Principle and mechanism of action of gastroprotectors
Depending on the principle of action, gastroprotectors can be film-forming or non-film-forming. Specialists separately identify prostaglandins. Doctors cannot accurately trace the mechanism of action of all gastroprotectors, since the effect on the body differs depending on the composition and some other features.
- Film-forming drugs create a kind of protective film on the surface of the stomach, which prevents the negative effects of food, drinks and other substances on the tissue. Under this film, gradual restoration of the mucous membranes occurs, and the progression of the disease stops. Such drugs are prescribed when there is damage to the tissues, and hydrochloric acid, necessary for normal digestion, negatively affects the walls of the stomach.
- Non-film-forming drugs usually suppress the production of hydrochloric acid, which leads to a weakening of the negative effects on the walls of the organ. An additional property of these medications is the ability to activate the body's natural defenses, which leads to tissue restoration and improvement of general condition.
- Prostaglandins are not used so often for the treatment of gastric pathologies due to the increased risk of complications. The principle of their action is based on increasing the production of mucus and substances with protective properties by the stomach.
Complications of gastric stenting for gastric cancer
All patients who have a stent placed in the stomach experience pain immediately after surgery. Persistent pain after stenting persists in less than 13% of patients. The most intense pain occurs when using large diameter stents. In 10-20% of patients who have undergone a stand for stomach cancer, the following complications develop:
- bleeding,
- perforations and fistulas;
- aspiration pneumonia and fever.
When a stent is placed in the gastric cardia, migration of uncovered stents may occur. Migration of covered stents is observed more often when stenting the esophagogastric junction. Preliminary dilation of the narrowed stomach, photodilatation, thermal ablation and radiation therapy increase the risk of complications during stenting and increase the risk of stent migration.
With repeated narrowing of the stomach in case of germination of tumors not covered by the stent, the need for repeated endoscopic intervention arises. When installing self-expanding stents with plastic coating, repeated dysphagia develops due to tumor growth of the proximal or distal edge of the stent.
Late complications of stenting include erosive bleeding, ulcerative esophagitis, perforation or fistula, rotation or migration of the stent, fracture or failure of the device structure. In comparison with other methods of palliative care for patients with tumoral stenosis of the stomach, for whom radical surgery is contraindicated, endoscopic stenting with self-expanding metal stents is the best option for complex treatment.
You will receive detailed information by calling the Yusupov Hospital, where oncologists provide treatment and palliative care for patients with stomach cancer. Patients who have a stent placed in the stomach have a significantly improved quality of life.
Advantages and disadvantages
Gastroprotectors (the list of drugs with proven effectiveness includes drugs with different components in their composition) have many advantages, therefore they are often used to treat pathologies of the digestive tract and prevent complications:
- They help to quickly eliminate the manifestations of diseases, which alleviates the condition of patients.
- Can be used for a long time. This is especially important for patients who suffer from chronic forms of disease.
- Drugs from this group can be used in combination with other medications to increase the effectiveness of therapy.
- Less likely to provoke negative reactions when used correctly than other medications.
- Many products have a positive effect not only on the mucous membranes, but also stimulate regeneration processes, improve microcirculation and tissue nutrition, and have a beneficial effect on the entire digestive system.
- Prevents the development of complications such as peptic ulcers or perforation of the stomach walls against the background of damage to all its layers.
Such advantages make it possible to use medications for different patients and at different stages of the pathological process.
But I also have disadvantages. Some of them are sold in pharmacies only with a doctor's prescription and are used only for the treatment of adults, as they act aggressively. Many medications are used only in long courses because they do not have a therapeutic effect immediately. Another disadvantage is the dosage form of medications, which is not always convenient to take.
Types and list of gastroprotective drugs
They can be divided into 2 broad groups:
- film-forming;
- non-film-forming.
Film-forming agents
Their main function is mechanical protection of the mucous walls of the stomach. This group includes the following active ingredients:
- Sucralfate . Now it remains only under the trade name Venter; previously Sukrat was produced. It is an aluminum salt. Its mechanism is based on interaction with the proteins of the dead mucous layer: together they form a special film that can protect ulcerated areas from the influence of hydrochloric acid for a long time.
- Bismuth tripotassium dicitrate . Produced under the names: De-Nol, Ulkavis, Escape, Novobismol. It has an astringent, anti-inflammatory and bactericidal effect. Stimulates the synthesis of prostaglandin E2. In an acidic environment, bismuth forms a protective layer with proteins that covers the mucous wall, preventing hydrochloric acid and pepsin from acting on it. Improves scarring of ulcers.
- Basic bismuth nitrate . Contained in combination drugs: Vikair, Vikalin. The mechanism of action is similar to bismuth tripotassium dicitrate.
Non-film-forming agents
They affect the physiological processes of the defense mechanism. This group includes:
- Sodium carbenoxolone. Trade names: Biogastron, Duogastron. The substance combines with the proteins of the mucous membranes, lengthens the period of existence of the epithelium lining the walls of the stomach, and reduces the healing time of ulcers.
