Types of diarrhea
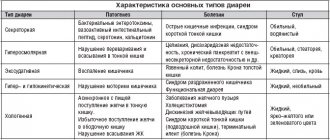
Diarrhea in an 8-month-old child is expressed not only by the presence of loose stools. There are 6 types of the disease, each of which is characterized by signs and manifestations.
Infectious diarrhea
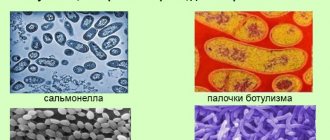
Its appearance is associated with the penetration of an intestinal infection into the body due to poisoning with poor-quality products, when infected with dysentery or salmonellosis.
Alimentary diarrhea
The main reason for its appearance is a sudden change in diet, a negative reaction to new foods introduced into the baby’s diet, and an allergic reaction to medications.
Dyspeptic diarrhea
If, after eating food, an 8-month-old child has poor production of enzymes for high-quality digestion of food.
Toxic
In children, this type of diarrhea can occur as a result of poisoning with any chemicals: arsenic, mercury, salts of heavy metals.
Medication
This type of diarrhea is associated with the baby taking medications. Antibiotics have a particularly negative effect on the gastrointestinal microflora, causing dysbiosis, which causes loose stools.
Psychological diarrhea
With this type of diarrhea, various psychological factors play an important role: poor sleep, stress, changes in habitual lifestyle: moving to a new place, disruption of the daily routine, fear or fright. In this case, loose stools may pass on their own when the baby is again in a comfortable environment.
Therapy methods
If diarrhea is caused by early complementary feeding, there is no need to treat the child. All you have to do is cancel this product.
It is recommended to return to your previous diet, trying to breastfeed your baby more often and more at 10 months.
If the diarrhea does not worsen and does not stop, while the baby is active, it is necessary to examine it with a pediatrician, prescribing an ultrasound of the peritoneal organs. What to do with diarrhea in this case? It is necessary to give the child 800 ml of water.
If diarrhea is accompanied by fever, parents do the following:
- mild intestinal upset - up to 100 ml per day, as well as low body temperature, make it possible to treat a child of 10 months at home. The baby is weighed twice a day. Weigh the diaper separately. This will take into account the amount of urine and the amount of water lost due to dehydration. What should I give my baby? Chamomile infusion and semi-sweet tea are prepared for the child. At 10 months you can give Oralit or Humana Electrolyte;
- Infants prone to increased acetone need to measure this indicator frequently. To do this, use a special test strip and a rota test. Using the latter method, rotavirus can be detected in a child at 10 months;
- will help eliminate diarrhea in a child Smecta. One sachet of the product is dissolved in 200 ml of water. The prepared solution must be drunk one day before. You can replace Smecta with White Coal. The last solution or tablets are given to the child an hour before meals;
- if the rota test is negative, it is recommended to eliminate diarrhea with Nifuroxazide. Take up to 5 ml of this product per day. In some cases, vomiting occurs during such therapy. Therefore, the drug is given to the child after consultation with a doctor;
- if the test for oral infection is positive, diarrhea is eliminated with Viferon or Laferobion suppositories;
- The child should not be fed new foods. The diet should be presented in the form of mashed potatoes and liquid rice porridge.
Causes of diarrhea in a baby
Diarrhea in an 8 month old baby can occur for a number of reasons. The main ones include:
- Food poisoning due to food that has expired, poor food quality, violation of proper food preparation standards, infection with E. coli or staphylococcus.
- If parents have introduced unusual or new foods into the diet.
- When moving or changing climatic conditions.
- With poor water quality.
- If your baby is afraid or anxious.
- In stressful situations.
- If parents have introduced cow's milk into the diet, and he has a negative tolerance to lactose.
- If the intestines are affected by an intestinal infection.
- If your baby is being treated with certain types of medications, the side effects of which include loose stools.
- If your baby is infected with intestinal flu.
- Eating sour or salty foods.
- For colds and flu.
- Due to overeating.
Useful video
Source
Diarrhea in a child can accompany a wide variety of diseases. However, this symptom is dangerous in itself, especially when it comes to young children. The famous doctor and author of books and articles on children's health, Evgeny Komarovsky, tells us what the danger of diarrhea is and what parents should do if such a “trouble” happens to their child.
Symptoms
Parents will know what to do and how to treat their child if they study the symptoms of diarrhea. These also include:
- nausea or vomiting;
- temperature and fever;
- stool may change color;
- there may also be mucus or blood clots in the stool;
- moderate or unbearable abdominal pain;
- strong gas formation.
