What is biliary reflux gastritis?
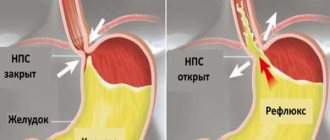
What is biliary reflux gastritis? This is a disease as a result of which the gastric mucosa becomes inflamed, which is caused by the reflux of the contents of the duodenum into it. The cause of inflammation is the pressure exerted by bile on the walls of the stomach.
Biliary reflux gastritis is a disease as a result of which the gastric mucosa becomes inflamed and is caused by the reflux of duodenal contents into it.
The main reasons causing the development of the disease include: stagnation of duodenal secretions along with bile in the stage of chronic development; irritable bowel syndrome; decreased activity of the sphincter between the stomach and duodenum; pyloric closure disorder; poorly performed surgical treatment; violation of the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract, etc.
There are several forms of biliary reflux gastritis, which differ in the nature of the damage to the stomach: erosive; surface; antral; catarrhal
Inflammation of the superficial type is easier than other forms. It consists in the appearance of degeneration of the epithelial tissue of the organ. The catarrhal form is characterized by the appearance of edema, and inflammation of the gastric mucosa is observed. Often the deeper layers of the organ can be affected. With the development of the antral form, only the antrum of the stomach becomes inflamed.
Methods for treating biliary reflux gastritis
Therapy begins after a conversation with a specialist. Basically, complex treatment is prescribed. Therapeutic measures consist in the fact that the patient must take prescribed medications, follow a strict diet, it is mandatory to quit smoking and not drink alcohol, and physical therapy is also necessary.
Diet is of particular importance in the treatment of biliary reflux gastritis
Diet is of particular importance in the treatment of biliary reflux gastritis. Patients need to eat small portions, but often. You should not often consume chocolate, citrus fruits, and fats. With drug treatment, doctors most often prescribe drugs such as antacids, drugs that speed up bowel movements and increase sphincter activity (Metoclopramide, Domperidone). If the acidity of gastric juice is high, it is recommended to take antisecretory drugs.
In this case, such drugs include proton pump inhibitors. To restore the cells of the gastric mucosa, it would be correct to use Sucralfate. Today, pharmacies have a drug called Ursofalk. It is the most important medication used in the treatment of biliary reflux gastritis and reflux esophagitis.
To obtain the necessary results from treatment, you must get rid of all provoking factors; in case of obesity, it is necessary to reduce body weight. It is necessary to stop taking medications that provoke the disease. The duration of treatment is determined by a specialist doctor. Typically therapy lasts 2 months.
Causes
The appearance of biliary reflux gastritis is associated in most cases with bad eating habits. Alcohol abuse, excess body weight, lack of food hygiene are risk factors for the disease.
The cause of biliary reflux gastritis can be pregnancy. This is due to the fact that during pregnancy the abdominal organs shift somewhat.
The reasons may be the following:
- Gastrointestinal diseases. The reason for the development of biliary ryuflux gastritis is stomach disease, chronic gastritis, oncopathology, for example. It can also be associated with frequent constipation, inflammation of the duodenum, and various diseases of the pancreas. Gastroptosis, prolapse of the stomach, can also cause the appearance of biliary reflux, because the position of the organ in such cases becomes lower than the duodenum or at the same level with it, this leads to retrograde reflux.
- Excessive physical activity. Frequent lifting of weights leads to increased pressure in the abdominal cavity, which leads to a weakening of the pyloric sphincter and, as a result, the reflux of bile into the stomach.
- Surgical interventions. Patients who have undergone certain surgical operations are most susceptible to developing the disease: gastric resection, pyloroplasty, cholecystectomy.
- Diseases of the biliary tract.
- Use of certain medications. A risk factor is taking medications that weaken the tone of the sphincters, which, in turn, leads to the reflux of bile into the stomach. Such drugs include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, tranquilizers, beta-blockers and others.
Biliary reflux gastritis
Biliary reflux gastritis is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa as a result of its damage by bile retrogradely coming from the intestines. The disease is manifested by a dull pain, a feeling of heaviness in the upper quadrant of the abdomen, which intensifies after eating. Belching, nausea and vomiting, flatulence, and stool upset occur.