Prostaglandins
They also belong to non-film-forming agents, but they stand apart. They increase the production of protective mucus covering the walls of the stomach and suppress the production of pepsin and hydrochloric acid. They have many side effects, so they are used quite rarely. Such products are dispensed strictly according to a doctor’s prescription! In Russia the following substance is used:
- Misoprostol. Produced under the names: Topogin, Mirolut. Improves blood flow in the gastric mucosa, reduces vascular permeability. There is an increase in the production of mucus that protects the walls, and existing ulcers heal much faster. The duration of the effect is short.
Be sure to read: Duodenal erosion: symptoms, treatment and prognosis for life
Indications for use
Gastroprotectors are prescribed for various diseases of the digestive tract. The list of drugs is extensive and allows you to select products with proven effectiveness that have the maximum therapeutic effect:
- Peptic ulcer in acute and chronic form with damage to the walls of the stomach. The remedies are also used in cases where not only the stomach is affected, but also the duodenum.
- Gastritis with increased and decreased acidity of gastric juice. Some medications in the group are not prescribed for low acidity, but in most cases medications are indicated.
- An erosive form of gastritis with the threat of developing a peptic ulcer.
- Dyspeptic disorders due to damage to the mucous membranes of the stomach. At the same time, medications help eliminate heartburn, nausea, vomiting, pain and belching.
- The development of gastritis and peptic ulcers against the background of frequent stressful conditions, nervous disorders, chronic psycho-emotional disorders or overwork.
The drugs can be used in the treatment of ulcers that develop while taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
How to protect your stomach from NSAIDs - expert advice
Indications for use. Prescribed as an enveloping agent to protect sensitive nerve endings from the effects of irritants and to slow down the absorption of drugs. Method of administration and dose. Externally in the form of powders and powders with zinc oxide, talc, etc.
Pharmachologic effect. It has antispasmodic, antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory and moderate antacid properties to reduce stomach acidity. For exacerbation and for the prevention of gastric and duodenal ulcers, chronic gastritis with preserved secretory function of the stomach, erosive gastritis, inflammation of the gastric mucosa with the formation of its defects.
Orally 0.2 g once a day, one minute before meals for a week. Ripe and dried flax seeds Linum usitatissinum L. Contain fatty linseed oil Oleum Lini and mucilage. Used as an enveloping and softening agent. As an enveloping, antacid, gastric acid reducer and mild laxative. Orally, adults are prescribed 1 g, children under 1 year - 0.5 g, from 2 to 5 years - .5 g, from 6 to 12 years - 1 g once a day.
Apply externally as a powder. Release form. Powder and tablets containing basic magnesium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate, 0.5 g each. Contain basic magnesium carbonate, basic bismuth nitrate, sodium bicarbonate, calamus rhizome powder and buckthorn bark. Used for gastric and duodenal ulcers and hyperacid gastritis, inflammation of the stomach due to a persistent increase in acidity.
Side effect. The stool turns dark when taking Vikair tablets. Tablets containing: basic bismuth nitrate - 0.35 g, basic magnesium carbonate - 0.4 g, sodium bicarbonate - 0.2 g, calamus rhizome powder and finely ground buckthorn bark - 0.4 g, in a package of pieces.
Contains basic magnesium carbonate, basic bismuth nitrate, sodium bicarbonate, calamus rhizome and buckthorn bark powder, rutin, kellin. The tablets have a complex effect. Basic bismuth nitrate, sodium bicarbonate and magnesium carbonate provide an antacid, reducing gastric acidity and astringent effect; buckthorn bark, although in a small dose, promotes a laxative effect. The presence of rutin allows one to count on some anti-inflammatory effect, and kellina - on an antispasmodic effect that relieves spasms.
The course of treatment usually lasts a month. During treatment you must follow a diet. The tablets usually do not cause side effects; sometimes there is an increase in bowel movements, which stops when the dose is reduced. The stool turns dark green or black when taking the pills. Tablets containing: basic magnesium carbonate - 0.4 g, basic bismuth nitrate - 0.35 g, sodium bicarbonate - 0.2 g, calamus rhizome powder and buckthorn bark - 0. g each, rutin, etc.
Magnesium oxide is one of the main representatives of antacids used to reduce high acidity of gastric juice. When magnesium oxide is introduced into the stomach, it is not absorbed and neutralizes the hydrochloric acid of the gastric contents to form magnesium chloride. Carbon dioxide is not released, therefore the antacid effect of magnesium oxide, which reduces gastric acidity, is not accompanied by secondary hypersecretion.
The phenomena of alkalosis are not observed. Passing into the intestines, magnesium chloride has a laxative effect. With hyperacid gastritis, inflammation of the stomach due to a persistent increase in acidity, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum.
Prescribed orally at 0., g for increased acidity of gastric juice, acid poisoning and as a mild laxative at a dose of g per dose. However, it should be noted that when taken on an empty stomach. For a long-term antacid effect, it is advisable to take them 1 hour and 3 hours after meals. Synthetic analogue of prostaglandin E.
Has antisecretory activity. When taken orally in tablet form, it reduces the secretion of hydrochloric acid, stimulates the secretion of bicarbonate and mucus, and has a cytoprotective effect that protects cells. The action usually develops 30 minutes after administration and lasts about 3 hours. It is used mainly to prevent the ulcerogenic, ulcer-causing effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including acetylsalicylic acid.
