What is a peptic ulcer
A peptic ulcer is a pathology that occurs when the level of acidity of the stomach increases and is accompanied by the formation of a defect in the mucous tissues of the gastric wall. Ulcerative formation is characterized by a long healing time and frequent relapses; it can be round or oval, and can be several mm or several cm in size. Usually a single crater is formed, less often multiple lesions are observed.
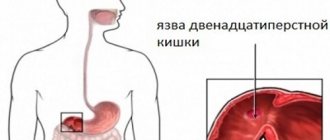
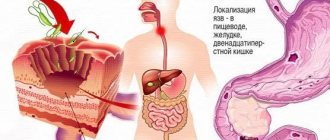
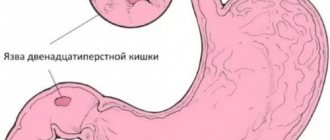
Peptic ulcers are classified by anatomical location or developmental causes. Duodenal ulcer is the most common type of pathology, which is localized in the initial segment of the duodenum. A gastric ulcer (stomach) most often forms in the lower part of the stomach. When the stomach is operated on, marginal ulcerative formations may develop in the area where it connects to the duodenum. A stress ulcer forms in the stomach and duodenum due to stress caused by a serious illness, burn or skin damage.
Peptic ulcers are classified into several types based on location:
- Lesser curvature of the stomach. It most often affects people under 40 years of age.
- Stomach and duodenum.
- Pyloric part of the stomach. Usually occurs in young people.
- 12 duodenum.
Things to remember
- A peptic ulcer is a sore in the lining of the stomach, duodenum, or esophagus.
- The bacterium Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is the most common cause of peptic ulcers.
- The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)—such as aspirin and ibuprofen—is the second most common cause of peptic ulcers.
- Neither stress nor spicy foods cause peptic ulcers. But, like smoking or drinking alcohol, they can worsen the ulcers or prevent them from healing.
- If the ulcers are caused by H. Pylori, then antibiotics are necessary to eradicate the microorganism.
- If your ulcers are caused by taking NSAIDs, your doctor may consider giving you more appropriate treatment.
- Medicines that reduce stomach acid production and protect the lining of the stomach and duodenum help ulcers heal.
Measures to prevent ulcers caused by H. Pylori infection include:
- washing hands after using the toilet and before eating
- eating properly prepared food
- drinking clean water from safe sources
Causes
A peptic ulcer develops when the protective and regenerative properties of the mucous tissues of the stomach or duodenum are weakened, and they are damaged under the influence of stomach acid. Functional dysfunction is caused by the following reasons:
- infection of the stomach by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which comfortably exists in an acidic environment;
- long-term use of a number of medications (NSAIDs, bisphosphonates, etc.) that disrupt the production of enzymes that protect the mucosa;
- smoking increases the likelihood of developing ulcers in people infected with Helicobacter pylori infection;
- alcohol consumption. Alcohol-containing drinks have an irritating and corrosive effect on the mucous tissues of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, ethanol increases stomach acid levels;
- stress is not considered the root cause of the pathology, but is considered as a predisposing factor. People are constantly exposed to stressful situations: emotional overload, physical injuries, operations, illnesses, etc.;
- hereditary predisposition, which is expressed in excessive production of acid and gastrin. According to statistics, approximately 30% of patients with peptic ulcers are genetically predisposed to this pathology;
- blood type. Affects the likelihood of pathology and the ability to produce a specific antigen in the digestive juice. People with blood group 0 (1) most often suffer from intestinal ulcers, with group 2 - peptic ulcer;
- surgery on the esophagus (for gastroesophageal reflux). The consequences of surgical intervention disrupt the mechanical conductivity and peristalsis of the stomach.
Causes and risk factors
Peptic ulcers develop when the normal defenses and constant renewal mechanisms of the lining of the stomach or duodenum are weakened, making the lining more likely to be damaged by stomach acid.
The two most common causes of peptic ulcers are:
- Helicobacter pylori infection of the stomach;
- use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
H. pylori infection is present in 50–70% of patients with duodenal ulcers and in 30–50% of patients with gastric ulcers. Helicobacter pylori infection is rare in people under 40 years of age.
