GastrituNet.ru » Stomach diseases » Gastritis » Treatment » Diet
In this article we will tell you how alcohol affects the stomach, what chronic alcohol abuse leads to, and how to minimize the adverse effects on digestion.
- 1 In what quantities and what kind of alcohol does it negatively affect the stomach?
- 2 Effect of alcohol on the stomach
- 3 Clinic of acute alcoholic gastritis
- 4 Symptoms of chronic alcoholic gastritis
- 5 How you can protect your stomach
- 6 Useful video
- 7 Ways to relieve and treat stomach pain after drinking alcohol
- 8 Alternative Ways to Relieve Stress
The effect of alcohol on the stomach
At the time of consumption, ethyl alcohol, which is part of alcoholic beverages, has the following effects:
- Being a strong detergent, alcohol has a direct damaging effect on the walls of the stomach, causing coagulation (clotting) of cell membrane proteins and destroying the protective layer of gastric mucus.
- Strengthens the production of gastric juice. Gastric secretion stimulated by alcohol has its own characteristics: the secretion contains high concentrations of hydrochloric acid and a small amount of digestive enzymes. As a result, despite high acidity, the efficiency of digestion and absorption of nutrients is reduced.
- The irritating effect of alcohol on the gastric mucosa leads to the development of chronic hyperemia and edema.
- Under the influence of ethyl alcohol and its metabolic products (acetoacetate), the motor activity of the stomach is inhibited, so food remains in it for a long time. This is an additional damaging factor leading to the development of inflammatory and dystrophic processes.
With chronic alcohol abuse, temporary disturbances in the functioning of the stomach take a permanent form - chronic alcoholic gastritis develops. The disease causes atrophy of the gastric mucosa and digestive glands and in more than half of cases leads to the development of stomach cancer.
Ethyl alcohol negatively affects not only the stomach, but also other organs of the digestive system: the esophagus, liver, pancreas and intestines. The result is the development of esophagitis, pancreatitis, fatty infiltration of the liver with subsequent cirrhosis, colitis.
The liver receives a toxic load through the intestines
Alcohol is a threat to the liver. Alcohol destroys hepatocytes - liver cells - and thus undermines the functioning of the organ. Everyone knows this, we will not open America. Something else is new: the liver receives not only a direct toxic load, but also an indirect one - through the intestines.
Liver disease is often associated with increased gastrointestinal permeability. The breakdown of the intestinal barrier allows bacteria and toxins to move from the intestinal lumen to other organs. Most of the venous blood from the digestive system is drained into the portal circulation, which is part of the liver's dual blood supply. Thus, the liver is the first organ in the body that encounters not only nutrients, but also intestinal bacteria.
Russian scientist Doctor of Medical Sciences Igor Bakulin conducted a study studying the connection between alcohol, liver and intestinal microflora. His results showed that under the influence of acetaldehyde, an intermediate product of ethanol metabolism, the barrier function of the mucous membrane decreases. Because of this, the composition of the intestinal microflora changes: in alcohol abusers, the active growth of gram-negative bacteria begins. The latter are a source of endotoxins, which provoke inflammation in the liver.
Alcohol can significantly change the quantitative and qualitative composition of the intestinal microflora. It leads to bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine and contributes to the development of leaky gut.
Those. in order to cure alcoholic liver disease, you need not only to give up alcohol and take hepatoprotectors, but also to take medications to restore the mucous membrane and improve the composition of the intestinal microflora.
Clinic of acute alcoholic gastritis
Strong alcoholic drinks with an alcohol content of more than 28% have a strong damaging effect on the gastrointestinal mucosa. Their long-term use reduces the reparative capabilities of cells and sooner or later leads to gastritis. The difference between the alcoholic form of the disease is that in the initial stage there are no inflammation processes in the mucous membrane.
Cell damage occurs “directly” as a result of the action of alcohol and its metabolites (acetaldehyde). The acute form develops when drinking a large amount of strong alcoholic drinks at the same time.
The following main symptoms develop:
- sharp pain in the upper abdomen;
- severe nausea;
- vomiting, often multiple times.
Very often, acute alcoholic gastritis occurs against the background of alcohol poisoning. In this case, the following symptoms will be observed:
- euphoria;
- loss of coordination;
- dizziness;
- convulsions;
- rapid noisy breathing.