Taken simultaneously with anti-inflammatory drugs for the entire duration of their administration. Adults are prescribed 0.2 mg mcg once a day with meals. The last dose is taken shortly before bedtime. In case of poor tolerance, reduce the single dose to 0.1 mg mcg. The drug is not prescribed to children under 18 years of age. When using the drug, nausea, diarrhea, diarrhea, stomach pain are possible, rarely - skin rash, swelling, drowsiness, hypo- or hypertension, decreased or increased blood pressure and other side effects.
Pregnancy causes the muscles of the uterus to contract. For kidney disease, it is necessary to reduce the dose. The drug has an antacid, gastric acid-reducing, adsorbing, absorbing and enveloping effect. Neutralizes gastric acid, inhibits the secretion of pepsin, an enzyme that breaks down peptides and proteins. When entering the stomach, it forms a polymeric protective film on the surface of the mucous membrane and has an itoprotective effect that protects cells.
Prescribed to adults for peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, hyperacid gastritis, inflammation of the stomach due to a persistent increase in acidity. The tablets are swallowed whole, without chewing, with a small amount of water.
Course of treatment weeks. If necessary, the course is repeated. Constipation is possible when taking the drug. Sucralfate should not be prescribed together with tetracyclines, as the absorption of tetracyclines is impaired. The composition of the drug includes pectin and agaragar gel. The drug has an enveloping effect and antacid activity that reduces gastric acidity, helping to protect the gastric mucosa. Used for peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, gastritis, inflammation of the stomach, dyspepsia, indigestion, food intoxication and poisoning.
A combined drug that has an antacid effect that reduces gastric acidity. Sodium bicarbonate, which is part of it, reduces the acidity of gastric juice. Magnesium sulfate has a laxative effect. Acute gastritis, inflammation of the stomach, chronic gastritis with normal secretory function of the stomach, secretion of gastric juice in the acute phase, acute duodenitis, inflammation of the duodenum; peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in the acute phase; pain, a feeling of discomfort in the epigastrium of the abdominal region, located directly below the convergence of the costal arches and the sternum; heartburn after excessive consumption of alcohol, nicotine, coffee, sweets, errors in diet, taking medications; constipation.
For adults with epigastric pain and heartburn, take 1 teaspoon of powder per 1 glass of water. If necessary, the drug can be used 4 times a day.
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug; diabetes. Powder for the preparation of a solution for oral administration in bottles of g and g, in sachets of 5 g. It has an astringent, antacid, reducing gastric acidity, enveloping effect.
When taken orally, it forms a uniform protective film on the surface of the gastric mucosa. The drug is usually well tolerated; Nausea and vomiting are possible. It is not recommended to use the drug in severe renal impairment. In bottles of ml and 5 or 10 ml in plastic bags. Storage conditions. In tightly closed bottles or bags, protected from light. Antacid, reduces stomach acidity, astringent, protects the stomach lining.
As an astringent, weak antiseptic disinfectant, fixative for gastrointestinal diseases. It also has a local astringent and anti-inflammatory effect. Orally 0.5 g for children 0..5 g per dose once a day before meals, min. Topically once a day for dermatitis, skin inflammation, erosions, surface defects and small skin ulcers. With long-term use in large doses, methemoglobinemia is an increased content of methemoglobin in the blood.
A combined preparation containing bismuth nitrate main and bismuth subgallate. In the acidic environment of the stomach and duodenum, bismuth subgallate and bismuth subnitrate form complexes with glycoproteins and proteins released from the damaged mucosa.
This resulting complex, containing bismuth, forms a protective layer on the surface of mucosal defect erosions and ulcers, which protects them from the effects of hydrochloric acid and pepsin, an enzyme that decomposes peptides and proteins. The drug enhances the regeneration processes of the mucous membrane, increases the production of mucus and improves its protective properties.
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum; chronic gastritis in the acute stage; a feeling of fullness in the epigastric region of the abdomen, located directly below the convergence of the costal arches and the sternum. The drug is prescribed orally, 2 tablets 3 times a day, one hour before meals. The tablets are taken without chewing, with a small amount of liquid. The duration of treatment is determined by the clinical course of the disease and should be at least 4 weeks even with rapid improvement or disappearance of complaints.
At the same time, as with all bismuth preparations, the duration of treatment should not exceed 8 weeks. If it is necessary to repeat the course, you should take a break of 8 weeks.
Since the drug acts most actively in the acidic contents of the stomach, antacids, drugs that reduce gastric acidity, as well as milk should not be taken simultaneously with bismofalk. If necessary, these drugs are taken no earlier than 30 minutes before taking bismofalk or 30 minutes after taking it, so as not to weaken the effect of bismofalk.
Possible dark coloration of stool due to the formation of bismuth sulfide. With long-term use in high doses, it is possible to develop encephalopathy, brain diseases associated with the accumulation of bismuth in the central nervous system, characterized by its degenerative changes.
Contraindications
Medicines are not always allowed to be used, as they can cause complications.
Contraindications include the following conditions:
- The period of lactation and childbearing. Only some medications are allowed to be used at this time, but in each case, consultation with a specialist is required.
