What does it look like?
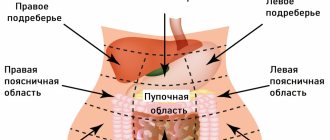
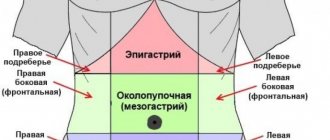
Appendicitis is suspected when there is pain under the right ribs that does not go away when changing position, after sleep. The pain is worse with activity. There is a one-time vomiting, and when moving to a more severe stage - diarrhea. The temperature increases slightly, weakness and nausea occur. Inflammation of the appendage of the cecum is confused with:
- Gynecological diseases;
- Intestinal infections, poisoning;
- Kidney diseases.
During long-term pregnancy, pain is generally barely felt, and inflammation risks starting asymptomatically. The child has complaints that raise thoughts of poisoning or gastritis.
Alarming symptoms
Appendicitis is a disease that affects both adults and young children. Depending on age, the manifestations of the disease may differ. However, there are characteristic signs that may indicate the onset of an inflammatory process in the appendix:
- pain in the right iliac region that does not disappear after sleep or when changing body position;
- slight or sudden rise in temperature;
- single vomiting in adults, multiple vomiting in children;
- nausea, weakness;
- in some cases, stool disturbances are possible.
It is especially difficult to determine the disease in women, since these symptoms may be characteristic of gynecological pathologies. Pregnant women may not pay attention to the manifestations of appendicitis, confusing them with toxicosis in the early stages. In the later stages, pain is not very pronounced or practically absent.
The appendix can be mistaken for poisoning, an exacerbation of gastritis. However, in no case should the symptoms be ignored, since appendicitis in extreme cases can lead to death or numerous complications.
Who should I contact?
Who should you contact if you suspect inflammation of the appendix? If you suspect appendicitis, there is no point in contacting your local physician; a surgeon will help. People go to him if the symptom is only pain, the person is able to go, wait in line.
An acute attack involves calling an ambulance to your home, work, or any public place. Not knowing where to turn, call an ambulance, a patient with appendicitis needs urgent help, the doctors will come.
When a woman, especially a pregnant woman, is diagnosed, it makes sense to consult a gynecologist to rule out gynecological inflammation.
Signs of appendicitis in a child's blood test
It is difficult to determine inflammation of the appendix in children by the presence of symptoms. This is due not only to the characteristics of the child’s body, but also to the fact that the child, as a rule, cannot correctly describe his feelings.
Diagnosis of appendicitis in children is carried out using the same methods as in adults (examination, palpation and laboratory tests). The main difference is the result of the analysis. In accordance with the fact that the norms of the child’s blood parameters are lower, the leukocyte level, indicating pathology, will be different.
In a child, appendicitis is also confirmed with the help of tests; examination does not always provide accurate information
Leukocytes in children with appendicitis will be more than 11. If the figure approaches 15 - 16, then the probability of peritonitis is high. However, it should be taken into account that the normal number of leukocytes depends on the age of the child.
Standard leukocyte parameters according to age are shown in the table.
| Age | Leukocyte norm |
| from 0 to 3 years | 6-17 |
| from 3 to 6 years | 5-12 |
| from 11 years old | 9-12 |
The ESR level also changes. At the initial stage of the inflammatory process, no significant changes are observed. The rate at which red blood cells settle changes sharply during an acute attack of appendicitis.
The decision about the need for surgery is made by the doctor, taking into account the results of all tests
Only a qualified specialist who will take into account both the patient’s condition and the diagnostic results can recognize the pathology of the appendix and not make mistakes in assessing the research results.
How is it diagnosed?
To make a diagnosis, the doctor will perform a series of manipulations. Inflammation spreading to the appendix is diagnosed by palpation. Attention is paid to complaints and the general condition of the patient. They may prescribe an ultrasound and other studies to rule out other diseases. General tests and abdominal tomography are prescribed, and the diagnosis is made based on the data obtained. If it is confirmed that the cecum and appendix are to blame, the patient is hospitalized and prepared for surgery. Conservative treatment does not help.
Signs of appendicitis according to blood tests
After laboratory tests, the doctor evaluates the changes in the indicators that the blood test gave for appendicitis.