The higher the degree, the more severe the damage
A scientific work by American scientists published in 2015 discovered an interesting nuance. Intestinal permeability becomes more severe the higher the ethanol concentration (>40%). Moreover, even a low dose of alcohol is enough to provoke the development of “leaky gut” and disruption of the intestinal microflora.
Any alcohol is dangerous not only for the liver, but also for the intestines, and therefore for the whole body.
So, liver diseases are closely related to the condition of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract and intestinal microflora. Alcohol damages both the liver and the intestinal barrier. This entails not only the accelerated progression of alcoholic liver disease, but also the development of other diseases. Scientists continue research in this direction, but it is already clear that the intestines keep a great many secrets and that soon the approach to the treatment of known diseases will change. Changes are coming, as the hero of “Pokrovsky Gate” said.
Symptoms of chronic alcoholic gastritis
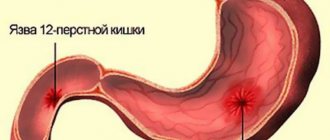
Long-term alcohol abuse leads to the transition of the acute stage of the disease to a chronic form. Inflammatory and dystrophic processes develop in the gastric mucosa. Acute erosions become chronic, and gastric ulcers may form. In severe cases, stomach bleeding is possible.
The stomach of an alcoholic is characterized by a large number of connective tissue filaments - a kind of thickening and hardening of the mucous membrane, which complicates its regeneration. With long-term alcoholism, the general resistance of the body decreases, hypovitaminosis develops, and the functioning of not only the stomach, but also other organs of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted.
The main symptoms of the chronic form of the disease:
- severe nausea, especially on an empty stomach, regardless of the time of day;
- vomiting on an empty stomach;
- pain in the upper abdomen (under the stomach), gradually becoming permanent;
- decreased appetite, especially in the morning;
- change in taste preferences;
- fast saturation;
- feeling of fullness in the stomach when eating even a small amount of food
- prolonged constipation.
Dysbacteriosis and alcohol
Many people are interested in the answer to another question. Is it possible to drink alcohol if you have dysbiosis? This is not recommended, since both beer and strong alcohol further irritate the intestines, which leads to increased symptoms . The condition will not worsen just from a small single dose, but it would be better to refuse serious volumes of the drink.
Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages can lead to serious health consequences, and this applies not only to the intestines, but to the entire body as a whole. It is worth thinking about your chosen lifestyle in advance, because it will be impossible to restore health after many years of abuse. And if you decide to sit down at the table and drink alcohol, do it wisely, because there are a lot of tips on how to reduce the risks of drinking strong drinks, and support and strengthen your body both before taking them, during, and after. Take care of your health, but if you need help, immediately contact the Private Ambulance No. 1 clinic!
How can you protect your stomach?
The best way to protect your digestive system from the effects of ethyl alcohol is to avoid drinking alcohol. But since this is not always possible, it is advisable to adhere to certain rules:
- Do not drink on an empty stomach. Before the feast, it is important to eat a small amount of fatty, but not spicy food. A good option would be a small piece of butter. A fresh chicken egg has the same effect. It forms a kind of protective film on the surface of the mucous membrane that protects cells from damage.
- Drink and have a bite. After drinking any alcoholic drink, especially high strength alcohol, it is important to eat a small amount of food. It is advisable that it be of a dietary nature: dairy products, boiled potatoes, oatmeal. Such food envelops and protects the walls of the stomach.
- Do not mix alcoholic beverages with soda. Carbon dioxide not only accelerates the absorption of alcohol, but also has a direct irritant effect on the stomach, exacerbating the effect of ethyl alcohol.
If you have existing diseases of the digestive system (chronic gastritis, stomach ulcers, cholecystitis, pancreatitis), you must take medications before the feast. So, for gastritis and stomach ulcers, you can take proton pump inhibitors ( Omeprazole , Rabeprazole ), which will reduce the acidity of gastric juice and prevent heartburn. Preliminary intake of antacid drugs ( Phosphalugel , Gastal , Almagel ) is effective. However, the best option is to avoid drinking alcohol.
Why does dysbiosis occur when drinking alcohol?