- Acute cerebrovascular accident.
- Diagnosing intestinal obstruction, in which the use of medications can provoke severe complications.
- Acute or chronic severe renal failure.
- Detection of severe forms of liver failure in patients with impaired functioning of the organ.
- Intolerance to any component in a particular medicine.
- Colitis in acute form with disruption of the large intestine.
- Intestinal atony, when the passage of food through it is disrupted. At the same time, many medications can provoke complications and aggravate symptoms against the background of stagnation.
- Childhood. Each medicine has its own age restrictions, so you should first consult with a specialist.
- Acute period after myocardial infarction.
Any drug may have other contraindications, so it is important to first study the instructions for use, which describe all the features. Medicines are used with caution in the treatment of elderly patients who suffer from severe pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
Prevention of gastropathy
To prevent drug-induced gastropathy, it is necessary to take painkillers only as prescribed by a doctor and strictly in the dosages prescribed by him. During therapy, you need to avoid foods that irritate the mucous membranes of the stomach: spicy, fatty foods, fast food, strong drinks. Eating very hot or cold food is not recommended.
Additional intake of protective drugs will protect the stomach when taking NSAIDs. Among the traditional methods, it is recommended to drink aloe juice on an empty stomach with water or honey, linden honey and propolis. All methods must first be discussed with your doctor.
Side effects
Gastroprotectors (the list of drugs with proven effectiveness includes medications that reduce the acidity of gastric juice) can provoke complications, especially if the instructions are not followed. Compliance with all the rules does not guarantee the absence of complications.
Disorders can affect the nervous system and provoke:
- headache;
- weakness;
- fatigue.
During treatment, it is possible to develop insomnia, decreased performance, and irritability due to these symptoms. Manifestations usually disappear after stopping the use of the medicine, but in some cases special symptomatic treatment is required.
Complications from the digestive tract occur frequently. The most common is stool disorder in the form of constipation or diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. Patients may report pain in the stomach and intestines. Sometimes, if the medication is not suitable for a particular patient, the symptoms of the underlying disease may worsen.
Disorders from the urinary system rarely occur.
Sometimes patients talk about:
- frequent urination;
- pain in the kidney area;
- change in urine color;
- the appearance of pus or blood impurities.
Allergies to medications from this group occur frequently and are accompanied by classic symptoms such as:
- rash;
- irritation;
- peeling of the skin.
Patients talk about itching and the spread of the rash to large areas of the body. To prevent complications, you should use the medication only for its intended purpose and in the absence of contraindications.
Gastric stenting methods
Currently, oncologists use metal self-expanding stents for gastric stenting. Doctors use several methods to install self-expanding stents in the stomach:
- under direct fluoroscopic control without the use of endoscopic techniques and preliminary balloon expansion or after balloon dilatation, which is performed through a stent delivery device;
- the endoscopic method of installing stents under direct X-ray television control is used in the tortuous course of the stenotic section of the stomach or the area of postoperative anastomosis;
- endoscopic stent installation without direct fluoroscopic control is used using modern small-diameter video endoscopic technology;
- intraoperative installation of a stent under manual control (rarely used in palliative operations).
Gastric stenting is an endoscopic operation that is performed in an X-ray endoscopy room under local or general anesthesia. Before installing a stent, oncologists restore the lumen or mechanically expand the stomach to at least the diameter of the delivery device.
Considering the elimination of dysphagia as the main stage of providing palliative care to patients with tumor narrowings of the digestive tract that cannot be completely cured, oncologists individually select a scheme for preparing and stenting the gastric cardia or the area of postoperative anastomosis. When stenting under X-ray endoscopic control, a metal conductor is inserted into the lumen of the stomach through the channel of an endoscope passed below the narrowed area, and radiopaque marks are placed on the skin of the chest. They determine the location of the proximal and distal edges of the stent. Then the endoscope is removed and a container with a stent is inserted through the guidewire into the narrowed area of the stomach, and the delivery device is smoothly removed from the stent.
When endoscopic stenting without the use of direct X-ray television control, the stomach lumen is first expanded or restored, esophagogastroscopy is performed, and the proximal and distal boundaries of the tumor are clarified. A string is passed through the endoscope, along which a container with a stent is inserted. The position of the upper edge of the stent is controlled when the endoscope is reinserted.
The stent, under endoscopic control, is smoothly pushed out of the delivery device and straightened in a given area of the cardia. In order to determine the position of the lower edge of the stent and the degree of its expansion, a control x-ray examination is performed. Oncologists select the length of the stent individually in each specific case. Full deployment of the stent in the narrowed area of the stomach occurs within 2-5 days.
Overdose
Medicines can provoke an overdose, which significantly worsens the patient's condition.
The most common manifestations of overdose:
- Severe headache and dizziness.
- Repeated vomiting during the day, not associated with food intake.
- Cramps.
- Severe pain in the stomach area.
- Flatulence and bloating.
- Stool disorders accompanied by frequent loose stools.
- Impaired consciousness.
- The development of acute urticaria, which is accompanied by swelling of the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose and mouth. In this case, patients may notice lacrimation, discharge of a large amount of mucus from the nose, as well as difficulty in nasal breathing.
