Basic information
Black stool can be a serious symptom
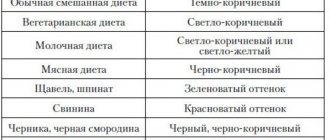
People often pay attention to the nature of their discharge. A change in the color of urine or stool often causes alarm and is a reason to consult a doctor. Normal stools are brown in color because the stool contains bile residues.
If food is digested faster than expected, the stool may acquire a greenish tint due to insufficient decomposition of bile. White stool may indicate blockage of the bile ducts.
In medical practice, black tarry stools are primarily associated with hemorrhage in the esophagus or stomach. The fact is that the blood released in the upper parts of the digestive tract undergoes chemical decomposition during the digestion of food.
It takes a long time before such blood reaches the rectum. As a result, the blood turns black. In contrast, blood released in the lower intestines will have a characteristic bright red color.
Fortunately, bleeding is not the most common cause of dark stool. This color can be the result of food eaten, metabolic characteristics, or diseases. However, any change in a child's stool should be a reason for diagnosis, since the health of the digestive system is of primary importance for a growing organism.
Possible reasons for stool turning black
A child may develop black stools for various reasons. Some factors are normal and do not pose any danger, while others need to be addressed urgently. That is why it is important to understand why a child has black stool. The following phenomena and reasons can affect the coloring of stool:
- Bowel movement in the first days of life. The fact is that babies are not born with an empty intestine, but with meconium inside. This term refers to fecal matter consisting of prenatal hair and epithelial cells, mucus, bile and water. The child swallows these particles along with amniotic fluid. Black feces in a newborn are observed only for the first 2-3 days, then meconium completely leaves the intestines, and the color of the feces becomes yellow.
- Using a mixture with a high iron content. Darkening of the stool can be caused by switching to a new formula that contains a lot of iron. This reaction is absolutely normal, since iron oxidation occurs in the stomach. Next, the substance is mixed with feces and colors them black.
- Introduction of complementary foods. In the first year of life, the child’s intestines are just beginning to adapt to work and external influences. At this time, the digestive system is still learning to digest foods, so the introduced complementary foods do not undergo complete processing. During this period, as a rule, black spots are observed in the stool. In addition, particles of undigested food can also be found among the stool.
- Nutritional features. Your baby may develop dark stools as a result of eating certain foods. For example, beets, currants, cherries, blackberries, and prunes have coloring properties. As well as liver, kidneys, apples, pomegranate and some other foods high in iron. The stool may be completely dark in color or have black specks if the food is not completely digested. In this case, black poop can persist for the next two or three days.
- Application of vitamins and minerals. Doctors often prescribe special complexes for children with a lack of vitamins and minerals. If they contain iron, the child will empty his intestines with black feces. Sometimes a change in the color of stool occurs due to the use of hematogen.
- Taking activated carbon. This substance is not absorbed into the blood and is not digested by the intestines. Activated carbon is a sorbent that absorbs all harmful substances and then removes them out. Parents often note black, fairly large inclusions in their stool.
- Taking medications. Some medications, for example, paracetamol, ibuprofen, antibiotics, as well as products containing bismuth, can affect the color of a child’s stool.
These factors are harmless and go away on their own after 2-3 days. Or after changing your diet and stopping taking certain medications. However, in some cases, a change in the color of stool is explained by the presence of inflammation or other pathologies in the organs of the digestive system. In this case, the black color of the stool, as well as various grains of sand and specks, are an alarming sign.
Common Causes of Stool Discoloration
Light yellow stool is often observed in children and is considered normal.
The food eaten travels a long way in the human digestive tract. After swallowing, food substrates almost immediately end up in the stomach.
Digestion in the stomach lasts from two to three hours, after which the food enters the intestines. Intestinal digestion is distinguished by its duration - food can be processed for 6 hours and subsequently deposited in the colon during the day.
Read: How to treat thrush in men - causes, symptoms and treatment of the disease
Thus, consumed food turns into feces 18-36 hours after consumption. During this time, a variety of factors can affect the color of the stool.
Reasons for color change:
- Changing your diet. Eating beets, tomatoes, beans, green leafy vegetables, and foods with food coloring can affect the color of your stool.
- Medicines. The color of the discharge can be affected by intestinal antibiotics, anticoagulants and other drugs.
- Diarrhea, characterized by watery discharge.
- Constipation. Stagnation of food masses in the colon can lead to a change in the color of the discharge due to the decomposition of individual components.
- Hemorrhoids and anal fissures.
- Rectal cancer.
- Intestinal ischemia.
- Colon polyps.
- Gastritis and gastroduodenitis.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases: Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Celiac disease. With this disease, the intestines do not absorb gluten. The stool may be yellow and greasy.
- Intestinal injury due to ingestion of a foreign body.
