04/21/2019 Alena Masheva Health
Transport of food from the mouth to the stomach occurs through the esophagus. If smooth muscle peristalsis functions normally, then the bolus of food easily and quickly reaches the stomach. If its activity is disrupted, a spasm occurs. Food has difficulty moving through the esophagus, causing pain. The individual is bothered by heaviness and pressure in the throat and chest as a result of spasm of the esophagus. How to remove it and how to alleviate the condition? This will be discussed in the article.
general information
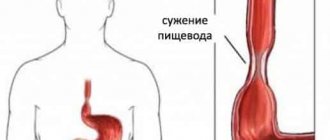
Esophagospasm, or in other words spasm of the esophagus, is a disease as a result of which from time to time a malfunction of peristalsis occurs, i.e., an increase in pressure and spastic contractions of its walls occur in the lower esophageal sphincter. The diagnosis is made on the basis of diagnostic measures, which include: pH and manometry of the esophagus, radiography, endoscopy. The disease manifests itself as chest pain, belching, dysphagia, and heartburn. Treatment is mainly conservative, aimed at reducing intra-abdominal pressure and myotonus of the esophagus, and dietary nutrition is also indicated.
Common types of esophagospasm
Often in practice there are two types of esophageal spasm:
- Diffuse, the symptoms of which are manifested by a failure of motor activity, with occasional spastic uncoordinated contractions of the smooth muscles of the food tube. At the same time, muscle tone is preserved, as is reflex opening during swallowing. Severe pain occurs in the area of the sternum and stomach, which spreads to the shoulder and even the jaw. Severe pain disturbs the individual at rest and at night, i.e., it is not associated with food intake. When the contraction stops, regurgitation occurs. Swallowing disorders are more pronounced when drinking liquids or eating soft foods. The attack lasts from several minutes to several hours.
- Segmental ("nutcracker" esophagus) - with this type, smooth muscle contraction occurs with greater intensity in certain areas of the esophagus and stomach. The spasm manifests itself as follows. Pain when swallowing liquids. Dysphalgia, which appears when eating pureed foods, porridge, cottage cheese. Difficulties with swallowing are present when swallowing foods enriched with plant fiber. The duration of the spasm is several seconds. In some cases, its duration increases to three hours. The pain is moderate and passes quickly. The attacks begin suddenly and gradually decrease in intensity.
The following types of esophagospasm are known:
- Idiopathic, often called primary, is an organic change in the nervous system.
- Reflex, or in other words secondary, is a companion to ulcerative lesions of the digestive organs, hiatal hernia, cholelithiasis, i.e. those pathologies in which the mucous membrane of the food tube is affected.
Spasm in osteochondrosis
Spasms that periodically occur in the esophagus are often a clear symptom of the presence of osteochondrosis of the cervical or thoracic spine. In medicine, this type of pathology has a separate name: vertebrogenic esophagospasm, which develops as a result of pinching of the nerve fibers of the spinal cord. Destructive changes in the vertebrae, leading to compression of the nerve roots, provoke contractions of the smooth muscles of the esophagus, which occur completely uncontrollably.
Symptoms of esophagospasm in osteochondrosis are sometimes very difficult to distinguish from manifestations of other types of pathological processes; it is for this reason that it is so important to undergo a medical examination, as well as perform the necessary diagnostics in order to accurately determine the etiology of the disease.
Other types of esophagospasm
In medical practice, there are other types of esophageal spasm:
- Nervous - it is characterized by feverish muscle contraction due to mental disorder (depression), sleep disturbances, stress, increased tendency to anxiety, fear. The attack lasts only a few minutes.
- When swallowing, the following symptoms indicate such a spasm: a feeling of a lump in the throat accompanies a panic attack; during convulsions there is a feeling of suffocation; when there are sharp unexpected sounds, vomiting begins; in a neurosis-like state, a spasm can prevent even saliva from being swallowed; attacks of nausea and vomiting are considered frequent accompaniments of neurosis; in the chest area there are pain sensations similar to cardialgia, and their intensity is not constant and varies from insignificant to severe.
