People who belong to a group of increased risk of morbidity should become more familiar with what tubular adenoma of the colon is, as well as study the causes, symptoms and treatment of the disease.
Neoplasms that arise in the tissues of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) are usually called polyps. Such formations include villous tumor, tubular adenoma with or without dysplasia, and tubulovillous adenoma. The predominant number of diagnosed polyps on the intestinal mucosa are prone to degeneration into a malignant form.
What is tubular adenoma of the colon
In medicine, tubular adenomas of the colon are benign formations originating from epithelial tissues and mucosal cells that have a predisposition to degenerate into malignant neoplasms. There are different types of gastric adenomas, which have different features:
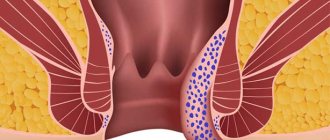
- Tubular adenoma is a neoplasm that is red in color and measures up to 10 mm. As it grows, it rises on a thin stalk above the surface of the mucosa.
- Villous adenoma of the rectum is a formation that grows along the intestine and can grow to impressive sizes.
- Tubular villous adenoma - the tumor combines the properties of villous and tubular adenomas and often forms in the large intestine. The size of the neoplasm can reach 30 mm. As the disease progresses, the tumor may degenerate into a malignant form.
When the development of an adenoma with dysplasia is diagnosed, this indicates the beginning of the transformation of this tumor into a malignant cancer. Even a small amount of undifferentiated elements can provoke intestinal cancer. If you suspect the presence of the disease, you should immediately seek medical help and undergo examination in a hospital setting. When a tumor is identified, the doctor will definitely tell you in detail what it is, and how further diagnosis and treatment are carried out, which usually involves surgical intervention.
A type of malignant adenomatous polyp
Tubular villous adenoma resembles villous and tubular polyps. Very often there are neoplasms measuring two to three centimeters. This tumor is mainly found in the colon and sigmoid colon. It may be malignant. And in such cases, surgical intervention is necessary.
This type of adenoma can be expressed in three degrees of dysplasia (mild, moderate and severe). And the tumor itself has a lobulated surface that resembles the appearance of a raspberry. A villous polyp is larger in size than a tubular one. This type of adenoma has two forms - creeping and nodular.
Tubular villous adenoma arises gradually from previous types of polyps. This transition requires an average of three to four years for each form of polyp to develop into a specific type of cancer. The process of malignancy also requires a period of two to three years. In total, the formation of the above type of adenoma requires an average of ten to fifteen years.
Often this disease can be eliminated only by surgical methods. In such operations, the main complication is bleeding. It occurs within ten days after surgery. The appearance of blood from the anus on the first day after resection of tubular villous adenoma is associated with a small process of coagulation of the vessels of the tumor pedicle. Later bleeding may also occur. Their appearance is noted from five to twelve days after surgery.
Also, during surgical intervention in the presence of tubular villous adenoma, a complication such as perforation of the intestinal walls occurs. This is associated with a large burn of its walls in the area where the resection part was formed during electrocoagulation.
Tubular adenoma is localized in different parts of the intestine and often has a papillary structure. This type of tumor rarely grows beyond one centimeter. The tumor poses a potential threat because it is often a precursor to colon cancer. Malignant transformation occurs quickly, so the seal must be removed immediately after the diagnosis is confirmed.
Causes
Despite many years of research in this area, the exact reasons why rectal tubular adenoma can form have not yet been proven. But still, some factors that can provoke the proliferation of tumor cells have been identified. First of all, the formation of formations is associated with the presence of somatic diseases that arise through external factors. Also, tumors still arise due to heredity. Other factors can also trigger tumor development:
- Improper diet - with prolonged consumption of carcinogens and high-calorie foods with little fiber, intestinal function deteriorates, which leads to changes in the microflora, which can trigger the appearance of tumor formations.
- Professional activities that involve contact with harmful substances can also lead to the appearance of polyps.
- The presence of bad habits, in particular smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Chronic gastrointestinal diseases.
- Obesity.