We have selected useful articles on the topic
How gut health affects the heart
26.02.2021
Research using ultrasound machines
15.02.2021
How hobbies affect the body
12.02.2021
Blood donation is carried out for several types of studies:
- general indicators;
- amount of C-reactive protein;
- leukocyte count;
- ESR;
- hCG indicator.
A general blood test shows the presence of an inflammatory process, so the level of leukocytes in appendicitis is exceeded. The acceptable indicator is 9, if inflammation progresses, then the analysis may show 14. With pathology of the appendix, the level of leukocytes increases - more than 18.
If some indicators in the general blood test are elevated, this may indicate the presence of inflammation
The number of white blood cells may increase under the influence of other diseases. Also, in older people this indicator may not change. For this reason, other tests are additionally carried out, the results of which together help to obtain an accurate clinical picture.
ESR is an indicator of the sedimentation rate of red blood cells (erythrocytes). ESR with appendicitis is also increased, but in pregnant women this indicator is natural, as is the level of hCG.
The diagnosis can be confirmed by testing the amount of C-reactive protein, which also increases under the influence of the inflammatory process.
You can talk about appendicitis if there is a large number of neutrophilic leukocytes in the blood
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will need to correlate all the changes, and only when the level of each indicator increases above acceptable standards can a diagnosis be made.
Note! In pathology of the appendix, there is an excess of neutrophilic leukocytes.
Complications if you don’t see a doctor
The child's body is especially susceptible; if the child has doubtful symptoms, it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor. Adults shouldn’t drag things out either, the count goes on by the day, by the hours.
Non-purulent inflammation
In the first stages, with non-purulent inflammation, it is possible to remove the appendix by laparoscopic intervention. Three incisions of 1.5-2 cm are made, the organ is removed, the wounds are sutured, leaving cosmetic stitches that are not noticeable after healing.
The operation is carried out quickly, the stitches are removed after 3 days, recovery is quick and painless. This is a gentle intervention that disrupts a person’s usual way of life for a short time; rehabilitation takes place within a month.
Purulent appendicitis
With purulent appendicitis, there is no choice; abdominal surgery is required with an incision of about 8 cm, performed on the side, with longer healing. Peritonitis leaves no choice at all; an incision is required, the organ is removed, and the abdominal cavity is cleansed of contents. In this case, the wound is not completely sutured; a catheter is inserted into it to remove residual fluid, in order to avoid the new development of peritonitis and other complications. Recovery after surgery will require three months or more in case of complications, the rehabilitation process will be more difficult and slower.
Where to go if you suspect appendicitis
Having recorded presumable signs of appendicitis, you must not delay a medical examination. When deciding who to contact if you suspect inflammation of the appendix, you can go in several ways:
- In case of acute, severe pain or severe deterioration in health, you will need to call an ambulance at home or at your place of work. After examining and palpating the abdomen, the emergency doctor will decide whether you need further immediate examination or whether the diagnosis of the body can be postponed for several days.
- In case of dull abdominal pain with unclear localization, there is also no need to delay the examination. In this case, you can contact your local paramedic or therapist. After the examination, the doctor will write out the necessary directions for tests and refer you to specialists for additional examination.
- Appendicitis can also occur during pregnancy. In pregnant women, acute inflammation can develop according to an atypical scenario, and therefore, if she feels any disturbing signs in the abdomen, the expectant mother should definitely notify her gynecologist about the change in well-being.
- In women, signs of appendicitis are often similar to ectopic pregnancy. If there is a delay or abdominal pain, it will not be superfluous to undergo an ultrasound scan and examination by a gynecologist in a short time.
Postoperative complications
Complications arise in the preoperative period, during surgery, and after the event. During surgery, risks are created by anesthesia and allergies.
Medical errors and difficulties associated with the patient’s unstable condition and the need for prolonged cleansing of the abdominal cavity from pus are dangerous.
Main reasons
After surgery, complications are associated with the initial serious condition of the patient in advanced cases, non-compliance with diet, hygiene, and suture care.
Fusion of internal and external seams
It is possible for the internal suture to fuse with the external one in case of pain, when the patient strives not to move and refuses to perform a physical training complex. Physical activity after surgery is contraindicated, but as your condition improves, you need to start moving. When the sutures fuse, it is necessary to cut them out and apply new ones, which delays discharge and forces you to stay in the hospital for weeks.
Supuration of sutures
Suppuration of sutures occurs due to improper care, infection, or non-compliance with hygiene rules. It is necessary to remove stitches and disinfect surfaces. The person remains in the hospital until the infection goes away and healing begins.
