The secretion of gastric juice occurs through the work of the gastric mucosa. It is a colorless, odorless liquid with small lumps of mucus. Any deviations from this norm, such as changes in color and thickness, indicate problems with the gastrointestinal tract. The composition of gastric juice is complex, since it is produced by various cells of the gastric mucosa. Its main component is hydrochloric acid, which, in turn, has a concentrated composition.
Composition of gastric juice
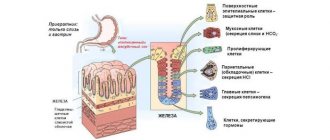
In addition to hydrochloric acid, gastric juice contains the following components
- Bicarbonates (they neutralize the harmful effects of hydrochloric acid on the walls of the stomach).
- Pepsinogen, which turns into pepsin (the latter is responsible for the breakdown of proteins). Pepsin is divided into another family of enzymes, each of which has its own functions.
- Mucus (it also protects the mucous membrane from destruction).
- Castle factor (an enzyme that helps absorb B12).
However, the main component of gastric juice is still hydrochloric acid. This is what we will talk about.
What is hydrochloric acid?
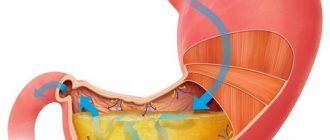
It is produced by the parietal cells of the gastric glands, located on the body and bottom of the organ. In essence, the mucous membrane is divided into several zones: one produces hydrochloric acid, the other secretes bicarbonates that neutralize it. It is noteworthy that men have several times more parietal cells than women.
The content of other acids in the stomach is insignificant. So, if lactic acid is found in it, this indicates that hydrochloric acid is produced in small quantities (low stomach pH) or not produced at all. The latter may indicate such serious failures as oncology.
Hydrochloric acid in the stomach has a strict concentration level - it is 0.3-0.5% (or 160 mmol/l). Its composition is so concentrated that if there were no protective substances in the gastric juice and mucous membrane, it would burn out its own stomach. That is why, when there is insufficient production of mucus by the stomach, a person develops gastritis or duodenal ulcers. Acid is constantly present in the stomach, but its amount increases in response to food intake. Basal secretion of hydrochloric acid (that is, morning) is 5-7 mmol/hour.
A healthy stomach produces up to 2.5 liters of hydrochloric acid per day!
The secretion of hydrochloric acid has 3 phases.
- Reaction to the taste and smell of food. It is triggered and transmitted from the central nervous system to gastric cells through nerve endings.
- After food enters the body, a more significant phase begins. Gastrin acts on parietal cells, stimulating the production of hydrochloric acid.
- The final phase begins after chyme (already digested food) enters the duodenum. Due to an increase in hydrochloric acid, the stomach produces somatostatin, an acid blocker.
How is acid neutralized?
It is known that gastric juice consists of bicarbonates. Why is such a component included? Gastric juice begins to be released as soon as the corresponding reflex becomes active in a person. But this does not always depend on the ingestion of food. In this case, the acid will begin to damage the organ. To prevent this from happening, bicarbonate ions come to the rescue. The cells that produce it are called superficial.
Interesting! Concept and indications for use of natural gastric juice
The formula for such a reaction has been known to us since school. Under the influence of the ion, carbon dioxide and water are formed. What kind of environment is formed in this case? Bicarbonate gives the juice its alkaline properties.
Such properties can prevent throat burns or laryngeal burns when acidic contents reflux into the esophagus. This happens in many gastrointestinal pathologies.
What functions does hydrochloric acid perform in the stomach?
First of all, it improves digestion, destroys most bacteria that enter the stomach with food, which slows down or even interferes with the putrefactive process.
What are the functions of hydrochloric acid in the stomach? Below is a list that details this issue.
- Denaturation of proteins (this is the destruction of their molecular structure) and their swelling.
- Activation of pepsinogen, which turns into pepsin - one of the most important enzymes that break down proteins.
- Creating an acidic environment under which enzymatic digestion occurs much easier.
- Evacuation of food from the stomach to the duodenum, where digestion continues.
- Antibacterial effect - many bacteria cannot live in such an aggressive environment.
- Stimulation of pancreatic juice secretion.
The role of hydrochloric acid in the breakdown of proteins deserves special attention. The importance of proteins in the body is enormous. This question has been studied by scientists for many decades. It has been established that hydrochloric acid in the stomach stimulates the production of pepsin, creating a favorable environment for its activity, and promotes partial denaturation and swelling of proteins. In the duodenum, hydrochloric acid stimulates the production of secretin, improves iron absorption and has a bactericidal effect.
Hydrochloric acid in stomach fluid
In the human body there are special cells - parietal cells, which produce HCl.
They are formed with the help of gastric glands. And those, in turn, are located in the area of the body and bottom of the organ. The accumulation of juice secreted by such microorganisms is constantly maintained. Its level is 160 mmol/l. However, the degree of subacidity of the gastric solution can vary due to the variable importance of parietal organisms.