- Lack of mobility, which can occur due to prolonged periods of sitting.
We recommend reading Ovarian fibroid - causes, types, treatment
All of the above factors cannot exactly cause the development of a neoplasm, but they are often observed in patients with this disease.
Causes
The following symptoms of adenoma exist:
- painful defecation due to injury to the neoplasm;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, symptoms of dysbacteriosis;
- small pink bleeding that occurs due to injury to the mucous membrane;
- copious discharge of mucus from the anus;
- weakness, fatigue;
- decreased immunity;
- anemia and dehydration;
- sudden weight loss.
Tubular and tubular-villous formations do not show signs of manifestation on x-ray, unlike malignant ones.
The main cause of the disease is improper diet. Eating a large amount of animal fats along with a small amount of vegetables and fruits in the diet leads to metabolic disorders, which, in turn, provokes the growth of the polyp.
There is a genetic predisposition to the disease.
In this case, the appearance of a tumor is possible, including in preschool children. Most often, a hereditary factor is the cause of serrated adenoma.
The occurrence of the disease is influenced by the presence of bad habits and unfavorable working conditions. Excess weight and a sedentary lifestyle can also lead to pathology.
Kinds
Tubular adenoma of the stomach can be single or multiple. Based on external features, the following types of polyps are distinguished:
- Tubular is the most common type of neoplasm, characterized by a red color, dense structure and non-convex shape. Usually the size of such neoplasms does not exceed 1 cm, but in some cases tumors of 2-3 cm or more are diagnosed. Tubular adenomas of the intestinal mucosa have the most favorable prognosis for patients.
- Villous (villous) is the most dangerous type of disease, having a 40% risk of malignant degeneration. Villous adenomas of the colon are characterized by extensive growth and a loose structure. In the majority of cases, the size of these adenomas exceeds 3 cm, and the fleecy surface gives them a seaweed-like appearance.
- Tubulo-villous (tubulo-papillary) is a mixed form of neoplasm, which is often called a pseudotumor. The size of these tumors reaches 3 cm or more, and the formations combine the characteristics of tubular and villous adenomas.
- Serrated (papillary) is a polyp-like neoplasm, which is characterized by the presence of dysplasia in the near-surface areas and jaggedness of the epithelial surface.
Typically, almost all tubular adenomas of the colon are diagnosed with dysplasia. Regardless of what type of adenoma was discovered - tubular, villous, serrated adenoma of the colon or adenoma of the sigmoid colon - only the attending doctor can accurately give prognosis for patients after conducting a detailed examination and prescribing further treatment.
Adenomatous polyps and their types
An adenomatous polyp forms on the surface of the mucous membrane of the colon. In this case, polyposis develops, and there is a risk of cancer.
An adenoma is classified depending on its size. If it consists of 1 or 2 polyps, then the tubular adenoma is considered solitary. A larger number of polyps indicates multiple adenoma. Diffuse tumors develop due to genetic predisposition and are characterized by a large number of polyps.
Diffuse adenoma begins during puberty, and symptoms become obvious by age 30. If medical assistance is not provided in time, the number of polyps can reach 1000. They grow on the intestinal mucosa and can develop into a malignant tumor.
Based on the nature of growth, the following types of adenoma are distinguished:
- tubular;
- villous;
- tubulovillous;
- serrated
Tubular tumor is the most common. It is red in color, has a smooth surface, clearly defined boundaries, and a uniform and dense structure. Its size most often is 10 mm, but there are also adenomas whose size exceeds 30 mm. With this form of tumor there is a high probability of cure. Tubular adenomas are not accompanied by atypical cell division.
Villous adenoma, also known as villous adenoma, has a high risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor - more than 50%. This species is characterized by multiple soft tumors, the size of which can reach 10 cm in diameter. The surface of villous polyps has a loose, velvety structure.
Tubulovillous adenoma is a mixed type, characterized by signs of 2 types. The polyp grows up to 30 mm or more.
Papillary serrated adenoma is manifested by cell division on the surface of the polyps, which results in serrated appearance.
