Most pathologies of the biliary system are treated through a combination of medications, diet therapy, surgery and traditional recipes. It is this set of measures that allows you to restore the functioning of the gallbladder, bile ducts and liver, remove the inflammatory process, eliminate pain and normalize the outflow of bile.
The attending physician selects medications individually in each clinical case, based on the course of the pathological process, the presence of complications, the causes of the disease and symptoms. Next, we consider questions about how to treat the gallbladder and what medications are recommended to be taken for certain ailments of the biliary tract.
General recommendations
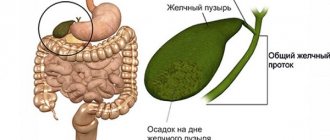
The list of gallbladder diseases is quite wide. This includes the following conditions:
- cholecystitis (inflammatory changes);
- cholelithiasis (GSD), which is manifested by the formation of various types of stones in the bladder itself or bile ducts;
- dyskinesia of hypo- or hypermotor type. In the first case, the motility of the structural elements of the system is weakened, which is why bile does not enter the duodenum in sufficient quantities to participate in the digestive processes. The second option is characterized by increased functioning, against the background of which spasm and severe pain occur;
- benign and malignant neoplasms. In the first case we are talking about the formation of polyps and cysts, in the second – about cancer;
- helminthiases.
Against the background of each pathological condition, changes occur, characterized by the appearance of pain, spasm, disruption of the outflow of bile, accumulation of mucus or suspension of various origins in the cavity of the gallbladder. Treatment of the gallbladder with medications involves the prescription of antibiotics and sulfonamides, choleretic agents, drugs with antispasmodic effects, hepatoprotectors and enzymes, enterosorbents. Below are the names of representatives of each group and the features of their use in therapy.
Antispasmodic and choleretic drugs, as well as drugs for the treatment of gallstones
Can your gallbladder hurt? Yes, and quite strongly.
As a rule, pathologies of this organ cause severe pain in the right hypochondrium. For gallbladder pain, only the attending physician decides what to take. This pain syndrome is relieved with the help of antispasmodic drugs.
Such drugs are divided into two main types:
- selective anesthetic (bromide, mebeverine hydrochloride). This medicine relieves pain specifically in the gastrointestinal tract.
- broad-spectrum antispasmodics (papaverine and drotaverine (more familiar to everyone as no-spa). Such drugs remove the spasm that causes pain, acting on all organs that have smooth muscles.
Read also: The best choleretic drugs - complete list
Analgesic drugs can also relieve pain (or relieve pain) in such cases, but antispasmodics are usually more effective.
Choleretic drugs for treatment at home are selected by the doctor individually, based on the diagnosis and the characteristics of the individual patient’s body.
These medications are designed to prevent the formation of biliary sludge that forms stones. Such preparations may contain both natural (plant or animal) ingredients and substances obtained through chemical synthesis. They are also divided into two types:
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | means for improving bile formation, which include components of this enzyme. This group includes drugs such as allochol (in our country it is the most popular remedy), decholin, cholenzyme, tanacehod, zolecin, and so on. |
| 2 | medications that activate bile secretion in the liver. This group of drugs is represented by the following medications: cholecystokinin, sorbitol, pumpkinol, choleritin, magnesium sulfate, olimethine and others |
Even such a dangerous disease as cholelithiasis, which is caused by biliary sludge, can be cured at home, without surgical intervention (if the disease is detected in time and timely therapy is started). The following medications help dissolve gallstones: ursofalk, ursosan, henochol, henodiol, henofalk or henosan.
Treatment of gallstones with these drugs is based on the action of the urso- and chenodeoxycholic acid they contain, the effect of which dissolves the gallstone. If you have gallstones, you need to be very careful with taking choleretic drugs so as not to cause the movement of these stones and not to block the bile duct.
Methods for treating the gallbladder for gallstone disease also include laser and shock wave lithotripsy (crushing large single stones into smaller particles that are removed from the body naturally). However, both methods of therapy have a number of limitations, which significantly narrows the range of their applicability.
Antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs are used to combat pathogenic microflora, which is caused by the development of inflammation, swelling, etc. All representatives of the group are divided into several types depending on their origin: synthetic, semi-synthetic and natural. Antibiotics can not only stop the growth and reproduction of pathogenic bacteria, some even have an antitumor effect, and therefore are used in the treatment of cancer.
Antibiotics are prescribed both in tablet form and as injection solutions
Antibacterial agents are prescribed in the treatment of cholecystitis (acute and chronic), as well as in the presence of stones in the gall bladder and ducts, to prevent the development of complications. Also, representatives of the group are used before and after removal of the bladder (cholecystectomy). The duration of treatment is at least a week, in some cases a repeat course is necessary. The choice of drugs is based on a microbiological study of the bile fraction obtained through duodenal intubation. In laboratory conditions, the type of pathogenic microflora and the name of the drugs to which the greatest sensitivity has been identified are determined.
Important! Initially, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed, and based on the results of the analysis, the treatment regimen is changed or supplemented.
Drugs for the treatment of the gallbladder from the group of antibiotics must have the following characteristics:
- high degree of penetration into bile;
- long period of circulation in the bloodstream after a single use;
- minimal number of side effects;
- minimal negative effect on liver cells;
- no effect on the fetus if therapy is selected for a pregnant woman.
It is imperative to simultaneously prescribe medications with lacto- and bifidobacteria, which will prevent the development of intestinal dysbiosis. Perhaps a specialist will recommend taking an antifungal agent to prevent candidiasis of the female genital organs. The table below discusses frequently used representatives of the groups, their characteristics and contraindications to treatment.
| Drug and relationship to subgroup | a brief description of | When not recommended for use |
| Ampicillin (penicillins) | A semi-synthetic product with a wide spectrum of action, available in tablets and powder for the preparation of an injection solution. Can be used to treat infants | Hypersensitivity to components, infectious mononucleosis, colitis, liver failure and lymphocytic leukemia |
| Oxacillin (penicillins) | Antimicrobial agent for systemic use. Effective against gram-positive and gram-negative cocci, some actinomycetes. Injected into muscle and vein | Hypersensitivity, severe allergic reactions |
| Cefotaxime (cephalosporins) | Semi-synthetic drug of the 3rd generation. Active against many gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms | Hypersensitivity to components during breastfeeding and pregnancy. Children under three years of age should not be injected into the muscle. |
| Erythromycin (macrolides) | It is used for the treatment of diseases of the hepatobiliary tract in tablets. Does not show activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Shigella and Salmonella | Hypersensitivity, severe liver and kidney damage in combination with Terfenafine, Astemizole, Pimozide or Cisapride, ergotamine and dihydroergotamine |
| Ciprofloxacin (fluoroquinolones) | Can be used to treat children over 1 year of age | Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, combination treatment with Tizanidine |
| Furazolidone (nitrofurans) | Antibacterial and antiprotozoal agent, which is combined with representatives of other subgroups of antibiotics | Malabsorption syndrome, severe disorders of the liver and kidneys, pregnancy and breastfeeding |
| Tetracycline (tetracyclines) | A broad-spectrum bacteriostatic drug used in tablet form for the treatment of the gallbladder. | Hypersensitivity, mycoses, children under 12 years of age, pregnancy and lactation, combination with vitamin A and retinoids |
Antibacterial treatment
Antibacterial drugs for the treatment of cholecystitis are prescribed if the disease is caused by a bacterial infection or there is a risk of complications. They are also prescribed after removal of the gallbladder. The antibiotic must not only act on pathogenic bacteria, but also penetrate into the bile and accumulate in it.
To suppress the bacterial flora, two antibiotics are prescribed. One of which is Furazolidone, and the other is a broad-spectrum drug (the most effective of them are Erythromycin, Azithromycin, Ciprofloxacin, Ampicillin, Roxithromycin). Furazolidone is produced in tablets and powder for suspension.
The antibiotic has a bactericidal or bacteriostatic effect (depending on the dose) on salmonella, shigella, campylobacter, protozoa and vibrio cholerae. Anaerobes and Pseudomonas aeruginosa are resistant to the drug. The drug is used to treat intestinal infections of bacterial and protozoal nature.