NSAID use is responsible for more than 50% of peptic ulcers. However, most people who take NSAIDs do not develop peptic ulcers.
Smokers are more likely to develop peptic ulcers than non-smokers, heal more slowly and are more likely to recur. Although alcohol increases stomach acid production, it appears that drinking moderate amounts of alcohol does not cause ulcers or slow down their healing. Psychological stress can cause ulcers. Doctors found a higher incidence of peptic ulcers in Japan after the earthquake and in New York after the 9/11 terrorist attacks.
A rare cause of peptic ulcers is a type of cancer that releases a hormone called gastrin, which causes excess acid production (see Zollinger-Ellison syndrome). Symptoms of malignant ulcers are very similar to those of non-cancerous ulcers. However, malignant ulcers usually do not respond well to the treatments used for non-cancerous ulcers.
Approximately 50–60% of children with duodenal ulcers have a relative with peptic ulcer disease. Recent evidence suggests that this occurs because H. pylori infection is passed between family members. Doctors doubt that the increased risk of contracting this infection is hereditary.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a peptic ulcer depend on its location and the age of the patient. For example, in elderly and pediatric patients and in cases where the pathology is caused by taking NSAIDs, symptoms may not be obvious or completely absent. Then the pathology is detected when complications develop. The most common manifestation of the disease is pain.
Pain syndrome with peptic ulcers is characterized by the following symptoms:
- It may appear from the navel area to the sternum.
- It becomes more intense on an empty stomach.
- Disturbs me at night.
- Periodically worsens and disappears.
- It is relieved by taking antacids.
In addition to pain, the following are observed:
- nausea with vomiting. When the vomit is dark in color, it indicates internal bleeding;
- weight decreases sharply;
- appetite is impaired;
- the stool becomes black (from blood).
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of peptic ulcer disease can vary depending on the location of the ulcer and the person's age. For example, children, the elderly, and people with ulcers caused by NSAID use may not have the usual signs and symptoms, or may have no symptoms at all. In such cases, ulcers are discovered only when complications develop.
The most common symptom of a peptic ulcer is:
- mild to moderate pain in the upper abdomen.
The pain is usually described as a constant aching, burning, dull, or aching sensation or sometimes a feeling of hunger, and is usually felt in the upper abdomen just below the sternum. It is usually relieved by eating or taking antacids. A typical ulcer usually heals and recurs. Thus, the pain may be felt for days or weeks, then decrease or disappear, and then return with a recurrence of the ulcer. Only half of people have typical symptoms.
The symptoms of duodenal ulcers usually follow a pattern. Patients usually do not have pain upon awakening, but it appears by mid-morning. Drinking milk or eating foods (which act as a buffer against stomach acid), or using antacids often relieves the pain, but it usually returns after 2 or 3 hours. Pain that disrupts sleep is often noted. Often the pain occurs one or more times a day for one to several weeks and then may go away without treatment. However, the pain usually recurs, often within the first 2 years, and in some cases after several years. People usually notice a pattern emerging and can often predict from experience when relapse is more likely (usually in the spring and fall, and also during periods of stress).
Diagnostics
To diagnose peptic ulcers, a comprehensive study is carried out:
- Tests for the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori: blood and stool tests, breath test.
- Clinical analysis of blood and urine.
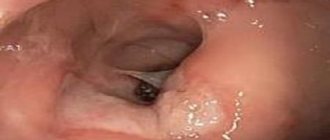
- Endoscopy with biopsy sampling. During the procedure, a flexible endoscope is inserted into the esophagus and passes through the stomach to the duodenum. Helps assess the condition of mucous tissues and determine the localization of the pathological process. Tissue samples are also taken for histological examination.
- X-ray with contrast agent. Helps visualize ulcerative defects.
- Coagulogram. Blood clotting is determined. Low coagulability indicates chronic blood loss.
- pH-metry. Determines stomach acidity.
