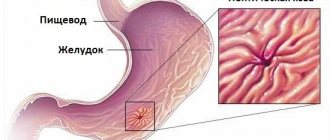
When damage to the abdomen occurs without compromising the integrity of the skin, gastric rupture is possible. The main reason is mechanical impact. The walls of the organ and ligaments may be damaged. Symptoms depend on the severity of the injury. Such an injury is dangerous, so patients are urgently hospitalized. The surgical method of eliminating the problem is more often used. Medicines are intended to relieve symptoms and prevent infection with inflammation. Diet allows the digestive system to adapt to the post-injury state.
Reasons for the breakup
The mucous membrane can rupture spontaneously. This is often due to congenital or acquired weakness of the gastric walls, as well as from overeating. The problem is diagnosed in patients:
- with increased stomach volume;
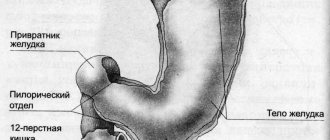
- with pyloric stenosis - cicatricial stenosis of the pyloric part of the stomach of ulcerative origin, which is dangerous by disrupting the movement of the food bolus into the intestine;
- with repeated hyperextension in chronic gastritis, diabetes, mental disorders, neurasthenia.
The stomach also ruptures under traumatic circumstances, such as:
- blows with a blunt object to the peritoneum;
- pressing of organs to the spine by a heavy traumatic element;
- falling and unsuccessful landing;
- consequences of surgical intervention of any nature.
Is it possible to “eat yourself” to death?
Is it possible to fit so much food into yourself that you die? We're used to joking about Americans' problems with overeating, but what's wrong with that? Nobody died from eating three Big Macs.
People have died more likely from eating three Big Macs twice a week for thirty years.
But each of us found ourselves in a situation where, after three servings of salad, chicken, potatoes, bread, appetizers, sausages, mayonnaise, fish, more salad... “this dessert” just didn’t fit anymore. Would you fit in?
Gizmodo interviewed medical professionals who have serious concerns about overeating and regularly encounter burst stomachs in their practice.
Chief Medical Officer John O. Clark, Stanford University School of Medicine:
“Feeding yourself to death is extremely difficult, but in theory it is possible. Stomachs seem to burst frequently, but in reality this is a rare event - the stomach is much stronger than any other segment of the intestine and is capable of expanding. It handles large meals well, but if you stretch your stomach too much, it will cause you to vomit.
Therefore, although there have indeed been cases of stomach rupture, overeating to such an extent is extremely rare, because the stomach quickly expands and simply manages to escape from the critical pressure of food. The average person's stomach expands by about a liter after any meal, but, of course, it is capable of expanding further.
People who can eat fifty to sixty hot dogs usually have extremely dilatable stomachs and, amazingly, they actually slow gastric emptying. It is not yet entirely clear why this is so. Perhaps the slow emptying of the stomach eliminates hunger to some extent so they can continue to eat.
In such situations, despite the massive amounts of food they ingest, none of them ever suffered a stomach rupture.
Vomiting occurs more often from overeating. There is, for example, Boerhaave's syndrome, in which vomiting and strong movements of the esophagus can cause a rupture of the esophagus. In my career, I have never seen a gastric rupture, but with Boerhaave's syndrome, I have seen a couple.
There is another option that is not quite similar to a rupture - a Mallory-Weiss rupture, when the esophagus ruptures at the gastroesophageal junction. It can cause significant bleeding, although not such that the person bleeds to death on the spot. But if this happened far from medical care, theoretically you could die from it.
In theory, if you were to overeat something that was high in a metal or mineral that could cause an overdose, you would have problems.
Personally, I have not seen this in practice, but a friend told me that someone ate a huge amount of lobster - three kilograms - and ended up in the hospital with iodine poisoning.
But you would have to eat a really lot of foods that are high in mercury or iodine or something else that is usually found in trace amounts.”
Chief Medical Officer Barbara Jung of the University of Illinois:
“Over the long haul, definitely: you can feed yourself to death. The rise in obesity among the population of developed countries is an obvious sign. Our high mortality rate in the United States is associated with obesity directly, either from complications caused by obesity, or from related problems - cardiovascular disease, cancer, and so on.
If people are concerned about not dying from a holiday feast: you have to understand that the body wants to live, so it will tell you when enough is enough and when nothing else can be eaten. Very few people will be able to overcome themselves and continue to eat, because it is difficult.
