected polyps includes:
- examination, collection of complaints and life history, identification of factors influencing the digestive organs, appointment of instrumental and laboratory diagnostics;
- conducting an endoscopic examination, which allows you to assess the condition of the walls of the organ, identify the formation and conduct a biopsy to determine the morphology of the disease;
- X-ray or MRI are additional methods when it is necessary to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of tissue damage.
Endoscopic examination is a method for diagnosing esophageal polyp
Esophageal polyp: symptoms
The clinical picture of the pathology is nonspecific; symptoms and treatment of a polyp in the esophagus are determined by its location and size.
If the formation is small in size, patients complain of:
- discomfort when swallowing;
- sensation of a foreign body in the esophagus;
- loss of appetite.
When the tumor reaches a sufficiently large size, symptoms are caused by compression of adjacent organs.
If the polyp is located in the upper third of the organ, the following symptoms occur:
- difficulty breathing;
- cough;
- choking on food and water.
The location of the tumor in the lower third of the organ causes pain during eating and when bending over. The location of the tumor directly in the cardia leads to disruption of the esophagogastric sphincter. Then the disease manifests itself with frequent belching and heartburn.
The degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant form leads to the development of intoxication and exhaustion. A person loses his appetite and quickly loses weight. He is bothered by frequent nausea and vomiting.
Causes
The appearance of polyps is promoted by prolonged exposure to unfavorable environmental conditions, frequent stressful situations, and smoking. Some authors consider a violation of the embryogenesis of the mucous membrane to be the cause of the formation of polyps at the site of the cardioesophageal junction, which leads to dystopia of the embryonic tissues from which epithelial neoplasms are formed. The pathogenesis of esophageal polyps is based on hyperregeneration of esophageal epithelial cells under the influence of harmful factors. Inflammatory processes, injuries, irritation with food and chemically active substances stimulate excessive proliferation of the epithelium and stop its differentiation. As a result, in some areas of the mucous membrane, foci of hyperplasia form, from which polyps form. Depending on the type of cells involved in the tumor process, polypous neoplasms are hyperplastic (with a typical cellular structure) and adenomatous (with dysplasia of glandular epithelial cells).
Polyp in the esophagus: treatment
If a polyp of the esophagus is detected, treatment is carried out only by surgery. Medicines and folk remedies cannot remove tissue growth. Before surgery is scheduled, the polyp is treated with medication only for the purpose of temporarily eliminating symptoms.
Typically, removal of polypous formations is carried out as planned, after the necessary examination and preparation of the patient. Elective surgeries are performed for small hyperplastic polyps.
Urgent operations are prescribed for:
- rapid growth of education;
- bleeding caused by a polyp (urgent surgery);
- high risk of malignancy.
In such cases, the tumor must be removed as quickly as possible.
Alternative medicine as adjuvant therapy
The use of folk remedies, like medications, has only symptomatic effectiveness. Reducing discomfort with the help of folk recipes is possible only in the early stages of the disease.
- Honey with butter: take 1 kg of butter, melt it in a water bath. Mix with 1 kg of liquid honey. The mixture is taken one tablespoon before meals.
- Celandine decoction: 20 grams of dry or fresh plant, pour half a liter of boiling water, bring to a boil. Take a tablespoon of decoction in the morning.
- Pine decoction: take 50 grams of pine needles, pour boiling water over it, cook for 10 minutes. Then add 50 grams of hop cones and let it brew. Take 50 ml in the morning.
Attention! You should consult a specialist about the possibility of using folk remedies.
Medical nutrition
To reduce discomfort while eating, you must follow a special diet. Its purpose is to reduce trauma to the mucous membrane and improve peristalsis of the organ.
The following foods should not be eaten:
- high in fiber - fresh fruits, legumes;
- canned food;
- stringy meat;
- baking;
- coarse cereals - pearl barley, buckwheat, rice.
It is necessary to establish a strict diet. Take food at the same time, in small portions. The frequency of meals is 5-6 times during the day. Dinner should be no later than two hours before bedtime.
How to remove an esophageal polyp
The type of surgical intervention to remove polypous growth depends on its characteristics - size, location, structure.
- Endoscopic removal of a polyp in the esophagus is possible if the formation is pedunculated, small in size, and located in an area accessible to the endoscope. The surgeon uses an esophagoscope to remove the tumor and cauterize the vessels with a coagulator. The operation lasts only a few minutes, and after 2-3 days the mucous membrane is restored.
- Wide-based polyps are usually located in the upper part of the esophagus. It is impossible to remove them endoscopically; open access is required. An incision is made along the side of the neck, then the esophageal tube is opened, and a section of tissue with a polypous growth is excised. The defect is sutured. Recovery takes 7-10 days.
- Laparotomy surgery. An incision along the anterior abdominal wall is made if the neoplasm is located near the entrance to the stomach, 3-5 mm from it. The operation is carried out extremely carefully, and the extracted polyp is sent for urgent histological examination, since tumors with a similar location often turn out to be malignant. Recovery takes 10-14 days.
- Resection of the esophagus. Required if the malignant nature of the tumor has been confirmed. The organ wall is excised at a distance of 2 cm around the tumor. After this, radiation or chemotherapy is prescribed.
After any operation, a strict diet is required for at least 2 weeks. Working capacity is limited for 7-21 days depending on the type of surgery.