- Cardiospasm can be acute or chronic. Acute – characterized by pain in the chest and epigastric region; feeling that a lump of food is lingering over the stomach. However, drinking water does not bring relief. At the end of the attack, regurgitation or belching occurs. With slight excitement, the pain intensifies. Late therapy is dangerous due to sudden weight loss and esophageal vomiting. The development of pneumonia cannot be ruled out. One of the main causes of esophageal spasm, the symptoms of which are described above, is considered to be a long-term ulcerative lesion. The main provocateurs are smoking, inhaling toxic fumes, and drinking strong alcohol.
- Lower sections - with such a spasm, the organ tube expands along its entire length.
- Non-sphincteric - several of its parts are affected simultaneously along its entire length. Individuals complain of regurgitation of mucus, chest pain, and episodes of dysphagia, lasting from a few seconds to several weeks.
Esophageal spasm also occurs with other anomalies. For example, as a symptom it is observed in tuberculosis, syphilis, scarlet fever, inflammation of the pleura or aorta.
Neurological spasm
Difficulty swallowing usually occurs when eating or drinking. Characteristic signs of an attack while eating:
- food stuck in the esophageal tube;
- involuntary vomiting;
- the separated masses consist of undigested contents without impurities of mucus and gastric juice.
Spasm when swallowing leads to the reverse movement of food, which the person is unable to control. The smooth and transverse muscles of the esophagus contract sharply, making breathing difficult.
The causes of convulsive compression are nervous shock, fear, prolonged depression, anxiety. A spasm can occur without connection with food intake. The esophagus contracts due to nervousness. The pain is localized in the chest and mediastinum. Because of this, many people confuse involuntary muscle contractions with a heart attack. The severity of discomfort varies in intensity. Pain may include a feeling of tightness, burning, or squeezing.
If motor activity is impaired in the upper segment of the esophagus, it is difficult to swallow saliva. In this case, there is a feeling of a “coma” in the throat. An attack can be triggered by a sharp sound, unpleasant news.
Esophagospasm during pregnancy
While waiting for a baby, the appearance of spasms in the esophagus, the causes of which will be discussed below, occurs quite often. Despite the fact that carrying a baby is a natural process, in some cases pathological conditions may occur. Changes in the position of the diaphragm and hormonal imbalance contribute to the retention of food in the esophagus and provoke vomiting. The occurrence of GERD is influenced by a malfunction of the muscles of the stomach and the motility of esophageal contractions. In addition, as a result of the increased acidity of the digestive juice, which is characteristic of this period, acidic contents are thrown into the esophagus, causing a chemical burn. In practice, esophagitis occurs in every fifth pregnant woman. Clinical picture:
- burning sensation in the cheeks and tongue;
- cough, possible sensations of severe lack of air;
- hoarseness, voice disturbances;
- belching, heartburn, pain in the chest and some other phenomena associated with damage to the esophagus;
- flatulence, feeling of fullness in the stomach.
Classification
There are several classifications of spasms in the esophagus. The first is depending on the reasons for its formation. The second - as symptoms manifest and localize. According to the second type, the disease is divided into:
- diffuse spasm of the esophagus - the spread of spasm along the entire length of the esophageal tube. The attack lasts no more than a few hours. During this time, signs such as pronounced pain, impaired swallowing and belching appear;
- segmental spasm of the esophagus - differs in that contractions occur in separate areas of the esophagus. The duration of the attack varies from a couple of seconds to three hours. In this case, there is slight pain and discomfort when swallowing solid or pureed food;
- neurospastic spasm of the esophagus - characterized by involuntary convulsive muscle contraction. Vomiting, belching, pain spreading to the chest area and a feeling of suffocation occur.
Regardless of the type of illness, treatment occurs in several ways - medication, physiotherapy and folk remedies.
Causes
Often, spasms occur at the exit or entrance of the esophagus, since there are many nerve endings in these places, and they are the first to respond to a malfunction.
The main causes of esophageal spasm, the symptoms and treatment of which are discussed in this article, are as follows:
- swallowing disorder;
- chemical poisoning;
- presence of a foreign body;
- ulcerative lesions of the stomach or duodenum;
- very cold, hot, dry or hard foods;
- exposure to concentrated organic or mineral acids;
- exacerbation of gastroesophageal disease;
- minor injuries to the walls of the esophagus resulting from swallowing a foreign body or eating hard foods;
- inflammatory processes in internal organs located next to the esophagus;
- infectious diseases, for example, scarlet fever, rubella and others;
- nervous diseases;
- incorrectly selected dentures;
- pathologies of intercostal nerves;
- consumption of strong alcoholic drinks;
- excessive emotional stress, overwork.
