Causes
Factors that provoke the development of gastric ulcers in children can be divided into three groups:
- Exogenous or external.
- Endogenous or internal.
- Minor factors that have an indirect effect on the development of the disease.
Among the internal factors, the most common are:
- Active activity of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. It is this microorganism that is the main provocateur of peptic ulcers.
- Problems associated with insufficient motility of the gastrointestinal tract. For this reason, stagnation and problems arise in the process of digesting food.
- Predisposition to the development of the disease at the genetic level.
- Complicated course of other pathological processes, in particular gastroenteritis or gastritis, which are chronic.
The most common external causes of peptic ulcers are:
- Poor nutrition: lack of eating routine, consumption of potentially harmful foods.
- Treatment with certain medications.
- Lack of first courses in the child’s daily diet.
- Overeating or having long breaks between meals.
- Frequent consumption of spicy and fatty foods.
- Poor chewing of food.
The disease can develop under the influence of secondary factors:
- Stress. Severe and prolonged stress conditions can create favorable conditions for the development of ulcers.
- Emotionality. If a child has increased nervous excitability, he may develop a peptic ulcer.
- The presence of factors that adversely affect the fragile psyche of the child.
Prevention
If there is a hereditary predisposition to this disease, parents should pay special attention to preventive measures. To do this, you should adhere to the following rules:
- Baby food should be regular and balanced.
- The diet is appropriate for the child’s age.
- Correct lifestyle: eliminate smoking, alcohol; involve in sports.
- A comfortable psychological atmosphere should reign in the family - without stress and conflicts.
Properly organized by parents diet and life in general will help to avoid the development of a dangerous disease in the child.
Symptoms
The main symptom of a stomach ulcer in children is pain in the navel area. At the same time, unpleasant sensations tend to radiate to the lumbar and back areas. As a rule, such pain is rhythmic, periodic in nature and can both increase and subside as the disease further progresses.
In children, a stomach ulcer is manifested by the following symptoms:
- a noticeable decrease in appetite or its complete absence;
- periodic nausea and vomiting;
- the presence of belching that has a sour taste;
- development of vetetative dysfunction;
- problems with stool, when diarrhea alternates with constipation;
- severe heartburn.
This is the main symptom, which may be supplemented by other symptoms.
Important! If a child has at least two of the signs described above, it is necessary to immediately take him to a specialist. Symptomatic manifestations of ulcers are often accompanied by colds.
As a rule, stomach pain in children worsens in the morning, immediately after waking up. Half an hour after eating, the pain syndrome can reach its peak. It is also possible to experience night pain, the intensity of which can be reduced by drinking a glass of water or milk.
Pain in the abdomen can be of a different nature, depending on the location of the inflammation. During periods of exacerbation, the child subconsciously tries to take the fetal position, pulling his legs towards his stomach.
In this way he manages to reduce discomfort. If the ulceration forms on the anterior surface of the stomach, then to reduce pain the patient should take a supine position.
Summary for parents
Peptic ulcer disease can develop at any age of a child, but most often occurs in adolescents. This is a fairly serious pathology that can cause severe complications requiring surgical treatment. Proper nutrition of children from an early age is important, one of the main preventive measures to prevent stomach ulcers.
If a child has complaints from the digestive organs, one should not delay contacting a pediatrician or pediatric gastroenterologist and prescribing an examination. Properly administered therapy and strict adherence to all medical recommendations will lead to a cure for peptic ulcer disease.
School of Dr. Komarovsky, in the “Pharmacy” section, Evgeniy Olegovich talks about medicines for gastritis and stomach ulcers (from 12:00 min.):
Complications
If a stomach ulcer in a child is not treated in a timely manner, it can cause the development of serious complications:
- Bleeding. This is one of the most common and dangerous consequences of peptic ulcer disease. With the development of internal bleeding, a sharp deterioration in the patient’s well-being appears, blood pressure drops, and the stool becomes black. Vomiting “coffee grounds” is possible, which directly indicates the development of bleeding.
- Penetration. The ulcer grows through the wall of the stomach and spreads to other organs located near the stomach. This is a very rare complication that develops as a result of the wrong choice of therapy or prolonged ignoring of the symptoms of the disease.
- Perforation. As a result of an ulcer, a through hole appears in the wall of the stomach through which food can enter the peritoneum. In this case, the patient experiences extremely severe pain. This condition requires urgent hospitalization of the patient. As a rule, such a defect appears at the last stage of peptic ulcer disease.
- Perforation. It is characterized by the development of severe pain that can cause the patient to go into shock.
Important! If a patient develops perforation against the background of a peptic ulcer, then during palpation of the peritoneum, the specialist may note the disappearance of hepatic dullness. This occurs due to the entry of air into the abdominal cavity.
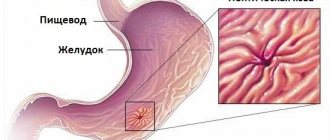
What is peptic ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease is a violation of the integrity of the internal walls of the stomach or duodenum in the form of ulcers of different sizes. They are the result of the action of acids, digestive enzymes, bacteria and many other factors on the walls of the stomach.
The localization of these ulcerations can be in various parts of the digestive tract. This disease is characterized by a long and persistent course, which is especially difficult for the child’s body.
The appearance of ulcers on the lining of the stomach or duodenum in children (even very young ones) is no longer a rare occurrence. Therefore, parents should arm themselves with information regarding this pathology.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is carried out by a pediatrician and gastroenterologist. The examination of the patient's condition begins with collecting anamnesis and palpation. An experienced doctor is able to make a preliminary diagnosis to the patient based on examination, after which the patient is sent for examination. The following procedures are distinguished for diagnosing peptic ulcer disease:
- X-ray of the upper intestine. The stomach, esophagus and duodenum are examined. For this, a contrast agent is used - a barium solution, which the child drinks before the procedure.