Diagnostic measures include examination by a gastroenterologist, FGDS, X-ray contrast examination of the stomach, and 24-hour pH measurements. Treatment involves the complex administration of ursodeoxycholic acid derivatives, antacids, antisecretory drugs, prokinetics, together with dietary nutrition and healthy lifestyle.
Biliary (bile) reflux gastritis is a chronic disease of the gastrointestinal tract, in which bile entering the duodenum is thrown into the stomach, causing inflammatory changes in its mucous membrane.
Biliary reflux gastritis is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa as a result of its damage by bile retrogradely coming from the intestine.
Based on the severity of the process, acute and chronic biliary reflux gastritis are distinguished. Based on the volume of the lesion, focal and diffuse forms of the disease are distinguished.
The main symptom of the disease is pain localized in the right hypochondrium or epigastrium, radiating to the spine. Pain sensations develop during or after a heavy meal and are dull, aching in nature. After eating, there is a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the stomach.
With timely differentiation of the diagnosis and proper treatment, the prognosis is favorable. Compliance with all medical recommendations and the use of drug therapy together with diet improves the quality of life of patients and reduces the number of episodes of biliary reflux.
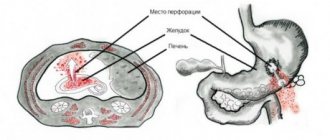
Lack of treatment and the development of complications can lead to life-threatening consequences (peritonitis, gastrointestinal bleeding, sepsis). Prevention of the disease consists of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, which includes giving up bad habits, eating high-quality, fresh and dietary food, maintaining a sleep and rest schedule, reducing stress, walking in the fresh air, doing gymnastics and Nordic walking under the guidance of specialists.
Varieties
According to the severity of the clinical picture, biliary reflux gastritis is:
- sharp;
- chronic.
According to the degree of damage, the disease is classified into two forms:
- Focal. This is a more common form of the disease, in which certain areas of the stomach are affected.
- Diffuse, when inflammation spreads to the entire mucous tissue of the organ.
Based on the type of epithelial damage, several types of biliary reflux gastritis are distinguished:
- surface. The epithelium of the mucous layer of the gastric walls is gradually affected. Damaged cells are replaced by intestinal epithelial cells, and intestinal metaplasia develops. This type of pathology is characterized by a long chronic course and possible degeneration into oncology;
- catarrhal It is characterized by inflammatory processes of the epithelium, which are accompanied by edema. In addition, the mucous membrane decreases and degenerates;
- erosive. Defects form on the surface layer of the gastric mucosa. Areas of erosion can increase and spread to the submucosal and muscular layer of the stomach, forming ulcers;
- atrophic. It is considered the most dangerous type of pathology with a high probability of malignancy. The mucous layer becomes thinner, and atrophy of the stomach walls causes hypersensitivity to any aggressive environment, including gastric juice.
Biliary reflux gastritis contributes to dysfunction of the endocrine glands. The disease can cause nervous system disorders.
Symptoms of biliary reflux gastritis
Biliary reflux gastritis is not accompanied by any specific symptoms. In general, the accompanying clinical picture directly depends on how deep the layers are affected by the pathological process.
Biliary reflux gastritis is not accompanied by any specific symptoms; the main complaint of a sick person is a complaint of pain
The main complaint of a sick person is pain. The pain syndrome is localized in the epigastric region, has a dull or aching character and intensifies after a short period of time after eating. There is also a feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating.
Symptoms such as heartburn, attacks of nausea and vomiting, and bloating occur. A distinctive point is that the vomit contains a large amount of gastric juice. The clinical picture is complemented by unstable intestinal activity. The patient indicates periodic diarrhea, followed by constipation.
Due to the fact that the disease disrupts the process of absorption of substances from food, patients experience a decrease in body weight, cracks in the corners of the mouth, anemia, dry and pale skin. With a long course of the disease, constant weakness, sleep disturbances and increased fatigue develop.