Tablets are prescribed to children from 3 years of age, and the suspension can be given from the 32nd day of life. Adults should take the antibiotic 0.1 g with meals 4 times a day for 1–1.5 weeks; children should take a daily dose of 0.01 g/kg (it should be divided into 3–4 times). Aminoglycosides and Tetracycline enhance the effect of Furazolidone.
Amoxicillin (it is with it that Furazolidone is most often combined) is active against gram-negative and gram-positive cocci, some types of gram-negative rods. Adults and children over 10 years old are recommended to take 2 capsules (0.5 g) three times a day, children 5–10 years old are given 1 capsule of Amoxicillin (0.25 g) 3 times a day for a course of 5–12 days.
If there are allergic reactions to penicillin, then Amoxicillin is replaced with a drug from the macrolide group (Azithromycin). Antibacterial agents are recommended to be combined with choleretic drugs, which additionally have an anti-inflammatory effect. For example, with Cyclovalon (0.1 g three times a day before meals) or hydroxymethylnicotinamide (0.5 g 3 or 4 times a day before meals).
The antibiotic negatively affects liver function, so a minimum effective course of therapy should be prescribed
Sulfonamides
This group of medications is used instead of antibiotics if the latter for some reason cannot be prescribed for treatment. Used for acute cholecystitis. Experts opt for those representatives that have a long-lasting effect. Rules for taking sulfonamides:
- it is important to take the medicine at the strictly indicated time;
- It is forbidden to skip taking the next pill so that a high concentration of active components in the patient’s blood is constantly maintained;
- You need to drink plenty of fluids during therapy to prevent the formation of kidney stones.
Important! Representatives of the group are Sulfalene, Sulfadimethoxine, Sulfapyridazine.
Medicines for pain relief
To relieve pain that may occur due to inflammation and dyskinesia of the gallbladder, medications with antispasmodic effects are used. Direct-acting drugs are recommended for spasms of the biliary tract that occur against the background of increased motility (Papaverine, Drotaverine). Painful sensations are also relieved by taking M-anticholinergic drugs (Platifillin, Atropine), but their use is indicated only after a comprehensive examination and exclusion of conditions in which use is prohibited.
In some cases, the appointment of prokinetics (Metoclopramide, Motilium) is required. Representatives of the group are used if the gallbladder hurts due to weakened motor skills. The drugs also speed up bowel movements, which causes the patient to go to the toilet frequently.
To quickly relieve pain, the drug is used in the form of a solution for intramuscular injection.
Drugs to combat pathogenic bacteria
If an inflammatory process is detected in the patient’s gallbladder, the doctor prescribes antibiotics that prevent the further proliferation of harmful bacteria and fight existing ones.
Stagnation of bile caused by the pathology of this organ, as well as depletion of the mucous membrane and decreased immunity lead to an increase in the number of unwanted microorganisms.
As a rule, the course of antibiotic therapy at home is seven days (in some cases up to ten). If a course of any remedy to combat harmful bacteria does not achieve the desired effect, then the doctor prescribes another type of antibacterial drug. Antibiotic therapy is perhaps the most effective and practical method of treating diseases caused by bacteria, such as acute and chronic cholecystitis. Their dosage form can be in the form of tablets and capsules, as well as in the form of injection solutions.
When choosing a specific antibiotic, you cannot rely on advice received from the Internet or from friends and relatives and treat with tablets recommended on the basis of “it worked for me.”
The prescription of a specific drug is within the exclusive competence of the attending physician, who, using laboratory tests, determines the sensitivity of bile produced by the liver to a particular antibacterial agent.
An important factor in the process of selecting such a medicine is its activity in the fight against the pathogen. Pathogenic microorganisms that have occupied the gallbladder should not have immunity to the pharmacological substances contained in the antibiotic. This can be foreseen in advance by carrying out the necessary tests, as well as on the basis of individual symptoms (if probing for some reason is not possible).
To achieve the desired effect, an important factor is the high level of penetration of the drug into the bile. This is necessary so that the medicine acts not only on the gallbladder itself, but also on all digestive organs, without causing any harm to them or destroying the liver. Sometimes, to speed up the positive effects of the medication, gallbladder tablets are replaced with injections.
