What is sigmoidoscopy of the intestine?
The procedure is prescribed to almost everyone who turns to a proctologist with complaints in the gastrointestinal tract, allows you to examine the rectum and sigmoid colon within 5 minutes, identify pathologies and prescribe treatment.
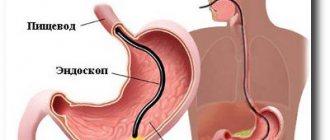
To examine the mucous membranes of the anus of the rectum and the lower part of the sigmoid colon to a depth of 35 cm, a special sigmoidoscope device is used.
It has high-precision eyepieces that help to visually detect the smallest tumors and immediately take a piece of tissue for histological examination.
This helps to detect cancer at an early stage and save the patient’s life.
Rectoscopy of the rectum is a procedure that each of us after 40 years of age should undergo once a year, as paraproctologists advise, for preventive purposes.
Using a sigmoidoscope, a proctologist can evaluate the most important parameters of the intestinal walls:
- color and tone of mucous membranes;
- condition of the submucosa;
- relief design;
- elasticity of blood vessels;
- the presence of hemorrhoids, polyps, ulcers and erosions;
- cracks, scars, foreign bodies.
A professional will quickly recognize inflammatory processes and what causes them, assess the performance of the intestines and be able to make the correct diagnosis. But only if the pathology is located no more than 35 cm from the anus.
Otherwise, or if a controversial situation arises, the patient is sent for a colonoscopy.
The device allows you to: right during the inspection:
- take tissue from a suspicious area of the rectum for a biopsy;
- remove polyps;
- cauterize the tumors;
- stop bleeding of blood vessels by coagulating them;
- to bougie, that is, to expand the anal canal when it narrows.
Rectoscopy for hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoidal cones cannot always be identified by visual examination or rectal, digital, and perineal examination. They are often located very high and can only be diagnosed using a sigmoidoscope.
Hemorrhoids can be a sign of serious inflammatory processes, including cancer. Timely diagnosis will detect cancer and save your life.
Acute hemorrhoids almost always cause unbearable pain. In this case, sigmoidoscopy is performed after the inflammation has been relieved. In case of emergency, local anesthesia is given.
Contraindications to sigmoidoscopy
In addition to its indications, the procedure for examining the rectal organ has contraindications, but these restrictions apply for some time until the patient’s condition improves. Sometimes the patient has pathological manifestations in which testing of the rectum and sigmoid colon is postponed.
It's connected with:
Specialist
- acute anal fissures;
- narrowed lumen of the rectal organ (prioritized or genetic feature of the body);
- significant blood loss from the anus;
- acute inflammatory phenomena in the peritoneum (for example, peritonitis);
- pulmonary and heart failure;
- mental disorders;
- general serious condition.
If at least one of the above signs of the condition of the anorectal zone is observed, proctologists say that these are temporary contraindications to rectal manoscopy. However, there are cases when the patient still undergoes diagnostic tests despite contraindications, then before the procedure the patient is administered a local anesthetic to relieve pain.
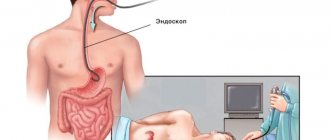
Sigmoidoscope: what kind of device is it?
This is a metal or flexible hollow tube with a lighting device at the end, which is connected in series as needed:
- air supply system to the intestines to better view the folds of the mucous membrane;
- optical eyepieces for inspection;
- forceps for collecting tissue for histological examination;
- special loop for removing tumors.
Sometimes the device is connected to a monitor, and then the proctologist sees the results of the examination on the screen.
In modern clinical centers, a sigmoidoscope is often used, the tube of which is flexible and has a small diameter, maximum 12 mm.
The device comes in different lengths, from 25 to 35 cm. The diameter is also selected individually. It comes in 10, 15 and 20 mm.
Proctologists are especially careful when choosing the size of a sigmoidoscope when examining a child.
