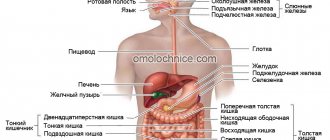
Esophageal obstruction is a pathological course characterized by partial or complete obstruction of the esophageal tube. As a result, food and water are not able to follow through the esophagus and penetrate the gastrointestinal tract. In case of inflammation of its walls and subsequent healing, the formation of coarse scar tissue occurs, which reduces the lumen of the tube.
Development of the disease
Sometimes difficulty with the passage of food occurs due to tumor growths squeezing the tube from the outside. There is benign stenosis, provoked by scars formed after various injuries (ulcers, chemical lesions) or penetration of a foreign body behind the sternum, and malignant narrowing, caused by the appearance of a cancerous tumor in the esophagus.
Often, this condition can create cardiospasm - an involuntary and very painful contraction of muscle tissue in the area where the esophagus joins the stomach. Most people confuse the disease with the heaviness that appears after eating, but cardiospasm is based on dysfunction of the vagus nerve, which is responsible for intestinal motility.
Reasons for the development of pathology
There are a large number of factors and diseases that can trigger the development of esophageal obstruction. The most frequently noted are the following:
- Stenosis can be caused by ingesting chemical liquids or too hot drinks; it is for this reason that you should not drink very hot drinks.
- Malignant and benign neoplasms in the esophagus.
- Mechanical injury to the esophagus, which is possible as a result of foreign objects or injury.
- Irritation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus by the contents of the stomach and gall bladder.
- Obstruction can develop as a result of infectious, inflammatory diseases.
- Connective tissue pathologies.
- Parts of the esophagus can also be damaged as a result of pathologies of the thyroid gland, for example, nodular goiter develops.
- There is even congenital obstruction, which develops in the child during intrauterine development.
Stages
Pathology can occur at any age: in young children, adults and the elderly. The disease has several stages:
- the person feels slight discomfort at the moment of swallowing, severe pain occurs in the chest;
- the subsequent stage of development is manifested in the fact that large pieces of food are difficult to pass; drinking liquid will help alleviate the condition;
- It is difficult to consume ground foods;
- a feeling of pain occurs when drinking water;
- the further stage is critical, absolutely the entire lumen of the esophagus is blocked, even liquid is not swallowed.
To prevent this, it is important to start treatment at the first sign.
Stages of disease development
This pathology goes through several stages in its development:
- The patient begins to feel some discomfort when swallowing, and pronounced unpleasant sensations appear behind the sternum.
- At the next stage, large pieces of food pass with difficulty; it becomes easier if you drink liquid at the same time as eating.
- It becomes difficult to eat even pureed food.
- Pain in the esophagus occurs even when drinking any liquid.
- Esophageal obstruction at the next stage is a critical stage when the passage of the esophagus is completely blocked. It becomes impossible to even swallow water.
It must be borne in mind that the earlier the pathology is detected, the more effective the therapy will be.
Degrees, forms of obstruction
There are 2 forms of the disease:
- The organ passage is narrowed due to damage to the esophagus by a benign tumor.
- And in the case of esophageal cancer, malignant forms of the disease are distinguished.
The pathology contains 4 degrees of stenosis, each of which has its own diameter:
- I – 9-11 mm.
- II – 6-8 mm.
- III – 3-5 mm.
- IV – 1-2 mm.
Prevention of pathology
To prevent the disease you need to:
- Take measures to prevent the development of tumor processes in the esophagus.
- Store all chemical and caustic liquids only in containers with labels so as not to accidentally mix them up and in a place where a child cannot reach.
- If gastroesophageal reflux occurs, you must follow a strict diet: do not overeat, do not eat irritating foods.
- Do not eat before bed: last meal no later than 3 hours before going to bed.
- After eating, do not immediately take a vertical position.
- Watch your weight.
- Do not wear too tight clothes or tight belts.
- Don't overexert yourself physically.
It is much easier to prevent the development of the disease than to engage in long-term treatment later. When the first unpleasant symptoms appear, it is better to immediately visit a specialist rather than self-medicate.