The main reasons for the appearance of black stools:
- Taking aspirin, warfarin, clopidogrel, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and bismuth preparations. Painkillers can also cause bleeding if you have a peptic ulcer.
- Consuming licorice, blueberries and other coloring foods.
- Taking iron supplements.
- Lead ingestion.
- Bleeding varicose veins of the esophagus.
- Inflammatory diseases of the esophagus and stomach.
The listed reasons can cause not only a change in the color of stool, but also provoke the appearance of certain symptoms.
If the cause of black stool is gastrointestinal disease
Medical practice shows the rarity of cases of extensive internal bleeding in children. But if the diagnosis reveals such a fact, urgent surgical intervention is prescribed.
If the cause of the discoloration of stool is a chronic disease, prescribing medications will be sufficient. They are divided into 3 groups:
- The first is represented by intestinal antibiotics.
- The second includes drugs whose action is aimed at reducing the acidity of gastric juice.
- The third category of medications refers to anti-inflammatory drugs. This will allow you to establish metabolic processes in the digestive tract, which will lead to the restoration of well-being.
Symptoms of various conditions
Food also affects the color of stool
Black stool may not be the only sign of a digestive tract pathology. The following symptoms may also occur:
- Abdominal pain and cramps.
- Bloating due to increased gas production.
- Increased intestinal motility.
- Profuse diarrhea with bloody inclusions.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Change in stool odor.
- Poor appetite.
- Pain and burning in the anal area.
- Unexpected weight loss.
Read: Why is there blood in stool? Should we panic?
Some of the listed symptoms indicate dangerous processes in the body. Immediate consultation with a doctor is required if the following symptoms are detected:
- Prolonged unexplained weight loss, fatigue, loss of appetite, sharp pain in the lower abdomen. These signs may indicate an oncological process in the large intestine. However, colorectal cancer is rarely detected in children.
- Prolonged vomiting with bloody inclusions. Bleeding may also be indicated by vomit the color of coffee grounds. Such signs indicate hemorrhage in the upper digestive tract.
- Stopping internal bleeding is possible only in a hospital setting.
First aid for black stool in a child
Constant diarrhea leads to dehydration of the baby. Dehydration is characterized by dry skin, lips, tongue, and severe thirst. No urine is released for 3–6 hours. This condition threatens the child's life. At the first such signs, call an ambulance and take urgent measures:
- The main help of parents is to prevent dangerous dehydration. To do this, you need to give the child 1 tsp of water. every 10–12 minutes. The fastest way to restore the water-salt balance are pharmaceutical powders that are pre-diluted with water - Regidron, Glucosolan. A product of this composition can be easily prepared at home. Dissolve 2 tbsp in 1 liter of bottled or any water. l. sugar and 1 tsp. soda and salt. Pour 1 tsp into the baby's mouth. solution every 10–12 minutes.
- Give enterosorbents - Smecta, Laktofiltrum, Enterosgel. These drugs contain substances that bind toxins that have entered the body.
- If the temperature is elevated, use a rectal suppository with Efferalgan or Paracetamol or give the child a syrup containing these drugs to drink
The child needs to be unsoldered until a team of doctors arrives.
No antidiarrheals should be given to infants. They stop peristalsis and prevent self-cleansing of the intestines.
Melena
Stool can be different shades for each person
As already mentioned, the appearance of black stools may indicate bleeding in the upper digestive tract.
The red color of blood is due to iron-containing hemoglobin. Any changes in blood color are also caused by chemical changes in hemoglobin molecules.
In the stomach, digestive juices act on the blood, which can cause black stools or vomit the color of coffee grounds. Doctors call this type of stool melena.
It is also important to be able to distinguish signs of bleeding in different parts of the digestive tract. Blood released below the stomach may be bright red, burgundy or crimson in color. This condition is called hematochezia.
The appearance of stool of a different color is explained by the fact that in the intestine food is exposed to the influence of other enzymatic environments. Bright red or scarlet blood almost always indicates bleeding in the colon or rectum.
The appearance of black, tarry stools in the absence of bleeding is called pseudomelena. The causes of this condition are less dangerous and are most often associated with dietary patterns. For doctors, the difference between melena and pseudomelena is an important diagnostic criterion.
Causes of melena:
- Liver pathologies.
- Malignant tumors.
- Dieulafoy's disease (rare disease of the stomach).
- Erosive esophagitis or gastritis.
- Varicose veins of the esophagus.
- Trauma to the esophagus and stomach by a foreign object.
- Insufficient blood supply to the intestines.
- Peptic ulcers.
- Mallory-Weiss syndrome.
- Vascular anomalies of the esophagus and stomach.
Read: Flatulence, what is it - a symptom or a disease?
Only a doctor can distinguish melena from a less dangerous anomaly.
How is the examination carried out?