Before acquiring a stable form, esophagospasm occurs periodically and is associated with fatigue, fear, nervous overexcitation, fever or lack of sleep. The disease becomes chronic when the vagus nerve is inflamed, the nerve endings located near the esophagus are affected, and there are disorders of the central nervous system, i.e., there is constant pressure on the muscles of the esophageal tube.
Diagnostics
To determine the exact cause of spasms when swallowing, the following diagnostic methods are provided:
- gastroesophagoscopy;
- X-ray with contrast agent;
- manometry to determine the pressure on the walls of the esophagus during drinking water;
- determination of stomach acidity.
If tumors are detected in the esophagus, a biopsy is performed.
Signs of esophageal spasm
“A lump stuck in my throat” is usually the phrase used by an individual to describe his feelings about such a problem. The clinic depends on the form and location of the pathological process. Typical symptoms of any form of the disease are difficulty swallowing, chest pain that occurs when swallowing saliva and food, but it can also be spontaneous. Stressful situations aggravate discomfort. In addition, the pain radiates to the back, shoulders, lower jaw, and shoulder blades. The duration of the attack is about sixty minutes. In some cases it lasts longer. After taking antispasmodics, the pain subsides.
Dysphagia occurs when eating both solid and liquid foods. It appears immediately with pain and is irregular in nature. Heartburn occurs in every fifth person. Severe spasms and a large volume of food in the esophagus provoke regurgitation.
Mostly spasm of the upper narrowing of the esophagus occurs in persons predisposed to sudden changes in mood, neurosis-like states or hysterics, i.e. nervous spasm of the esophagus. It manifests itself as nausea, cough, oppressive pain behind the sternum, anxiety, a feeling of fear, and redness of the face. Spasmodic phenomena occur acutely or gradually increase. The intermittent nature of the disease contributes to the following: the individual becomes restless, fearing the return of symptoms, eats irregularly and thereby worsens the situation.
Chronic spasm of the upper narrowing of the esophagus is typical for older individuals with chewing disorders and dental defects. In such patients, the passage of solid food is difficult, unpleasant sensations are noted behind the sternum, and there is a need to wash down liquids with every swallow of food. Permanent obstruction of the esophagus leads to the formation of its compensatory expansion in the spasmodic area.
Therapeutic measures
After confirming the diagnosis, individuals are interested in the question of how to relieve spasms of the stomach and esophagus. If the exact cause of the disease has not been identified, then doctors do not recommend treating it yourself. Therapy involves the use of:
- medicines;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- diet;
- lifestyle changes;
- medicinal herbs.
If there is an underlying gastrointestinal disease that provokes esophagospasm, then initial treatment should begin with it in order to prevent the occurrence of new attacks. Next, we will consider in more detail how to treat reflex esophageal spasm. For this purpose, drugs of different pharmacological groups are used:
- Antacids, or antacids, protect the mucous membrane of the digestive canal.
- Gastrointestinal motility stimulants - promote the passage of a bolus of food by improving the peristalsis of the muscular tube.
- Antispasmodics – remove spasms.
- Alginates – envelop the mucous membrane, protecting it from aggressive hydrochloric acid.
- Sedatives – a calming effect on the central nervous system.
- Antidepressants, tranquilizers and medications that normalize sleep are prescribed if necessary.
- Analgesics and anesthetics – have a local anesthetic effect.
- B vitamins.
The above medications, doses and treatment regimens are selected by the attending physician individually.
Let's look at how to relieve spasms of the stomach and esophagus with the help of physiotherapeutic treatment. It is aimed at normalizing the functions of the nervous system and includes:
- Electrophoresis with an anesthetic - a direct electric current is applied to the affected organ together with a drug, which helps relieve pain.
- Radon baths - thanks to them, the sensitivity of nerve endings is reduced.
- Galvanization - current is supplied through electrodes with a constant frequency, low strength and low voltage. As a result, the sensitivity of the nerve fibers weakens. This method is especially effective for spasm of the esophagus that occurs against the background of osteochondrosis.