Intestinal upset after alcohol does not always go away without a trace after a person stops drinking alcohol. Often diarrhea or constipation takes a chronic course. The thing is that under the influence of alcohol, the intestinal microflora has undergone pathological changes :
- Due to the pronounced aseptic properties of ethanol, beneficial lactic acid bacteria died.
- Pathogenic microorganisms began to actively multiply in the vacated areas.
- Pathogens move up the digestive tract, causing inflammation of the small intestine and stomach.
During the growth process, pathogenic bacteria release toxic substances into the surrounding space. Once they enter the bloodstream, they spread throughout the body, reducing the functional activity of all vital systems. It is not without reason that people who abuse alcohol have problems with their liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, and brain.
Ways to relieve and treat stomach pain after drinking alcohol
If drinking alcohol causes pain, then to improve the condition it is important to do the following:
- If possible, rinse the stomach to remove alcohol.
- Drink weak sweet tea.
- For heartburn, take medications that coat the stomach wall and reduce acidity: Gaviscon , Almagel , Rennie .
- Take proton pump inhibitors (omez, pariet) or bismuth-containing tablets ( De-nol ).
- To relieve symptoms of intoxication, you can use the latest generation enterosorbents ( Enterosgel , Polyphepan ).
- Follow a gentle diet.
Typical gastrointestinal diseases in alcoholism
With frequent alcohol consumption, the glands of the mucous membrane are depleted. Because they work in extreme mode. As a result, the secretion of gastric juice decreases, and the lining of the stomach itself becomes thinner. As a result, the likelihood of chronic gastritis increases.
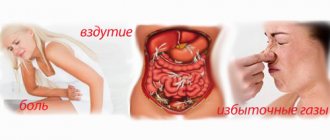
Most often, anacid gastritis occurs (a disease in which the production of pepsin is reduced, and hydrochloric acid is almost completely absent or completely absent). In this case, the patient loses his appetite (after all, his stomach is simply not able to digest food), heaviness occurs in the epigastric region, belching , heartburn and abdominal pain.
So-called “alcoholic” gastritis is accompanied by intestinal diseases. Inflamed intestines cause a lot of trouble! The patient may experience diarrhea and constipation. The pancreas and liver also become inflamed, duodenal ulcers, the appearance of polyps, and changes in the acidity level of gastric juice may occur. As a result, the likelihood of developing a malignant tumor, that is, stomach cancer, increases.
Alternative ways to relieve stress
By acting on the central nervous system, alcoholic drinks enhance the synthesis of serotonin and endorphin in the brain. As a result, a person’s mood improves and anxiety levels decrease. But the effect of alcohol wears off quickly and a new portion is required to maintain the effect. What are some possible alternatives to reduce stress other than alcohol:
- Sports activities. Muscle work is one of the most powerful natural stimulators of endorphin synthesis and an excellent way to maintain a good mood.
- Communication with nature. A change of scenery, a beautiful view and fresh air increase the body’s tone and energy. In this state, problematic situations are comprehended and solved more easily.
- Taking vitamin and mineral complexes. There are vitamins and minerals that are natural antidepressants. These include magnesium, vitamins B, D and iodine.
How does alcohol affect the human body?
The harmful effects of alcohol on the human body are difficult to overestimate. Which organ or system does not suffer from its negative effects?
Excessive and prolonged abuse of alcoholic beverages leads to intoxication of the body and the formation of alcohol dependence, accompanied by serious negative consequences. As a rule, this process occurs unnoticed by the addict and his relatives.
Effect of alcohol
Absorption of ethanol into the walls of the stomach (a couple of minutes after consumption).
- Increased blood flow and dilation of blood vessels, unimpeded passage of blood.
- Decreased pressure.
- Blood does not flow to the extremities and they do not receive oxygen.
Next, vasoconstriction occurs, putting the body in a state of shock. Long-term systematic consumption of alcohol and similar processes affect the functioning of the body and lead to wear and tear on the functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
As a result, pressure increases, tachycardia develops, the heart begins to work in an increased mode, causing the vessels to be supplied with an abundant mass of blood. In this case, muscle wear becomes inevitable, and the production of adrenaline when drinking alcohol only enhances the negative effect.