Often, an overdose provokes Quincke's edema, in which swelling of the mucous membranes of the throat is observed, disrupting the passage of air, suffocation and even respiratory arrest. Such complications threaten the patient's life. If signs of overdose appear, it is important to immediately visit a doctor who will prescribe symptomatic therapy.
Gastroscopy (FGDS, EGDS)
The stomach is one of the most important internal organs; not only digestion, but also the general condition of the body depends on its health. At the same time, the gastrointestinal tract is a rather fragile system. Poor nutrition, alcohol, and taking certain medications can seriously interfere with its functioning. We tell you how to maintain a healthy stomach and what medications exist to protect the gastric mucosa. By the age of 30, almost everyone is faced with at least one more or less serious gastrointestinal disease. The most common are gastritis and duodenitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. If gastritis is not treated, peptic ulcers may develop over time. Very often, people are also affected by irritable bowel syndrome - a disease that is not particularly dangerous, but extremely unpleasant, fraught with pain, flatulence and bowel dysfunction. Is it possible to avoid the development of stomach diseases and maintain the health of the digestive tract?
Catheter feeding tube for enteral nutrition and drug administration for children, blue size 8 Fr, diameter 2.8 mm, length mm Galmed.
The best drugs of the group with proven effectiveness
Gastroprotectors (the list of drugs with proven effectiveness includes medications in different dosage forms) are available in several forms, which allows you to use the most convenient option in each case.
Most often used:
- pills;
- capsules;
- gels;
- suspensions for oral administration.
Solutions for parenteral administration are often prescribed.
Capsules
Drugs in this dosage form are considered the most popular and effective, as well as convenient to use. There are several proven medications prescribed to patients.
| Facilities | Main component of the composition | Indications and application regimen |
| Gastrozol | Contains omeprazole as the main active ingredient | Prescribed for stomach ulcers, gastritis and gastroduodenitis. The product suppresses the production of hydrochloric acid, which helps prevent negative effects on the walls of the stomach and stimulates tissue repair. Take 2-3 capsules per day 30 minutes before meals. The course of therapy lasts from 2 to 6 weeks, depending on the degree of advanced disease and the presence of associated complications |
| Omeprazole | The drug contains the active ingredient of the same name in the composition | Capsules are prescribed for gastritis, detection of peptic ulcers, gastroduodenitis, and dyspeptic disorders. The medicine helps reduce the production of hydrochloric acid, has a positive effect on the walls of the stomach, and prevents the progression of the disease. Take 1 capsule 3 times a day 20-30 minutes before meals. Use is continued for 2-5 weeks depending on the severity of symptoms |
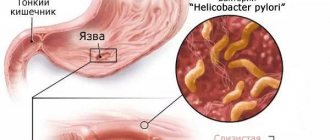
| De-nol | The drug contains bismuth as an active ingredient | The medicine reduces the acidity of gastric juice, therefore it is used for gastritis with high acidity. The medication is highly effective and helps prevent the development of peptic ulcers. Take 1 capsule 2-3 times a day, depending on the severity of the symptoms. Treatment lasts from 1 to 4 weeks, in each case the duration of the course is determined individually. Additionally, the medicine coats the walls of the stomach, destroys the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which often provokes the development of gastritis |
Such drugs should be prescribed by a doctor, who will determine the dosage and duration of the medication course.
Pills
The tablets are considered very effective and are used often, especially when taking the course at home. Products in this form may contain different active ingredients.
Vikair
Vikair contains bismuth, as well as several other components that have a healing effect:
- Buckthorn bark.
- Mania carbonate.
- Sodium bicarbonate.
- Calamus rhizome.
This composition helps improve the condition of the mucous membranes of the stomach and prevents complications. Tablets are prescribed for gastritis, dyspeptic disorders accompanied by constipation and increased acidity of gastric juice.
Take 1 tablet 3 times a day for 2 weeks. After this, the patient visits a doctor, who determines the advisability of further use or discontinues the medication.
Novobismol
Novobismol is used to eliminate heartburn, pain in the stomach and destroy Helicobacter pylori. The drug is indicated for gastritis, peptic ulcers and dyspeptic disorders.
It is prescribed in long courses of 30 days with daily intake of 2 tablets per day at equal intervals. Repeated courses can be prescribed after a 2-3 month break.
Venter
Venter is a drug from the group of gastroprotectors, which belongs to the subgroup of prostaglandins. The drug has pronounced properties and contains sucralfate as an active ingredient.
Most often, the medicine is prescribed for peptic ulcers, since it has pronounced gastroprotective and antiulcer properties. When taken, the component of the composition increases the local protective forces of the stomach walls and prevents the progression of pathologies.
Take tablets for 2-4 weeks, 2 tablets per day at equal intervals. If necessary, treatment is extended or shortened, but always after completion of the course a re-examination is required to assess the effectiveness of therapy.
Gels and suspensions
Medicines in this form usually contain components aimed at reducing the acidity of gastric juice and protecting the walls of the stomach from the aggressive effects of hydrochloric acid.