- Warm baths with decoctions of medicinal herbs that have a sedative effect.
- Inductotherapy is the effect of a high-frequency electromagnetic field with a predominance of the magnetic component. The uniqueness of this manipulation is that heat is generated in the muscle layer, which ultimately reduces tone and eliminates spasm of the esophagus. How else can you remove it? Physical activity is especially important, i.e. performing simple exercises aimed at strengthening the spinal column and normalizing the functioning of the central nervous system.
Phytotherapeutic treatment involves the use of medicinal plant materials that have different effects:
- anti-inflammatory – elecampane;
- sedative – peony, valerian, motherwort;
- antispasmodic – chamomile, sage, mint.
Alternative treatments include:
- Acupuncture. The course of treatment is up to ten days, three times a year.
- Medical hypnotherapy.
- Psychotherapeutic methods - sand therapy, autogenic training according to Schultz, art therapy.
Massage of certain points that are located on the midline of the chest is another non-standard way of treating esophageal spasm. How to remove it using this method? The locations of the points are as follows:
- under the cervical fossa;
- between the breasts;
- between the first and second points (at an equal distance from each).
These areas are massaged with the finger bones, making clockwise rotational movements for five minutes. It is noted that when performing this manipulation, the individual experiences severe pain. There is an opinion that this is a normal phenomenon, and after twenty minutes of intense exposure to these points, the pain will completely disappear.
All of the above methods give good results.
Actions for esophageal spasm
How to remove it? If chest pain occurs, you need to calm down and lie down. If the spasm does not go away within five minutes, then do the following:
- If pain occurs while eating, drink a glass of plain water.
- Perform the following exercise four to six times - take a deep breath, hold your breath for literally two seconds and exhale slowly.
- Take a sedative. If it is not available, prepare a tea drink with mint or suck on a mint candy.
- If previous manipulations did not produce results, then an injection of Atropine is indicated.
The main thing is to cope with panic and remember that there is no threat to life.
Proper nutrition
Treatment of spasms in the esophagus, the causes of which have been identified, is impossible without a properly selected diet. The basic principles of dietary nutrition include:
- Eat food at room temperature no more than five to six times a day, with your last meal at least three hours before bedtime.
- You can't overeat.
- Dishes are steamed, boiled and stewed.
- Food should not irritate the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus. It is preferable to use it in a puree form.
- Strong drinks, spices, marinades, canned food, hot, cold and spicy foods are prohibited.
Useful video
Patients also experience cardiospasm of the esophagus, the symptoms of which are discussed in this video. When diagnosed with cardiospasm of the esophagus, treatment should be timely.
Proper nutrition
When there is a spasm in the esophagus, the symptoms of which are clear, it is important in its treatment to follow the diet and rules of food consumption. Such patients are recommended to eat small portions 5-6 times a day . It should not be hard, hot or very cold.
During the meal, you need to chew food thoroughly so as not to injure the esophageal mucosa and not swallow large pieces of food, which can cause an involuntary spasm.
Dishes should not contain hot, sour or spicy ingredients and should not be boiled, steamed or baked. You should not drink alcohol, carbonated water and strong drinks, foods containing a lot of fiber (radishes, apples, cabbage).
The last meal should be 2-3 hours before bedtime . It must be remembered that during the meal it is necessary to keep your back straight to prevent kinking of the esophagus.
Prevention
To prevent recurrence of the disease, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations regarding proper nutrition and undergo a course of medication. In addition, you need to reconsider your lifestyle: do not subject your body to excessive stress, normalize your emotional state, do not lead a sedentary lifestyle, and do physical exercise. A set of exercises is developed by a physical therapy doctor for independent practice, and when visiting health groups, this is done by an instructor.
Persons prone to nervous disorders are advised to drink herbal teas that have a sedative effect (mint, lemon balm). Instead of tea, you can take tinctures of motherwort, peony, and valerian, which help relieve nervous tension. Such treatment should be carried out in courses, alternating 1 month of admission and 2 months of break.
Compliance with such rules can prevent the recurrence of the disease. But you need to remember that a visit to the doctor when symptoms appear is mandatory, since such signs have very serious diseases, which cause spasm of the esophagus when swallowing.