Read also: Pathologies of the gallbladder ducts
Modern pharmacology offers a very wide list of antibiotic drugs to choose from for treatment at home. According to most medical experts, the most effective among them are:
- Cephalexin;
- Ampicillin;
- Erythromycin;
- Cefazolin;
- Norfloxacin;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Azithromycin;
- Oxacillin;
- Lincomycin;
- Ampiox.
Tetracycline, roxithromycin, doxycycline and penicillin also rightfully deserve good reviews. In some cases, doctors, along with the main antibiotic, prescribe furazolidone as an additional one.
This therapy makes it possible to more completely clean the gallbladder from pathogens. With the help of antibiotics, it is possible to prevent complications that may arise against the background of existing inflammation. However, like any other medications, antibiotics have their side effects and contraindications.
The most common undesirable consequences that occur after taking antibiotics include:
- dysbiosis. Antibacterial drugs, in addition to pathogenic ones, also destroy beneficial bacteria, thereby disrupting the balance of intestinal microflora. In order to prevent this, special preparations rich in beneficial microorganisms are used - probiotics and prebiotics. If the pathology is severe and accompanied by bleeding from the gums and nose, the doctor prescribes medications containing vitamin K, as well as hemostatic agents;
- candidiasis of the mucous membranes of internal organs. Antibacterial medications can provoke the proliferation of pathogenic fungi. In this regard, a qualified medical doctor prescribes antifungal drugs along with them. It is worth noting that modern pharmacology has already developed complex medications for the treatment of the gallbladder, which include both antibacterial and antifungal active ingredients, because it is much easier to treat the disease by taking one tablet rather than drinking several at once at each dose. In any case, the prescription of drug therapy is the prerogative of only a qualified medical specialist;
- allergies and hypersensitivity. In some cases, the patient has an individual intolerance to a particular drug. As a rule, in such cases, strong antibiotics are replaced with drugs from the sulfonamide group (for example, sulfalene or sulfadimezin).
Means to accelerate the formation and outflow of bile
The drugs are used for stagnation of bile as a result of dyskinesia of the biliary system. Not recommended for gallstone disease, since taking medications can provoke “wandering” of stones along the ducts with further obstruction and increased development of inflammation. The first subgroup of choleretic drugs is choleretics. The action is based on increasing the amount of bile acids in bile. Choleretics can be of plant, animal, or synthetic origin. Used to treat chronic inflammation of the gallbladder and biliary tract, biliary dyskinesia and constipation.
Important! Choleretics are not prescribed as monotherapy; they are combined with antibiotics, sulfonamides and antispasmodics.
Effective drugs and their brief description:
Bend of the gallbladder and its treatment with folk remedies
- Allochol - used only for the treatment of adults, the drug stimulates the process of bile production by hepatocytes and prevents its stagnation in the bladder;
- Hofitol is a herbal preparation, which is available in the form of syrup and tablets, not only stimulates the outflow of bile, but also restores the functioning of liver cells, being a representative of hepatoprotectors;
- Gepabene is a herbal product that is available in capsules with a gelatin shell;
- Cholenzym - tablets for the gallbladder based on components of animal origin, are used to treat adolescents over 12 years of age and adults.
The second subgroup is cholekinetics. They are used for hypomotor type dyskinesia to enhance the motility of the gallbladder, as well as to combat the symptoms of high pressure in the biliary tract. Representatives include xylitol and sorbitol. Diabetics know them as sugar substitutes. Available in powder form, diluted in warm tea or water before use. Not recommended for inflammatory bowel diseases. Other representatives of the subgroup are Platifillin, Odeston, Duspatalin, Papaverine.
Medicines for the treatment of the gallbladder
Depending on the diagnosis, the doctor gives a prognosis and prescribes medications necessary to normalize the functioning of the gallbladder.
It can be:
- Antibiotics;
- Antispasmodics;
- Choleretic agents.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are prescribed to treat cholecystitis caused by a bacterial infection.