Possible reasons
There are many causes of esophageal obstruction, the most common are:
- constant intake of solid, hot foods;
- injury due to small fish bones, hard food;
- peptic ulcers - a consequence of the constant reflux of acidic juice into the esophagus;
- food does not go well with the development of tumors;
- inflammation of the intercostal nerve;
- obstruction due to inflammatory, infectious pathologies;
- cardiospasm;
- the formation of bag-like bulges in the walls of the esophagus - diverticula;
- open wounds;
- initial stage of gastroesophageal reflux;
- connective tissue diseases;
- penetration of foreign particles;
- development of esophagitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane with the formation of pronounced defects;
- ingestion of liquid chemicals (vinegar) into the body, causing burns of the mucous membrane with narrowing of the lumen;
- hernia in the diaphragm area;
- diseases of the thyroid gland (appearance of nodular goiter).
Obstruction of the esophagus in newborns is also possible, which develops in the child while still in utero.
Causes of esophageal obstruction
Conventionally, all the reasons for the sensation of food obstruction in the esophagus in adults can be divided into two large groups:
- Malignant oncological processes of the esophagus or adjacent organs (adenocarcinoma, mediastinal tumors, lung cancer).
- All other reasons:
- the result of scar changes after chemical burns;
- benign tumors;
- forms of obstruction caused by the formation of rings of the esophagus (these are benign concentric formations that narrow the lumen of the esophageal opening, the reason for their formation is not clear, many researchers associate the formation of rings with impaired motility of the organ, more often the pathology occurs in older people);
- complications of various diseases (tuberculosis, scleroderma, syphilis, cirrhosis of the liver).
All these causes cause similar symptoms: dysphagia, odynophagia, retrosternal pain.
Obstruction of the esophagus in oncology
During oncological processes, partial or complete obstruction of the organ lumen occurs. This is especially clearly visible with exophytic growth of esophageal cancer (with endophytic growth of the tumor, the clinical picture is not so pronounced). Dysphagia in esophageal cancer is constant and increasing. However, in advanced cases, when the tumor disintegrates, the severity of dysphagia may decrease.
Obstruction of the esophagus in an adult and elderly person can also occur due to oncological processes in nearby organs (lung cancer, mediastinal tumors, bronchial cancer) due to its compression.
Esophageal obstruction in liver cirrhosis
With cirrhosis of the liver, when portal pressure reaches a critical value, varicose veins bulge in the esophagus above the surface of the mucosa, creating in the patient a feeling of food obstruction. The only thing to do in this situation is to immediately seek help. Obstruction of food through the esophagus in an adult against the background of liver cirrhosis is a sign of stage 3 varicose vein disease, which can lead to fatal bleeding.
Symptoms
Abdominal, thoracic, cervical - these are the sections the esophagus has. Obturation (blockage) mainly appears in the thoracic region; it is this region that is most sensitive to the formation of malignant neoplasms.
The main symptoms of esophageal obstruction are as follows:
- dysphagia - impaired or difficult swallowing, manifested by discomfort at the time of eating food, the inability to swallow hard, dry or poorly chewed food, and subsequently the inability to take even liquid meals;
- unexpected vomiting immediately after eating food, while blood streaks are noted in the contents, belching occurs with a fetid odor of rotten eggs;
- odynophagia - pathological, unpleasant sensations in the sternum area, which worsen when swallowing. Sometimes it can be assumed that this is a heart attack, since the pain provokes changes in the blood circulation of the heart muscle;
- sudden weight loss - with difficulty swallowing, the patient often refuses to eat another meal, even if he has an excellent appetite.
Dysphagia - obstruction of food through the esophagus - occurs in several stages. Belching and vomiting occur at stages II and III of the development of the disease, and the very last stage (IV) is characterized by the inability to swallow liquid. Well, when trying to take a sip, a person begins to feel a burning sensation, squeezing, and discomfort.
Treatment with traditional medicine
In case of esophageal obstruction, treatment with folk remedies is purely symptomatic. It is impossible to get rid of the disease in this way. Treatment is aimed at reducing the symptoms of inflammation, enhancing regenerative processes, reducing symptoms of psycho-emotional agitation; many recipes have an analgesic effect. Herbal medicines are used in the form of infusions and decoctions. Oak bark, chamomile flowers, mint leaves, sea buckthorn oil, aloe, and honey are widely used.
Complications
Stuck food leads to anorexia, perforation, and water-salt imbalance.
The most dangerous is perforation of the walls, which threatens the appearance of peritonitis - an inflammatory process of the peritoneum. This condition is quite complex, life-threatening, and requires urgent hospitalization.
At risk are people whose relatives suffered from gastrointestinal disorders, gastritis, ulcers, or who work with hazardous chemicals.