Causes of the disease
In addition to the imbalance between the secretion of pepsin, hydrochloric acid and a decrease in the protective function of the digestive organs, the following causes of the development of peptic ulcer are identified:
- Helicobacter pylori infection,
- taking certain medications,
- genetic predisposition,
- bad habits
- malignant and benign neoplasms,
- chronic inflammatory processes,
- HIV, syphilis, tuberculosis,
- cancer,
- diabetes.
Stress peptic ulcers of the stomach are often diagnosed with prolonged chronic stress, depression, anxiety due to inflammation of the vagus nerve, which provokes excessive secretion of pepsin and hydrogen chloride and a decrease in the production of protective mucus.
Treatment
The treatment regimen for peptic ulcers includes:
- drug therapy;
- therapeutic nutrition;
- surgical intervention.
The main goal in the treatment of peptic ulcers is to reduce gastric acidity, relieve pain and accelerate reparative processes. In the presence of helicobacteriosis, antibiotics are taken for 1-2 weeks, acid-reducing agents – for several months.
According to the clinical recommendations of the Russian Gastroenterological Association for the diagnosis and treatment of ulcers, the following drugs are prescribed:
| Group of drugs | Name |
| Antibiotics |
|
| Proton pump inhibitors |
|
| H-2 histamine blockers. |
|
| Antacids |
|
| Cytoprotectors |
|
In some cases, radiation therapy is used for peptic ulcers to reduce the production of gastric juice for a long time. It is prescribed to patients who experience frequent exacerbations, as well as to elderly patients or those for whom surgical or drug treatment is contraindicated.
Reasons for treatment failure
Most often, drug therapy for peptic ulcers is effective and ends with complete scarring of the defect. However, if unpleasant manifestations of pathology continue to bother you, it is necessary to be examined to exclude more serious diseases. Sometimes ulcerative formation simply does not respond to drug treatment.
The most common reasons for ulcer resistance to therapy:
- Medicines are taken incorrectly or irregularly, doses are underestimated.
- Some strains of Helicobacter pylori are resistant to antibiotics.
- NSAIDs and other ulcerogenic medications are taken regularly.
- Smoking during treatment.
In some cases, the reasons for the failure of therapy for peptic ulcers may be:
- malignant tumor of the stomach;
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (acid overproduction);
- infection with other bacteria (not Helicobacter pylori);
- other gastrointestinal diseases with the formation of ulcerations (Crohn's disease).
Diet
A therapeutic diet plays an important role in the treatment of peptic ulcers. When prescribing diet therapy, the stage of the disease (exacerbation or remission), features of the clinical picture, existing complications and concomitant diseases are taken into account. Nutrition should help create favorable conditions for the healing of defects, that is, it should be aimed at sparing mucous tissues, inhibiting the production of gastric juice and reducing peristalsis.
During the diet, foods that stimulate gastric secretion are prohibited. The body must be provided with proteins of animal origin, which stimulate tissue regeneration. It is necessary to include in the diet fats that suppress excess gastric secretion. Boiled or steamed pureed dishes are recommended.
The main foods that are recommended to eat for peptic ulcers, and which should be excluded from the diet:
| Recommended | Prohibited |
| Lean boiled meat, steam cutlets, meatballs | Fatty meat, sausages, smoked meats |
| Low-fat boiled fish | Canned meat, fish, vegetables |
| Dried wheat bread | Fresh or rye bread |
| Vegetable puree | Confectionery, chocolate |
| Boiled liquid porridge (rice, buckwheat) | Dried fruits |
| Steam omelette | Citrus fruits, legumes, mushrooms |
| Fruit compotes and jelly, still mineral water, herbal tea | Alcoholic and carbonated drinks, coffee |
Surgical intervention
Surgical operations for peptic ulcers can be emergency or planned. Planned surgical intervention is carried out in the following cases:
- The presence of ulcerative lesions for more than a year.
- Formation of a malignant tumor.
- Penetration.
- Ineffectiveness of drug therapy.
- Short duration of remission.
- Multiple ulcerative lesions.
