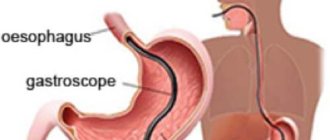
Gastroscopy is an effective endoscopic diagnostic method that allows you to examine the condition of the gastrointestinal tract. For this type of examination, a special device called a gastroscope is used, which is a flexible tube with fiber optics. A medical video endoscope equipped with an electronic sensor is also used, using the device to obtain an image on the screen.
There are a number of types of endoscopic examination:
- Fibrogastroscopy, gastrofibroscopy, gastroendoscopy or gastroenteroscopy (abbreviated name - FGS) is used when examining the stomach to evaluate the mucous membrane of the organ and identify diseases.
- Esophagoscopy involves examining the mucous membrane of the esophagus.
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (abbreviated as EGDS). With this type of diagnosis, the esophagus, stomach and duodenum are examined.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy, gastroduodenoscopy (abbreviated as FGDS). During this procedure, the stomach and duodenum are examined.
This division of types of research using a gastroscope is not rigid. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract have similar symptoms. If, during examination of the esophagus, suspicions arise about the occurrence of pathological processes in other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, the doctor may decide to examine the suspicious areas.
Table of contents
- What is gastroscopy: the essence and principle of diagnosis. Indications
- Necessary tests before the examination
- What does endoscopic diagnostics show?
- How the research works
- Nutrition before gastroscopy
After the procedure
Upon completion of gastroscopy, the patient may experience a feeling of bloating, belching, and nausea. Within two days after the procedure, the presence of these conditions is normal. After gastroscopy under anesthesia, among other things, the patient may experience slight dizziness. But if you don’t feel well, you should consult a doctor. You also need to return to the clinic if severe, incessant pain in the stomach appears, the temperature rises, vomiting begins with the release of blood, and the stool becomes liquid and black. If the procedure was performed by experienced specialists using modern equipment, then complications are unlikely to arise. Nevertheless, they cannot be excluded from attention.
Nutrition after gastroscopy
You can eat and drink after the tongue and swallowing reflex have returned. This will take from 10 minutes to several hours. On the first day, a light meal is recommended: steamed lean meat, boiled vegetables, liquid porridge. Banned are sweets, baked goods, legumes, nuts, and fiber. In the following days, it is advisable to remove fast food, fatty and smoked foods from your diet. Further, if the patient does not have serious gastrointestinal diseases, there are no strict food restrictions.
Gastroscopy - what is it?
Invasive methods are widely used to diagnose gastroenterological pathologies.
Gastroscopy is an examination of the upper digestive tract, including the stomach and part of the duodenum. The path of the gastroscope passes through the esophagus, so the doctor can also examine its standing. In this case, the method is called esophagogastroscopy.
The examination is performed using a special device, which is equipped with a fiber-optic system. Patients should be aware that endoscopy and gastroscopy are names for the same test. Fibrogastroscopy is prescribed in cases where it is necessary to check the condition of the mucous membrane, evaluate the anatomical and functional features of the organ, determine the presence of defects and additional formations, such as varicose veins, ulcers, erosions, gastric atrophy or neoplasms of a malignant or benign nature.
Indications
Gastroscopy is performed routinely and in emergency cases. For patients with chronic pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, the study is prescribed by a gastroenterologist. The method is informative when:
- acute gastritis;
- inflammatory processes of the mucous membrane of the upper parts of the digestive system of a chronic nature;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- malignant neoplasms;
- polyps;
- suspicion of the presence of a bezoar, ectopia of the mucosa;
- signs of intestinal metaplasia;
- changes in blood vessels in the esophagus.
This is interesting!
The study is prescribed to conduct a test for Helicobacter pylori and for dynamic monitoring of pathological processes.
Emergency diagnosis is carried out in the following situations:
- if gastrointestinal bleeding occurs;
- to remove a foreign body in the lumen of the esophagus and stomach;
- in order to verify functional or anatomical stenosis in the pyloroduodenal area.
Gastroscopy can be diagnostic and therapeutic.
