Analysis of concepts
Bulbopathy is by no means a specific diagnosis, but a generalized name for many pathologies of the bulbus, which inevitably lead to disruptions (to one degree or another) of intestinal digestion along the entire length of the digestive tube.
The causes of bulbopathy can be purely functional (impaired motility of the muscle layer, secretion, indigestion) and organic (intestinal deformations, tumors localized in the intestinal wall or in the immediate vicinity). Thus, the concept of bulbopathy includes bulbitis (inflammatory diseases of the mucous membrane), which give a diverse clinical picture, and the identification of atypical cells, which is classified as a precancerous condition and requires special attention.
Note! It is at least incorrect to replace the concept of “bulbit” with the concept of “bulbopathy” - it is much broader and more general.
Classification of bulbits
Bulbits of different types give similar clinical symptoms, although they look different upon visual examination.
“Erythema” literally means “redness” in Greek. The rush of blood to the tissues, which causes redness, is not without cause; it is caused by certain irritating factors. This phenomenon occurs due to the thinning of the upper layer of the bulb and stagnation of blood in the vessels of the inflamed area, which is clearly visualized upon examination in the form of individual foci or a continuous surface.
But it is a characteristic sign of inflammation in general and bulbitis of any form in particular, therefore the expression “erythematous bulbopathy”, like the expression “congestive bulbopathy”, is not only not a diagnosis, but also illiterate from a medical point of view.
Another thing is that stagnation, disturbances in the motor properties of the intestine can and often become the cause of chronic and acute bulbitis. Stagnation of food provokes a significant narrowing of the lumen of the bulbus precisely in the place where the intestine sharply changes its spatial orientation, taking on a conditionally vertical position. Therefore, a slight weakening of peristalsis sometimes causes large-scale consequences.
Erosion is a superficial defect of the mucous membrane, but this name should not mislead anyone. This is a dangerous destruction of its upper layer, where the development of any ulcer begins, its forerunner. Erosive forms of bulbitis indicate that the disease is far advanced, and the patient did not receive adequate treatment, or the irritating agent acted for a short time, but had a high degree of aggression. For example, a person drank a concentrated solution of acid or consumed low-quality alcohol (which happens much more often).
How to treat erythematous bulbopathy
The treatment of erythematous bulbopathy is based on diet therapy.
Heavy foods, spicy seasonings, as well as alcohol, soda and drinks containing caffeine should be excluded from the diet.
During an exacerbation, you can only eat food in liquid or semi-liquid form, and it should be warm.
The patient is recommended to use slimy porridges, jelly, chicken broth in his diet; later, crackers, boiled meat and pasta can be gradually included in the diet.
To speed up the healing process, you need to take two tablespoons of vegetable or olive oil daily: it coats the mucous membrane and has a mild laxative effect.
With the permission of a doctor, traditional medicines can be used as additional therapy: gastric tea, decoctions of chamomile, calendula and St. John's wort.
Along with the normalization of the diet, drug therapy is carried out. Depending on the cause and form of the pathology, as well as the presence of concomitant diseases, doctors may prescribe the following drugs:
The correct selection of food and medications provides a favorable prognosis for recovery even with advanced forms of bulbitis.
Causes of bulbopathy
The function of the duodenum (in Latin - duodenum), like the entire gastrointestinal tract, is carried out by regulators in the form of:
- the nervous system, or rather, its vegetative department, while the mental, emotional state of a person has a strong influence on him, albeit implicit;
- hormones secreted by the endocrine glands - the so-called hormonal adjustment;
- special biologically active substances - proteins, which are catalysts for complex processes and the secretion of enzymes, local level regulators that control the production and activation of digestive juices (in the duodenum, one of such regulators is trypsin).
Violation of such regulation can definitely lead to bulbopathy.
Among its external causes:
- nutrition factor;
- injuries to the mucous membrane of the bulbus by swallowed foreign bodies (one of the causes of erosive bulbitis);
- infections of the digestive tract, including the biliary tract and pancreas.
Note! Contamination with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori weakens local immunity and greatly increases the risk of developing bulbopathy.
Conditionally external (not directly related to the duodenum) causes of bulbopathy:
- neoplasms of different localization, complicating both motility and the secretion of enzymes in the lumen of the duodenum;
- disorders of nervous regulation, leading to spasms, disruption of blood supply to certain areas of tissue and having an indirect effect on peristalsis;
- violations of the acidity of gastric contents;
- helminthic infestations;
- congenital defects of the bulbus (duodenum).
As a rule, the basis of bulbopathy of any kind is a combination of a number of the listed reasons.