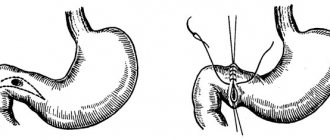
There are several types of surgical operations:
- radical, in which the stomach is completely removed or vagotomy is performed;
- partial, when the affected part of the organ is removed;
- palliative, when complications are eliminated (bleeding, perforation).
Etiology and pathogenesis
The main cause of peptic ulcer is the high acid-producing function of the stomach, which persists in a number of patients after surgery. Education P. I. after operations that exclude the flow of bile into the stomach, the lack of neutralizing effect of bile on gastric juice contributes. So, according to S.S. Yudin, after gastroenterostomy according to Roux, the frequency of P. i. reaches 80%.
After drainage operations in combination with vagotomy, one of the reasons for the remaining high gastric secretion may be incomplete vagotomy, as well as chronic duodenal obstruction, causing impaired gastric evacuation.
After economical resection of the stomach, the formation of P. i. possibly as a result of leaving the pyloric mucosa in the area of the duodenal stump, which causes gastric hypersecretion due to the permanent release of gastrin or due to increased function of the vagus nerves (incomplete vagotomy). P. I. also develop in Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (see Zollinger-Ellison syndrome).
According to M. M. Levin (1961), 80% of all P. i. refers to marginal ulcers of the anastomosis. P. I. can also be localized in the efferent loop (up to 40 cm from the anastomosis), sometimes in the afferent loop and rarely in the gastric stump.
Complications
As the pathological process progresses with a peptic ulcer, dangerous complications may develop:
- Bleeding. Gastrointestinal bleeding is often slow and is manifested only by anemia and the presence of blood in the vomit and stool. However, they can also be severe, requiring emergency hospitalization and blood transfusions.
- Pyloric stenosis. An abnormal narrowing of the pylorus, located between the stomach and intestines, is formed.
- Scar formation. When a peptic ulcer becomes scarred, scar tissue is formed that interferes with the movement of food.
- Penetration. The pathological process spreads to the tissues of neighboring organs (usually the lesser omentum and pancreas).
- Perforation and peritonitis. An ulcerative defect can make a hole in the stomach or intestinal wall, which will cause infection to enter the abdominal cavity.
- Malignization. Degeneration of a peptic ulcer into a malignant process.
Process in the duodenum
The main manifestations of duodenal ulcer are dyspeptic syndrome in the epigastric region. Based on localization, they are divided into bulbous and postbulbar (less common). According to the nature of the course, acute, chronic and severe forms are distinguished. May be combined with peptic ulcers of the stomach and esophagus. More than half of patients experience an increase in hydrogen chloride levels, which is associated with the growth of parenteral cells that produce it. More than 70% of patients are diagnosed with Helicobacter pylori infection. More often, the initial part of the duodenum is damaged and ulcers form. A duodenal ulcer is also called a duodenal ulcer.
Triggers for the development of the disease are:
- eating disorders,
- physical inactivity,
- influence of drugs,
- infections,
- parasites,
- prolonged and chronic stress,
- smoking and substance abuse.
Prevention
Prevention measures for peptic ulcers are as follows:
- adhere to fractional meals 5-6 times a day in small portions (250 g);
- have dinner 3 hours before going to bed;
- follow a therapeutic diet;
- be observed by a gastroenterologist and follow all doctor’s recommendations;
- avoid stressful situations;
- quit smoking and alcohol.
References: https://www.lotos74.ru/about/blog/pepticheskaya-yazva/ https://www.msdmanuals.com/ru/home/digestive-disorders/gastritis-and-peptic-ulcer-disease/peptic -ulcerative disease https://www.regionaalhaigla.ee/sites/default/files/documents/Maohaavand_ja_kaksteistsormiksoole_peptiline_haavand_-_vene_keeles.pdf https://www.krugosvet.ru/enc/medicina/YAZVA_PEPTICHESKAYA.html https://ru. wikipedia.org/wiki/Stomach_ulcer https://crimtj.ru/Journal.files/4-2005-2/121.pdf https://diseases.medelement.com/disease/peptic-ulcer-k27/12248 www.cmei .com.ua/article/pepticheskaya-yazva-zheludka-i-dvenadcatiperstnoy-kishki-prichiny-simptomy-diagnostika-i https://www.ionx-gkt.com.ua/pepticheskaja-jazva.html https://www .kp.ru/guide/dieta-pri-jazve-zheludka.html Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/18/2020
Is it possible to cure an ulcer?