Ideally, before prescribing an antibiotic, it is necessary to take a bile sample to understand which bacteria have attacked the gallbladder, however, in reality, this happens, unfortunately, extremely rarely. Therefore, two drugs are prescribed, one of which:
- Erythro- or Azithromycin;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Ampicillin;
- Amoxicillin;
- Roxithromycin,
And the other is Furazolidone. Although this allows you to completely cleanse the gallbladder of bacterial pathogens, it has a detrimental effect on the intestinal microflora and liver health.
Most often, doctors prescribe drugs of the penicillin group (Amoxicillin, less often and, as a rule, older doctors - Ampicillin). When a patient has or is allergic to penicillin, such drugs are replaced with macrolides - Azithromycin. Therefore, recently, in order not to take risks, the prescription of Azithromycin is gaining increasing popularity.
Contraindications to the use of antibiotics
Antibiotics should not be used for treatment in the following cases:
- Non-bacterial causes of acalculous cholecystitis and cholelithiasis;
- Allergic reaction to the components of the product;
- Kidney failure;
- Furazolidone is contraindicated during pregnancy and infancy.
Antispasmodics
As already mentioned, gallbladder diseases are accompanied by pain in the right hypochondrium. Sometimes the pain is almost unbearable, so the first aid should be an ambulance, because the stronger the pain, as a rule, the sooner hospitalization is needed and the help of a surgeon, rather than a therapist, is needed.
You can independently try to relieve tolerable pain due to cholelithiasis with antispasmodic drugs before going to the doctor. There are two types of antispasmodics:
- Selective antispasmodics, acting only on the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, and represented by Mebeverine hydrochloride (Meverin, Duspatalin, Mebsin, Milorin, Spark) and Bromide.
- Broad-spectrum antispasmodics, marketed under the names Drotaverine (No-Shpa) and Papaverine, but acting on all organs with smooth muscles.
Contraindications to the use of antispasmodics
Antispasmodics are contraindicated for:
- Crohn's disease;
- Bacterial diseases of the intestinal tract;
- Enterocolitis;
- Tuberculosis;
- Enlargement of the walls of the colon.
Choleretic drugs
There is a huge selection of choleretic drugs on pharmacy shelves. They are prescribed by a doctor depending on the required active composition, although it is no secret that the prescription of this group of drugs pursues the same goal.
Choleretic drugs are usually divided into seven groups:
- Cholekinetics;
- Cholespasmolytics;
- True choleretics;
- Hydrocholeretics;
- Synthetic;
- Based on medicinal herbs;
- Preparations with litholytic effects.
Cholekinetics
Cholekinetics are choleretic drugs that help increase the outflow of bile, increasing the tone of the gallbladder itself. This series includes the following medications:
- Magnesia;
- Sorbitol;
- Xylitol;
- Berberis-plus;
- Flamin;
- Holosas;
- Holemax.
Contraindications
It is not recommended to take cholekinetics in case of impaired renal function, as well as in acute enteritis. Pregnancy is also a contraindication for treatment with this group of drugs. It is not without reason that doctors advise stopping treatment with cholekinetics during menstruation.
It is necessary to use any choleretic drugs for cholelithiasis very carefully and only after a complete examination.
Cholespasmolytics
Cholespasmolytics are those drugs that relax the muscle tissue of the gallbladder and bile ducts. Due to this relaxation, the biliary effect is achieved.
Cholespasmolytics include three groups of drugs:
- Herbal cholespasmolytics - extracts of valerian, lemon balm, calendula or a combined herbal preparation Cholagol;
- Synthetic cholespasmolytics - Drotaverine, Papaverine, Spasmol, Eufillin, Mebeverine;
- Anticholinergics - Bellalgin, Besalol, Platifilin, Fubromegan.
True choleretics
True choleretics are considered to be products containing bile components. These choleretic drugs are divided into three groups:
- Products with natural animal bile – Cholenzym, Allohol, Liobil;
- Products with dehydrocholic acid – the drug Hologon;
- The sodium salt of dehydrocholic acid, contained in Decholin, Kholamine, Biliton, is also isolated separately.
Contraindications
It is not recommended to use true choleretics in the following cases:
- Acute stage of viral hepatitis;
- Obstructive jaundice;
- Acute pancreatitis;
- And also for ulcers of the stomach and duodenum.