Degrees of dysplasia
Most often, the course of the disease, especially tubulovillous adenoma of the intestine, is accompanied by dysplasia, the progression of which is divided into three stages:
- Weakly expressed (grade 1) - has a slight thickening of the epithelial layer. Due to the mitotic activity of cells, an inflammatory process is observed.
- Moderate (grade 2) - tumor cells with grade 2 moderate dysplasia acquire different sizes and shapes.
- Severe (grade 3) - more than half of the epithelial cells are altered cells, which have even more differences in shape and size.
We recommend reading Follicular tumor of the thyroid gland - causes, symptoms, treatment
Dysplasia can also be highly differentiated or poorly differentiated. Villous adenoma with dysplasia is a precancerous condition, and therefore is often confused with a malignant process.
Symptoms and tubulovillous type of the disease
Speaking about the disease, it should be noted that colon adenomas, depending on the histological structure, are divided into three large groups: villous, tubular and mixed.
Such differences not only determine the morphology of the polyp, but also affect the symptoms of the disease, as well as the further prognosis for the patient.
Tubulovillous adenoma of the colon is the most malignant variant of the disease due to the possibility of rapid tumor transformation.
There are three degrees of change in cell morphology in such a polyp: first, second and third.
Tubular adenoma of the colon with grade 1 dysplasia is a precancerous condition that can become the basis for the growth of a malignant tumor, and therefore, any person should know the main symptoms of the growth of adenomas in the intestine:
- for a long time, polyps do not lead to the appearance of any symptoms, especially if they are isolated;
- an increase in their size to 1 or more centimeters leads to the development of minor intraintestinal bleeding, which may go unnoticed or may be manifested by splashes of blood in the patient’s stool;
- at the initial stages of the disease, there are no disturbances in the motor function of the digestive system;
- a significant increase in the size of the adenoma or their multiple growth leads to chronic constipation, a feeling of discomfort in the rectum and flatulence.
The progression of changes in the polyp leads to the formation of a tubular adenoma of the colon with grade 2 dysplasia. This stage of the disease is characterized by changes in the morphology and biochemical processes in the cell, being a harbinger of the subsequent growth of a malignant tumor .
Due to the possibility of progression of any colon adenoma to a dangerous neoplasm, patients should always contact their doctor if the symptoms described above appear.
Symptoms
Depending on the type of intestinal adenoma, its morphological structure and clinical symptoms and treatment depend. In the early stages of development, the symptoms of tubular adenoma of the colon do not manifest themselves in any way, so detection of the tumor often occurs either in the later stages of progression, or during a random examination when the patient comes in for other reasons.
As the tumor develops, when its size reaches 2 cm or more, the patient may experience the following symptoms:
- pain during defecation;
- pain in the abdominal cavity and a feeling of a foreign body in the intestinal area;
- presence of itching in the anus;
- mucous blood impurities in feces;
- the presence of constipation, which occurs alternately with diarrhea.
The development of a tumor leads to a narrowing of the intestinal lumen, which can cause serious complications.
Diagnostic methods
It is difficult for doctors to diagnose lumps at an early stage. Sometimes it is present in the human intestines for several years, and does not manifest itself in any way. Typically, symptoms are characteristic of tubular adenoma of the colon with dysplasia.
During the initial examination, the doctor determines the presence of a foreign body by palpation. To clarify the diagnosis, several types of examinations will be prescribed:
- colonoscopy (using an endoscope to examine the rectum). During the study, it is also possible to remove the tumor or take material for further sending for histological examination;
- irrigoscopy is an x-ray that is done using a contrast chemical reagent. The procedure allows you to identify any deviations from the norm on the mucous membranes;
- a biopsy is necessary in order to exclude the malignant nature of the tissue;
- general and biochemical blood and urine tests.
Treatment of tubular adenoma of the rectum is only surgical. Drugs cannot cope with the tumor or prevent an increase in the degree of dysplasia. To avoid cancer, the tumor must be removed.