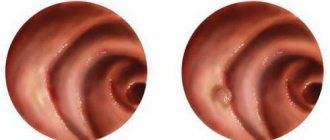
Clinical manifestations of stenosis and obstruction
The main symptom that allows one to suspect obstruction of the esophagus in a patient is difficulty swallowing (dysphagia). Patients usually feel a lump in the throat, pain, inability to swallow food, and nausea. After eating, they may experience vomiting, which, unlike that with GERD, does not cause a feeling of heartburn and does not have a sour taste.
At the same time, the severity of symptoms increases gradually; in the first stages of the disease, patients usually have almost no complaints. Usually these are minor difficulties when swallowing, profuse salivation and mild discomfort in the chest. In some cases, there may be no symptoms at all, and narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus may be detected as an incidental finding.
There are five stages in the development of dysphagia, from the absence of this symptom to complete dysphagia, in which no substances can penetrate the stomach at all. In the intermediate stages, difficulty in swallowing solid and coarse food first develops, gradually the patient's condition worsens, they can only swallow liquid, and then even liquid food does not pass into the stomach. In some cases, pain in the chest may resemble that during angina attacks, which can lead to misdiagnosis and the wrong treatment being prescribed.
In cases where the narrowing is located high, food can enter the trachea, which leads to the development of cough and hoarseness. Such patients may develop attacks of suffocation while eating. Also, insufficient intake of nutrients into the body leads to the development of exhaustion, weight loss, and the appearance of astheno-neurotic and astheno-vegetative syndromes. The behavior of such patients may change - they may become irritable, nervous or, conversely, depressed and inactive.
Attack of severe cough
Among the causes of esophageal obstruction, cardiospasm should be considered separately. This is a condition that develops as a result of improper innervation of the muscular wall of the esophagus, resulting in muscle spasm and narrowing of its lumen. A distinctive feature of this type of esophageal obstruction is that problems with swallowing food are not always present. They may appear and disappear. Sometimes it is possible to develop paradoxical dysphagia, in which the patient normally swallows solid foods, but cannot swallow liquid foods.
Diagnostics
It is very important to accurately identify the disease. The structure of the esophagus is such that it is not easy to visually identify the disease, therefore the following is used for diagnosis:
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy - this technique assesses the condition of the lumen of the esophagus, the structure of the epithelium, and if necessary, a biopsy can be taken;
- radiography;
- Ultrasound – detects the presence of any disease;
- MRI, CT - allow you to recognize the disease and identify associated problems.
You will also need to take tests (urine, blood, hemoglobin), and a stool test for occult blood.
Nutritional Features
The menu for esophageal cancer is similar to the nuances of the diet for other problems with the digestive system. The basic rules are:
- Eating up to 6 times a day or every 3 hours in small portions. Over long periods of time, the gastric juice produced irritates the membranes.
- Grinding products so as not to injure the organ and improve peristalsis processes. To prepare the puree, use a sieve or blender.
- The maximum amount of food consumed per day is 2 kg per day, water – 1.5 liters.
- Compliance with temperature indicators . Dishes are eaten warm, since cold ones are difficult to digest, and too hot ones lead to irritation of the mucous membranes.
- The preferred cooking method is stewing, steaming and baking.
The treatment plan depends on the stage of cancer and the patient’s well-being. In the initial stages of cancer, it is permissible to eat ground, semi-liquid and liquid food.
At stages 3-4, when the patient finds it difficult to swallow even water, feeding occurs through a gastrostomy tube. This is a probe that passes through the anterior abdominal wall directly into the stomach cavity, bypassing the esophagus. Food, accordingly, is only liquid.
The pharmaceutical industry offers special nutritional mixtures - dry or in the form of ready-made food, hermetically sealed to increase shelf life. The powder mixture is diluted with drinks or water according to the principle of baby food, and as a result, a couple of liters of the finished cocktail are obtained from one package.
Treatment
If during a meal a person feels that food is stuck, he needs to help alleviate his condition on his own before contacting a specialist. First aid is to try to induce a gag reflex.
Further methods of therapy will be determined by the complexity of the disease and the factor of its occurrence. In case of penetration of a foreign body, elimination occurs through an esophagoscope with an increase in the lumen. For oncology, complex treatment will be required.
Drug and surgical therapy
Disturbances in the passage of food through the esophagus can be combated with the help of medications; generally, the doctor prescribes:
- antacids (Almagel, Maalox);
- prokinetics (Reglan, Cerucal);
- tissue renewal stimulators;
- proton inhibitors.
When the symptoms do not go away with the use of medications, surgical treatment methods are used. Most often, this method is needed for organ cancer. Gastroenterology involves the following operations on the esophagus:
- removal of an organ and subsequent replacement with other tissues;
- chemotherapy with anticancer drugs;
- Radiation treatment in combination with chemotherapy helps to shrink the tumor to facilitate further removal.