Carefully!
Gastroscopic examination is contraindicated if it is impossible to pass the endoscope through the esophagus due to narrowing. This condition may be caused by scar changes after chemical and thermal burns, aortic aneurysm, and tumors.
Necessary tests before the examination
FGS refers to invasive interventions. In rare cases, complications may occur during the examination. In order to reduce the likelihood of negative reactions and protect the patient, the attending physician prescribes an examination before performing the procedure.
The list includes the following tests:
- general clinical blood test with a detailed formula, HIV, hepatitis B and C;
- determination of blood group and Rh factor;
- coagulogram;
- electrocardiogram (for persons with diseases of the cardiovascular system).
What the study shows
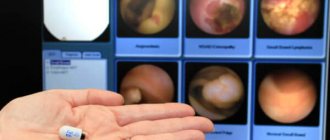
The examination shows changes on the inner wall of the stomach. Gastroscopy of the stomach is done to confirm or refute:
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane. At the same time, the degree, nature and prevalence of the process are assessed.
- Erosion and ulcerative lesions. If necessary, tissue sampling (biopsy) is performed to study morphological changes at the cellular level.
- Tumors. Depending on the type of tumor, a biopsy may be performed.
- Changes in the morphology of organ folds.
With the help of gastroscopy, differential diagnosis of hypertrophic and atrophic processes on the mucous membrane of the organ, varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach is performed. The study shows the volume of mucus in the lumen of the stomach, as well as the functional state of the pyloroduodenal area. The appearance of bile in the stomach indicates reflux gastritis. Advanced visualization helps to choose the optimal location for a biopsy, correctly assess the degree of organ damage and select the correct therapy.
Performing a gastroscopy procedure
Gastroscopy is performed in a special room at a medical institution, most often using local anesthesia. Sometimes general anesthesia is prescribed. To relieve the gag reflex, the patient’s larynx and esophagus are subject to mandatory irrigation with the drug. The effect of the drug stops after 30-40 minutes. The endoscope and all medical instruments undergo mandatory multi-stage disinfection in antibacterial solutions. This completely eliminates the transmission of infection!
The patient lies on the couch on his left side, bending his knees to his chest. There is a nurse nearby who helps the patient during the procedure. The doctor carefully inserts the probe through the oral cavity into the esophagus and stomach, and, if necessary, into the intestine. When inserting a flexible tube, you need to breathe deeply and try to relax. The doctor will ask you to make swallowing movements. Don't be afraid of the air supplied through the tube. It is necessary for straightening the walls of the esophagus and stomach.
The resulting image is transmitted to the monitor. Based on the picture seen, the diagnosis is established or refuted. In acute cases, a biopsy or emergency treatment methods are immediately performed - stopping bleeding, removing polyps. The information obtained as a result of examination of internal organs is recorded and written to disk. The typical procedure takes approximately 15 minutes. After all the manipulations, the gastroscope is carefully removed.
During gastroscopy, the patient may experience slight discomfort - an unpleasant feeling of a foreign body inside himself. Some people experience strong vomiting, which can be stopped with calm, deep breathing.
How to do gastroscopy of the stomach
The examination is carried out by a qualified specialist. Diagnosis can be performed using local anesthesia or under general anesthesia (during sleep). In any case, medication support is necessary. A gastroscopy of the stomach is performed using a fiberscope.
The device is equipped with an optical system and a light bulb, which serves to illuminate the internal surface of the organ, tools for manipulation and taking a biopsy. The device is inserted through the mouth, gradually advancing the tube to the stomach, and, if necessary, to the upper intestines.
How the research works
Patient preparation is required to perform the procedure. It differs depending on the type of anesthesia. If local anesthesia and subsequent examination of the stomach are planned, gastroscopy is performed in such a way that the patient remains conscious for the entire period. This study is done quickly - 7-10 minutes. If there are circumstances where an examination is needed over a long period of time, a drug for general anesthesia is administered intravenously to the person. For this it is important to prepare in advance.
Attention!
Gastroscopy in medicated sleep is prescribed in the morning on an empty stomach.