There is no known way to cure stomach ulcers. There are opportunities to slow down the process.
The first is “freezing” the disease. The patient will need to monitor his diet for life and eliminate fatty foods. Such a scheme will allow a person to avoid unbearable pain in the presence of a disease. The patient will have to constantly take the medications prescribed by the doctor, which is considered a small sacrifice.
The second way to solve the problem is surgical intervention. Complete removal of the affected organ is unlikely to have a positive effect on the condition of the body. You should not exclude options with possible partial intervention.
A stomach ulcer is an unpleasant, nasty disease. People who consciously approach treatment should not worry. You can learn to live with a disease.
Treatment of ulcers with folk remedies
Drug treatment can be combined with traditional medicine to quickly achieve a positive effect. One common remedy is rosehip oil. You need to take a glass of oil and mix with 1 tsp. propolis powder. Place the product in a water bath for half an hour, stirring it occasionally. Then let it cool, strain and drink 30 ml before meals.
Bananas are beneficial for peptic ulcers. They contain a component that forms a coating on the inside of the stomach. It helps reduce pain and irritation caused by peptic ulcers. It is recommended to consume bananas regularly, 2 bananas per day, combined with a glass of milk. During treatment, it is effective to eat honey mixed with fresh aloe juice. Both ingredients should be taken in equal proportions. Another useful remedy is chamomile tea. You can mix it with other ingredients, for example, linden or mint.
It is recommended to drink 100 ml of blackcurrant juice for 30 days. To replenish protein reserves in the body, it is beneficial to take almond milk. It neutralizes acids and helps treat peptic ulcers. As a preventive measure against exacerbations of peptic ulcer disease, it is recommended to drink fresh potato juice before meals at least 3 times a day. The course of admission is 10 days.
To prevent pain, you need to drink 2 egg whites at night. It is best to take homemade country eggs. You can drink goat's milk to relieve pain.
Description of the disease
During the normal functioning of the organ, protective factors traditionally predominate. These include:
- stomach mucus;
- adequate blood flow occurring in the microvasculature of this organ;
- alkaline bicarbonate secreted by the mucosa;
- constant synthesis of prostaglandins;
- renewal of cells of the gastric mucosa.
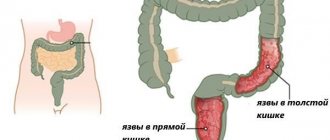
The disease affects not only young people, but also older people, regardless of their gender. According to the location of the pathological process, ulcers are divided into types, differing in the location of the mucosal lesion:
- fundus of the stomach;
- duodenal bulbs;
- postbulbar region;
- combined, having dual localization.
The classification of the course of this disease is as follows:
- with uncomplicated development;
- aggravated complication with bleeding;
- penetrating gastric ulcer;
- with pyloric stenosis;
- complicated by perivisceritis.
We recommend reading: Table in cm and age
In pathology, gastric defects (perforated or through area) are considered small if they are up to 0.5 cm, giant - more than 3 cm, everything in between these values is the average.
What types of stomach ulcers are there? We list only some forms and types of stomach ulcers, which few ordinary people have even heard of:
- peptic ulcer of the stomach;
- callus ulcer;
- mirror stomach ulcer;
- infiltrative gastric ulcer;
- stress stomach ulcer;
- callous gastric ulcer.
Treatment methods for peptic ulcers
In case of uncomplicated course and low acidity, conservative treatment in a hospital followed by a sanatorium stay is recommended. The main method of therapy is surgery to eliminate defects from previous operations.