You could die from overeating if the temperature of the food was too cold and you would simply become hypothermic by swallowing large amounts of cold food. Or if you have eaten much more than your stomach can accommodate.
Food goes to the stomach, passing through the intestines, and if the stomach is clogged, it can only move upward, that is, in the opposite direction. Complications caused by vomiting may include choking (when food is inhaled) or bleeding due to a ruptured esophagus.
But this happens very rarely, because the body regulates itself and does not want to overeat.”
Merlin Butler, professor of psychiatry, behavioral sciences and pediatrics at the University of Kansas Medical Center:
“Feeding yourself to death is a phenomenon we see in Prader-Willi syndrome, which is the most common known cause of morbid obesity in humans. It is a rare disease - perhaps 400,000 people worldwide suffer from it.
Individuals with Prader-Willi syndrome go through two main clinical stages. The first stage is the inability to develop normally: they are born very weak, with reduced fetal activity. They are also hypotensive, which leads to different feeding habits.
This continues for several months, up to a year, maybe longer, and then their appetite begins to grow. It grows extremely - hyperphasia develops. The body quickly gets fat. Everything that comes to hand is eaten until a person falls asleep or his stomach bursts. Gastric rupture is a common cause of death in Prader-Willi syndrome. This is the main feature.
They are often placed in a controlled environment with a strict diet so that they have no access to food and their stomachs become smaller. And then it may happen that they overeat, and their stomach will look like a shriveled prune: they overeat, and their stomach bursts.
They know they are overeating because they have been restricted from eating, but they continue to eat and do not feel full. The brain says, “I’m hungry, I’m hungry, I’m hungry,” but it doesn’t say, “I’m full, I can’t eat anymore.”
Patients with Prader-Willi are also unable to vomit. It even happened that children with Prader-Willie could jump out the window when they heard the horn of the ice cream truck. They can even eat things that are not suitable for food.
This can be very life-threatening."
THE HIGHER MIND RECOMMENDS: A mummy of a young man without a brain was found in Egypt. How could this happen?
Ancient Egypt is full of secrets, when uncovered, scientists make very creepy discoveries. In 2021, archaeologists revealed details about an unusual exhibit at the Maidstone Museum - a 2,100-year-old mummy was kept there, but it was too small in size for an embalmed human body. Due to the fact that the image of a falcon was applied to the mummy, historians assumed that it had […]
Read more Experiment: how do the bodies of vegans and meat-eaters differ?
Most people on our planet eat meat with appetite, while others prefer to eat exclusively plant foods. What vegetarians and vegans do is commendable—not only are they trying to improve their health by eating a plant-based diet, but they are also speaking out against the killing of defenseless animals. But is there a difference between the bodies of meat eaters and people sitting on […]
Read more
Source: https://Hi-News.ru/eto-interesno/mozhno-li-obozhratsya-do-smerti.html
How to recognize the problem?
Main symptoms
Acute stabbing pain radiating to the lower back may be the result of a complete rupture. Diagnosis becomes difficult when, along with the damaged stomach, there are lesions of other tissues and organs.
Against the background of severe abdominal pain, a person experiences weakness.
Shock is the main symptom when the stomach ruptures. Later, a deceptive period of “imaginary well-being” begins, at the end of which the patient feels acute unbearable pain - acute abdomen syndrome. A short dull sound when tapping the injured area is explained by the presence of fluid in the peritoneum and the risk of developing peritonitis - inflammation of the abdominal cavity. And:
- presence of gases;
- weakness;
- temperature increase;
- nausea, vomiting blood.
Symptoms of bleeding that occurs during rupture:
- lowering blood pressure;
- decreased heart rate;
- weakness.
Diagnostic methods
The exact extent of the mucosal rupture is determined only during surgery. The following methods allow you to make the right decision in making a diagnosis:
The extent of organ damage can be assessed during laparoscopic surgery.
- Laparoscopy. An invasive technique that involves inserting a device with a microcamera into the peritoneum through small incisions and simultaneous treatment - repairing the rupture.
- Laparocentesis. It involves a puncture in the anterior abdominal wall to detect or exclude the presence of blood, bile, exudate, gas in the abdominal cavity. Often performed before laparoscopy.
- A variation of abdominal puncture with the yaw catheter technique for visualization of blood clots.
- Contrast fluoroscopy, which is used after relief of inflammation and pain to evaluate the final result of the operation.