The general methodology includes the following steps:
- The patient is placed on his left side with his knees brought to the stomach. In this case, your back should be perpendicular to the couch.
- The pharynx is pre-irrigated with an anesthetic to reduce the occurrence of the gag reflex and involuntary cough.
- Install a mouthpiece.
- The tube is inserted into the oral cavity, gradually moving along the digestive tract.
- The specialist pumps air into the stomach for better visualization.
- The walls of the organ are examined.
- During the examination, a histological examination is performed, if necessary.
- The fiberscope is removed slowly to avoid traumatic damage to the soft tissues of the stomach, esophagus and duodenum.
During gastroscopy, a scaled image is displayed on the monitor.
Biopsy
Adult patients can undergo advanced diagnostics - perform a gastric biopsy using gastroscopy. During the procedure, tissue samples are taken with special forceps at the border of the changed and healthy areas of the mucosa. The number of samples required for histological examination is from 3 to 5.
If a tumor is suspected, chromoscopy is additionally used. The method consists of staining mucosal tissues with safe dyes in the area of suspicious areas. This allows for differential diagnosis between benign and malignant processes, as well as determining the extent of organ damage.
Helicobacter pylori
In addition to identifying pathological formations, a biopsy helps to identify Helicobacter pylori. Various studies of the obtained tissue sections are carried out.
Testing for Helicobacter pylori includes:
- microscopy;
- immunohistochemistry;
- PCR to clarify the presence of pathogen DNA;
- cultural method;
- pH-metry;
- urease test.
Additionally, swabs are taken from the surface of the stomach and the degree of contamination of the mucous membrane is determined.
How long does gastroscopy of the stomach take?
When performing FEGDS, the fiberscope is advanced to the duodenum. This allows the specialist to examine the upper digestive tract, the initial parts of the small intestine, including the nipple of Vater. Depending on the manipulations that are planned during the procedure, gastroscopy of the stomach lasts from 3 minutes to half an hour. A visual examination of internal organs without a biopsy takes 3-10 minutes. If additional studies, biopsy, and therapeutic manipulations are performed, the procedure is carried out from 15 to 30 minutes.
How to behave during the procedure
During the examination, it is important to be in the optimal position, despite physical and emotional discomfort. To do this, before the study, the patient is told how to behave and breathe correctly. It is necessary to take evenly slow inhalations and exhalations through the nose. This allows you to relax and ensures that enough oxygen reaches your lungs.
How is diagnosis carried out?
To know how to properly prepare for gastroscopy of the stomach, you need to understand how it is performed. This will help you understand what factors can change the reliability of the final indicators.
All information that the endoscope camera sees is used to make an accurate diagnosis and monitor the course of treatment
To carry out the examination, local anesthesia is used, and in some cases the procedure is carried out in a state of medicated sleep. The traditional method of gastroscopy lasts no more than 15 minutes. The patient is placed on his left side, and a mouthguard (a special device) is placed between the teeth, allowing the insertion of an endoscopic probe with a video camera. To gradually penetrate the esophagus, the patient takes a deep sip, after which saliva cannot be swallowed - excess is removed by suction.
Biopsy forceps and other instruments can be attached to the probe, allowing not only to obtain an image, but also to perform the necessary medical procedures.
How to prepare for gastroscopy of the stomach in an adult
The gastroenterologist prescribes examinations for adults according to indications. Preliminarily determines how the procedure will take place: with or without a biopsy, with anesthesia or under local anesthesia. After this, he tells the patient how to properly prepare for gastroscopy of the stomach. Recommendations depend on the time of the procedure, the presence of bad habits, and the need to take medications. They take into account the risk of complications and warn about the appearance of discomfort after the examination.