Diagnostics
To diagnose biliary reflux gastritis, a comprehensive examination is carried out:
- taking anamnesis;
- blood tests (general and biochemical);
- analysis of stool for blood;
- analysis for the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection (for chronic cases);
- FGDS. The examination reveals the presence of inflammation, swelling, and redness of the gastric walls (especially in the pylorus area). Areas of damage and atrophy of the mucous membrane and the formation of ulcers are determined. To clarify the diagnosis, a biopsy of the mucous membrane is taken for histological examination;
- X-ray with contrast agent. Violations of the integrity of the mucous layer of the gastric walls are detected. In addition, the study helps to detect the reverse movement of the contrast agent from the small intestine to the stomach;
- pH-metry. During the day, the intragastric pH level is measured, and changes in the level of acid in the stomach are assessed.
When diagnosing biliary reflux gastritis, it is necessary to differentiate this pathology from other diseases with similar symptoms: pancreatitis, cholecystitis, ulcers, gastritis, cholelithiasis.
Treatment of biliary reflux gastritis
If characteristic signs appear, you should immediately consult a doctor and begin treating the disease. Detection of the disease in the early stages of its development will prevent more serious consequences and will contribute to a speedy recovery. If, after the examination, you have been given such a diagnosis, immediately begin to eliminate the causes of the disease, as well as the factors contributing to the development of the disease. It is necessary to get rid of bad habits, such as drinking alcohol and smoking, because they slow down recovery.
Medicines relieve symptoms, stop inflammatory processes, restore motility of the biliary system and digestive functions. The course of medication may vary depending on the severity of symptoms and the severity of the disease. Antacids, prokinetics to increase sphincter tone, antihistamines, and drugs that neutralize bile acids are usually prescribed.
Together with drug treatment, a specialist prescribes a strict diet to reduce the load on the digestive organs. Fatty, fried, spicy foods, smoked foods, fast foods, and carbonated drinks are completely excluded from the diet. It is recommended to consume natural, easily digestible foods. Also, don't overeat. The food should be warm and the meals should be small; it is better to eat more often, but limit yourself to small portions.
Treatment along with diet can last several weeks or months. Along with complex therapy, you can take vitamins to strengthen the immune system. If biliary reflux gastritis is severely neglected and medications are ineffective, surgical intervention may be required. The operation is performed using endoscopic devices.
You can avoid such unpleasant diseases as biliary reflux gastritis and reflux esophagitis or prevent their recurrence if you lead a healthy lifestyle, spend more time in the fresh air, eat right and protect yourself from stress.
Treatment
Goal of treatment: normalization of digestion, functioning of the sphincters and gallbladder, relief of the inflammatory process, improvement of the general well-being of the patient. Treatment of biliary reflux gastritis often becomes lengthy and requires the efforts of not only the doctor, but also the patient himself.
Important! You should not rely only on medications prescribed by a doctor, and continue to eat prohibited foods. Treatment in this case will be ineffective.
Nutrition
Nutrition should be as balanced as possible. You should not go to extremes, refusing food, or being half-starved all day. This has nothing to do with therapeutic nutrition. It is the background against which other therapeutic factors are applied: without a balanced diet, there is no rational treatment . This is especially true for gastrointestinal diseases, when diet for a disease is also a treatment.
In Russia there is a unified number system of diets from No. 0 to 15. Zero is surgical, the rest are therapeutic. In case of exacerbation of gastritis, for the first 6–7 days you should adhere to therapeutic diet No. 1a, then, when the condition improves, diet No. 1b, and at the recovery stage, diet No. 1. The presence of active inflammation requires a transition to the most gentle diet - No. 1a.
(to enlarge, click on the image)
You can ask your gastroenterologist for a nutrition plan. The diet is gentle; it is recommended to consume semi-liquid, pureed foods at a normal temperature that does not injure the mucous membranes. For example, light vegetable broths, steamed meat, porridge with water. Some patients switch to pureed baby food during periods of exacerbation.
Refusal from carbonated and alcoholic drinks, sour, salty, fried foods, as well as any bread. Spicy food is also prohibited. Only at the recovery stage, some doctors advise eating dried bread, but no more than a couple of slices per day.