Alcohol consumption also causes red blood cells to clump together and lose their membrane, which causes thick blood cells to clog the capillaries. The result is oxygen starvation of cells and overgrowth of blood vessels with a fatty layer.
Loading …
How does alcohol affect the human body?
Drinking alcohol is stressful for the body. Long-term consumption of alcoholic beverages leads to the development of:
- Disorders related to psychosomatics and neurology, neurosis, depression, mood swings, epilepsy.
- Cardiovascular disorders.
- Blood clots, pressure changes.
- Liver disorders.
- Fluid accumulation in the brain.
- Unconscious state, etc.
Effect of alcohol on the brain
Drinking alcohol and developing alcoholism leads to irreversible destruction of brain cells. The cells responsible for intelligence, dying, enter the blood through the lymph, then into the kidneys and are excreted from the body naturally.
One hundred grams of alcohol kills about 10 thousand neurons that support the thought process. This phenomenon does not occur without consequences for the body: as a result, the human brain loses mass and volume due to desiccation.
Then the person becomes inadequate, loses the sense of shame, and degradation occurs. Memory and thought process, coordination of movements deteriorate, and reflex arc disorders are formed. Brain damage eventually results in mental problems.
Related article: How to get out of binge drinking at home on your own?
The effect of alcohol on the cardiovascular system
There is an opinion that drinking alcoholic beverages in moderate doses leads to a decrease in blood pressure, dilates blood vessels and relieves stress. This is wrong.
According to research, ethanol is a poison, a toxic substance that cannot benefit health in any way and has a detrimental effect on all systems of the body. The effect of intoxication occurs due to the suppression of human health.
The vasodilation itself does not last long. Then the vessels narrow again, causing redness of the skin of the face and increased heart rate due to wear and tear of the organ.
According to statistics, the highest mortality rate from heart and vascular diseases is observed in people who abuse alcohol.
The effect of alcohol on the digestive system
What is the mechanism of alcohol's effect on the digestive system? The main part of alcoholic drinks is absorbed through the stomach, so the harmful consequences do not pass by this organ.
Alcohol has a negative effect on the digestive system: when absorbed into the walls of the stomach, it burns and injures them, causing inflammation, heartburn and the development of chronic diseases in the body. There is a disruption in the production of gastric juice, salt, and catalysts. The glands that produce protein catalysts for the normal digestive process gradually die off.
Pancreatitis often develops, because The pancreas does not have the necessary enzymes to break down alcohol. Alcohol also affects the mucous membrane: causing gastritis, gastric ulcers, diabetes, and cancer.
The effect of alcohol on the liver
About 90% of alcohol is broken down in the liver. It can break down about 1 glass of alcohol in 10 hours, and the rest of the alcohol that enters the body destroys cells.
The liver suffers primarily from:
- Obesity.
- Hepatitis A.
- Cirrhosis.
If alcohol consumption is not stopped in case of liver cirrhosis, the disease will develop into cancer.
Effect on the kidneys
The kidneys not only produce and excrete urine. They balance the acid-base and water balance and influence the production of hormones.
What kidney problems does alcohol cause?
When a person drinks alcohol, the excretory system begins to work in enhanced mode. The kidneys circulate a lot of fluid and remove harmful substances from the body.
Constant overload weakens renal functionality - they gradually lose the ability to work hard. The effect of alcoholic drinks on the kidneys can be seen after the holiday by a swollen face and increased blood pressure.
The body also accumulates fluid that the kidneys are unable to remove, resulting in the formation of stones. In the absence of timely treatment, renal failure develops. The organ loses the ability to form and excrete urine. Severe intoxication occurs and, as a result, death.
The effect of alcohol on reproductive function
Drinking alcohol also negatively affects human reproductive function. Cell damage in women is irreversible : they remain in the system and pose a danger to the fetus.
A fertilized cell damaged by alcohol increases the risk of serious disorders, development and occurrence of genetic diseases, i.e. has a negative effect on the fetus.
No one guarantees that the diseased cell will be fertilized, but no one is immune from sad situations.
The male body is built differently and has the ability to update reproduction. However, in order to completely restore the composition of sperm, it should take about 3-6 months. If no alcohol was consumed during this time, the sperm are completely renewed.