To carry out the intervention, one of several methods of influence is chosen. If the polyp is less than 1 cm in diameter, it can be removed using cold or laser. But in most cases, electrocoagulation is used. For the operation, an endoscope is used, which is inserted through the anus to the part of the intestine where the compaction is localized. Using an electric current, the doctor cauterizes the leg and removes it. This method is used for tubular polyps in the large intestine.
To avoid malignant transformation, resection of the internal organ may be prescribed. During the process, tissue is excised if the polyp is single. In case of multiple structures, it is impossible to perform the operation. After surgery, part of the intestine may be removed. The recovery process will be long and painful for the patient. In addition, re-growth of the adenoma cannot be ruled out. Therefore, you will need to regularly undergo scheduled examinations.
If a malignant process is confirmed, a significant part of the intestinal section where cancer is found can be removed. This is necessary to prevent metastases. Subsequently, the patient is fitted with an artificial internal organ to remove the remains of digested food.
Diagnostics
Timely diagnosis of the disease presents some difficulties due to the fact that tubular, villous or tubulovillous adenoma can develop for many years without causing any manifestations. Sometimes it is possible to detect a tumor during a random examination. The most informative studies when diagnosing tubular adenoma are:
- Colonoscopy is an endoscopic method that allows you to identify neoplasms on the mucous membrane. Subsequently, a biopsy is performed, during which tumor biomaterials are taken for further morphological examination.
- Irrigoscopy is an X-ray examination of the large intestine using X-ray contrast agents. Thanks to this procedure, it is possible to identify the contours of the intestinal mucosa in the area where the polyp is located. When prescribing irrigoscopy, it is important to find out all the patient’s possible allergies, since X-ray contrast agents are powerful allergens.
To prescribe optimal and effective therapy, the results of the studies should be deciphered only by an experienced oncologist.
We recommend reading Vaccine against human papillomavirus - types and description
Diagnosis and treatment
The difficulty of diagnosing and treating the disease lies in the fact that it can proceed for a long time without symptoms, and general clinical blood and urine tests may not show the presence of pathology. In addition, in some cases it can be confused with hemorrhoidal cones in the inflammation stage, since the symptoms are similar.
As part of the examination of the large intestine, palpation is first performed, and the presence of a hereditary predisposition is confirmed or refuted. A laboratory test of blood, urine and feces is carried out.
Specific methods for examining the rectum include:
- Colonoscopy. This method allows you to most fully understand the clinical picture of the disease. It is carried out using special equipment and is accompanied by painful sensations. A probe with a light bulb at the end is inserted into the anus and passed through the entire intestine. At the same time, an image of the intestinal mucosa appears on the monitor. The doctor receives a complete picture of the disease. During colonoscopy, it is possible to biopsy individual areas for histological examination; most of the polyps are removed.
- Sigmoidoscopy. It is performed in the same way as a colonoscopy, but the area of examination does not exceed 30 cm.
- Tomography. Before the procedure, the patient is given an enema with a special contrast agent so that the desired areas are highlighted in color on the resulting images. Barium sulfate can be used as such a substance.
Treatment of adenomatous polyps is carried out surgically. Conservative therapy does not make sense due to the lack of effect except for tumors with a low degree of dysplasia. Mechanical excision of the polyp or its cutting using an electrode is performed. In this case, the device is inserted either through the oral or rectal cavity.
Treatment
Once a patient has been diagnosed with a colon adenoma, its treatment can be carried out in two ways:
- Electrocoagulation;
- Excision of the polyp through surgery.
Therapy without surgery is not able to completely rid the patient of the disease, since there is still a possibility of malignant degeneration of tumor cells. Complete resection is the most effective way to cure the disease, since surgery can almost completely rid the patient of the tumor that has arisen.
After the operation, further histological examination of the removed polyps is possible to make an accurate diagnosis, thanks to which it is possible to determine the onset of the development of malignant growth.
Electrocoagulation is carried out only when a large number of polyps are detected, since due to extensive damage to a large part of the intestine, resection is not rational. But even in this case, formations that are more suspicious can be excised through a biopsy.