Important! After eating, you should not take a horizontal position. If you need to lie down, your head and chest should lie higher. The same goes for night sleep.
Also regarding behavioral recommendations - you should not overeat and expose yourself to increased physical activity.
Drug therapy
Biliary reflux gastritis should be treated only under the supervision of a doctor. Drug therapy for this type of disease should be comprehensive:
- Ursodeoxycholic acid preparations prevent the damaging effects of bile acids on the mucosa.
- To improve intestinal motility and normalize the passage of intestinal contents - prokinetics.
- Increased acidity requires the use of antacids.
- Proton pump inhibitors are prescribed to relieve mucosal irritation.
- For symptomatic treatment, antispasmodics, analgesics and antisecretory drugs are used.
In addition, while taking selected medications in the initial stages, good results are achieved by physical therapy - magnetic therapy, ultra-high-frequency inductothermy and other procedures.
Symptoms and complications of biliary gastritis
The clinical picture of the disease is very diverse. Symptoms depend on the extent of damage to the walls of the stomach, that is, they differ in the forms listed above. The main signs of any form are pain, which is most often felt in the right hypochondrium or epigastric region, but can radiate to the spine.
With a long course of the disease, a favorable environment arises for the development of gastric ulcer
Usually occur during meals or after heavy overeating. The pain is predominantly dull. Every time after eating, patients note a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the stomach. Dyspeptic symptoms occur: nausea; belching sour; vomit. Due to intestinal dysfunction, stool becomes unstable, and constipation is replaced by diarrhea.
Since nutrients are less absorbed, a person loses weight and develops painful “stubs” in the corners of his mouth. Anemia and dry skin are noted. With a long course of reflux gastritis, a general deterioration in well-being occurs, weakness occurs, sleep is disturbed, and the person becomes irritable.
Complications of the condition are not only esophagitis. When gastric contents, along with bile acids, enter the vocal cords or trachea, laryngospasm occurs, and even asphyxia develops. With a long course of the disease, a favorable environment arises for the development of gastric ulcer.
Since the symptoms of biliary reflux gastritis are nonspecific, additional studies are prescribed. This is fibrogastroduodenoscopy, which helps to visualize changes in the gastric mucosa. An X-ray of the organ is performed with the introduction of a contrast agent. Laboratory tests are also necessary.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis includes a thorough interview of the patient, his external examination (palpation of the abdomen), instrumental examination, as well as laboratory research. The correct diagnosis will depend on how accurately the patient describes his complaints. The appearance of pain and heaviness after eating is not direct, but still indicates biliary reflux. Information from the anamnesis will be of great importance, whether gastric surgery has been previously performed. The development of reflux gastritis is promoted by: organ resection, vagotomy, gall bladder surgery. The most informative method is to determine the situation in the stomach and duodenum. This examination is performed using gastroduodenoscopy.
This type of study reveals some signs of this disease: areas of redness; not fully closing the gatekeeper; swelling of the gastric mucosa; changed color of the stomach contents (a yellow tint is observed); presence of bile.
Biliary reflux gastritis and reflux esophagitis symptoms and treatment
The disease is a chronic inflammation of the esophagus, which occurs due to the constant entry of acidic stomach contents into it. The pathology is associated with insufficiency of the lower esophageal sphincter, which normally protects the esophagus from the penetration of gastric juice into it.
The main symptoms of reflux esophagitis are heartburn and sour belching, which usually occur after eating, as well as when bending forward. In addition to this is discomfort in the epigastric region.
Biliary reflux gastritis has a more intense clinical picture. Symptoms of this disease include pain and other disorders. Often patients are bothered by a feeling of fullness and bloating, as well as heaviness usually appear on an empty stomach, and their intensity can vary - from severe acute to aching. Vomiting is often observed.
Biliary reflux gastritis and reflux esophagitis require immediate treatment. This will help improve the patient's condition and avoid possible complications. If esophagitis is detected, you should give up bad habits, as well as intense physical activity on the abdominal area.