Even if parents know what to do in this situation and what remedies can be used for diarrhea, self-medication in children under one year of age is not recommended. There are cases when diarrhea causes complications that can pose a danger to the health and life of the child. Dehydration is especially dangerous, as a result of which the mucous membranes become dry and the child may experience convulsions. In this case, you should call an ambulance as quickly as possible. This symptom requires professional medical attention.
Fighting fever
Fever with diarrhea is common in infants. Therapy is carried out after measuring the temperature and examining the child.
Most often, the temperature is measured in the groin area or under the arms. Infants can have their temperature taken through the rectum.
If the fever lasts for several days, it is recommended to keep a diary. Using the dynamics of the symptoms of the disease, the doctor makes a diagnosis. Body temperature to 38.5 degrees is not reduced by medications.
The risk group includes children prone to seizures. They are registered with neurologists, cardiologists and pulmonologists. It is also necessary to reduce the temperature in children up to 2 months of age.
If a high temperature is accompanied by chills, pale skin, and muscle pain, the child is given an antipyretic drug:
If the above symptoms appear, the child should be given the following assistance, after calling a doctor:
- undress or easily dress the child;
- constant drinking with frequent breastfeeding;
- Do not roll the baby, otherwise there will be heatstroke. It is better to undress the child and cover him with a diaper;
- rubbing the baby with warm water in the folds of the neck, legs and arms. It is better to start this procedure with the face. You can place a damp cloth on your forehead. It is changed once every 30 minutes. This therapy technique will slightly reduce body temperature;
- Give your baby an antipyretic. If he has diarrhea, it is better to use the medicine. For vomiting, use suppositories. In the latter case, the temperature will begin to decrease 40 minutes after input. The syrup or solution takes effect within 20 minutes.
If your body temperature rises and diarrhea appears, you need to call a pediatrician. Before his arrival, the baby is given water from a teaspoon or bottle.
With the doctor's permission, a decoction of salt, soda, raisins and sugar is prepared for the child. For this, use 100 grams of raisins. It is boiled in a liter of water for 30 minutes. Add 1 tsp to the composition. salt, 4 tsp. sugar and ½ tsp. baking soda.
The medicine is boiled for 2 minutes. The resulting product is cooled and given to the child throughout the day. Children at 10 months can be given rice and carrot-apple decoction. These remedies remove toxins from the body.
It is definitely recommended to record the amount of stool, its color, the presence of mucus with blood and odor in the stool.
It is recommended to save the last diaper and show it to the pediatrician. Self-administration of medications is contraindicated.
Treatment
What to do if your 8-month-old baby has diarrhea. Pay attention to the frequency of going to the toilet, the color and consistency of stool.
Mild diarrhea
It is not frequent and without pain. The child's lifestyle has not changed. In this case, you can give decoctions of medicinal herbs, slightly change your diet and give more fluids.
Diarrhea is a protective reaction of the body and tries to cleanse the intestines of harmful substances and toxins. And if the diarrhea is not prolonged, it is not necessary to resort to taking medications.
Prolonged diarrhea
If diarrhea is prolonged, and stool is not very abundant, but lasts more than 5 days, medical attention is necessary. There is a possibility of infection in the intestines. In this case, astringent decoctions and medications are used. It is also worth paying attention to why lingering diarrhea appeared. If it is associated with stress or with moving and changing climate conditions, it is enough to adjust the diet and give the baby as many positive emotions as possible.
With blood
In this situation, you need to urgently consult a doctor or call an ambulance. Feces with blood clots can signal pathologies and serious diseases. Quite often, this symptom indicates intestinal obstruction. This requires first of all surgical treatment.
With severe pain
Pain in the baby's tummy requires the appointment of an antispasmodic. Such a symptom should be a reason to visit a doctor. Quite often, with appendicitis or intestinal obstruction, diarrhea with pain or discomfort in the baby’s tummy is possible.
With mucus
First of all, there may be a rotavirus infection, an intestinal infection, or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Perhaps your baby is starting to teethe. This may also be due to poisoning from low-quality products.
Parents should consult a doctor, and until the doctor arrives, the child should be given plenty of fluids to drink. Self-medication in this case is contraindicated. The only thing you can give is activated carbon.
Green stool color
The most common reason for this color of stool is the sudden introduction of new foods into the baby’s diet. If this is a common reaction to foods, there is no need to treat such diarrhea. As soon as the child gets used to the introduced product, the diarrhea will go away on its own.
But it may be associated with the presence of infections. In this case, you need to visit a doctor to prescribe treatment.