There are other types of similar compounds present in the body of a healthy person, but their quantity is insignificant. For example, lactic acid, which is a waste product of lactic acid microorganisms such as enterococci, lactobacilli or lactococcus lactis. The absence of HCl is the only way for them to survive. The content of lactic acid in the gastrointestinal tract indicates that secretion is insufficient. In most cases, this element is tracked in the content of gastric juice in gastric cancer.
In order to correctly assess the normal state of the digestive system, measurements must be taken simultaneously in different parts of the esophagus or in different locations of the stomach, in the duodenum. During the examination, it is necessary to track how bacteria produce HCl and how it changes over time, its dynamics - the reaction to the use of provoking drugs and stimulants.
What functions does it perform?
HCl is the main element of gastric juice, with its help food is digested.
If secretion is insufficient, such a function becomes impossible, i.e., the supply of nutrients to the blood will be disrupted and a favorable environment will need to be restored. In addition, HCl plays an antiseptic and bactericidal role in the esophagus. When there is little HCl in the stomach, its protection is at risk.
How is it produced and neutralized?
As already mentioned, HCl in gastric juice is produced by special cells - they are located in the upper and middle parts of the stomach. With a substance norm of 1600 mmol/l, deviations in their work make it possible to identify symptoms that appear in cases where secretion does not occur. The lower part of the stomach produces mucus, which prevents damage to the stomach walls. In addition, this section produces hydrochlorides, due to which alkali appears in the stomach, since it is the last “resort” before food enters the intestines. Coherence in work helps restore normal acid levels.
Proteins and acidity of gastric juice
The role of hydrochloric acid in the digestion of proteins is still unclear. However, it has been established that with inflammatory diseases of the stomach, its secretion and, as a consequence, the digestion of proteins are disrupted.
The importance of proteins in our body can hardly be overestimated. This group is divided into many subgroups, each of which does its own thing. Thus, hormone proteins control life processes (growth and reproduction), enzyme proteins provide chemical processes (respiration, digestion, metabolism), hemoglobin saturates cells with oxygen.
Denaturation of proteins (this facilitates the process of their subsequent breakdown) allows the body to use their properties to the maximum. Every protein is made up of amino acids. Most of them are synthesized by our body, but there is a group of so-called essential amino acids that enter the body only from the outside.
Gastric acidity
Such an important aspect as the pH of the stomach directly depends on hydrochloric acid. And if there is a deviation from the norm, gastritis, dyspeptic disorders and other unpleasant conditions occur. Acidity in the stomach can be low, normal or high.
Despite the “popularity” of increased pH, people often have low or normal acidity. The latter ranges from 0.8 to 1.5.
Gastric environment
Enzymes are involved in the digestion of food to a state sufficient for its absorption. In the stomach it is pectin, and for it to act effectively enough a certain environment is necessary. Considering the effect of gastric juice and the acid it contains on the digestive processes, it is easy to assume that the environment in the stomach is acidic and its level is measured in pH. This indicator is necessary when assessing the condition of the gastrointestinal tract. However, the more samples in different areas of the stomach are taken, the higher the accuracy of measurements. This indicator should also be taken into account in the duodenum and esophagus. After a certain amount of time, tests should be repeated in order to determine the dynamics of therapy with pharmaceutical drugs.
Now let's talk about the environment in certain gastric sections. The maximum acidity level in the stomach can reach up to 0.86 pH. The minimum value is 8.3 pH. If we consider the areas, then:
- The acidity in the gastric lumen falls between 1.5 and 2 pH.
- In the upper layer of the epithelium the pH is from 1.5 to 2.
- In the depth of the epithelial layer up to 7 pH.
- The antrum has a pH of 6 to 7.
- If we consider the duodenal bulb, the acidity reaches from 5.6 to 7.9 pH.
Low stomach acidity
Low acidity occurs with constant stress and inflammatory diseases. This happens due to the stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system, which directly affects the production of gastric juice. A decrease in acidity leads to worse digestion of food and stomach spasms. Food remains in the cavity and begins to rot, increasing the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. A person suffers from flatulence and nausea. The latter is a response to stomach spasms. Moreover, the process of absorption of all nutrients contained in our food is actively disrupted, which leads to disruption of the functioning of the entire body. By the way, it is precisely because of the natural decrease in pH that after 40 years a person begins to age rapidly. That is, hydrochloric acid in the stomach actually affects the health of the entire body.
The stomach, surprised by the excessive proliferation of bacteria, begins to turn on its protective function, resulting in inflammation. It is treated with drugs that further inhibit the production of hydrochloric acid - and the circle closes. A person is forced to constantly visit a doctor.
Even heartburn, which we are accustomed to considering as a consequence of an increase in the amount of gastric juice, is considered only a product of acetic acid fermentation.
In a diseased stomach, lactic acid begins to actively form. Due to the inability of the stomach to produce enough mucus, it damages the walls of the organ. In such cases, a diagnosis of gastroduodenitis is made.
How is the production of gastric juice regulated?