Adenoma in the intestine - symptoms and treatment
The tumor in the intestine develops slowly. Cellular structures go through several stages of pathology.
Among them are:
- Epithelial dysplasia. Pathological cells divide without causing any symptoms or changes in the internal organs.
- Second stage of pathology. The division of pathological cells accelerates, cellular structures change.
- Interepithelial neoplasia. A serious mutation of cellular structures occurs. The disease becomes cancerous and affects internal organs.
At the initial stage of the disease, there are most often no symptoms. When the size of the polyp increases, the following symptoms appear :
- sensation of a foreign body in the pelvic organs;
- lack of appetite;
- discomfort in the affected area;
- itching and burning;
- painful sensations during bowel movements;
- flatulence and diarrhea;
- impurities of mucus and blood in stool;
adenoma leads to intestinal obstruction . The patient is bothered by cutting pains in the intestines, which are cramping in nature. Such symptoms appear if the size of the tumor exceeds two centimeters.
Forecast
If a patient has undergone removal of a tumor whose size is 2 cm or more, he must undergo a colonoscopy to exclude the possibility of tumor tissue remnants. After therapy, patients should undergo follow-up examinations every six months, as relapse is possible after removal of the tumor. With an effective operation or electrocoagulation, the probability of reoccurrence of adenoma is reduced to 10%.
The likelihood of such tumors occurring in a healthy body is much lower, so to prevent the disease it is worth getting rid of bad habits and leading a healthy lifestyle.
Symptoms of tubular adenoma
Like many tumor diseases, this type of adenoma occurs almost unnoticed at an early stage. Patients with a low degree of tissue dysplasia do not feel any discomfort. Symptoms appear when the tumor reaches a significant size and disrupts digestion.
With a diameter of 10 mm, bleeding may already occur that is not associated with hemorrhoidal cones. Light scarlet streaks of blood appear in the stool, which eventually leads to anemia. Due to the growth of the tumor, problems with bowel movements appear. Further attempts provoke even greater growth of the polyp, so the condition only worsens. Other characteristic signs of tubular adenoma:
- chronic bloating;
- discomfort and itching in the anal area;
- sensation of a foreign body in the intestines;
- the appearance of mucus in the stool;
- pain during bowel movements;
- stool instability, alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- intestinal obstruction.
Is tubular adenoma treatable?
If the patient has grade 1 neoplasia, then doctors choose observational tactics. Experts monitor the dynamics of the development of pathology. At the same time, therapy is carried out to prevent further growth of polyps. The prognosis of treatment depends on the stage at which the tumor was detected. The earlier it was diagnosed, the higher the percentage of complete recovery.
Timely operation and continued registration at the dispensary help reduce the risk of relapse by up to 10%.
The type of adenoma influences the outcome. Tubular-villous tumors more often degenerate into cancer, and therefore have a less favorable prognosis for therapy. Surgical treatment is the only possible way to get rid of adenoma. Drug treatment is carried out to improve the patient's condition. The treatment regimen includes the following medications:
- Vitamins A, C, E4 and folic acid.
- Probiotics: Linex, Bifiform, Normobact.
- Calcium preparations: Calcium D3 Nycomed, SupraVit.
Removal of the tumor
For tubular adenoma, excision of the tumor is indicated, sometimes along with part of the intestine. The operation is carried out after a histological examination, which confirms or denies the presence of cancer cells.
Removal of the adenoma is mandatory if the tumor diameter exceeds 1 cm.
With grade 2 dysplasia, minimally invasive intervention is possible - electrocoagulation, i.e. cauterization of pathological tissues. Large polyps are excised in parts. Possible ways to remove a tumor:
- Laparoscopy. This is the removal of a tumor through small punctures in the anterior abdominal wall.
- Transanal excision. Indicated only for rectal adenomas located near the anus.
- Laparotomy. This is an open operation in which the tumor is removed through an incision in the abdominal wall.
- Complete resection of the adenoma. Indicated if cancer is suspected or if the polyp is clearly malignant. More often, complete excision is performed when an adenoma with grade 3 dysplasia is detected.