Dehydration: Signs and First Aid Techniques
The health of the body largely depends on the correct balance of water and electrolytes (salts). With diarrhea and vomiting, dehydration occurs and this ratio is disrupted, which threatens serious disruptions in the functioning of organs.
With moderate dehydration, children lose up to 5% of their weight, with severe dehydration - up to 10%. The symptoms of apathy also increase, urination becomes less frequent, and the urine becomes dark yellow. The skin turns pale, dries out, and dry mouth appears. Diarrhea in a child 10 months and older, although accompanied by pain, the baby does not cry. The eyes are drooping, the fontanel is sunken.
Doctor's recommendations
- If dysentery or infection is detected, the doctor prescribes Fthalazol.
- Enterofuril quickly copes with intestinal infections, diarrhea, and restores the microflora of the digestive system.
- The drug Sulgin effectively treats diarrhea, colitis and dysentery.
- An effective remedy for diarrhea that has excellent astringent properties is Tannacom. This drug is harmless even for babies of one month. Also, this drug very quickly relieves spasms and relieves pain.
- If acute intestinal obstruction is not detected, Enterosgel can be given to the child.
- An excellent solution is to use the drug Polysorb, which quickly stops diarrhea and has an excellent adsorbing effect.
When treating diarrhea, probiotics must be used. The drugs include:
- Lactobacterin;
- Bifidumbacterin;
- Bifiform;
- Hilak Forte.
They not only cope with diarrhea, but also restore intestinal microflora.
The norm and deviations from it in the youngest
In newborns, especially those who are breastfed, stool is frequent: up to 10 times a day, and a liquid consistency is the norm. On the contrary, you should worry if defecation is difficult due to too much density of feces, because the baby consumes only milk, and, ideally, hardness has nowhere to come from.
True diarrhea in a child at 4 months is a rare occurrence, and you need to know all its signs in order to respond to the problem in time. In the first few days, the baby’s body cleanses itself, and its stool is very dark. Then it acquires a golden hue with greenish splashes, with admixtures of mucus and white veins. The smell is slightly sour, it becomes sharper if complementary foods are added to breast milk.
But what should definitely alert parents and cause them to call a doctor? There are a number of dangerous symptoms of diarrhea in a child aged 10 months or earlier:
- Lethargy, apathy, drowsiness, refusal to eat;
- Abdominal pain, sometimes sharp;
- Nausea, vomiting, dry mouth;
- Rash on the body;
- Increased body temperature;
- Dehydration with loss of body weight up to 5%.
The last sign is especially dangerous: with low weight, even a loss of 300 g due to dehydration can be critical, even fatal.
Folk recipes
- For children 8 months of age, you can prepare rice water. To do this, you need 2 tablespoons of rice for 2 glasses of water. The rice is cooked until tender, but the water is not drained. Grind rice and water in a mixer. Give your baby a teaspoon to drink several times a day until the stool returns to normal.
- Dried blueberries or berry compote help. If you give dried berries, it is enough to take a teaspoon 3 times a day. But for such small children it is better to boil compote and give it to the baby in any quantity.
- Grind the pomegranate peel and pour a glass of boiling water over it. Leave for about an hour and give the child a tablespoon 3 times a day.
If the child does not have an intestinal infection or pathology, parents can help the child on their own. But if loose stools continue for more than 2-3 days, you should still consult a doctor.
Diarrhea in a 10 month old child without fever
The child's body is especially sensitive to environmental influences. Intestinal upset is a common symptom. It may indicate an infectious disease. In a child, diarrhea without fever can also be caused by factors of other etiologies. How to correctly determine the reasons? And in what situation is it necessary to immediately seek medical help?
Loose stools or diarrhea?
Children in the first years of life learn about the world around them through direct contact. The main organ of perception is the mouth. The little ones are eager to put a new toy, an interesting pebble picked up on the street, into their mouths, or to taste the sand. Raising a baby in sterile conditions is no less dangerous than allowing the possibility of contact with dangerous objects.
Including a child in a children's group (nursery, kindergarten, school) increases the likelihood of contracting various infections. Each student brings its own microflora into the general environment. Intestinal bacteria that cause diarrhea are frequent visitors in places where there are large concentrations of children.
Diarrhea is the main sign of intestinal dysfunction.
Adults often confuse loose stools with diarrhea. The first can be caused by a change in the usual diet, foods that have a laxative effect. It happens 1-2 times a day and is not accompanied by other symptoms. Water diarrhea in a child without fever is a pathological condition when bowel movements occur more than 5 times per day.