Regulation ensures the desired chemical composition of gastric juice, its quantity and daily acidity. The following periods of digestion are distinguished:
- interdigestive - when there is no food in the stomach (neutral mucus is secreted);
- digestive (begins after eating, when gastric juice has an acidic reaction).
Interesting! How to reduce stomach acidity - signs and how to treat
The composition of gastric juice at one time or another depends on the amount of food and its composition. All people have one or another characteristic of a secret. There are two phases of regulation of this secretion.
The complex reflex phase includes the following components:
- conditioned reflex (secretion processes are stimulated by visual, olfactory, auditory and other factors);
- unconditionally reflex (the processes of acid and enzyme production begin from the effect on the receptors of the upper digestive tract).
The reflex arc begins from the receptors, from where the excitation goes to the medulla oblongata. The activity of the medulla oblongata leads to stimulation of the secretion of gastric juice. Because of this, the so-called delicious juice will begin to stand out.
Neurohumoral regulation includes nervous and humoral processes. The sympathetic department inhibits digestive activity, and the parasympathetic, on the contrary, activates it. The role of hormones in the formation of this fluid is as follows:
- insulin stimulates secretion;
- the influence of ACTH is stimulating;
- Hormones produced in the gastrointestinal tract additionally regulate the amount of stomach contents.
Increased stomach acidity
Despite the opinion of many gastroenterologists, high acidity is much less common than low acidity. The danger is that with prolonged hypersecretion of gastric juice, ulcers of the esophagus and stomach appear. The patient is bothered by heartburn and pain. This is where proton pump inhibitors - Omez and its analogues - will be useful. Symptoms are relieved with the help of antacids - Gaviscon, Phosphalugel, etc.
To diagnose high acidity, an instrumental examination must be used, because its symptoms can easily be confused with decreased secretion.
What happens with low acidity
Hyposecretion of gastric juice is much less common. Do not assume that this condition is better (based on information obtained from television advertising). On the contrary, gastric hypofunction is much more dangerous.
Some people do not know how much acid a person should produce, and they believe that the less it is, the better, because then “there will be no heartburn.” The mechanism of the stomach is such that for its normal function, its secretion must have an acidic reaction. If little acid is produced, gastric activity decreases, and many disease-causing organisms can enter the body.
What does a person feel with low acidity? There is no need to think that this changes the color of the gastric discharge. It has reduced enzymatic properties, which contributes to the appearance of the following symptoms:
- a sharp drop in appetite;
- belching with an unpleasant odor of spoiled eggs;
- bad odor coming from the mouth and not going away after brushing your teeth;
- constipation;
- signs of intestinal upset;
- nausea, worse after eating;
- the presence of helminths in the stomach or intestines (they are not neutralized by acid);
- flatulence.
Interesting! How to get rid of acid in the mouth - reasons and what to do
The danger of this condition is as follows:
- due to a decrease in the intensity of digestive processes, a large amount of food accumulates in the body
- amount of decomposition products;
- decreased absorption leads to anemia, hair loss, etc.;
- the development of autoimmune pathologies and even cancer;
- the appearance of allergic reactions even to once familiar products;
- due to a decrease in the effect of gastric juice on proteins, the patient may develop protein starvation;
- decrease in blood pressure.
To treat this condition, it is necessary to choose a therapy that gives the juice normal acidity. Sometimes the patient needs to consume hydrochloric acid preparations.
Types of determination of stomach acidity
Hydrochloric acid in the stomach (that is, its level) is determined by several methods.
- Probing. It is done using a special tube through which the contents of the stomach are sucked out.
- Intragastric pH-metry. The sensors measure acidity directly in the stomach.
The second method is considered the most informative.
Stomach acidity is something that most doctors don't pay attention to, but it is actually extremely important in diagnosing and treating gastrointestinal diseases.
Acid production and neutralization in the stomach
Digestion of food at the gastric stage is carried out under the influence of enzymes, the most important of which is pepsin. They must certainly be in an acidic environment. Before the chyme, which includes food and gastric juice that has begun to be digested, is evacuated to parts of the intestine, where the environment is alkaline, the acid in it must be neutralized.
Conventionally, the stomach is divided into zones. Acid formation occurs in the upper one, and its neutralization occurs in the lower one. They are separated from each other by an intermediate zone, in which slightly acidic pH values from 6.0 - 4.0 pass to strongly acidic ones with values of 3.0. During diagnostic tests of the stomach, acidity is measured in two parts of the stomach to ensure that it is functioning normally.
Hydrochloric acid is secreted by the fundus in its main body and bottom, which predominate in it. The hydrochloric acid released has a constant concentration, but gastric juice changes its acidity. This happens because the parental cells change in number and the alkaline substances they form lead to its neutralization. In this case, the level of neutralization also depends on how quickly the glands secreting acidic secretion work. The higher the rate of secretion, the higher the level of acidity in the stomach.
The secretion of hydrochloric acid is activated during the digestion process. But this does not mean that the rest of the time it is not in the stomach. Secretion occurs constantly, but on an empty stomach it occurs in much smaller quantities.
Return to contents