If a benign neoplasm is detected, it is removed by increasing the lumen of the esophageal tube with special instruments.
Diet
In case of impaired digestion, when a person has food stuck in the esophagus, dietary nutrition will be required:
- Table No. 1 – nutrition should be correct, complete. I grind the food, consume it steamed or boiled. You cannot eat cold or hot food. It is recommended to eat a little, but often.
- Table No. 2 - you are allowed to eat semi-liquid, liquid foods. The intervals between meals should be no more than 2.5 hours. Reduce the use of salt, eliminate sour fruits, flour products, bread, and smoked foods from the diet. Avoid strongly brewed tea and coffee and give preference to herbal infusions and fruit drinks.
- Table No. 3 – low-calorie diet is used, do not consume foods that excite the mucous membranes. Eat pureed, liquid dishes.
After surgery, you will also need to follow a diet prescribed by a specialist.
Traditional treatment
In addition to medications, treatment with folk remedies is used. Herbal decoctions help improve a person’s condition and reduce the symptoms of the disease.
The most effective recipes for obstruction are:
- Combine 50 g of wormwood, 100 g of femoral root with 75 g of arnica, mix thoroughly. From here, take 45 g of the mixture, pour 400 ml of boiling water and keep in a thermos for about 10 hours. Can be used four times a day, 100 ml half an hour before meals.
- Make a tincture of walnuts (only young ones) in alcohol, use 1 teaspoon after meals.
- Boil quince seeds until they become mucous; taking the product means 1 teaspoon three times a day.
- You will need 30 g of cinquefoil, oak bark, 20 g of oregano leaves, combine all this with 40 g of St. John's wort, walnut leaves, mix. Take 30 g of the composition, add 700 ml of plain unboiled water. Leave for 3 hours, then cook for 5 minutes, strain and consume 100 ml 30 minutes before meals.
- Grind alder bark, pour boiling water, let it brew for at least 3 hours, drink after meals four times a day.
- Mix olive oil, raisins, natural honey, grass hay. Take 1 tablespoon before going to bed with plenty of liquid.
Before using traditional recipes, you should consult a doctor so as not to complicate your situation.
How to treat esophageal obstruction
The choice of treatment method depends on the etiology of the disease, the degree of esophageal obstruction, and the patient’s age.
If there is a feeling of food obstruction in the esophagus, therapeutic methods, surgical treatment are used, and alternative medicine methods are widely used.
Treatment with medications
Conservative treatment of esophageal obstruction in the initial stages of the disease, when GERD symptoms predominate, is quite justified. To reduce inflammation, medications are prescribed in tablet form:
- drugs that reduce the aggressive effect of reflux on the mucous membrane (antacids, PPIs, IGRs);
- drugs that accelerate the movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract (prokinetics)
- antispasmodics that reduce pain;
- metabolism;
- sedatives.
Surgical treatment
For malignant neoplasms in adults, if possible, a radical operation is performed to remove the affected organ, followed by plastic surgery and the entire complex of anti-cancer treatment.
If the tumor is inoperable, then endoscopic stenting is performed to eliminate food obstruction syndrome, improve the patient’s condition and maintain oral feeding.
In cases of benign esophageal obstruction, the endoscopic bougienage method is used - non-surgical dilatation of the narrowed area using a bougie or an inflated balloon to restore patency.
Prevention
For preventive measures, the following recommendations should be followed:
- prevent the development of tumors in a timely manner;
- do not eat at night;
- avoid obesity;
- wear loose and comfortable clothes;
- after eating food, do not go to rest immediately;
- exclude physical activity.
It is much easier to prevent blockage of the esophagus than later treatment will be long and unpleasant. When the initial signs of the disease appear, you should immediately go to the doctor to determine an accurate diagnosis.
We recommend: What is catarrhal esophagitis and how to treat it?
Disease prevention
Following simple preventive measures will help to avoid the development of esophageal obstruction. It is important to promptly treat pathologies that can lead to this condition, eat properly, avoiding excessively hot or cold foods, and not consuming acids and alkalis. Such dangerous aggressive substances should be kept away from children.
You should avoid overeating or following a strict diet, avoid spicy, fatty or smoked foods - they irritate the mucous membranes and can lead to the formation of ulcers or erosions. It is important to eat often, but in fractional portions. Physical activities that require bending or lifting heavy objects should be avoided.