Meals before the examination
One of the main questions is: what can you eat on the eve of diagnosis. Most often, the procedure is prescribed in the first half of the day. Therefore, the last meal should be in the evening. It is recommended to refrain from eating after 19:00. Nutrition before gastroscopy of the stomach has the features presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Allowed and prohibited foods before gastroscopy
| Can | It is forbidden |
| Mashed potatoes, porridge (rolled oats, buckwheat) | Fatty meat, fish |
| Vegetable soups | Pickled vegetables, smoked meats, canned food |
| Steamed meat cutlets from lean meats and fish | Mushroom dishes |
| Fruit decoctions | Seasonings, hot sauces, mayonnaise |
| Boiled eggs | Whole milk, full fat cottage cheese |
| Dried white bread | Pasta, yeast bread and baked goods |
| Baked vegetables, vegetable stew | Citrus fruits, tomatoes, legumes |
Important!
The diet should be followed for 48 hours.
Is it possible to drink water before gastroscopy of the stomach?
Experts advise drinking drinks at room temperature or warm the day before the test. Avoid carbonated water, strong tea, coffee, and juices, because they affect the acidity of gastric juice. It is strictly forbidden to take alcohol, given its irritating effect on the mucous membranes and an increase in the gag reflex. Stop drinking water 3 hours before gastroscopy.
Is it possible to smoke
Tobacco smoke has an irritating effect on the upper digestive tract. You should not smoke the day before, because such a negative factor can cause difficulty in carrying out the procedure and incorrect interpretation of gastroscopy data. It is recommended to refrain from bad habits 3-4 hours before diagnosis.
Preparation for gastroscopy of the stomach in the morning
A more comfortable option is to conduct the examination in the first half of the day. If the appointment is at 10 am or earlier, then preparation consists of the following points:
- do not eat after waking up in the morning;
- drink before gastroscopy of the stomach in the morning only 2-3 hours before the start of manipulations in an amount of no more than 100 ml of liquid;
- limit oral intake of medications;
- You can brush your teeth first.
Important!
Taking pills immediately before the test is prohibited. Discuss with your doctor in advance which medications should be temporarily limited.
If flatulence (bloating) occurs, sorbents and defoamers (Espumizan, Infacol) are prescribed before diagnosis.
Preparation for the study in the afternoon
In some clinics, patients are received for endoscopic diagnostics in the evening (until 18.00). Therefore, we will consider how to prepare for gastroscopy in the afternoon and how much you should not eat before diagnosis. Given the functional characteristics of the stomach, digestion of food can take from 1.5 to 3 hours. Therefore, there are recommendations for nutrition and drinking regime (Table 2).
Table 2. Recommendations for preparing for gastroscopy in the afternoon
| Study execution time | Recommendations |
| Reception at 14.00 | It is better to refrain from eating. If you need to adhere to your diet, you can eat a light breakfast before 7.00. Drink water before 12.00 |
| Reception at 16.00 | Last meal before 8.00. They drink water until 14.00 |
| Reception at 18.00 | You are allowed to have breakfast in the morning from 9.00 to 10.00. You can drink water after lunch until 16.00 |
What to take with you to the examination
You should sign up for the study in advance. On the eve of the procedure, the doctor who will perform the gastroscopy tells you what you need to take with you.
Standard requirements - the patient must bring with him:
- medications for routine therapy (pills that the patient takes);
- referral for research, which contains the patient’s data, a preliminary diagnosis, confirmed by the seal of the institution and the signature of the doctor;
- previous FGDS conclusions to compare results and control therapy;
- outpatient card;
- towel or disposable sheet;
- shoe covers or replacement shoes.
You can take medications to lower your blood pressure and sedatives with you.
Preparation for gastroscopy under anesthesia
In this case, more thorough preparation is required. The patient must provide the results of an electrocardiogram and fluorography, as well as a number of laboratory tests. The doctor collects a thorough medical history and asks about existing chronic diseases. If the patient has taken any medications in the last few weeks, he should inform the specialist about this.
In order to prepare for anesthesia, doctors offer muscle relaxants. They help the body better absorb anesthesia.
- Sedation (superficial drug-induced sleep). There is a forced relaxation of the esophageal muscles.
- General anesthesia. Involves complete immersion of the patient into sleep. The option is more complex and requires the use of breathing and tracking devices. Done only in case of emergency.