If certain digestive diseases or surgical pathologies are suspected, a number of examinations of the child are carried out. These include primarily a general blood test. It evaluates hematocrit (the ratio of plasma to blood cells) and hemoglobin with the level of red blood cells. With blood loss and internal bleeding, they are reduced, and the ESR rate increases. In a biochemical study, the levels of proteins and urea may be changed; blood is also needed for coagulation; its indicators may be changed in certain pathologies of the body that lead to bleeding. It may also be necessary to determine the volume of circulating blood, if technically possible in the clinic.
From instrumental studies, the child undergoes an abdominal x-ray, if necessary with contrast, as well as computed tomography. They can indirectly indicate the source of bleeding in the digestive tract.
EGD is also indicated - examination with a special system with a camera and illumination at the end of the tube, the condition of the mucous membranes of the esophagus, stomach and the initial part of the small intestine for ulcerative and erosive defects, bleeding and injuries. Diagnostic laparoscopy or sigmoidoscopy may also be prescribed.
Depending on the specific diagnosis, the treatment tactics for the child are already determined, right up to surgery.
Alena Paretskaya, pediatrician, medical columnist
21, total, today
( 37 votes, average: 4.73 out of 5)
Staphylococcus during pregnancy: causes, treatment, prevention
Paracetamol while breastfeeding: can I take it for headaches or high fever?
Related Posts
Diagnostics
If in doubt, visit a doctor!
A change in the color of stool alone is not a sufficient diagnostic criterion for internal bleeding. The doctor will need to confirm the presence of blood in the stool using various methods.
Sometimes examining the anal area is sufficient, but more often laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are used.
Laboratory methods can detect even small amounts of blood in the stool. The method is called a fecal occult blood test. Special substances are used to detect blood components. To speed up diagnosis, you can collect material for analysis at home.
Once the presence of blood in the stool is confirmed, the doctor will need to determine the cause and source of the bleeding. The most commonly used method is esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
Using this study, it is possible to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. Any damage will immediately attract attention. Other diagnostic methods:
- Radiography using barium sulfate.
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging.
- Blood analysis.
- Colonoscopy (endoscopic examination of the intestines).
Accurate determination of the cause of melena or pseudomelena is important for prescribing treatment.
Treatment of black diarrhea in a child
Infections in infants are treated in the infectious diseases department. Complex therapy consists of drugs with different effects:
- in case of dehydration, solutions of Laktosol, Chlosol, Kvartasol are infused intravenously by drip;
- antibacterial drugs - Tsiprolet, Tsiprobay - are prescribed individually, depending on the test results;
- after a course of antibiotics, eubiotics are used to normalize the intestinal microflora - Bifidumbacterin, Hilak Forte, Probifor.
When treating mild forms of intestinal infections at home, the following drugs are used:
- to restore the water-salt balance - Regidron, Tsitroglucosolan, Glucosolan;
- enzymes that facilitate the digestion of food - Mezim Forte, Panzinorm Forte, Festal;
- for 3-5 days, give enterosorbents - Smecta, Polyphepan, Polysorb, Enterosgel.
For any form of the disease, the main treatment is to prevent dehydration. If you don’t have Regidron pharmaceutical powder at home, prepare a solution of salt, soda and sugar yourself.
Treatment
Baby has black stool
Treatment options depend on the severity of the child's condition and the cause of the black stool.
Urgent surgery may be required to stop bleeding; however, most often, the appearance of melena in children is not associated with extensive hemorrhage.
Other therapies may be aimed at treating chronic digestive diseases. The following medications can be used for this:
- Intestinal antibiotics.
- Drugs that reduce gastric acidity.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
If a child's black stool is caused by a particular diet, prescribing a diet may be sufficient.
The video will explain what the color of the chair says:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sjVLKPYF7vE
Read along with this article:
- Green stool in an adult, basic information, reasons...
- Light yellow stool: is it worth worrying about?
- Black stool: causes of pathology and when to panic
- Bloody diarrhea: signs of bleeding, risk factors and treatment measures
- Dark green stool is a sign of malfunction...
- What to do if the stool is light yellow
- Why is black stool a reason to see a doctor?
- Black diarrhea in an adult: causes and treatment
- Blood comes out when I poop: causes, symptoms and treatment of pathology
Causes of black diarrhea in a child
Black, loose stools in a child can be caused by the following reasons:
- consumption of coloring foods;
- taking certain medications;
- intestinal infections;
- bleeding from the digestive organs.
In addition, the baby's first stool after birth is also dark in color.
Let us consider in detail the appearance of dark feces in a child in each individual case.
Meconium
This is the name of the first feces of a newborn baby. The intestines excrete original feces for 48 hours. The color of stool varies from marsh-dark to black with a green tint. The resinous substance sticks to diapers and is difficult to wash off.