The most commonly used effective means are:
- Maalox – a medicine based on magnesium hydroxide and algeldrate, which has a pronounced gastroprotective and antacid effect. The drug is prescribed for nausea, vomiting and heartburn against the background of gastritis, peptic ulcers and some other stomach pathologies. It is highly effective and helps cope with acute symptoms, prevents complications against the backdrop of rapid progression of manifestations. Take 15 ml 3-4 times a day for 5-10 days. Usually long courses are not required.
- Almagel has an effect due to algeldrate and magnesium hydroxide, has gastroprotective and antacid properties, helps prevent the progression of pathologies, protects the walls of the stomach from the aggressive effects of food and other drugs. The drug is available in the form of a suspension for oral administration and is prescribed for gastritis, gastroduodenitis, peptic ulcers, and stomach pain of various origins. A single dosage is 5-7 ml, take the product 3-5 times a day for 2 weeks.
- Phosphalugel also has gastroprotective properties and creates a kind of protective film on the walls of the stomach that prevents the progression of pathologies. Most often, the medicine is used for acute and chronic peptic ulcers, gastritis and dyspepsia of various origins. The medication contains aluminum phosphate as the main active ingredient. The gel is taken 16 g 3-5 times a day for 10 days. The medicine is highly effective and can be used not only in courses, but also in case of a one-time occurrence of heartburn and other manifestations.
Such drugs are usually used in combination with other medications, as this increases their effectiveness.
Solutions and lyophilisates for parenteral administration
Gastroprotectors (the list of drugs with proven effectiveness may include medications that are available not only in oral dosage form) in the form of solutions and lyophilisates for obtaining solutions are considered quite effective. They are used when, for one reason or another, patients cannot use capsules, gels or tablets.
The most effective and relatively safe medications are:
- Pantoprazole – a product in the form of a lyophilisate to obtain a solution that is administered intravenously by drop or stream. The drug helps reduce the acidity of gastric juice and improves the condition of the mucous membranes due to the content of omeprazole as the main active substance. The drug is prescribed for peptic ulcers and gastritis, as well as when complications arise from this condition in the form of pancreatitis, cholecystitis. The drug is used for 10 days. For intravenous jet administration, you need to take 1 bottle of medicine and 20 ml of sodium chloride; for drip infusion, you need to take 200 ml of sodium chloride per 1 bottle of medicine. The procedure is repeated once a day.
- Dalargin is a drug in the form of a lyophilisate for the preparation of a solution that is administered intravenously. The medicine contains tyrosyl-alanyl-glycyl-phenylalanyl-leucyl-arginine diacetate as the main active ingredient. It has antiulcer and gastroprotective properties. It is prescribed for gastritis, peptic ulcers and gastroduodenitis. The powder is dissolved in 200 ml of sodium chloride and administered intravenously. Repeat the procedure for 10 days in a row. If necessary, a repeat course is prescribed.
- Gastrocepin is also available in the form of a parenteral solution. It contains pirenzepine and helps eliminate the symptoms of gastritis, gastroduodenitis, dyspeptic symptoms against the background of stomach pathologies. The drug is administered intramuscularly at a dose of 2 ml per day for 7-14 days, depending on the severity of symptoms. The drug not only reduces the acidity of gastric juice, but also has gastroprotective properties, therefore it helps restore the mucous membranes, which prevents the development of complications in the form of erosions and ulcers.
Any of the medications is prescribed to patients after a preliminary examination and identification of the cause of the disorder.
Gastroprotectors are considered the most popular and effective in the treatment of stomach pathologies.
The list of drugs includes drugs with proven effectiveness that help improve the condition and prevent the progression of diseases and the development of complications. The use of drugs is allowed only after examination and identification of the disease and its degree of neglect.
GASTROCYTOPROTECTORS: TO PROTECT THE Gastrointestinal Mucosa
Preferanskaya Nina Germanovna Associate Professor of the Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Pharmacy named after. A.P. Nelyubin First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenov (Sechenov University), Ph.D.
They increase the resistance of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract to the action of increased pepsin activity or a strongly acidic reaction of the stomach (pH 0.8–1.5). Gastrocytoprotective agents stimulate the formation of mucin by glandular cells and the gastric mucosa, thereby maintaining the integrity of its protective barrier. The drugs help maintain the pH of gastric juice at a level of 3.0-3.5 by increasing the secretion of bicarbonates. When used, the synthesis of protective factors (prostaglandins) increases and their inactivation decreases. The regeneration of cells in the gastric mucosa improves by reducing microvascular damage and improving regional blood flow. Epidermal growth factor is stimulated, the barrier function of the mucous membrane is increased. Proliferation and turnover of epithelial cells are stimulated. All this significantly improves reparative processes and contributes to the restoration of desquamated (Latin desquamo - remove, peel off) epithelium in the stomach.
For this purpose, several subgroups of gastrocytoprotective drugs are used:
1. Synthetic analogues of prostaglandins - Misoprostol.
2. Drugs that increase the synthesis of prostaglandins - Rebamipide.
3. Preparations that form complex compounds (chelates) - Bismuth tripotassium dicitrate, Sucralfate.
4. Bismuth preparations: Bismuth subnitrate, Vikalin, Vikair.
5. Preparations of natural origin - Solcoseryl, Mumiyo, etc.
Gastrocytoprotective drugs differ from each other not only in composition, but also in pharmacological effects. Each drug protects the mucous membrane in different ways and stimulates the restoration of cells in the stomach wall.