Also, in addition to the germ cells, the entire system suffers: there is a decrease in libido and a deterioration in the quality of organ function, which affects the entire body as a whole.
The effect of alcohol also causes hormonal mutations (hormones break down due to toxins, incorrect production occurs). Over time, a woman’s body begins to suffer from an excess of male hormones (testosterone), and of men – female hormones (estrogen). The appearance and character change, mental disorders occur and impotence develops.
The effect of alcohol on the respiratory system
Some time after drinking alcohol, many people experience bad breath and heavy breathing. This is due to the fact that part of the ethanol is excreted from the body through the lungs.
Alcohol (especially strong alcohol - cognac, vodka) that enters the body dries out the bronchi, the lung surface, and causes a lack of oxygen. Patients experience shortness of breath and attacks of suffocation. Associated chronic diseases appear.
The consequences of drinking alcohol on the human body
Each stage of addiction has certain symptoms and distinctive features. There are 4 of them in total.
The initial stage of alcoholism
This stage is characterized by a gradual increase in the consumed dose of alcohol, the formation of dependence and the influence of alcohol on a psychological level.
Symptoms:
- Pathological desire to drink alcohol, inability to control oneself or see a problem, positive attitude towards alcohol.
- Swaggering and inappropriate behavior, inconsistency.
- Memory impairment, increased irritability and aggression.
- No hangover, feeling unwell in the morning.
- Condemnation in a sober state of other addicts, the ability to realize the harmful effects of alcohol.
- Development of alcoholic thinking, defending the right to alcohol and temporarily reducing the dose of alcohol.
Second stage of alcoholism
There is a desire to increase the dose of alcohol. Addiction develops at the physical level, i.e. The influence of alcohol is so significant that the body cannot function normally without alcohol. The volume of strong alcohol consumed per day is approximately 500 ml.
Symptoms:
- The appearance of a hangover syndrome (the body’s message about the formation of addiction), which lasts from 1 to 5 days - the patient experiences an irresistible desire to drink alcohol in the morning. If the patient does not receive alcohol during this period, autonomic disorders appear in the form of thirst, dry mouth, increased anxiety, loss of appetite, and lack of sleep.
- Disorders of the digestive system.
- Mental disorders (memory disorders, depression, extreme egoism, individualism).
Related article: What pills help with a hangover?
Third stage of alcoholism
Destruction at the physical and psycho-emotional level, the formation of dementia.
Symptoms:
- An enlarged abdomen in an alcoholic as a result of cirrhosis or weight loss.
- Impaired speech and thinking activity, dementia.
- Speech disorders as a consequence of damage to the central nervous system.
- No hangover.
- Suicidal thinking, depression.
- Alcohol becomes a means of maintaining the body.
Fourth stage of alcoholism
The disease at this stage cannot be treated and leads to the death of the addict.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t9q9leLU194
The patient suffers primarily from:
- Alienation from society: relatives, friends.
- Severe mental disorders.
- Inability to think adequately.
- Lack of interest in the outside world.
Failure of body systems and death occurs.
Teenage alcoholism
The negative effect on organs is characterized by rapid development due to the rapid absorption of ethanol into the blood.
Developing alcoholism in adolescents is more difficult to identify, and binge drinking is usually absent.
Often the disease develops in conjunction with drug addiction and substance abuse.
Symptoms:
- Increased tolerance to ethyl alcohol.
- Mild hangover syndrome.
- Memory impairment.
- Staying in a state of euphoria, increased desire to talk.
- Formation of chronic diseases.
- Depressive thinking, intellectual disorders.
- Disadaptation in society.
Alcoholism in women
The course of the disease in women is more rapid due to reduced tolerance to ethyl alcohol.
Briefly about the symptoms:
- Lack of gag reflex or control over the amount of alcohol consumed.
- Unflattering appearance.
- Trembling in hands.
- Emotional imbalance.
- Disorders of the digestive system.
- Mental disorders (memory impairment, depression, extreme egoism, individualism, delirium delirium).
As you already understand, drinking alcohol accelerates the development of irreversible consequences and leads to a malfunction of all internal organs and systems, however, if you stop drinking it in a timely manner, it is possible to restore cells and stop the destruction of internal organs. Take care of your health!