The mass contains desquamated intestinal epithelial cells, stomach and gall bladder juice. Meconium contains amniotic fluid swallowed during the prenatal period.
Taking medications
For some diseases, children receive medications prescribed by a doctor:
- vitamins containing iron – Multitabs Baby;
- Activated carbon;
- preparations containing iron - Ferrum-Lek syrup, Sorbifer;
- painkillers non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - Nurofen, Ibuprofen, etc.
After using charcoal and Sorbifer, black poop appears in the child the next day. This is a completely natural phenomenon. It's a completely different matter when the stool becomes dark after taking NSAIDs. Drugs in this group cause irritation of the stomach walls to such an extent that they can cause bleeding. Blood cells mixed with food cause black, loose stools in children and adults.
A child in this condition needs urgent examination.
Coloring foods
In 1-year-old infants and older children, the stool becomes dark after consuming dark-colored juices and vegetables. Red beets, raw or cooked, turn stool red to black. You shouldn’t think about it if you don’t have abdominal pain. Other foods that cause black diarrhea in a child include:
- pomegranate juice;
- blueberries, currants;
- blood sausage and fresh blood dishes;
- prunes, chokeberry;
- dark grapes.
The black color of feces disappears after removing the product from the menu.
Intestinal infections
In addition to foods, dark, loose stools in a child can be caused by intestinal infections:
- salmonellosis;
- typhoid fever:
- Escherichiosis;
- rotavirus infection.
Diseases caused by pathogenic microorganisms occur with fever, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Feces contain mucus and blood.
Black stools are not typical for dysbacteriosis.
Escherichiosis
An acute infectious disease caused by various pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli.
When infected with a hemorrhagic species of E. coli, a child develops cramping pain in the lower abdomen and vomiting against a background of low-grade fever. Bloody feces 4-5 times a day. A week later, hemolytic anemia develops with signs of intoxication. Acute renal failure soon follows. Escherichiosis in a child, if left untreated, is complicated by brain damage with paresis and seizures. Mortality rate is 3–7% in young children.
Salmonellosis
The infection often occurs in infants in the summer. Salmonella pathogens are transmitted through eggs, chicken, quail, and turkey meat.
Important! Infected products do not change their appearance, smell or color.
When infected, children experience vomiting and diarrhea with clots of mucus and blood within 3–4 hours. The temperature rises to 40 ° C. Intestinal colic causes abdominal pain. Greenish stools have a foul odor.
Salmonellosis occurs with severe intoxication. Dehydration occurs quickly. A child with signs of nausea, vomiting and diarrhea should be taken to the infectious diseases department as quickly as possible.
Typhoid fever
This dangerous disease is caused by bacteria from the genus Salmonella. Infection occurs through fly-infected food, as well as household items used by a sick person. Bacteria from the intestines are carried with the blood throughout the body, causing intoxication.
Characterized by a violent onset in the form of enteritis. Repeated vomiting and loose, profuse green stools appear 10–15 times a day. A rash sometimes occurs on the front surface of the abdomen. The liver and spleen enlarge. A complication of typhoid fever is ulceration of the intestinal wall. Dark brown diarrhea in a child occurs in case of ulcer bleeding.
Rotavirus infection
The source of the disease - rotavirus - is transmitted through dirty hands, household items, and food. The infection occurs in the form of gastroenteritis. Signs of rotavirus infection are frequent vomiting, nausea, screaming and crying of a child without tears. Pain with rumbling is felt throughout the abdomen.
Important! Liquid, foamy stool with a sharp, sour odor does not contain food or blood. Rapid dehydration leads to loss of consciousness and convulsions.
Diseases that can cause black stool
Black spots in the stool of an infant, or simply a change in the color of the stool to black, at this age sometimes indicate diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Such pathologies are quite rare in children under one year of age, however, there is still a possibility. Most often, the black color of stool indicates bleeding in the digestive tract, which is a very dangerous deviation from the norm.
Along with bleeding, other associated symptoms are usually observed. For example, internal bleeding is almost always accompanied by nausea and vomiting, general weakness of the body, dizziness, pain in the abdominal area and constipation. Sometimes you can find bloody streaks in the stool if the bleeding occurs in the lower part of the intestine. In addition, sometimes parents notice mucus in their child’s stool. If you notice such symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance.
If the color of the stool and consistency are normal, and the baby feels well, is not worried and eats normally, it is possible that the cause of small inclusions of blood is a rupture of the anus. This happens to children, especially with constipation. The rupture, as a rule, is insignificant; it’s just that a small artery passes through its place, which was the reason for the appearance of blood in the stool. The most reliable indicator of a baby's health is its condition. When there are painful symptoms inside, children always cry, act restless and refuse to eat. Therefore, black feces in combination with such signs is a very dangerous sign.