To prevent complications, gastroscopy under anesthesia is performed in the presence of an anesthesiologist. Sleep duration is about 30 minutes. During this time, you can have time to conduct a study, take a biopsy and perform simple medical procedures (stop bleeding, remove a polyp).
After general anesthesia, it takes about a day to restore the nervous system. You cannot drive a car or engage in any activity that requires increased concentration.
When is it appointed?
The decision about the need for medicinal sleep or anesthesia is always made by the doctor. Emergency procedures are not carried out in this way due to lack of time to select and administer the drug. In addition, the specialist does not have information about the patient’s health status, there is no diagnosis and examination results.
Conditions for performing gastroscopy under anesthesia:
- availability of an anesthesiologist and appropriate equipment;
- the patient’s consent to perform the manipulation during medicated sleep or under anesthesia;
- research results (FLG, blood test and others).
The medical indication is a strong gag reflex, which makes the examination difficult. Also, these may be inflammatory processes in the digestive tract, causing problems with swallowing.
If you are concerned about any health problem, sign up for a diagnosis. The success of treatment depends on a correct diagnosis.
How often can fibrogastroscopy be done?
The decision to order an examination is made by a gastroenterologist. The specialist also determines how often the procedure should be done. There are no radical prohibitions on the frequency of conduct. The frequency of the study depends on the type of disease, the severity of the pathology, and individual tolerance of the procedure. For primary diagnosis and monitoring of the condition during treatment, gastroscopy is performed once every 12 months. If a tumor of the digestive organs or a stomach ulcer is detected, FGS can be done several times a year.
In children
Young patients may also require gastroscopy. The study is prescribed if the following symptoms are present:
- Nausea, belching, vomiting.
- Foreign bodies in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
- Congenital pyloric stenosis.
- Burns and injuries to the esophagus or stomach.
- Black stool (tar-like).
- Diarrhea or constipation.
- Slow weight gain.
Performing a gastroscopy on a child under anesthesia is justified, because when performing manipulations, a small patient can break out and thereby injure the larynx. At the same time, such behavior may interfere with obtaining reliable results during the study. Despite the fact that in this case the procedure is carried out with equipment of a smaller diameter than for adults, the child may still experience discomfort. However, given the age of the patients, sedation and anesthesia are not used as often. Only a doctor can make the final decision on how exactly the procedure will be carried out.
Before starting the study, it is important to talk with your child about how and why it is being carried out. Adults should speak in a calm and measured tone. Otherwise, you can provoke a very strong emotional reaction. The less the child is afraid of the procedure, the easier it will be for both him and the doctors. It is important to follow a diet. The last meal before the procedure is possible 8 hours before it. On the morning of the test, you can only drink a small amount of water. Otherwise, vomiting may begin during the study, which is extremely undesirable. In addition, food debris significantly reduces the information content of the study, as it impairs the view of all organ walls.
What can you eat after gastroscopy of the stomach?
After the study, many patients abstain from eating. Experts recommend eating when the procedure is completed, or drinking some water.
Allowed dishes and food products after gastroscopy:
- oatmeal;
- vegetable stew;
- mashed potatoes;
- pureed soup;
- yogurt or kefir.
You can drink sweet tea, fruit decoction or still mineral water. If no discomfort is noted after endoscopy, return to your normal diet. In the first days, limit foods that irritate the gastric mucosa - strong broths, fresh cabbage salads, legumes, fried and fatty foods.
Is it possible to perform gastroscopy without swallowing the probe?
As an alternative way to study the digestive system, an innovative technique is proposed - capsule endoscopy.
It involves inserting a small capsule into the patient's gastrointestinal tract that contains optical and lighting equipment. The capsule is small in size, so the patient can easily swallow it. As it moves through the digestive system, it takes images of the lining of the stomach and intestines, which are transmitted to a special machine. The capsule comes out naturally; no manipulation is required to remove it.