Hydrocholeretics
Hydrocholeretics include a separate group of medicinal mineral waters. These are not table waters, i.e. they are not suitable for regular use. We are talking about alkaline waters:
- Naftusya;
- Essentuki 4 and 17;
- Borjomi;
- Kvasovaya Polyana;
- Narzan;
- Izhevskaya;
- Slavyanovskaya;
- Jemruk et al.
Synthetic choleretics
Synthetic choleretics are choleretic drugs created on the basis of synthesized components of choleretic action. These are:
- Medications with hymecromone - Odeston, Cholestil;
- Osalmid (Oxafenamide);
- Preparations with hydroxymethylnicotinamide - Nicodin, Bilizarin, Felosan, Nikiform;
- Cyclalon.
Contraindications
It is not permitted to prescribe synthetic choleretics in case of an allergy to the main or auxiliary component of the drug. The following are also contraindications:
- Fatty liver degeneration;
- Blockage of the bile duct by a stone.
Choleretics from medicinal herbs
Medicinal herbs form the basis for the following preparations:
- Flamin with immortelle extract;
- Insadol with corn silk extract;
- Solaren or Tanaflon with tansy extract;
- Febichol with turmeric extract;
- Berberis-Plus with extract of barberry leaves and roots;
- Kholosas, made from rose hips;
- Chofitol with artichoke extract.
And there are also choleretic drugs based on a complex of plant components. For example, these are:
- Choleretic fees;
- Travochol;
- Urolesan;
- Phytohepatol.
Contraindications
Choleretics from medicinal herbs should not be used in the treatment of:
- Jaundice due to blockage of the bile duct with a stone;
- Personal intolerance to any components.
Choleretic drugs with litholytic effect
Choleretic drugs with a litholytic effect are called choleretic drugs with bile acids: ursodeoxycholic and chenodeoxycholic (drugs Livodexa, Ursoliv, Ursodez, Ursosan, Ursofalk, Henochol, Henofalk, Henodez, etc.), as well as drugs with Methyltrebutyl ether.
Such drugs are prescribed not only to enhance the flow of bile (treatment of gallbladder diseases), but also to dissolve deposits in gallstone disease.
Enterosorbents and enzyme-based products
Enzymatic preparations are necessary to support the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, since gallbladder pathologies are often combined with inflammation of the pancreas. Representatives are Festal, Mezim, Creon, Panzinorm, Enzistal and other enterosorbents accelerate the process of eliminating toxins, supporting the functioning of the liver and intestinal tract, and also effectively bind harmful substances formed during the activity of pathogenic microorganisms.
Enterosgel is a medicine that not only removes toxins, but also promotes rapid restoration of tissues and mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract. Effective in the development of dysbacteriosis. Smecta is used even in the treatment of newborns, but the product should not be used for more than 7 days. Smecta is prohibited in cases of intestinal obstruction and the presence of hypersensitivity to the active components of the drug.
Polysorb is a drug that is positioned by manufacturers as an assistant for removing harmful substances from the body during chemotherapy. That is, it can be safely added to therapy during the recovery period when fighting tumors of the hepatobiliary system. Lignin is an enterosorbent based on coniferous wood. Recommended in preparation for surgical interventions, for infectious processes of the gastrointestinal tract and liver.
Drugs that break up gallstones
This group of medicines includes medicines based on bile acids and dietary supplements. Ursodeoxycholic and chenodeoxycholic acids are the main active components of the group. They allow you to restore the ratio between bile acids and cholesterol in the patient’s body. Some drugs, when combined with cholesterol, change its structure, while others, when released into the bile, perform a stone-dissolving function.
Features of cholesterol metabolism in the human body
The period of drug use is quite long. It can last from 6 months to 2 years, but the effectiveness of the therapy has been proven for more than one decade. To monitor the results of treatment, an ultrasound examination must be performed every six months. Indications for taking drugs based on bile acids:
- the diameter of the stones does not exceed 1.5 cm;
- stones are concentrated only in the cavity of the gallbladder, but they are not in the ducts;
- calculi occupy no more than half of the organ cavity;
- Bladder contractility is normal.