Drug therapy is based on prescriptions that will reduce the aggressive effect of gastric juice on the mucous membrane of the esophagus. Among them are “Almagel” and “Maalox”, used in a course. They coat the walls of the stomach and reduce acidity.
In addition, it is recommended to use drugs that reduce the secretion of gastric juice (Omeprazole). Prokinetics improve the tone of the sphincter, which is protection against the reflux of acidic contents. Among such drugs are Motilium and Motilak. If conservative therapy does not produce results, surgical intervention may be required, which is performed using endoscopic equipment.
Vomiting due to bile reflux
Bile reflux is a condition in which bile flows in the opposite direction - from the duodenum into the stomach. The presence of this fluid causes irritation of the walls of the organ, so nausea and subsequent vomiting are a natural consequence of this pathology. Bile reflux itself is not a disease, but is characteristic of a fairly large number of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Among the most common causes of its occurrence are stomach and duodenal ulcers. Functional dispersion. Consequence of surgery to remove the gallbladder. Hernia. Tumors in the duodenum. Various conditions associated with disruption of the pylorus - a fragment between the stomach and duodenum. For example, pyloric stenosis can manifest itself with morning attacks of such vomiting.
Bile reflux is a condition in which bile flows backwards from the duodenum into the stomach.
Bile reflux cannot be ignored; if these symptoms occur, you should definitely consult a doctor. The fact is that this condition is not only a sign of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), but can also provoke a chronic form of inflammation of the stomach walls - reflux gastritis.
Since bile reflux leads to irritation of the walls of the stomach, in addition to vomiting, it is accompanied by other symptoms, including:
- pain in the upper abdomen;
- sour taste in the mouth; heartburn;
- cough and hoarseness.
What to do if you are vomiting bile
You should definitely call a doctor. Before his arrival, you can alleviate the condition by washing your stomach. To do this, you need to drink 2-3 liters of clean water and induce a gag reflex. After rinsing, rinse your mouth and drink a few sips of cold water. This can be done if vomiting is caused by poisoning or alcohol intake. If the cause is unknown, it is better to wait for doctors to arrive.
Repeated vomiting leads to dehydration, so the patient must often be given liquid: rosehip decoction, weak tea, still water. Drink liquid only in small sips to avoid recurrence of vomiting. Before the doctor arrives, you need to ensure peace, preferably sleep. Vomiting can accompany serious diseases - myocardial infarction, strokes, exacerbations of chronic diseases of the liver and pancreas. Self-medication for such diseases is unacceptable!
Diagnosis and drugs for the treatment of biliary reflux gastritis
The symptoms and treatment of gastritis are somewhat different from other forms of inflammation. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately understand the problem and establish the correct diagnosis. Gastroendoscopy will help determine “biliary reflux gastritis”. When examining the mucous membrane of the digestive organs, you can find a picture characteristic of this pathology.
To confirm the diagnosis, an X-ray examination of the stomach using a contrast agent is also prescribed. Stool analysis is a necessary test to establish the disease. The presence of blood clots and bile inclusions allows one to suspect improper functioning of the digestive sphincters and prescribe a more detailed study.
The first place to start treatment is to normalize proper nutrition and select a diet that helps the stomach easily and quickly digest the food it receives. Food should only be boiled, preferably in a liquid state. Avoid taking spices, hot and salty foods.
The first thing to start treatment with is the normalization of proper nutrition and the selection of a diet that helps the stomach easily and quickly digest the food it receives.
Foods such as eggs, white and brown bread, legumes, mushrooms, and sour fruits should be removed from your diet for a very long time. Unhealthy and heavy food slows down the digestion process, deteriorates the quality of digested food, slows down the transition of food chyme into the intestines, thereby provoking the reflux of food gruel back into the stomach.
When the disease develops, it is simply impossible to do without drug treatment. Experts immediately prescribe a whole range of medications aimed at reducing the symptoms of the disease and normalizing proper digestion.