Advantages and disadvantages of the alternative method compared to classical gastroscopy:
| Advantages | Flaws |
|
|
Thus, capsule gastroscopy is an innovative diagnostic method that is highly informative and safe for the patient. However, it cannot completely replace the classical technique, which is much more effective in diagnosing benign and malignant neoplasms of the digestive system.
In continuation of the topic, be sure to read:
- Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori: antibodies, breath test and biopsy
- Details about the coprogram: preparation, conduct and interpretation of the analysis
- How to properly do an enema with an Esmarch mug to cleanse the intestines?
- Rectal fissure: causes, symptoms and treatment of pathology
- Preparation and performance of intestinal irrigoscopy
- The procedure for scraping for enterobiasis and its interpretation
- The procedure for performing an enema with a syringe to cleanse the intestines
- Details about intestinal colonoscopy: preparation and procedure
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs: the essence of the procedure, preparation and implementation
- Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom: examination algorithm and interpretation
Be sure to read:
Ileitis (inflammation of the ileum): types, symptoms and treatment
Diagnosis of the stomach without gastroscopy: alternatives
Gastric endoscopy is a standard diagnostic test to examine the upper digestive tract. In some cases, an alternative to gastroscopy without swallowing the tube is necessary.
Contraindications to gastroscopy:
- scoliosis 4 degrees with displacement of internal organs;
- previous hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke;
- acute myocardial infarction;
- pathological formations of the mediastinal organs, which are accompanied by a violation of the anatomical position of the esophagus - aneurysm, tumors, congenital anomalies;
- blood clotting disorder;
- severe hyperplasia of the thyroid gland;
- mental illness;
- an epileptic condition that is difficult to correct with medication;
- cicatricial narrowing of the esophagus;
- persistent arterial hypertension;
- a person’s categorical refusal of this type of diagnosis.
It is possible to check the stomach without gastroscopy. The doctor decides which method is best to replace the examination. In addition to general clinical tests, non-invasive diagnostic methods are used to check the condition of the stomach, which are presented in Table 3.
Table 3. Alternative diagnostic methods
| Method | Peculiarities |
| Capsule endoscopy | It is produced by swallowing a special light-weight capsule. The device is equipped with a light diode and a camera that shoots video and takes pictures several times per second for 5-8 hours. After output, the obtained result is analyzed by connecting the mechanism to a computer. A significant disadvantage is the high cost of the study, the lack of the possibility of biopsy and collection of material to determine Helicobacter pylori |
| CT scan | Sections are made using X-ray radiation. Determine space-occupying formations, ulcerative defects, developmental anomalies of the abdominal organs |
| MRI | A layer-by-layer study is performed using nuclear magnetic resonance. Differentiate the degrees of the malignant process, the presence of metastatic foci |
| Ultrasound of the stomach | A special sensor is used to look at the size and structure of the organ, determine the presence of ECHO-positive formations and defects, and the functional characteristics of the stomach |
| X-ray with barium | Before the examination, the patient drinks a contrast agent - barium suspension. After this, fluoroscopy is performed and the movement of the substance through the esophagus and stomach is observed. If a specialist observes pathological areas, additional radiographs are taken |
| Electrogastroenterography | In the projection of the stomach and intestines, electrodes are attached to the skin, which pick up impulses and transmit them to a computer monitor. In this way, the functional ability of the digestive organs is determined |
None of the listed methods can fully replace standard gastroscopy of the stomach. Gastroscopy is an important multifunctional study that allows you to differentiate a number of gastric diseases, and also helps to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and the dynamics of the disease.
Purpose of gastroscopy
The EGDS method is indispensable in diagnosing diseases of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum: esophagitis, GERD, gastritis, all forms of peptic ulcers and other tumors in the early stages, unlike other methods that diagnose only late stages of the disease.. With the help of a modern endoscope, polyps and erosions are not only detected, but also effectively treated.
Additional functions of the endoscope allow the following treatment procedures:
- injections or spraying with medications,
- removal of polyps,
- stop bleeding,
- treatment of diseases of the vascular and lymphatic system,
- solving the problem of narrowed lumen of the esophagus,
- insertion of a special probe designed to deliver the nutritional mixture into the stomach.