Today, MRI of the pancreas is an effective, informative method for visualizing its structures.
Using this technique, it is possible to identify large tumors, which guarantees timely treatment. The use of MRI allows you to build a three-dimensional picture of organ structures. The technique allows you to separate vascular elements and areas with fluid. This makes diagnosis much easier.
Advantages of the technique
Magnetic resonance today is the most highly accurate method for diagnosing lesions. The technique allows you to separate vascular elements and areas with fluid. This makes diagnosis much easier. An important advantage of MRI is the ability to obtain images in many projections. The procedure is harmless. Tomography is more informative than CT and ultrasound. The advantage is that MRI does not use harmful radiation.
Content:
- Brief information
- Advantages of the technique
- The essence of the technique
- Indications for the procedure
- Preparation and technique
- Application of contrast agent
- Contraindications to the procedure
- Safety of the procedure
- Price features
Carrying out an MRI procedure
- Magnetic resonance imaging is performed in a special room where a tomograph is installed. The room is maintained at a constant temperature of +18C, and there is an air conditioning and dimming system during operation of the device.
- The patient undresses to the waist and lies on the retractable tomograph table. To prevent unwanted movements during the procedure, the arms, legs and head are fixed with special fasteners. This is designed to avoid distortion of images due to unwanted movements.
- A contrast agent, if required - gadolinium - is administered intravenously using a syringe or a special catheter. Using contrast, it is possible to obtain clear images of neoplasms at the initial stage or small mechanical inclusions (stones). Gadolinium is harmless, is not deposited in tissues and is eliminated from the body within 48 hours.
- The tomography procedure is noisy; the patient is given special headphones that drown out external sounds and, using a built-in microphone, allow them to maintain contact with the doctor.
- After the preparations have been made, the scanning procedure is performed, which takes half an hour, and when using a contrast agent – up to 60 minutes.
- When using a contrast agent, the specialist takes a series of photographs - before the injection of the contrast agent, immediately after the injection and fifteen minutes later. This allows us to identify possible neoplasms and metastases in the pancreas.
After the procedure, the patient dresses and leaves the office. The tomography results are processed within an hour and given to the patient or transferred directly to the attending physician.
Correctly performed MRI diagnostics will help to identify disorders in the pancreas at an early stage, track the dynamics of the disease and take the necessary measures, prevent the disease and ensure the healthy functioning of this organ.
Preparation and technique
No special preparation is needed. You are allowed to eat and drink before the diagnosis.
If additional contrast will be used, then preparation is necessary. It is important to prepare for its implementation accordingly:
- Before contrast diagnostics, it is necessary to exclude fatty foods, do not drink alcohol, or take medications containing alcohol.
- Drinking coffee and tea is prohibited.
- Before the examination, it is recommended to remove any metal jewelry.
- It is prohibited to take the study with credit cards or telephones.
The table with the patient moves into the apparatus until the iron is under the magnet. There are innovative devices that eliminate the need to completely accommodate the patient.
Noise is generated during the study period. Therefore, it is possible to use headphones. The device is equipped with a speakerphone for two-way communication. It is allowed to have a loved one for support. To call a specialist, there is a button that is kept by the patient during the procedure.
Many more modern devices are additionally equipped with an internal camera to monitor the patient's condition. Therefore, during diagnosis, the patient is constantly under direct medical supervision for the entire duration of the scan (meaning from 20 minutes to a whole hour). Many cameras have special additional lighting and built-in air conditioners. Such solutions make the procedure even more enjoyable.
The procedure does not cause discomfort or pain to the patient.
It is extremely important to remain still - this is the key to high-quality photographs. At the doctor's signal, you will additionally need to hold your breath. Pictures are taken in series.
It is important to immediately report the first signs of pain or deterioration in health to your doctor.
The specialist receives images of the gland on the screen. Thanks to its versatility, the image is obtained in the desired projections. The doctor is deciphering. The patient receives the information in his hands.
Indications for MRI of the pancreas
As a rule, an MRI of the pancreas is prescribed to clarify or confirm the diagnosis. The examination begins with an ultrasound (ultrasound examination), such a diagnosis of the pancreas will show what the doctor needs to pay attention to, whether there is a suspicion of abnormalities in the structure of the organ. If the ultrasound doctor sees dark spots on the screen, this may be a sign of a neoplasm. In this case, a more detailed study of the organ is required. Ultrasound is prescribed primarily because this research method:
- fast;
- accessible;
- no special preparation required;
- There are ultrasound machines in almost every clinic.
MRI is an absolutely painless diagnostic method.
Indications are required to obtain a referral for an MRI. Ultrasound has certain disadvantages that do not allow us to limit ourselves to this method only when making a final diagnosis. This is a subjective method in which it depends on the professionalism and experience of the ultrasound doctor whether the attending physician will see that there are lumps or tumors or that they are absent. Therefore, when examining the pancreas, MRI is the preferred method.
Indications for examination of the pancreas using MRI:
- clarification of the nature of formations in the gland or organs of the abdominal cavity next to it, which were identified on ultrasound;
- confirmation of anomalies in the structure of the organ and their assessment;
- increase in organ size;
- chronic diseases of the digestive system;
- suspicion of pancreatitis;
- pancreatic cyst;
- suspected pancreatic cancer;
- constant abdominal pain of unknown etymology;
- suspicion of deterioration in the outflow of pancreatic contents;
- assessment of the condition of the organ after injury;
- abscess and development of purulent inflammation;
- as part of MRI of the stomach, other digestive organs and retroperitoneal space;
- monitoring the condition of the organ before and after surgery.