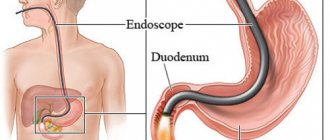
Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy: what is the difference
Which is better: sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy is not a completely correct question. Both procedures are prescribed and performed in hospitals with the same frequency, complementing each other.
The choice of method is made by the proctologist, taking into account the specific situation of the patient. Often, after rectoscopy, colonoscopy is prescribed if necessary, for example, when the patient feels unwell, but RRS (RetraRomanoscopy) did not reveal any pathology.
Devices and capabilities
A sigmoidoscope is a rigid or flexible tube that allows you to examine the walls of the rectum and distal sigmoid colon at a distance of no more than 35 cm from the anus.
Colonoscope – has a soft tube. At the end there is a powerful video camera and lighting device, the information is displayed on a computer monitor. Allows a detailed examination of all parts of the large intestine, including the cecum.
Indications for diagnosis
Rectoscopy is prescribed in the case of:
- long-term frequent constipation;
- stool disorders, when diarrhea is replaced by hardening of stool;
- feeling of incomplete bowel movement;
- painful syndrome, pain and burning in the perineum or lower abdomen;
- discharge of pus and mucus from the anus;
- chronic hemorrhoids;
- suspicion of a cancerous tumor or benign formation in the rectum;
- weight loss for no apparent reason;
- monitoring the effectiveness of previously prescribed treatment;
- preventive examination after 40 years, so as not to miss the initial stage of rectal cancer.
For all these symptoms, a diagnosis can be made by examining only the condition of the rectum.
Colonoscopy will be prescribed if pathology of the upper intestines is suspected and in the following cases:
- bleeding from the anus;
- anemia, a sharp drop in hemoglobin levels, fatigue and weakness.
- suspected Crohn's disease;
- sudden weight loss with a normal, habitual diet;
- hidden blood in stool according to test results;
- constant pain in the intestines and colic in the abdomen, feelings of discomfort;
- upcoming gynecological surgery;
- removal of polyps and cauterization of ulcers located in the upper gastrointestinal tract;
- suspicion of intestinal cancer.
Colonoscopy is much more informative and gives an idea of the condition of the organ and the changes occurring there as a whole.
But if we are talking about the lower sections, then it is more advisable to do a rectoscopy, since the colonoscope almost cannot view them.
RRS (sigmoidoscopy) :
- much easier to tolerate;
- has fewer contraindications;
- carried out mainly without anesthesia;
- takes only 5 minutes of time;
- preparation for it does not require special care;
- After the procedure, patients usually do not feel any discomfort or complications;
- there is a risk of missing the development of the disease in the upper intestines.
Colonoscopy:
- a more serious and painful procedure;
- often carried out with anesthesia, up to general anesthesia;
- can last up to an hour;
- allows you to diagnose more serious and profound pathologies of the organ;
- preparation at home or in a hospital setting takes longer;
- if the intestines are not properly cleaned, diagnosis is not carried out;
- has more contraindications and complications.
- makes it possible to identify serious pathologies in the early stages throughout the intestine with a high degree of probability.
How is sigmoidoscopy different from colonoscopy?
Many patients have heard about another method of diagnosing the intestines from the inside - colonoscopy - and want to know how it differs from sigmoidoscopy of the rectum. Although both procedures are equally valuable as diagnostic tests and can be performed alongside biopsies and medical procedures, they have a number of differences, which are presented in our table below:
| Options | Sigmoidoscopy | Colonoscopy |
| Field of study | Rectum and part of the sigmoid | All parts of the large intestine |
| Invasiveness | Small | High |
| Painful sensations | Minimal or absent. | Palpable and require anesthesia. |
Medical indications
The device is equipped with a high-precision modern optical system that allows you to identify problems in the lower intestine - erosions, cracks, deep hemorrhoids, ulcers, tumors, inflammatory processes.