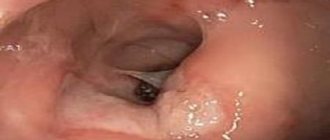
- Endoscopy. It involves inserting a probe into the child’s body through the esophagus. At the other end of the tube there is a camera with a small light, which allows you to determine the degree of progression of the disease.
- Biopsy. Damaged tissues are taken for analysis for the purpose of subsequent study for the presence of the microorganism Helicobacter pylori.
- pH-metry is a procedure that involves inserting a probe into the patient’s stomach to determine the level of acidity.
- Ultrasound of the stomach. Allows you to obtain additional information about the state of the organ. Due to the limitations of the visible contours of the organ, the procedure is prescribed quite rarely.
- Duodenal sounding. Usually performed on older children. The procedure allows you to examine the composition of gastric juice and bile and evaluate the functioning of the liver.
Treatment
Treatment of stomach ulcers depends on a number of factors and is prescribed individually. When developing a course of therapy, the doctor takes into account the characteristics of the patient’s body, age, and degree of progression of the pathology.
Medicines
The basis of treatment for gastric ulcers in children is taking medications that are prescribed based on a thorough diagnosis. Certain medications are used in complex therapy depending on the degree of development of the disease. The most commonly used drugs are the following groups:
- Antibiotics. These drugs help destroy pathogenic microorganisms Helicobacter pylori.
- Proton pump inhibitors. They block the production of stomach acid.
- H2 blockers. Suppress the production of hydrochloric acid, which has a destructive effect on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Medications with an enveloping effect that provide the mucous membrane with the necessary protection and prevent its further destruction.
Important! Most often, children are prescribed vitamin complexes that help increase the body's defenses.
Surgical intervention
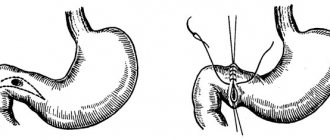
Surgery for ulcerative lesions is performed extremely rarely. Timely drug therapy allows you to get rid of the main provocateur of the disease and promotes the healing of existing defects.
Surgery is indicated in cases where the patient’s body does not respond to medications. Most often, the wound is sutured.
Diet
Diet for stomach ulcers is one of the elements of successful treatment of the disease. Significant adjustments will have to be made to the child’s diet by excluding the following foods:
- smoked, salted, peppered, fried food;
- canned and pickled foods;
- hot sauces and spices;
- fat meat.
Important! The diet should be balanced; the child’s daily diet should contain vegetables and fruits, both fresh and as part of various dishes.
Stomach ulcer in children
Peptic ulcer disease, which affects the stomachs of children and is accompanied by the occurrence of erosions in the epithelial part of the organ, is a rare disease. There are chronic, acute, recurrent forms of pathology.
Children suffer from ulcers for many reasons, the main ones being gastroduodenitis and chronic gastritis. In the absence of adequate treatment, the ulcer spreads to the epithelial mucosa in the duodenum.
Phases of gastric ulcer in children
There is a phase division into three types:
- An exacerbation occurring in two stages: a new or fresh ulcer;
- epithelization or spontaneous closure of an ulcerative wound.
Ulcers correspond to mild, moderate, severe, active and inactive forms.
Diagnostic procedures
Breath test for Helicobacter pylori (Hp+ or Hp-).
- Inspection and palpation. In adolescents, the localization of the pain syndrome, muscle tension in the abdominal wall, and the presence of regional (partial) spasm are determined.
- Laboratory tests performed to identify possible complications.
The range of tests includes blood and stool testing. - Instrumental diagnostics.
Consists of the following examinations: - fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy, which makes it possible to make a diagnosis and take a biopsy specimen for histological analysis in case of an increased risk of developing a tumor process;
- an electrometric method for measuring the acidity of the environment in the stomach, carried out to determine the pH level of gastric juice and assess the acid-forming properties of the stomach;
- Ultrasound performed to exclude background pathologies.
X-ray contrast examination of organs located in the upper gastrointestinal tract;
- CT scan, performed when there is an increased risk of the disease spreading beyond the stomach (penetration) or narrowing of blood vessels in the organ (stenosis);
Treatment
Children's ulcers are treated with diets and medications. Surgery is indicated only in severe, complicated cases. At any stage of peptic ulcer, the child must adhere to a certain diet.
Traditional Treatments
Taking a multivitamin complex is a traditional method of treatment.
Traditional treatment methods include the following set of measures:
- diet therapy;
- taking proton inhibitors such as Omeprazole, Lansoprazole, Rabeprazole, Esomeprazole;
- taking a multivitamin complex;
- treatment with mineral water with an alkaline environment.
At the acute stage, more effective antisecretory medications are additionally prescribed - histamine H2 receptor blockers. The course of treatment varies between 14 days and 5 weeks, depending on the complexity of the case. If bleeding develops, hemostatic therapy is carried out, cold is applied to the abdomen, and the diet is revised.
Surgical treatment options
Surgery may be prescribed in particularly severe cases, for example, when complications develop. In case of perforation of gastric tissue with the formation of a through ulcer or intractable bleeding, gentle surgical methods are used. For example, with a through ulceration of the wall, the wound is sutured.
Preventive measures
Peptic ulcer disease of children's stomachs is easier to prevent than to cure, since the pathology is chronic. Necessary preventive measures:
- Night rest should correspond to the age category of small patients: in 1-2 years, up to 14 hours of sleep are required;
- up to 5 years - 12 hours;
- from 7 years - 9 hours.