Digestive disorders are a reason for an MRI.
Application of contrast agent
Diagnosis usually takes place without contrast. Difficult diagnostic cases are always accompanied by contrast, especially if the vessels are affected.
Contrast is a special iodine-containing substance. It is necessary for maximum clarity of visualization of the examined elements. It is administered parenterally a few minutes before diagnosis. It is neutral, low toxicity, and therefore does not have any effect on the patient’s condition.
By staining the vessels, further contrast of the soft tissues is improved. This significantly improves the quality of visualization, and the use of contrast is primarily justified for tumors. The dosage of the contrast element is always selected individually. It all depends on the age and weight of the patient. The substance is excreted over several days. After diagnosis, it is important to drink plenty of fluids. This is necessary to cleanse the body of contrast in a short time.
How is an MRI of the pancreas performed?
Immediately before the examination, the doctor who will perform the examination will have a conversation with the patient. During it, he will familiarize himself with the patient’s medical history, the results of his tests and ultrasound, and will study the indications for MRI. Then he will tell the patient in detail how the procedure works, what he can feel and hear during it, what is normal and what is not during the scan. The doctor will ask the patient about possible contraindications, allergic reactions and everything that the patient knows about and that may interfere with the study. Then the doctor will have the patient sign informed consent for the procedure. Everything that the doctor has already said should be written there.
Examination of the pancreas is most often done with contrast. Salts of the rare earth metal gadolinium are used as contrast agents. It does not accumulate in the body and is excreted by the kidneys within 2 days. It improves the quality of the images obtained during the scanning process; it allows you to see even the smallest tumors in the images, which would be less noticeable without it. In rare cases, patients become allergic to it. Therefore, after signing the necessary documents, the nurse conducts an allegra test. To do this, a drop of the drug is applied to the patient’s wrist or back of the hand. If after 10-15 minutes there is no redness or itching at the test site, then begin scanning.
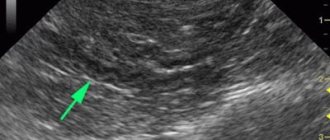
MRI helps reveal the size and shape of the pancreas.
The patient is asked to remove watches, jewelry, and clothing that have metal elements. They will often ask you to take off all your clothes and give you a hospital gown instead to prevent artifacts from appearing in the images. It is better to turn off your mobile phone because it may interfere with the operation of the tomograph.
Then a nurse will come and place the patient on a special table that slides into the tomograph. She will insert a catheter into the vein and add saline solution to it. It will secure the patient's arms and legs on the table with soft straps to prevent accidental movements, which would lead to inaccurate and blurry images during the scan.
The doctor operates the CT scanner from an adjacent office, which also has a speakerphone so the patient can be heard. When the nurse administers the contrast agent and leaves the room, the doctor turns on the tomograph. The contrast spreads throughout the body in an average of 2-3 minutes and accumulates in those places where blood flow is most intense. Such places are tumors and their metastases, so when performing an MRI of the pancreas with contrast, it is very difficult to miss them in the images.
The scanning process takes from 20 to 40 minutes. The examination time depends on the tomograph model. In more modern devices, the examination time is shorter than in older ones. From time to time, the doctor may ask the patient to hold their breath for a while or breathe more calmly so that the pictures are clearer.
MRI is a fairly expensive procedure.
Contraindications to the procedure
There are a number of contraindications to the procedure. First of all, this is the presence of decompensation in the work of the heart. The procedure is not performed if the patient is in serious condition, if there is a metal-containing implant in the body (we are talking about pacemakers, pins, insulin pumps, hemostatic clips). Contraindications are also liver or kidney failure, epilepsy.
Closed-plan devices are used by patients up to 150 kg.
Tomography is strictly contraindicated in the first months of pregnancy. If the patient has tattoos, diagnosis is prohibited. It's all because of the paint with metallic elements.
For young patients, the procedure is performed for safety reasons. If necessary, children are given sedation before the procedure.
Survey results
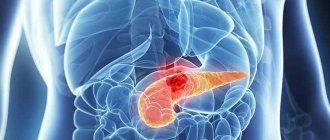
What can an MRI and CT scan of the pancreas show? Using this type of diagnostic examination, you can identify:
- inflammatory processes of acute and chronic type;
- neoplasms of malignant and benign types;
- anomalies of congenital and acquired type.
Using tomography, you can obtain data that will influence the course of further actions. In some cases, pathologies require surgical intervention.
After the examination, you can obtain information about:
- increase in organ size;
- inflammatory process. There are three types of them;
- form of neoplasm. If they have a round shape, then they are benign;
- organ contour. It must be clear. If the contour is uneven or cut, it indicates the presence of a malignant formation;
- metastasis to neighboring tissues and organs.
The patient does not receive the results of the study immediately, but a day after the examination.
What can be detected during diagnostics
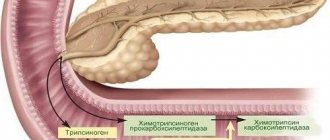
MRI of the pancreas gives doctors information:
- about the structure of the pancreas;
- organ structure;
- fiber condition;
- presence of formations;
- allows you to detect differences between a tumor and a cyst;
- provides data about the tumor process, allows you to determine its boundaries and how far it has spread;
- whether the formation has grown into nearby tissues;
- are there stones in the ducts;
- what condition do the vessels supplying the pancreas have?
Important! When an MRI reveals a tumor with clear boundaries, it is benign. When tumor processes are detected, MRI allows one to determine whether it is a primary or secondary process. If this is the second type, then the tumor has metastasized from other tissues, but if it is the first, then the oncology has formed directly in the pancreas.