The following patient complaints are the reason for prescribing the procedure:
- pus or mucus from the anus;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen, often accompanied by constipation and hard stool;
- pain in the perineum and lower intestine;
- hereditary predisposition;
- frequent problems with bowel movements, a feeling of fullness after bowel movements;
- bleeding from hemorrhoids;
- diarrhea followed by constipation;
- exacerbation of existing intestinal diseases.
After examination, the proctologist can confirm or deny:
- the presence of a cancerous tumor, take the material for histological examination;
- Crohn's disease;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- proctosigmoiditis;
- proctitis;
- ongoing pathological changes and inflammatory processes characteristic of a precancerous condition;
- polyps, internal fissures, erosions;
- congenital anomalies of the distal intestine;
- presence of internal hemorrhoids;
- prostate or pelvic cancer;
In addition, the procedure is often prescribed to women by gynecologists, and to men by urologists before surgery or as a preventive examination for the timely detection of malignancy.
Indications and contraindications
There are numerous indications for rectoscopy, but all of them are associated with dysfunction of the lower intestine. The procedure is used to identify inflammatory processes in the rectum (proctitis, paraproctitis), the presence of neoplasms (polyps, rectal cancer) and other proctological diseases. The reason for the examination may be:
- chronic constipation or alternating constipation with diarrhea;
- the presence of traces of blood on stool, underwear or toilet paper;
- uncomfortable bowel movements (painful, repeated);
- incontinence of feces and gases;
- excrement of feces in the form of ribbons;
- rectal prolapse;
- hemorrhoids and anal fissures;
- the presence of a foreign object in the rectum.
Previously identified rectal polyps are also indications for rectoscopy. An examination is also carried out to monitor previous operations.
Important! Doctors advise patients over 40 years of age to undergo rectoscopy once a year, even in the absence of alarming symptoms.
People of this age are at increased risk of developing colorectal cancer, which in most cases is asymptomatic.
There are no categorical contraindications to rectoscopy, however, in some cases it is necessary to postpone the procedure due to the inappropriateness of the examination or the high risk of complications. Such situations include:
- heavy bleeding from the anus;
- abnormal narrowing, spasm of the anal sphincter;
- acute inflammatory and purulent processes in the rectum;
- anal fissure in the acute stage.
The listed conditions make examination difficult due to increased pain, so you must first consult with a coloproctologist regarding their treatment, and then plan a diagnosis.
Also, rectoscopy is not performed if the patient has worsened diseases of the cardiovascular system: hypertension, arrhythmia, cardiosclerosis, heart attack and others. In patients with severe illness, additional discomfort may aggravate symptoms and lead to critical illness, so testing is delayed until the condition has stabilized.
Contraindications
Diagnosis using a sigmoidoscope is a simple, painless procedure with a minimum of contraindications. But they still exist.
Sometimes it should be postponed due to pain that may occur during examination as a result of inflammatory processes with:
- anal fissures;
- stenosis, i.e. narrowing of the rectal lumen;
- inflammation of the abdominal cavity, peritonitis;
- acute paraproctitis;
- severe bleeding during exacerbation of hemorrhoids.
And:
- with general malaise and weakness, poor health of the patient;
- for cardiac and pulmonary pathologies;
- in case of severe mental disorder.
The doctor will prescribe medications to relieve inflammation. And only then will he conduct research.
If the study is necessary for health reasons, the presence of an anesthesiologist will be required.
A woman's period of menstruation is not a contraindication. But it would be more correct to transfer the procedure to several days.
How to prepare properly
You need to start preparing 2 days in advance. Pay special attention to this, since not only the accuracy of the study, but also its painlessness will depend on thorough cleaning.
Preparation for sigmoidoscopy consists of two stages - a slag-free diet and cleansing the intestines of feces and gases.
The diet should be started 48 hours before the test. During this time, you should avoid foods that cause fermentation and a large volume of feces. These are fruits and vegetables, carbonated and alcoholic drinks, wholemeal bread, sweet and flour products, some types of cereals - millet, oatmeal and pearl barley. Avoid fatty, smoked and spicy foods, marinades and spices.