Peptic ulcers of gastroanastomosis and recurrent duodenal ulcer after vagotomy are complicated by penetration in more than half of the cases. This explains the severe pain and makes the operation difficult.
The most dangerous and severe complication of peptic ulcer anastomosis is gastrointestinal fistula. Symptoms change dramatically: pain disappears, diarrhea appears up to 15-20 times a day, and fecal odor from the mouth. The treatment method is surgical after intensive preparation.
Important in the treatment complex is not only drug therapy and surgical methods, but also diet, reducing physical activity and reducing stress.
When the first signs of a peptic ulcer appear, you should consult a doctor, undergo an examination and follow recommendations for taking medications, nutrition, daily routine and lifestyle. In the postoperative period, it is especially important to take all measures to avoid relapse of peptic ulcer disease and the development of complications, namely staying in the hospital under the supervision of medical personnel, performing all recommended measures, and taking the necessary medications.
Diet for illness
If you have a peptic ulcer, you must strictly adhere to your diet. The diet should include foods that have little effect on secretion. The products should be boiled, steamed or pureed in a blender. You can eat white bread, but yesterday's bread, not fresh. For cookies, it is better to choose biscuits or dry biscuits. Meat and fish need to be cooked. It is advisable to eat more dairy products; it is better to make soft-boiled eggs or cook an omelet. It is preferable to choose buckwheat, oatmeal and rice from cereals. It is recommended to consume more vegetable soups and puddings. Salads should be seasoned with olive or sunflower oil.
It is necessary to exclude sweet carbonated drinks, alcohol, chocolate, coffee, spicy and smoked foods, and fried foods from the diet. You should forget about canned food and fatty foods. It is not recommended to eat ice cream, foods high in salt, and mushrooms. Meals should be divided into 6 meals. Food should be eaten warm. You should eat slowly, chewing your food well. It is recommended to drink 200 g of oatmeal jelly after eating. It promotes rapid healing of the wound. It is advisable to be in a sitting position while eating food.
Development of the process in the esophagus
The most rare type of peptic ulcer disease is damage to the distal segment of the esophagus. In 20% of cases it is combined with peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. They are divided into chronic (when the cause exists for a long time) and acute (arising after surgery, accompanied by vomiting of acidic stomach contents). The ratio of ulcers on the esophagus to damage to the stomach and duodenum is 1:50. Peptic ulcers on the esophagus occur in the lower part of the organ, in a place where gastric contents are often thrown back, corroding the tissue. At the initial stage, when exposed to gastric secretions, hyperemia of the epithelium appears, followed by the formation of ulcers, which heal with the appearance of scars. Refusal of stomach contents occurs, among other things, due to dysfunction of the sphincter of the lower esophagus. Therefore, the precursor of peptic ulcer of the esophagus is reflux esophagitis. Etiologically, this disease is divided into symptomatic and peptic. Symptomatic ones are characterized by the absence of a hiatal hernia or gastroesophageal reflux.
A peptic ulcer of the esophagus develops when:
- the entry of hydrochloric acid and enzymes from the stomach into the esophagus,
- axial hiatal hernia,
- after surgery on the lower esophageal sphincter,
- violation of peristalsis,
- diseases of the biliary system.
Symptoms and clinical picture:
- frequent heartburn,
- vomit,
- pain when swallowing,
- melena (dark-colored stool due to blood present in it),
- dysphagia (swallowing disorder).
Medicines
Antibiotics for a course of 2-3 weeks for Helicobacter infection: “Ospamox”, “Klacid”, “Flagyl”, “Tetracycline”.- Blockers of acid secretion in parietal cells: “Omez”, “Pariet”, “Nexium”, “Proxium”, “Lanza”. To reduce gastric secretion, Ranitidine, Kvamatel, Nizatidine are prescribed.
- Antacids for the chemical neutralization of hydrochloric acid in the stomach with the elimination of heartburn, belching, nausea: “Rennie”, “Maalox”, “Almagel”, “Gastal”, “Gaviscon”, etc.
- Cytoprotectors for protecting the gastrointestinal mucosa: Cytotec, Venter, De-Nol.