HORMONE-LIKE LIPID MEDIATORS
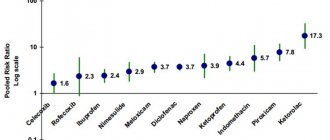
Numerous studies have shown that prostaglandins increase the resistance of the gastric mucosa to the effects of traumatic factors (hydrochloric acid, pepsin, bile, ethanol, NSAIDs, corticosteroids). This is due to their influence on the physiological functions of the body. NSAIDs and corticosteroids disrupt the formation of prostaglandins E and I2. The first drug in this group is a synthetic analogue of prostaglandin E1 - Misoprostol - TN " Mirolyut " - activates the regeneration of the mucous membrane, increases blood circulation in the microvessels of the stomach wall, suppresses the production of the digestive enzyme pepsin and reduces the production of gastric juice It increases the reproduction of special (additional) cells of gastric mucus, which protects its walls from aggressive factors. The drug has a weak stimulating effect on the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract through antisecretory activity. The stability of the gastric mucosa increases, which prevents the development of erosive and ulcerative lesions. Admission is often prescribed for the prevention of NSAID gastropathy. It is better not to prescribe Misoprostol on your own, even if aspirin was prescribed as the main medication, which for some reason many patients take off-label and quite often. In patients taking NSAIDs, the incidence of gastric and duodenal ulcers is reduced and the risk of ulcer bleeding is reduced.
Important! The drug is contraindicated in cases of coronary artery disease, hypertension, liver dysfunction, and pregnancy. Not recommended for children and adolescents. Prostaglandins have dangerous side effects, they cause: flatulence, diarrhea, nausea, headache, menstrual irregularities, vaginal bleeding, etc.
Before taking the drug, you must consult your doctor.
Rebamipid (Rebamipidum) - TN " Rebagid " - has a cytoprotective effect on the gastric mucosa under the damaging effects of ethanol, acids, alkalis and drugs (NSAIDs, GCS). Promotes the activation of enzymes that accelerate the biosynthesis of high molecular weight glycoproteins and increases the mucus content on the surface of the stomach wall. Rebamipide increases the content of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in the gastric mucosa and increases the content of PGI2 in the stomach. Helps improve blood supply to the gastric mucosa, activates its barrier function, activates alkaline secretion of the stomach, enhances the proliferation and metabolism of gastric epithelial cells. When taking the drug, the products of oxidative stress, inflammatory cytokines and chemokines are inhibited, while clearing the mucosa of hydroxyl radicals and suppressing superoxides produced by polymorphonuclear leukocytes and neutrophils in the presence of Helicobacter pylori. Absorption when taken orally is high. After administration at a dose of 100 mg, the maximum concentration is reached after approximately 2 hours and is 340 ng/ml. The half-life is approximately 1 hour. Repeated doses of the drug do not lead to its accumulation in the body. Approximately 10% of the drug is excreted by the kidneys, mainly unchanged.
The drug is taken orally, 1 tablet. 3 times a day, washed down with a small amount of liquid. The course of treatment is 2-4 weeks; if necessary, it can be extended to 8 weeks.
Important! When using the drug, side effects from the gastrointestinal tract may occur: constipation, flatulence, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, impaired taste, as well as allergic reactions and menstrual irregularities.
medicinal products forming a protective film of organometal complexes
Bismuth tripotassium dicitrate (Bismuthi trikalii dicitras) - TN " De-nol ", TN " Novobismol ", table. 120 mg. In the acidic environment of the stomach, the drug forms insoluble bismuth oxychloride and dicitrate. The combination of dicitrate with bismuth hydroxide forms molecular complexes of various structures and sizes, which leads to the transition of the aqueous solution into a colloidal form. The colloidal form of the drug allows it to effectively penetrate into the gastric mucus. The drug penetrates well into the depths of the gastric pits, which allows it to destroy bacteria that are out of reach of other antibacterial drugs. It has an anti-Helicobacter effect, which manifests itself in the form of coagulation of microbial cell proteins and the death of the spiral-shaped flagellated gram-negative bacterium Helicobacter pylori. When used, the drug is practically not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is excreted mainly in excrement.
Sucralfate (Sucralfatum) - TN " Venter ", tab. 1.0 g is a drug of mixed action: in the stomach it breaks down into two active metabolites: aluminum hydroxide, which has an antacid effect, and sucrose sulfate, which interacts with the proteins of necrotic tissue, forming a chelate complex in the form of an adhesive mass that lines and protects the ulcer from damage. Aluminum hydroxide has an antacid effect, neutralizes hydrochloric acid and increases the pH of the stomach contents. The main side effects are dyspeptic disorders and allergic reactions.
Bismuth preparations have an astringent, adsorbing and enveloping effect.
Bismuth subnitrate (Bismuthi subnitras) - a drug on the surface of the gastric mucosa coagulates proteins, forming a protective film of denatured proteins with the formation of dense albuminate. It has a vasoconstrictor effect, reduces local inflammation, suppresses the growth and development of Helicobacter pylori. In addition, bismuth preparations have local antimicrobial activity, acting directly on the bacterial cell wall and disrupting its integrity. Bismuth has a direct bactericidal effect, its minimum inhibitory concentration against Helicobacter pylori is quite high.