Source: https://otrav.net/alko/kak-alkogol-vliyaet-na-organizm-cheloveka/
In what quantities and what kind of alcohol does it negatively affect the gastrointestinal tract?
Any alcohol with a strength above 40% certainly damages the mucous membrane (chemical burn).
Of course, there are “heroes” whose mucous membrane is “accustomed” to such loads, but this means that the wear and tear on the resource of this tissue has increased significantly, and complications will manifest themselves after a certain time.
Strong alcohol provokes esophagitis, gastritis, gastro-duodenitis. With constant use, chronic inflammatory diseases are formed and the preconditions are created for cancer of the esophagus and stomach.
For daily consumption, no more than one glass of good wine or 50 ml of normal cognac is recommended, but not everything is so simple.
Who definitely can’t have that same 50 ml or glass of wine:
- persons with a developed dependence on alcohol. Those. if a person has a hangover (even rarely), he takes the initiative to drink alcoholic beverages at least 2 times a month - he should not drink at all;
- for those who already have inflammatory diseases of the stomach and intestines.
Should you drink alcohol if you have digestive system diseases?
Alcohol is contraindicated for any, even seemingly minor, disturbances in the functioning of the stomach and intestines. Of particular danger are the presence of ulcerative processes, bleeding, and acute inflammation.
It should be remembered that all alcoholic products provoke ulcerative-erosive processes.
When a person has a history of problems with the gastrointestinal tract, champagne, young homemade wines, and drinks that contain dyes and flavors are strictly contraindicated. In small volumes (up to 100-120 ml) it is possible to use vodka or high quality cognacs. It is highly undesirable to drink on an empty stomach.
You should eat food first, excluding spicy, fatty and smoked foods. When sharp pain in the stomach occurs during a feast, you should not immediately take medications. Priority rinsing is necessary to get rid of any remaining alcohol and food.
What is the danger of impaired blood supply to the stomach?
- trophism (nutrition) of the mucosal area deteriorates;
- the thickness of the mucous layer decreases, digestion processes degrade;
- gastric juice destroys the weakened area of the internal surface of the organ;
- a stomach ulcer forms.
In fact, everything happens even faster, since the mucous membrane is already provoked by the alcohol itself, and then the blood supply is also turned off.
It is at this moment that cutting pains occur after taking even a small dose of alcohol in a person whose stomach has already been provoked - the acid begins to destroy the “poisoned” area of the mucous membrane. Stomach pain can be constant if a person takes alcohol in frequent small doses.
In addition to the fact that the mucous membrane is burned by acid, it ceases to perform its secretory functions - less mucus is secreted, which accelerates the destruction process. The walls become thinner, and atrophic gastritis develops. After some time, acid synthesis also stops. This leads to indigestion, characteristic of alcoholics.
For alcoholism
Alcohol abuse quickly worsens the condition of the gastrointestinal tract. The following are negatively affected:
- esophagus – burn of mucous membranes;
- stomach – indigestion;
- liver – cell destruction;
- small intestine – development of dysbacteriosis, stool disorders;
- rectum - increased sensitivity of the organ, diarrhea;
- kidneys - the formation of stones, the occurrence of an inflammatory process;
- pancreas – decreased organ functions.
Strong alcohol has the worst effect on the gastrointestinal tract. Side effects from taking it increase with low immunity and the presence of chronic diseases. Alcohol negatively affects the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
What changes does alcohol cause in the stomach?
When drinking becomes a constant habit, the production of hydrochloric acid, which is so necessary for the digestion of protein foods, is gradually blocked. As a result, food rots, poisons the body, there is a rotten smell from the mouth, nausea and vomiting in the morning. A lack of enzymes and pepsin leads to protein starvation, and vitamins and minerals are no longer absorbed.
One of the functions of hydrochloric acid is to disinfect food entering the stomach, while pathogenic microbes do not penetrate deep into the digestive tract. When the cells of an organ atrophy, stomach poisoning occurs.
Insufficiently digested food containing pathogenic microorganisms enters the intestines. This leads to damage first to the small intestine and then to the large intestine. A drinking person develops enteritis, colitis, stool disturbances, flatulence, and pain in the intestines.