Types of diseases and their symptoms
Let's consider the varieties of bulbitis, differing in cause and symptoms:
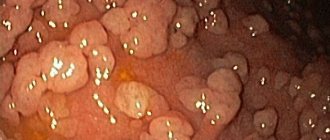
- Superficial - the upper part of the mucous membrane is slightly affected, is mild, and can be a precursor to other gastrointestinal diseases. Often called bulbitis 1st degree. It is characterized by symptoms such as rumbling in the stomach, aching minor pain during hunger. Due to the inflammatory process, swelling is observed, which makes the passage of digestive enzymes into the duodenum difficult. This causes poor digestion.
- Erythematous . Small localized ulcers form on the mucous membrane. But if the disease starts, the damage can reach the muscle layer. In the chronic form there is usually no pain. A quick feeling of satiety is experienced. Most often, this type of bulbitis is caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Heartburn occurs after eating. Abdominal bloating, weakness, belching, and nausea are also observed. Timely treatment is necessary. If the process is started, an ulcer is inevitable.
- Focal bulbitis . Ulcerative formations occur that spread throughout the intestines and even the stomach. Accompanied by heartburn, almost constant pain, regardless of whether the person is hungry or full. With this type of bulbitis, the doctor, upon diagnosis, discovers extensive lesions of the bulb, which is typical for focal bulbitis. They can spread throughout the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms may be similar to ulcers and erosive bulbitis. Experts warn that fasting and long-term diets leading to vitamin deficiency often provoke this type of bulbitis. Focal bulbitis takes a long time to be treated and requires the patient to eat properly with quality products, visit resort areas, and give up bad habits.
- Hemorrhagic . The mucous membrane of the bulb becomes covered with erosive formations, which leads to bleeding.
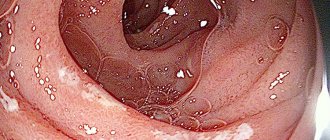
- Follicular . There is a type of diagnosis called fibrogastroduodenoscopy. With this diagnosis, follicles are detected on the walls of the bulb caused by inflammation. The cause of follicular bulbitis is parasites, namely Giardia and helminths, which arise due to poor personal hygiene, decreased immunity, and poor nutrition. The prognosis for cure is favorable.
- Catarrhal . Characterized by swelling of the mucous membrane. The swelling is caused by a disruption in the outflow of secretions. Stagnation of bile and enzymes is the cause of catarrhal bulbitis.
- Hyperplastic . Folds and polyps form in the bulb. The bulbous tissues grow. Usually occurs when bulbitis is running. The patient is in severe pain. Mainly caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
- Atrophic . Due to poor nutrition and untimely consultation with a doctor, the wall of the bulb reaches the blood vessels that supply it with blood. At the beginning of the disease, the disease does not manifest itself in any way.
- Diffuse . One of the very dangerous types of bulbitis, when lesions can spread not only in the bulb, but throughout all organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
For any symptoms, even mild ones, it is necessary to consult a doctor to clarify the diagnosis and determine treatment.
If the disease is advanced, a person loses weight, feels weak, and unwell, because due to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract associated with the disease, beneficial microelements that come from food are not absorbed properly.
Symptoms
The symptoms of bulbopathy depend on the nature of the pathology, and the symptoms of bulbitis are similar to the symptoms of inflammatory diseases of the stomach and are often of a blurred, implicit nature, making it difficult to make a diagnosis, among them:
- discomfort in the epigastric region;
- mild, so-called “spread” pain;
- bitter belching, occasional stool disorders.
Acute cutting pains are characteristic, as a rule, of erosive bulbitis. Pancreatic juice and concentrated bile, entering the lumen of the bile duct almost simultaneously, play the role of a hellish mixture for the inflamed mucosa.
Preventive recommendations
It is possible to avoid stomach bugs if you regularly monitor your diet. Do not overuse spicy, fatty and other unhealthy foods. You should eat regularly, eating small portions. Quitting smoking and alcoholic beverages helps prevent the pathological process. During long-term drug therapy, it is recommended to take probiotics that normalize the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract. An equally important preventive measure is regularly checking the body for helminth infection.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of bulbopathy is multi-stage and impossible without a detailed interview with the patient. To identify systemic pathologies, the time frame of disease symptoms is very important. Indicative is the duration of the leading symptom for at least 3 months during the current six months.
Among the instrumental examination methods, the most informative is esofibrogastroduodenoscopy. It allows the endoscopist to see areas of inflammation and/or pathological changes in the tissue, if any - suspicious tumors, polyps, so-called granular tissue degeneration. In this case, a microscopic piece of tissue is taken for analysis - a biopsy. Ultrasound monitoring helps assess the condition of the biliary tract and pancreas.