Nausea, vomiting, headache, pigmentation on the tongue and allergic reactions may occur when using this drug.
Vikalin (Vicalin), tablet, coating. obol., is a combined preparation, one tablet of which contains the active components: bismuth subnitrate (350 mg), magnesium carbonate - 400 mg, sodium bicarbonate (200 mg), alder buckthorn bark (25 mg), calamus rhizome (25 mg) , rutoside + kellina 5 mg.
The drug has reparative properties, has an astringent, adsorbent, enveloping effect. Additionally, vikalin exhibits antispasmodic, laxative, and anti-inflammatory effects. When using the drug, the acidity of gastric juice decreases and the activity of pepsin decreases, and an antacid and bactericidal effect occurs. When using Vicalin, frequent bowel movements, nausea, headache and allergic reactions may occur. Tablets are taken orally after 30-60 minutes. after meals, drink a sufficient amount of warm water (0.5 cups). There is a rapid action, good tolerability and affordable cost of the drug. The use of the drug is prohibited for sick children under the age of 18 years, with renal failure, pregnant women and during breastfeeding.
The drug is prescribed to adults, 1-2 tablets 3-4 times a day for 30 minutes. before or 2 hours after the last meal; Children from 6 to 14 years old can take 1 tablet. 2 times a day, with a small amount of water. The course of treatment is 28-56 days, break is 8 weeks.
Important! To avoid the accumulation of bismuth in the body, especially when the excretory function of the kidneys decreases, long courses of taking the drug are not recommended. When using the drug, nausea, vomiting and a metallic taste in the mouth may occur.
Vicair is a drug in a combination of bismuth subnitrate (350 mg), alder buckthorn bark (400 mg), calamus rhizome (200 mg), magnesium carbonate + sodium bicarbonate 25 mg. The effect of the drug is due to the properties of its components. This product contains calamus, which has an antispasmodic effect, and buckthorn, which has a laxative effect, helping to improve passage through the intestines. The drug exhibits an astringent, antacid effect.
The dosage regimen is individual, depending on the indications, the patient’s age and the clinical situation. The drug is contraindicated in hypoacid gastritis, chronic renal failure, chronic appendicitis, enterocolitis, children under 18 years of age, pregnancy, lactation and hypersensitivity to the components of the combination.
Important! It is impossible to take bismuth preparations for a long time, because they cause various side effects: intestinal dysfunction, manifested by constipation or diarrhea, disrupt the functioning of the kidneys and liver, and can cause insomnia, encephalopathy, and memory loss.
PREPARATIONS OF PLANT AND ANIMAL ORIGIN
Preparations successfully used to improve reparative processes: Solcoseryl, Aloe, St. John's wort, Propolis, Mumiyo .
Solcoseryl is a proven effective remedy for stomach ulcers, made from calf blood. This remedy was invented a long time ago and is still used today as a potent wound healing agent.
This is a biogenic stimulant, it quickly and effectively eliminates the symptoms of the disease and reduces the inflammatory process. It activates the processes of regeneration and metabolism in the body, removes inflammation. Solcoseryl triggers a self-healing mechanism, self-regulation of disorders of the mucous membrane of the digestive organ occurs. And not only does the stomach feel better, but also the liver. The drug removes toxic substances accumulated due to the disease from the body.
Its main purpose is to stimulate blood supply to the mucous membrane of the digestive organ and accelerate the scarring of ulcers; activate the regenerative capabilities of cells, prevent atrophy of the gastric mucosa; improve metabolism and immunity.
Methylmethionine sulfonium chloride ( Vitamin U ) has an analgesic effect and stimulates the healing of mucosal lesions. When used, the patient’s body is saturated with methyl groups, which are necessary for biochemical synthesis processes. Participates in the methylation of histamine, converting it into an inactive form, which helps reduce gastric secretion. Prescribe 2 tablets orally. 3 times a day, the course of treatment is a month, the course is repeated if necessary.
Herbal medicines containing chamomile flowers, flax seed mucilage, plantain leaves, St. John's wort herb have an enveloping and astringent effect. They are less effective, but they can be used as a prophylactic agent, after consulting with a gastroenterologist or allergist (herbal preparations also have contraindications for use).
Biogenic stimulants - aloe extract, Kalanchoe juice, PHYBS, sea buckthorn and rosehip oil - improve tissue regeneration.
, sea buckthorn oil protects biological membranes from damage, has a moderate inhibitory effect on the secretion of gastric juice and accelerates the healing process of ulcers. Patients with ulcers localized in the stomach and duodenum are prescribed 1 tsp. in 30 min. before meals 2-3 times a day and at night. For internal use it is contraindicated in case of inflammatory processes in the gallbladder, liver, pancreas and cholelithiasis.
Before prescribing a drug, a gastroenterologist takes into account all its characteristics: mechanisms and effects of action, negative types of action, side effects, contraindications and individually selects the necessary drug. Timely contact with a gastroenterologist and the correct use of gastrocytoprotective agents allows patients to level out the exacerbation phase and optimize the remission phase.