Diet therapy
If the diagnosis of peptic ulcer is not confirmed, then a person should still think about what he eats. A large number of diseases appear precisely because of poor nutrition. All kinds of fast foods not only spoil a person’s appearance, but create a favorable environment for the development of dangerous bacteria.
It is believed that diseases such as stomach cancer occur precisely because of poor nutrition. This is why diet for ulcers is very important. With it you will have to give up most of your favorite treats. Also, the first thing to remember is that during illness the body is not ready to spend all its energy on digesting heavy food. He should think only about recovery and strive for this in every possible way.
There are times when only proper nutrition will help a person get better. For example, if the valve between the stomach and esophagus does not close, then various medications simply cannot help.
But one of the advantages of diet treatment is that there are not so many restrictions. It's worth forgetting about:
- fried foods;
- fatty pork;
- all kinds of spices;
- alcohol;
- smoked meats
It should be said that such food will be especially harmful for a person in good health. And for the patient it is very dangerous.
You need to try to eat only healthy foods. Food should contain all the necessary vitamins, minerals, sufficient carbohydrates and proteins. In each of these groups there are such useful products that the body is ready to accept them with pleasure every day. This:
- Vegetables (beets, zucchini, carrots, fresh and stewed broccoli).
- Fruits and berries (apples, peaches, grapes, raspberries, wild strawberries, etc.) It is important to remember when choosing these fruits that if they grow in the region where you live, then the benefits from them are much greater. You can and should prepare a variety of juices, jellies, and compotes from them. The most useful drink for any diseases associated with the stomach is jelly.
- Grains and cereals (crackers, rice and oatmeal, which is unloved by many).
- Dairy products (sour cream, cream, kefir, curd products). When choosing them, you need to pay attention first of all to fat content. If it is exceeded, then it is best to avoid consuming such products. You can combine dairy products with fruits, berries or porridge.
- Protein (nuts, seafood, chicken, beans, eggs).
All these products need to be cooked correctly. There should not be a large amount of oil here. Dishes should be baked, steamed or boiled. Particular preference should be given to sea fish and seafood, as they are very healthy.
Surgery
In some cases, doctors are able to offer the patient surgery. This can happen because drug treatment does not produce positive results or in emergency situations. One of these is bleeding. Before surgery, patients receive special treatment so that the ulcer is desirable to decrease in size. After surgery, some patients may experience an unpleasant surprise—complications. This may occur due to surgical errors or non-compliance with the postoperative regimen.
Postoperative complication of pathology
Postoperative complications include functional or organic disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as intraperitoneal processes. But this division is very arbitrary, and only determines the tactics for a specialist. Many of the acute conditions can become chronic, including:
- postoperative pancreatitis;
- postoperative peritonitis;
- postoperative disorders of motor and evacuation functions of the gastrointestinal tract.
The last complication is the most common after operations in the early period. It can include various, sometimes contradictory, symptoms.
Diagnosis of peptic ulcer
To detect an ulcer, your doctor may order the following tests and procedures:
1. Test for H. pylori.
Tests are recommended first to determine the presence of H. pylori in the body. Tests can be different, depending on the situation. This could be a blood test, a stool test, or a breath test.
For a breath test, the patient drinks a glass of water containing a substance containing radioactive carbon. H. pylori breaks down this substance in the stomach. After this, the patient must blow into a special container. If a person is infected with H. pylori, the sample will contain that same radioactive isotope.
2. Endospokia.
For endoscopy, the doctor inserts a flexible hollow tube equipped with a video camera through the patient's mouth. This tube (endoscope) can pass through the esophagus and stomach, all the way to the duodenum. Using an endoscope, you can examine ulcers on the mucous membrane, as well as perform a biopsy - take a piece of tissue for analysis.
A biopsy helps identify H. pylori in the gastric mucosa. In addition, a biopsy is used to confirm cancer. For this reason, endoscopy is recommended for elderly patients who have signs of bleeding, as well as those who have abdominal pain accompanied by weight loss and difficulty swallowing.