Methods for treating esophagospasm
Various methods are used to treat diffuse esophageal spasm:
- Fractional meals - up to six times a day in small portions. Chewing food thoroughly. Do not take a horizontal position for two hours after eating.
- Pharmacotherapy is auxiliary in nature and is aimed at eliminating symptoms.
- Expansion of the cardia with special dilators - pneumatic or mechanical medical devices are used. A probe is inserted into the stomach, at the end of which there is a special balloon. When it gets into the lower sphincter area, they begin to pump air and then remove it. As a result, the required area of the digestive canal expands.
- Surgical intervention is indicated if the previous method is ineffective.
- Using herbalist recipes - drinking infusions, taking herbal baths.
To treat symptoms of diffuse esophageal spasm, conservative therapy is indicated:
- "Omeprazole", "Pancreatin" - to reduce acidity.
- "Cerucal" - suppresses attacks of nausea and vomiting.
- “Rennie”, “Almagel” - protection of mucous membranes from the aggressive effects of acid.
- "Nifedipine" - to normalize muscle tone and relieve spasms.
- "Anestezin", "Novocaine" - for pain relief.
- "Atropine" - for intravenous or intramuscular administration to provide emergency assistance.
In addition, individuals are recommended physiotherapeutic procedures: electrophoresis, radon baths, inductive and microwave treatment. Any physical activity is required.
Treatment
With esophageal spasm, symptoms and treatment are interrelated. For nervous disorders, the use of folk remedies is indicated. The patient must undergo a diagnosis of the digestive tract so that the cause of the pathology can be determined and the necessary diet and medications prescribed.
An important role in the treatment of esophageal spasm is a properly selected diet. Here are the principles of proper nutrition:
- Food should under no circumstances irritate the delicate membranes of the esophagus and stomach. Therefore, dishes should be stewed, boiled, steamed. Puree dishes are very useful.
- No need to overeat. The optimal number of meals is 5.
- You should eat so that your last meal is approximately 3 hours before bedtime.
- Strong drinks, dark chocolate, spices, spicy foods, marinades, pickles, smoked foods and canned foods are excluded.
- It is forbidden to eat frozen or hot food: it should only be at room temperature.
Sometimes massage helps restore the function of the nervous system, which helps in relieving the symptoms of esophagospasm.
The following physiotherapeutic procedures are indicated:
- microwave treatment;
- electrophoresis;
- radon baths;
- inductive treatment.
It is necessary for the patient to adhere to a certain physical activity. This is especially true in cases where his work involves prolonged sitting.
To eliminate the accompanying signs of the disease, drug therapy is indicated. The following medications are prescribed:
- To reduce acidity, Creon and Omeprazole (Omez) are used.
- Cerucal is indicated to suppress attacks of nausea and vomiting.
- Almagel, Rennie and other antacid drugs are indicated to protect the mucous membrane from the aggressive effects of acid.
- Calcium antagonists, such as Nifedipine and others, relieve spasms well and normalize muscle tone.
- To prevent pain in the esophagus and stomach, Novocain and Anestezin are prescribed.
- Atropine is used as an emergency treatment. It is administered intravenously or intramuscularly.
Interesting! Signs of gastroesophageal reflux disease with esophagitis
Folk remedies
Many patients are interested in how to relieve esophageal spasm. You don't need to take medication for this. There are effective folk remedies that relieve convulsive contractions of this area of the digestive tract. Below are some effective traditional ways to treat the disease at home.
- A decoction of flaxseed and anise, to which honey is added, is useful (take a tablespoon of these components for half a liter of water). Take 3 times a day.
- A decoction of dried plantain leaves and peppermint (with the addition of natural honey). You should drink it one tablespoon in the morning before meals.
- Neurological spasms are well relieved by tincture of peony, motherwort or valerian. You need to take 15 drops of these drugs before meals.
- Baths that contain a decoction of a mixture of motherwort, linden blossom, lemon balm, and valerian are good for relieving spasms and soothing. Additionally, add a few drops of natural essential oil to the water - ylang-ylang, orange or tea tree. The duration of water procedures is up to 20 minutes, and the water temperature should vary from 37 to 40 degrees.
- Sometimes they normalize the state of the digestive system and relieve reflux with breathing exercises. Slow, measured breathing sometimes helps prevent further development of the spasm.