Other examination methods include:
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- feces for helminths;
- biochemical blood tests, the volume of which is determined by the doctor.
Based on the survey results, the doctor may prescribe additional tests - a test to determine acidity and bacterial colonization.
Drug treatment of duodenal bulbitis
Therapy uses three types of medications:
- to reduce acid production (proton pump blockers, H2-histamine antagonists);
- to improve the protective properties of the mucous membrane (bismuth preparations);
- to accelerate tissue regeneration (actovegin, solcoseryl).
If Helicobacter-associated bulbitis is detected, the patient is prescribed a diet, de-nol, a representative of omeprazole and 1-2 antibiotics (metronidazole, clarithromycin, amoxicillin, tetracycline or another drug of choice).
What to do
The treatment regimen is built based on test results and based on the main symptoms and causes of the disease. Therapy for bulbitis comes down to eliminating the factors that caused the inflammation.
Drug therapy
The medicinal content of the treatment regimen depends on the type of pathology, the etiology of bulbitis, the patient’s condition (the nature of the symptoms present) and a bouquet of chronic diseases. A specific treatment regimen can only be drawn up for a specific patient. The list of drugs most often includes:
- anti-inflammatory and painkillers;
- antacids that reduce the irritating effect of stomach acid;
- enveloping agents that prevent further trauma to the mucous membrane and the development of complications;
- means that stimulate bulbus peristalsis and guarantee timely evacuation of food.
Bulbopathy of any type can lead to partial or complete loss of function of the entire duodenum.
Recommended Diet
Following a diet for any gastrointestinal disease is the most important condition for recovery. Food should be of such consistency, temperature and composition as to prevent irritation of the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines, especially if they have areas of erosion.
Traditional medicine
For inflammation of the duodenum mucosa, raw potato juice has worked well as an additional remedy. For a month, take it in the morning on an empty stomach, at least 100 ml (half a glass, preferably a glass). It is prepared without allowing the raw materials to come into contact with metal and without using a juicer - the potatoes are grated on a plastic grater, and then the resulting mass is squeezed out.
Doctors recommend flax seeds as an enveloping agent. A tablespoon of raw material is poured in a glass of water in the evening, boiled for 10 minutes in the morning, left for half an hour, and taken a third of a glass three times a day between meals for a month.
Clinical picture
Often people go to the hospital when bulbitis is already in a very advanced state. This disease develops gradually over one to three years. The main symptoms are the following:
- pain in the epigastric region;
- frequent “hunger pains”;
- weakness and lethargy;
- nausea and vomiting.
With this disease, the presence of blood streaks and a bitter taste in the mouth can often be observed in the vomit. The inflamed walls of the bulbous isthmus are very vulnerable, and rough pieces of food can scratch it.
If the bulbitis is in a very advanced state, then painful ulcers are very likely to appear, which can cause nausea.
When food enters the intestinal vestibule from the stomach, affected by erythematous bulbitis, unpleasant aching painful sensations occur in the epigastric region. This occurs because the inflamed mucosa is injured by food entering the bulbous isthmus.
Typically, “hunger pains” occur closer to lunch, when the production of gastric juice is activated. They can be easily removed by drinking a glass of milk or taking any antacid.
Since the digestive tract is inflamed, food is poorly digested and absorbed. Not enough glucose and other nutrients enter the blood. The body begins to save energy, and the person becomes weak and lethargic.
In most cases, bulbitis occurs as a result of the following reasons:
- stress and nervous tension;
- poor nutrition;
- side effects of medications;
- mechanical injuries.
The intense rhythm of life and constant nervous experiences directly affect the functioning of the digestive tract. Problems arise with gastric secretion, which then spread to the bulbous isthmus and the intestine itself, causing various types of inflammation.
Poor nutrition is the root of all evil.
An irregular diet, high-carbohydrate and fatty foods gradually form diseases of the digestive system. They gradually corrode the walls of the stomach and the bulbous isthmus as a whole, forming erythematous bulbopathy and other diseases.
Drug treatment has a negative effect on the entire digestive system. Almost all medications pass through the stomach to enter the bloodstream. Nonsteroidal drugs have a particularly severe effect on the bulbous isthmus. They suppress its secretion, causing bulbitis and poor absorption of nutrients.
There are three main types of erythematous bulbopathy:
- acute;
- chronic;
- erosive.
The most severe type is erosive, since it can provoke internal bleeding and cause peritonitis. It is also necessary to ensure that the acute primary form of bulbopathy does not become chronic.