Give preference to lean fish and meat, broths made from them, crackers and biscuits, semolina or rice porridge with water. Drinks allowed are plain water, herbal tea, kefir, fermented baked milk, and ayran.
The evening before the test and in the morning you should cleanse your intestines. Do an enema or use laxatives such as Fortrans, Microlax - the choice will be made together with the doctor at a preliminary appointment.
Read very detailed information on how to prepare for the procedure in our articles at the following links:
How to Prepare for a Bowel Exam
Slag-free diet and nutritional rules before examination of the rectum
Ways to prepare for research
To conduct RRS, you need to prepare. Preparing the patient for diagnostic sigmoidoscopy begins 48 hours before the examination. It is recommended to adhere to dietary nutrition and cleansing measures of the intestinal organ.
Diet during sigmoidoscopy
Proper nutrition
Preparing a patient for sigmoidoscopy using a dietary method involves eliminating foods that contribute to gas formation and fermentation. Such products are considered to be legumes, fruits and vegetables, rolled oats, millet, and pearl barley. You should avoid bread (black), fatty meat and fish products, soda, flour and confectionery products, and alcohol.
Allowed are semolina, rice boiled in water, biscuits, crackers. The day before the diagnostic procedure, bowel cleansing procedures are recommended.
Cleansing the body with medications
Preparation for the diagnosis
of sigmoidoscopy and preparation of the patient with medications are as follows. For the purpose of cleaning, the proctologist prescribes the use of the drug Fortans. This is a laxative medicine. If for some reason the drug is not approved for use by the patient, you can use a similar medication (Lavacol, Flit).
Frotrans is diluted with water - 1 pack. 1000 ml. Water can be used after boiling and cooling to a warm state. The prepared solution is drunk in small sips, the effect of the drug begins 1 hour after administration. In the evening, you should take up to 4000 ml of cleansing solution. It is allowed to divide the medicine into two doses (in the evening and morning, 3.5 hours before diagnosis).
The rectal drug Microlax is produced in finished form, in special packaging (tubes). For cleansing before sigmoidoscopy, the introduction of two tubes is prescribed, with a break between enema of 25 minutes. In the morning after waking up, the procedure is repeated.
The day before diagnosis, patients should have a light lunch; it is recommended to avoid evening and subsequent morning meals. It is allowed to drink tea (weak, green variety) and water.
Colon cleansing with enema
Enema is performed in the evening before the morning diagnosis, as well as after waking up in the morning on the day of the procedure. The session is held twice, with an hour break. The water should come out clean. During one enema, up to 1500 ml of water is poured into the rectal organ. The enema is given twice in the evening and twice in the morning.
The procedure for performing rectoscopy
An appointment with a proctologist on the day of the procedure begins with him explaining in detail how to behave in order to avoid complications and pain, how you can help yourself, and what is not recommended.
Then a mandatory digital examination of the rectum takes place.
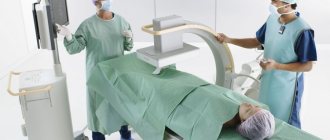
The patient undresses from the waist down and lies down on a special high couch on his side, closer to the edge, or takes a knee-elbow position with emphasis on his left arm. This depends on the purpose of the survey.
The position is chosen by the doctor, but most often this is the second option, since in this position the rectum and sigmoid colon are at the same level and the diagnosis is less painful.
Often embarrassment and shame causes the need to undress. Today at the pharmacy you can buy special disposable underwear - panties or shorts with a special hole in the crotch area. For more details, see our article at the link__.
Be sure to notify the proctologist if you:
- pregnant;
- suffer from cardiovascular pathologies or diabetes;
- have problems with the bronchopulmonary system;
- are taking medications prescribed by another specialist.