- Chewing mint gum and lollipops are suitable for the same purpose.
- Doing simple exercises and running helps normalize the function of the esophagus. Usually, regulation of physical activity helps to avoid further use of medications.
So, spasms in the esophagus can occur quite often in a person. Although in most cases they pass and the patient recovers, there is still no need to leave the disease unattended. Diet correction and medication as prescribed by a doctor help restore a healthy esophagus.
"Duspatalin": mechanism of action, advantages
Only the sphincter of Oddi and the smooth muscles of the digestive tract are affected by the drug, which distinguishes it from other antispasmodics. “Duspatalin” relieves spasm of the esophagus, through which the movement of a food coma is difficult, and also normalizes the natural function of the digestive tract, i.e. the medication does not have a negative effect on the functioning of the intestines, as it does not completely suppress contractions and does not disrupt normal peristalsis.
The main advantages are:
- slow release;
- constant concentration of the drug in the blood for 15–18 hours;
- selective action;
- absence of unwanted reactions inherent in other antispasmodics;
- does not accumulate in the body and can be used for a long period;
- in old age does not require dose adjustment.
Thus, the drug “Duspatalin” relieves spasm of the esophagus due to the sequential launch of the following processes:
- Reduces the permeability of intestinal muscle cells.
- Closes the channel for sodium ions to enter the cell.
- Prevents the reuptake of norepinephrine.
- Has an analgesic effect.
- Relaxes the smooth muscles of the intestines.
- Promotes better absorption of liquids.
- Improves the functioning of the intestinal tract.
- Eliminates colic, spasms and pain.
Taking this medication allows you to relieve symptoms while maintaining natural gastrointestinal motility. It is indicated for all types of digestive system disorders that are accompanied by spastic pain.
Alternative medicine
How to relieve esophageal spasm at home? This question is often asked to the doctor. It turns out that if the reason that caused this condition is known, then it is quite possible to cope with this problem yourself, using the following effective methods:
- Infusions of flax seeds and anise or mint and plantain. To prepare the drink, take 10 grams of each medicinal plant material and add 500 ml of water. Before use, strain and add honey.
- If the spasm is caused by stressful situations, then it is recommended to drink no more than fifteen drops of motherwort, peony or valerian tincture before meals.
- Baths with the addition of a herbal mixture, which includes lemon balm, motherwort, linden flowers, valerian and one of the oils (tea tree, orange or ylang-ylang), soothe and relieve spasms well. The duration of the procedure is no more than twenty minutes.
- Breathing exercises that are performed slowly. They help prevent further development of muscle contraction.
Now you know how to relieve esophageal spasm at home.
Recommendations for patients
If esophagospasm occurs, it is advisable to visit a gastroenterologist. He will prescribe the necessary examinations to exclude its secondary nature. Once confirmed, all efforts are directed toward treating the disease that provokes the spastic state. If the reason lies in a malfunction of the nervous system, then measures are taken to normalize it. Person-centered therapy is most often indicated. In addition, sanatorium-resort treatment in the Crimea and on the Black Sea coast has a good effect.
How to relieve esophageal spasm at home? The following tips will be useful for both segmental and diffuse spasm:
- Give the individual warm water. This simple method helps in most cases. The attack passes, the pain stops.
- If the cause of the spasm is a stressful situation, then the patient is prescribed herbal sedatives.
It is not recommended to use medications on your own, as they all have contraindications and side effects.
Prognosis and prevention
Esophageal spasm, the symptoms and causes of which you became familiar with by reading the article, reduces the quality of life of an individual, including in the absence of serious consequences. The prognosis is influenced by factors such as the severity of the disease, the patient’s age, and the duration of symptoms before seeking medical help.
Prevention is an annual examination, which is carried out with a special optical device using an endoscope, as well as treatment of associated gastrointestinal ailments. All patients are prescribed medical rehabilitation to prevent relapses.
Source: fb.ru
Prevention
You can reduce the risk of esophageal spasm if:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- exercise;
- avoid stressful situations;
- adhere to a balanced diet;
- be examined by a gastroenterologist at least 2 times a year.
- maintain a daily routine that provides an optimal balance of time between work and rest.
The prognosis for recovery depends on the degree of development of the pathology and the age of the patient. Timely consultation with a doctor is the key to painless treatment.