Causes of diarrhea without fever
- Violation of healthy eating rules. It is difficult to follow a children's diet perfectly. Sometimes kids reach for attractive food from the common table. Heavy, spicy, fatty foods are difficult for the child’s body to digest, and as a result, intestinal upset in the form of diarrhea may occur.
- Dysbacteriosis is an imbalance of the gastrointestinal microflora.
Accompanied by symptoms: cramps and pain in the abdomen, diarrhea or constipation, nausea, and possible vomiting. - Intestinal infections (rotovirus, salmonellosis, enterovirus, rubella). In some cases, they can occur without an increase in temperature. As a rule, they last more than 3 days and have additional symptoms (vomiting, nausea).
- Enzyme deficiency is the body's inability to completely digest food. In this case, particles of unprocessed food can be seen in the stool. Infants have a characteristic foamy stool shortly after feeding. This problem is typical for children under 1 year of age. It is caused by an inability to process lactose.
- Impact of the external environment.
Heat stroke, psycho-emotional stress, and an allergic reaction can cause diarrhea without fever in a child. - Individual intolerance to medications. Diarrhea is often caused by an individual reaction to substances included in the medications that the baby takes.
- Allergy to food.
In addition to skin itching and rashes, this disease may be accompanied by diarrhea, nausea, and discomfort in the abdominal cavity. - Intoxication of the body (food or chemical).
- Parasites. Their presence causes toxicity, the intestines become inflamed, diarrhea appears, and there may be vomiting.
- Appendicitis.
A disease that is accompanied by sharp and severe pain in the lower abdomen. May be accompanied by diarrhea and vomiting. - Hyperthyroidism of the thyroid gland. In some cases, diarrhea is one of the manifestations of the disease.
How to determine the cause
To find out why your baby started having diarrhea:
- analysis of his nutrition and contacts in the previous period;
- associated symptoms;
- results of medical tests.
Intoxication of the body has a disease picture similar to infections. As a rule, it occurs without fever.
Therefore, it is important to remember what the child ate the day before: exotic products, or fermented milk with a questionable shelf life. Have you had contact with chemicals whose vapors can cause poisoning?
For example, they were painting the floors in the house, spraying insect poison in the garden, and the baby was walking nearby.
Associated symptoms will help identify an infectious disease or problems with the gastrointestinal tract: pain and cramping in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting. In this case, you need to contact your local doctor. He will prescribe tests that will clarify the situation and prescribe treatment.
Diagnostics
There are several types of laboratory tests that will indicate the cause of diarrhea. What tests can be taken:
- feces for dysbacteriosis;
- feces for the presence of helminth eggs;
- blood for the presence of parasite antibodies;
- tests for intestinal infections;
- feces on the caprogram;
- blood for hepatitis A, B and C (to exclude the possibility of gastritis or appendicitis);
- general blood analysis.
An analysis for dysbiosis will show the ratio of beneficial and pathogenic bacteria in the body. Reproduction of the latter is a prerequisite for diarrhea. Parasites that fill the gastrointestinal tract release toxins.
This may cause nausea and diarrhea. The analysis will show the type of parasitic organisms with which the child is infected (worms, Giardia, Toxocara, Echinococcus, Trichinella).
To detect their presence, feces and blood are tested for antibodies.
Intestinal infections (salmonellosis, rotavirus, enterovirus) often cause diarrhea in children. A stool test will help confirm the diagnosis. Caprology will help identify problems with the pancreas. Characteristic signs of the disease are oily stools that are difficult to flush from the toilet and contain pieces of food.
Vomiting, nausea and yellow diarrhea sometimes indicate a malfunction of the liver. A complete blood test will help confirm liver failure. Additional diagnostic tools - ultrasound of the digestive organs. It will help to identify malfunctions and detect developmental pathologies.
It is better to take tests in special sterile containers. This will avoid the entry of foreign substances that will distort the results of the study.
When diarrhea is persistent
Long-term diarrhea (more than 3 weeks) often has several causes. The danger of such a protracted disorder is that beneficial substances are washed out of the body with feces, the water-salt balance is disrupted, which can cause dehydration.
The cause of prolonged diarrhea may be a disruption of the large and small intestines. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis after conducting research.
Treatment
If the child has diarrhea not for the first time, parents already know what to do. Loose stool therapy follows general rules.
- drugs (sorbents and prebiotics);
- diet;
- drink;
- folk remedies.
Medicines
During diarrhea, medications are prescribed to act in two directions:
- remove toxins from the body;
- restore microflora.
The main cause of diarrhea is toxicity (exposure to harmful substances). Sorbents are drugs that bind toxins and remove them from the body. For this purpose, the following are often used: activated carbon, enterasgel, smecta, povidone (enterodes), polysorb.