How is rectoscopy done:
- The tip of the tube, lubricated with a special agent, is inserted into the lumen of the rectum at a distance of 4-5 cm in depth using careful rotational movements. In this case, the patient must strain a little to facilitate the process.
- Then the doctor removes the obturator from the tube (a device that blocks the air supply) and puts an optical lens in its place.
- Pumping air with a pear, straightens the intestinal walls so that it is better visible, gradually moves the tube further, visually observing the process through the eyepiece.
- At this moment you should relax and follow the actions recommended by the doctor.
- If the examination is hindered by fecal residues, purulent or mucous discharge, they are removed with a cotton swab or electric suction device.
- If necessary, polyps are removed using a coagulation loop or forceps or tissue samples are taken for histology.
- The doctor releases air from the intestines and also carefully removes the sigmoidoscope from the perineum.
This completes the examination. It takes no more than 7 minutes. The result is usually ready in 1-2 weeks.
When finishing the knee-elbow position, you should lie on your back for a while.
After this, the patient can get up and go home.
Does it hurt?
No, the procedure is quite painless when compared, for example, with a colonoscopy. Unpleasant sensations comparable to those during an enema can only be felt while pumping air into the intestines. At this point, the doctor recommends taking a slow, deep breath in and out.
You can find reviews on the forums that confirm that the proctologist’s manipulations are absolutely painless.
For patients with anal fissures, severe inflammation or bleeding, and children under 12 years of age, the diagnosis is carried out under local anesthesia, simply by treating the insertion site of the sigmoidoscope with an anesthetic.
The intestinal mucous tissues do not have nerve endings, so the patient does not feel discomfort during the removal of polyps or other medical procedures.
Everything for work: SOP Sigmoidography
Target:
standardization of the procedure for performing rectoscopic examination.
Where:
endoscopic room of outpatient service (APS) and round-the-clock hospital (CSS)
When:
as prescribed by a doctor
Responsibility:
The person responsible for carrying out the procedure in accordance with the requirements of the SOP is the nurse in the endoscopy room. Monitoring compliance with SOPs is carried out by the senior nurse of the OPD
Regulatory and reference documentation
· Federal Law No. 323-FZ of November 21, 2011 “On the fundamentals of protecting the health of citizens in the Russian Federation”
· Order of May 31, 1996 No. 222 “On improving the endoscopy service in healthcare institutions of the Russian Federation”
SP 3.1.3263-15 “Prevention of infectious diseases during endoscopic interventions”
· SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations engaged in medical activities”
· SanPiN 2.1.7.2790-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the management of medical waste
· MU 3.1.3420-17 “Ensuring epidemiological safety of non-sterile endoscopic interventions on the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory tract”
Resources
:
1. Devices: Rectoscope with fiber light guide Rc-BC-3 35000/7700/26600, Rectoscope with fiber light guide Rc-BC-3 44095/78495/205/90199
2. Forceps, biopsy forceps.
3. Disposable gloves, 2 pairs.
4. Bathrobe, waterproof apron, cap, disposable mask 2 sets.
5. Disposable absorbent diaper - 1 pc., disposable panties - 1 pc.
6. Containers (3 liters - 2 pcs., 10 liters - 3 pcs.), filled with disinfectant solution according to the flow chart for processing the colonoscope.