- Blood, urine, and stool tests necessary to monitor the patient’s condition.
Diagnostic measures
According to statistics, the majority of patients who were taken to a hospital with such symptoms undergo immediate surgical treatment. As a rule, during surgery, surgeons identify a mucosal rupture, its location and size.
If the patient is delivered to a hospital in satisfactory condition, surgeons will carry out the following diagnostic measures:
- Tests (blood, stool, urine) are prescribed.
- An x-ray is taken with contrast liquid. This procedure is prescribed to patients only after the exacerbation has been relieved and the pain syndrome has been relieved.
- A procedure called laparocentesis is performed.
- An endoscopy is performed, during which surgeons carry out not only diagnostics, but also therapeutic manipulations.
- Laparoscopy is performed. This surgery is performed under general anesthesia. The patient undergoes several punctures in the abdominal cavity. Through these holes, the surgeon inserts a special instrument, on the tip of which a microcamera is fixed. Thanks to laparoscopy, it is possible not only to visually, through a monitor, assess the severity of the lesion, but also to carry out the necessary surgical manipulations.
- The “gentle catheter” method is used, etc.
Treatment: basic approaches
Help of drugs
Mild consequences of blows, namely tears, are treated with conservative methods. A wait-and-see technique is used, ensuring complete rest, fasting for the first 2 days and following a strict diet for the next 1.5 weeks. To relieve symptoms, it is recommended to apply cold (ice) to the abdomen. Antibiotics and drugs to support the heart are prescribed as auxiliary drugs during surgery to avoid infection of other tissues, the development of inflammation and complications.
Surgery for rupture of the gastric mucosa
Before surgery, the patient is prepared:
Plasma is given to the patient if he has lost a large amount of blood due to injury.
- give medications to support the heart;
- antishock solutions are administered intravenously;
- Plasma is drip-fed in case of severe blood loss;
- the stomach is emptied, but without rinsing, so as not to further disrupt the integrity of the tissues.
Sewing the walls with a seam in two rows is a method that is used, as a result, the edges of damaged tissues are better and faster renewed. If dead areas are detected, they are removed followed by sanitation of the cavity and peritoneum. In case of extensive damage, complete resection is performed - removal of the stomach. With simultaneous injury to the duodenum, a gastroenteroanastomosis is created when the stomach is connected directly to the small intestine.
Surgical intervention is performed in case of complications with signs of bleeding and breakthrough into the peritoneum.
Proper nutrition or need a strict diet?
For the first 2 days after the operation, the patient is fasting, on the 3rd day he is allowed to drink, and on the 4th day he can eat liquid food. Diet should become the basis for the patient’s future lifestyle. Important instructions:
- Do not drink alcoholic beverages.
- Do not eat fatty, spicy and smoked foods.
- Enrich your diet with boiled and steamed plant products.
- Provide liquid and light meals in small portions - at least 6 times a day.
What are the consequences of overeating?
What will be the consequences of overeating and what can really happen in our digestive system if we eat too much food and will this be a nutritional problem.
The human digestive system starts from a point of entry (the mouth) to a point of exit (the anus) but to the average person, what goes on between these two points is a mystery.
The function of the digestive system is to convert food into usable energy for the body to burn, grow, or store for future use.
This process begins in the mouth, where the teeth, tongue and salivary glands facilitate mechanical and chemical digestion, forming a bolus of food that travels through the esophagus to the stomach.
The stomach is a muscular sac that sits inside the abdomen and is usually no larger than a fist when empty. However, it has the capacity to expand and adapts to the amount of food. A specialized muscle is adapted to allow it to stretch as the stomach fills and expands with food intake.
An empty stomach contains about 40 ml of liquid, but the average “full” stomach volume is about 800-1000 ml and the size increases in people who are obese or binge drinkers.
After food has passed through the stomach, it enters the small intestine, where digestion continues and nutrients are absorbed into the blood.
The small intestine, which is about 5-6 meters in length, connects to the large intestine, which is about 1.5-2.5 meters in length.
The colon absorbs most of the water, absorbing it into the bloodstream, and the remaining waste becomes feces.
How is satiety determined?
We often feel full after eating for quite a long time because there is a delay in signals from the distension of the stomach to reach the brain.
One may wonder why a person still has a feeling of hunger, although in fact he has already eaten enough and can burst without any intermediate feelings.
Our body has a very complex way of notifying us when we are hungry and full; it requires a number of hormones that are produced in response to the presence or absence of food in the digestive system.