There are several groups of drugs to eliminate bile stagnation and complete digestion of food:
- choleretic drugs: Ursosan, Ursohol, Holosas;
- agents that coat the stomach: De-nol, Almagel;
- drugs that regulate the production of gastric juice: Omeprazole, Panzinorm;
- drugs that improve peristalsis of the stomach and intestines: Motilium, Itomed;
- enzymes that help digest food: Festal, Creon;
- products that normalize the natural balance of the intestines and restore the regular release of digestive residues: Linex, bifidumbacteria;
- if necessary, antibacterial agents;
- complex of vitamins to restore immunity.
To restore proper motility of the gastrointestinal tract, it is necessary to include physical therapy, which will tone muscle tissue and weakened sphincters, and also strengthen the functioning of the digestive glands. Procedures such as electrophoresis and phonophoresis can be prescribed by specialists only during a period of deep remission.
A comprehensive massage will enhance metabolism, improve blood circulation in all organs and tissues, and help relieve muscle tension. In extreme cases, if therapeutic treatment is ineffective, surgery may be performed. It is indicated for sphincter insufficiency, neoplasms, scar changes that do not ensure proper intestinal motility and provoke the reflux of food back into the stomach.
Traditional treatment for biliary reflux gastritis
For the treatment of biliary gastritis, herbal infusions or decoctions of various herbs are used.
Herbal infusions or decoctions of various herbs are used for treatment. The recipes include sedative, antispasmodic, choleretic and anti-inflammatory herbs. Under the influence of alternative treatment, the gallbladder with its ducts begins to function normally, its motor function and the outflow of bile improve.
It is necessary to take folk remedies regularly and for quite a long time: 1–2 months. You should not stop treatment only if the symptoms of the disease have passed and no longer bother you. For therapy with traditional drugs, it is better to use several recipes and alternate them every 2-3 weeks, otherwise addiction may develop and the drug will stop working.
Traditional medicine recipes:
- dandelions: gastritis can be treated with syrup from the flowers of this plant. Dandelion flowers are placed in a three-liter jar and poured into 0.5 kg of sugar. It is best to add layers. Then the flowers need to be crushed until a syrup appears. For half a glass of boiled water, take 1 tbsp. l. syrup. Take the drug 2-3 times a day;
- chamomile: prepare syrup from chamomile flowers according to the same procedure as described above for dandelion flowers. Dilute 1 tsp in half a glass of water. chamomile syrup. Drink three times a day;
- Potatoes: You can treat it with either raw potato juice or potato broth. Drink juice from mashed peeled potatoes, half a glass, twice a day before meals. It is necessary to prepare fresh juice every time. To prepare the decoction, potatoes along with their peel are cut into pieces and boiled for an hour. The strained broth is taken six times a day, half a glass, on an empty stomach.
Sources:
- https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_gastroenterologia/bile-reflux
- https://medaboutme.ru/zdorove/publikacii/stati/sovety_vracha/vospalenie_pri_biliarnom_reflyuks_gastrite/
- https://dvedoli.com/liver/gallbladder/biliarnyy-reflyuks.html
- https://rabbitprom.ru/what-is-reflux-gastritis-and-whether-it-can-be-cured-forever-symptoms-and-treatment-of-biliary-reflux-gastritis.html
- https://pobedigastrit.ru/lechsimpt/kak-lechitsya-biliarnyj-reflyuks-gastrit.html
- https://sammedic.ru/333489a-biliarnyiy-reflyuks-gastrit-prichinyi-simptomyi-i-osobennosti-lecheniya
- https://gastritinform.ru/ozhkt.com/zheludok/gastrit/lechenie-biliarnogo-reflyuks-gastrita.html
- https://gastritinform.ru/nmed.org/kak-lechit-biliarnyjj-reflyuks-gastrit.html
Bile in the stomach with gastritis: chronic associated reflux gastritis
Gastritis carries a danger to the entire body, including the gallbladder. This neighboring organ suffers from improper functioning of the digestive system and also begins to work abnormally. Gastritis occurs with bile reflux, which further complicates the chronic course of the disease. The patient experiences unpleasant symptoms, which are recommended to be eliminated under the supervision of the attending physician. The website gastritinform.ru provides information on the treatment of gastritis with bile reflux.