7. Containers for transporting the colonoscope from the dirty area and from the clean area.
8. Metal tray for napkins.
9. Brushes for processing a rectoscope, Janet syringe.
10. Formalin solution 10%, bottles for histological material, container for transporting bottles to the laboratory.
11. Alcohol 70% 50 gr.
12. Gauze napkins
13. Distilled water
14. Disinfectant solutions, technological maps. Hourglass for 1 min., 2 min., 5 min.
15. Test for azopyram test and phenolphthalein test strip for TLD.
16. Class A and Class B garbage bags.
17. Fleece napkins for surface treatment.
18. Soap, sanitizer and paper hand towels.
19. Emergency kit for anaphylactic shock, anti-HIV kit.
20. Patient registers
Main part of the SOP
1. Introduce yourself, identify the patient based on medical documentation or passport (ask for full name, date of birth). 2. Register the patient in the journal 3. Inform the patient about the study, check for informed consent for the procedure. 4. Invite the patient into the treatment room, explain how to undress for the procedure and put on disposable panties. 5. Lead to the couch and help the patient take the necessary position - knee-elbow position. 6. The nurse is located next to the endoscopist; during the examination, the nurse assists the doctor. 7. If a biopsy is necessary, he provides forceps and helps put the biopsy material into a bottle with formaldehyde. 8. After the procedure is completed, the nurse takes the endoscope and performs initial cleaning of the endoscope, then places the endoscope in a container and moves it to a dirty area, where the endoscope is processed in accordance with the requirements of SP 3.1.3263-15 “Prevention of infectious diseases during endoscopic interventions” 9. After completion During the procedure, it is necessary to help the patient get up from the table, after making sure that he is feeling well. 10. Remove the disposable diaper from the couch (class B medical waste), treat the couch with a napkin moistened with disinfectant. solution. 11. Treat hands hygienically, place gloves, mask and apron in a container for class “B” waste. 12. Register the doctor’s conclusion on the study in a journal, fill out a bottle with biopsy material and fill out a referral form to the histology laboratory, place the bottle and the referral in a container for transportation. 13. Give the patient a conclusion form and inform that the procedure is completed. 14. Invite the next patient to the office.
Preparation for sigmoidoscopy.
1. There are three options for preparing for the study (the study is carried out in the first half of the day):
· Option 1:
Using the drug Fortrans
(the preferred method!):
The drug is taken the day before. It is advisable to start taking the drug 1.5-2 hours after eating. 3-4 sachets of fortrans (at the rate of 1 sachet per 20 kg of weight) are diluted in 3-4 liters of water and taken from approximately 15 to 19 hours. The effect of the laxative is 16-21 hours. Each sachet dissolves in 1 liter of water. In 1 hour you need to drink 1 liter of solution, 1 glass each in small sips over 15 minutes.
· Option 2:
Using enemas:
Two days before the procedure, it is advisable to switch to a gentle diet (exclude potatoes, mushrooms, brown bread, legumes, limit the consumption of vegetables, fruits, herbs, etc.). On the evening before the study (20-21 hours) it is necessary to do 2-3 cleansing enemas. In the morning on the day of the study, repeat 1-2 enemas; breakfast is allowed - sweet tea with a sandwich or bun.
· Option 3:
Preparation with Microlax:
The laxative is available in special tubes and is administered rectally. In the evening, it is recommended to insert two tubes of the drug into the anus, with an interval of 20 minutes. In the morning the procedure is repeated.
2. For examination, have with you:
a doctor's referral indicating the purpose of the study, a large sheet, a towel, data from previous studies.
Parameters for assessing and quality control of the methodology:
- compliance with the technology of performing the manipulation, - timely execution of the procedure, - ensuring infectious safety of the procedure, - availability of a record of the fulfillment of the appointment in the medical documentation, - patient satisfaction with the quality of the procedure, - doctor satisfaction with the quality of the manipulation.
Distribution of this SOP
Copy Department Original Chief nurse Copy 2 Head nurse OLD
Responsible executors are familiar with and undertake to perform:
| No. | Surname | Signature | date |
What to take with you
To make the procedure comfortable, it is necessary not only to prepare the intestines, but also to collect the necessary things in advance. Pack your bag the day before and take with you:
- slippers and sheets, disposable;
- socks if you are afraid that your feet will freeze;
- all medical documents: insurance policy, test results, medical record, etc. This should be discussed with your doctor in advance;
- sometimes older people need to have an electrocardiogram done first;
- passport;
- wet wipes and toilet paper - just in case. Moreover, if the procedure is performed in a clinic and not in a private medical institution.
Disposable panties or shorts and shoe covers must be purchased in advance at the pharmacy.