Hernias, discrepancies
Hernias and discrepancies occur due to excessive stress and rejection. The problem forces you to stay in the hospital for a long time; the suture remains rough after discrepancies and inflammations, and the scar is very noticeable.
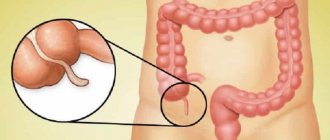
What is appendicitis?
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix - an appendage about 9 cm long, which is a continuation of the large intestine. No one knows exactly the function of the appendix, but one thing we know for sure: a person can live without it without obvious consequences.
Appendicitis requires emergency medical care, namely surgery to remove the appendage. If an inflamed appendix is not treated promptly, it will burst or perforate, spilling infected contents into the abdominal cavity. This can cause peritonitis , a dangerous inflammation of the inner lining of the abdominal cavity (peritoneum). If you do not immediately treat it with strong antibacterial agents, it can lead to death.
Sometimes abscesses filled with pus form outside the inflamed appendix - this is a source of infection, fenced off from surrounding tissues. Then the scar “ fences off ” the appendage from other parts of the abdominal cavity, protecting it from spreading the contents.
The appendix, in the abscess stage, is not an emergency, but, unfortunately, it cannot be identified without surgery. Because of this, all cases of appendicitis are classified as emergencies requiring surgical treatment.
You can get appendicitis at any age. It most often occurs in people aged 10 to 30 years, and least often before 2 years of age.
Timely consultation with a doctor is a guarantee of successful treatment
If you notice health problems, feel persistent pain in the abdomen, or symptoms reminiscent of appendicitis, you should immediately consult a doctor. Modern diagnostics will make it possible to clarify in detail the state of health, the origin of pain and ailments. Emergency assistance will eliminate risks to health and life, reduce the rehabilitation period by months, allow you to take advantage of the capabilities of laparoscopy, and perform the operation easily. An illness caught in time will not leave a negative imprint on your lifestyle for a long time. The risk of negative consequences and dangerous complications will remain minimal.
Prompt diagnostics and doctors will help diagnose the disease with minimal loss of time, excluding gynecological and other similar problems. Research will put an end to your thoughts. It is unreasonable to be afraid of surgery - unfortunately, there is no other way to treat appendicitis, and neglecting it is deadly.
How is the examination carried out?
Regardless of which doctor you consult, first of all tell him when the pain began, describe in detail all unusual sensations, and tell him about disorders of the digestive system.
If possible, take with you an outpatient card - it indicates all chronic pathologies, allergies to drugs and previous operations. If this is not possible, try to provide this information yourself in as much detail as possible. This will help to suggest or exclude other pathologies and select the best treatment regimen.
All medical care (examination, surgery, rehabilitation) for appendicitis in the acute phase in public hospitals is provided free of charge. All institutions receiving funding from the budget are required to examine Russian citizens.
Complications
Patients often try to delay their visit to the hospital, hoping that their condition will stabilize. Many people are afraid of surgery. Timely access to a medical institution, when appendicitis has not yet taken on an acute form, allows laparoscopy to be performed.
With this type of surgery, 3 small incisions are made in the abdomen into which an instrument is inserted. The operation itself takes little time, the patient quickly goes through the rehabilitation period and can return to a full life.
If the visit to the surgeon was delayed and peritonitis developed, then abdominal surgery is indicated. To do this, an incision is made on the side, the peritoneum is cleaned of residual pus, washed and internal and external sutures are applied. Recovery after such surgery takes longer, and the risk of complications is high.
They may be as follows:
- Suppuration of the sutures. If this happens, the suture is removed, the affected area is cleaned and disinfected. The stitches are applied again, and the patient is prescribed antibiotics. You will have to stay in the hospital until your condition stabilizes.
- Fusion of internal and external seams. Occurs if the patient does not engage in exercise therapy and tries to move as little as possible. This condition can negatively affect the functioning of internal organs, so the sutures are excised and re-sutured. Discharge time is delayed.
- Suture dehiscence and hernia formation. Occurs after abdominal surgery, when the patient lifts weights or exposes himself to excessive stress. The sutures separate and the abdominal organs can move into the cut hole. Often this is the intestines. In this case, repeated surgical intervention is performed, and the patient has to stay longer in a medical institution.