After cleansing the intestines, it is necessary to restore the natural balance of beneficial bacteria. For this purpose, drugs are prescribed that fill the gastrointestinal microflora with good bacteria. For example, hilak forte, bifidumbacterin, lactobacterin, acipol, bififor, acylact, linex and others.
Diet
When treating loose, watery stools, it is very important to follow a diet. It is necessary to exclude fatty, spicy, salty foods, dairy products, fruits and vegetables that have laxative properties.
For the first three days, it is recommended to adhere to a strict diet - drink a lot and unleavened porridge with water. With positive dynamics of treatment, other products are gradually introduced. As the child recovers, he returns to his usual diet.
Drink
Drinking plenty of fluids helps maintain the balance of fluids and microelements in the body and helps eliminate harmful substances.
Diarrhea flushes substances important for life from the body; prolonged distress leads to dehydration. This is why it is so important to give a sick child more fluids. REHYDRON powder is sold in pharmacies. It is diluted with plain boiled water and drunk within 24 hours. The drug effectively restores water-salt balance.
During the period of acute intestinal disorder, good drinks are: compotes, mineral water, jelly, strong tea. Milk, soda, and fermented milk products are prohibited.
Why can't you drink carbonated drinks and milk? These drinks cause fermentation processes, which can increase intestinal irritation.
Traditional methods
The principle of treatment with folk remedies is the use of plant decoctions that have adhesive properties.
For treatment at home, medicinal teas from:
- oak bark;
- bird cherry berries;
- pomegranate peels;
- oats;
- starch;
- unground black pepper;
- dried pear.
Oak bark decoction
It is necessary to boil for 25 minutes. For one tablespoon of the mixture you will need 1 cup of boiling water. The result is a dark brown infusion with a very tart taste. Take it 7 tbsp. spoons a day.
Decoction of bird cherry berries
For 50g of berries you will need 750 ml of boiling water. Keep on fire for 25 minutes. After this, cool and strain. Drink half a glass 2 times a day.
Pomegranate peels
Before use, they are dried and ground into powder. Boil for about half an hour. Take 6 spoons throughout the day. Drink the decoction warm.
Pomegranate peels have a binding and antimicrobial effect. For prolonged diarrhea and weakness caused by infections, this is an important property.
Oat grains
Boil until jelly. You will need 3 cups of grains per 2 liters of water. It envelops the intestinal walls, protecting it from damage. Relieves irritation and has astringent properties.
You can make an infusion of oats. To do this, soak the grains in water for about 12 hours. Drink the resulting liquid three times a day.
Black pepper
Has an antimicrobial effect and holds together. It copes well with certain pathogens of intestinal infections.
Patients with pancreatic problems should not use black pepper. It is irritating
Children are given 2-3 peppercorns 3 times a day. You need to drink plenty of fluids.
Pear drink
Properly prepared pear decoction quickly relieves diarrhea. Only dried pear is used. It is filled with water and boiled for about 20 minutes. If you don't have dried pears, you can bake fresh ones. Baked pear is a good dietary product. It will saturate and have a binding effect.
Source: https://dou99.ru/temperatura/ponos-u-rebenka-10-mesyatsev-bez-temperatury
Causes of acute diarrhea
The intestinal microflora and immune system of children are very unstable, so diarrhea may appear after eating new foods. Such symptoms are often observed when complementary foods are introduced.
In infants, diarrhea may occur due to food eaten by the mother.
Diarrhea can be a side effect of certain medications: choleretic drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics. Diarrhea occurs due to the development of dysbiosis, long-term treatment or dosage violation.
- Infections not related to the gastrointestinal tract: sore throat, otitis media, rhinitis.
These diseases are accompanied by the formation of mucus in the nasopharynx, which flows into the stomach and changes the consistency of stool. In children under one year of age, diarrhea often occurs due to teething.
- Food and chemical poisoning.
One of the most common causes of diarrhea in children. Toxic substances enter the body when consuming stale or low-quality products.
- Intestinal infections caused by bacteria and viruses (dysentery, rotavirus, salmonellosis, staphylococcus).
Children attending kindergarten and school are susceptible to such diseases. Infection occurs through contact with a carrier and failure to maintain personal hygiene.
- Diarrhea occurs when a child is infected with worms or other intestinal parasites. The waste products of helminths are toxic, irritate the mucous membrane, provoke its inflammation and intense contraction of the intestinal muscles.
- Diseases of the liver or pancreas, endocrine disorders provoke the development of enzyme deficiency and lead to disruption of the digestion process.