If we get the right amount of food we consume, we have a feeling of satiety—a fullness that suppresses the desire to eat.
Two of the most important hormones, ghrelin and leptin, are involved in determining satiety. If we look at these hormones in a simplistic way, ghrelin increases appetite and decreases appetite leptin. They are produced mostly in the stomach.
Ghrelin is usually high before you eat and decreases afterward. Leptin tells the brain that we are full. So more obese people need more leptin and are therefore more likely to want to eat something.
However, many people are aware of the consequences of overeating and resist the effects of leptin by reducing their appetite by restricting food.
What happens when you overeat
What will happen and what are the consequences of overeating? Excess food can come out in two ways. The first is into the digestive system or back to where it came in the form of vomiting. Overeating causes indigestion when stomach acid flows into the esophagus.
In addition, when overeating, the body must divert most of its energy to digesting food, thereby making us feel tired and drowsy.
Can a person's stomach burst from overeating? In rare cases, but unfortunately, yes. There are times when the stomach becomes so large that it bursts from the sheer volume of food inside it.
One 23-year-old lady had over 2500 ml in her stomach, which caused it to swell so much that it filled her entire stomach, from her ribs to her pelvis. Ultimately, the stomach burst and required emergency surgery.
Can a person die from overeating? Yes, there are a couple of reports of people dying from eating too much. This is very rare, but it happens. One person died from a rupture of the esophagus, the tube that connects the mouth to the stomach, and others actually had their stomachs ruptured, such as the consequences of overeating.
The consequences of overeating create emotional, psychological and physiological side effects that can significantly impair quality of life and hope for the future.
When an overeater consumes an excessive amount of food, he gets a euphoric feeling of using the drug.
They feel temporary relief from psychological stress and a distraction from feelings of sadness, shame, loneliness, anger or fear. An abnormality in endorphin metabolism in the brain contributes to the process of addiction to overeating.
Next, trying to abstain from overeating can lead to higher levels of depression and anxiety due to decreased serotonin levels.
conclusions
Some people with symptoms of overeating have what can be described as a human disease - food craving disease. They use food and eating as a way to hide or manage their emotions, fill the emptiness they feel inside or cope with the daily stresses and problems in their lives.
One of the largest recorded amounts of food ever consumed by one person was in the United States.
In 2010, a consumer ate 20 kilograms of chicken, 10 ham, 15 kg of potatoes, vegetables and toppings, which were then consumed with 2 liters of sauce and then savored with dessert.
This meal consisted of 30,000 calories; To put this in context, men and women are recommended to consume 2,500 and 2,000 calories per day, respectively. With higher consumption, problems associated with weight gain arise and this is one of the causes of obesity.
Source: https://havef.com/posledstviya-pereedaniya/
Prevention methods and prognosis
To make your organ stronger, you need to eat healthy foods.
Doctors' recommendations to protect yourself from weakening of the muscle layer and rupture of the gastric mucosa:
- Leading an active lifestyle, including playing sports.
- Healthy eating without overeating.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Weight control.
- Annual examination.
The mortality rate from gastric rupture is low - 3%, if the forms of the mucosa are preserved. When a wall breakthrough is noted, the figure rises to 40%, as peritonitis develops. Complete rupture of the mucous membrane is 85% fatal. It is important to provide assistance in the first 2-3 hours, then the chances of recovery will be high. A quick recovery occurs after incomplete ruptures of the mucosa.
Why is gluttony considered a mortal sin?
It doesn't seem that scary. We eat to live. But it's not that simple. If you eat to replenish your energy reserves, then this is normal. And, if you consume food to gain pleasure, then you are engaging in gluttony and sinning before the Lord.
Why is gluttony considered a mortal sin, although there are other more terrible sins? With gluttony, a person becomes a slave to his stomach. All goals are reduced to the lowest - obtaining immediate pleasure from food.
When people eat food to satisfy the need to replenish energy reserves, then all systems and organs work normally. And if a person eats away stress, loneliness, uncertainty or depression with food, then this can be called gluttony.
Many people understand that nicotine and alcohol can be classified as drugs, but the same can be said about sugar, when people regularly snack on gummies, chocolates, sweets or cakes with great pleasure.
A smoker wants to smoke, an alcoholic needs to recover from a hangover, and a sugar addict dreams of a sweet snack. In all cases, the behavior patterns are similar.