Important! At the same time, treatment with hormonal contraceptives that contain estrogen, drugs that help eliminate cholesterol, as well as drugs that reduce the pH level in the stomach is prohibited.
Effective representatives and their characteristics are described in the table.
| Drug name | Characteristic | Features of application |
| Ursosan | Available in hard capsules, used for the treatment of biliary reflux gastritis, primary biliary cirrhosis, and cystic fibrosis in children over 6 years of age | Do not use with antacids, Cyclosporine, Ciprofloxacin. Not recommended for frequent hepatic colic, for cirrhosis in the stage of decompensation |
| Ursofalk | Similar to Ursosan | Similar to Ursosan |
| Ursohol | Available in capsules and suspensions, there is no age restriction for use | If the patient weighs less than 47 kg, it is recommended to use the product in the form of a suspension |
| Henochol | Dissolves radiolucent stones less than 2 cm in diameter | Contraindications: non-cholesterol stones, inflammation due to cholelithiasis, hepatitis, peptic ulcer, pregnancy, malabsorption syndrome, severe pathologies of the liver and renal apparatus |
| Henofalk | Inhibits the production of cholesterol in the liver, used in preparation for lithotripsy and cholecystectomy | Contraindications: inflammation of the gallbladder and biliary tract, Crohn's disease, peptic ulcer, malabsorption syndrome, pregnancy |
| Hyeonosan | Increases the solubility of cholesterol on the surface of stones | Contraindications are similar to Henofalk and Henochol |
Gallbladder diseases
Before broaching the topic of medications, it is important to understand which gallbladder diseases are most common.
- Cholecystitis is an inflammatory process, the most common of all gallbladder diseases. It happens both with the deposition of stones and without them, therefore it is divided into two types:
- Acalculous cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder without visible deposition of stones in its cavity, manifested by tolerable, aching pain in the right hypochondrium, digestive disorders in the form of nausea, flatulence, constipation or frequent diarrhea;
- Calculous cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder with the presence of stones. It is characterized by severe, acute pain in the right hypochondrium, irresistible nausea, and repeated vomiting. When the stone, having moved from its place, stops, biliary colic occurs - unbearable pain of an acute nature, accompanied by nausea and vomiting;
- Dyskenesia of the gallbladder and bile ducts is a violation of the mobility of the organ or channels that remove bile, which leads to stagnation of bile or its frequent release into the duodenum. Depending on the manifestations of the disease, there are two types: hyper- and hypotonic dyskinesia. Hypertension is characterized by increased mobility of the gallbladder and ducts, which is why the normal volume of bile is not collected and food is not digested well enough. The main symptom of hypotonic dyskinesia is stagnation of bile and its absence in the intestines, which is why fats in food cannot be absorbed by the body.
dietary supplements
An example of a dietary supplement used to break up stones is Ziflan. This product is based on immortelle extract. Ziflan promotes the formation of bile acids from the cholesterol that is in the human body. It is taken for a month, then a break of 2 weeks is recommended. You can take up to 3 courses per year.
The dietary supplement is available in capsules and is taken three times a day. It is also important to monitor the dynamics of stone dissolution using ultrasound. Contraindications for use are the period of pregnancy and breastfeeding, age under 12 years, and the presence of individual hypersensitivity to the active components. Not recommended for jaundice of various origins and hypertension.
Fighting helminths
A number of helminths can “live” in the hepatobiliary tract. Such parasites include roundworms, flukes, echinococci, schistosomes, and lamblia (the latter are representatives of the class of protozoa). Therapy includes taking the following medications:
- anthelmintic and antiparasitic drugs (Metronidazole, Trichopolum, Furazolidone, Albendazole, Vermox, Vormil, etc.);
- enterosorbents;
- immunomodulators (tincture of ginseng, eleutherococcus);
- choleretic agents (cholekinetics or antispasmodics - as prescribed by a doctor, depending on the accompanying changes and symptoms);
- antihistamines – drugs that relieve allergic manifestations;
- vitamins.
Treatment of each disease requires an integrated approach. You should not use medications without consulting a doctor, since each clinical case is individual in its course and manifestations.