What is the procedure
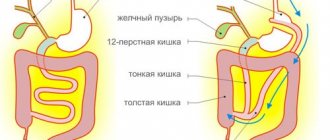
FCS is an examination of the entire length of the rectum and colon using a special probe.
The term "colonoscopy" is derived from:
- the Latin name for the large intestine is “colon”;
- Greek "skopiya", which means "I look";
- the “fibro” particle indicates the use of a flexible probe.
When performing a colonoscopy, the doctor has the opportunity to perform:
- taking tissue for biopsy;
- removal of tumors;
- coagulation of the source of bleeding;
- elimination of volvulus or intussusception.
Fibercolonoscopes, which are used in medicine, are a long, flexible tube made up of many optical fibers that send images to an eyepiece. The colonofiberscope also has an instrumental channel, by controlling which the doctor can pinch off tissue and carry out other manipulations.
Fibercolonoscopy and how it is done, you can learn about this in detail from the video of the European Clinic channel.
Colonoscopy with biopsy: what is it?
To clarify the nature of the disease, the extent of the spread of the pathological process and the stage of development of neoplasms, a colonoscopy with biopsy can be performed:
- Sighting. Targeted collection of tissue from a pathological lesion that was detected before the start of the procedure.
- Search engine. A diagnostic examination of the intestine, which is used in the early stages of the disease, when the pathology itself is not yet visualized during colonoscopy.
Tissue samples obtained during biopsy are further examined under a microscope to identify abnormal cells, which will help make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment for the patient.
What is liver fibroscanning?
The liver is an organ with a soft parenchymal structure. If the patient is healthy, it contains hepatocytes, nerve fibers and blood vessels. It is quickly damaged under the influence of negative factors. During inflammation, cells gradually die. In their place, connective tissue fibers are formed.
It is important to identify the disease in time to prevent complete degeneration of the organ into connective tissue fibers (cirrhosis). If the disease is advanced, it is impossible to cure the patient. The only treatment for cirrhosis is liver transplantation.
Many patients do not know what a liver fibroscan is, having only a biopsy. Fibroscan is a device that delivers waves of different lengths to the analyzed areas. If the liver has a parenchymal structure, waves leak through the tissue. When replaced by connective tissue, the process slows down.
The analysis reveals the resistance of the liver tissue to the electromagnetic waves emitted by the sensor. The therapist determines inflammation and the location of the fibrosis focus, so testing is more reliable. This function is not available in ultrasound examination.
Fibroscanning of liver tissue is a semi-automatic analysis. This eliminates errors when performing analysis. It is performed for several people at once within one day. After testing, the person’s well-being does not change, and no side effects occur. The result is given in printed form.
This is interesting: Signs and treatment of liver hepatosis in women
The procedure for examining the intestines through a colostomy
This option for examining the intestines is not fundamentally different from a colonoscopy performed through the rectal opening.
A colostomy is an anal opening formed during surgery to remove the rectum. The open end of the sigmoid or colon is brought out onto the abdominal wall on the left side. The doctor can use it for endoscopic examination.
Many patients fear that inserting a probe in this way and pumping air to straighten the folds of the mucous membrane can be traumatic. If the stoma heals without complications and is properly cared for, there is little risk of damage.
On the eve of the study, a special diet and bowel cleansing are required, as with the standard FCS procedure. It is important to provide the doctor who performs the colonoscopy with as complete information as possible about the nature of the operation undergone. This will increase the efficiency of the examination and help avoid misinterpretation of results.
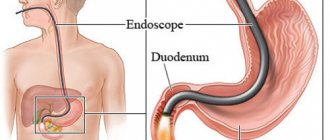
Fibercolonoscopy: what is this procedure?
This is an examination of the condition of the mucous membrane of the lower digestive tract using a flexible endoscopic device - a fiber colonoscope. This device contains fiber optics that allow the doctor to see the inside of the large intestine. Main blocks of a colonoscope:
- Optical system . Consists of a light source, optical fibers and an eyepiece. An important parameter is the viewing angle. The higher it is, the more information the doctor will receive.
- The insertion part of the endoscope . Includes insertion tube, flexible part and distal head. The main characteristic of this part of the device is flexibility, which increases from its central part to the peripheral part. In the middle of the tube there are holes for supplying water (for washing the lenses of the device) and air (for straightening the folds of the intestines).
- Control block . Allows you to change the position of the distal head of the device. Has a biopsy channel for inserting a surgical instrument.
Depending on which part of the intestine is examined, fibrocolonoscopy is distinguished, when all parts of the large intestine are examined, up to the cecum, and rectomanoscopy - the condition of the rectum and the final part of the descending sigmoid colon is studied.
One of the procedure options is video colonoscopy. Its difference is that the image of the intestinal mucosa is displayed on the monitor screen in an enlarged form, which increases the accuracy of diagnosis: thanks to modern equipment, intestinal neoplasms measuring 1 mm or more are detected. Examination data can be recorded on a digital medium and transferred to the patient, which gives him the opportunity, if necessary, to obtain the opinion of another doctor.
Differences between fibrocolonoscopy and colonoscopy. Previously, fibrocolonoscopy was considered a more modern diagnostic method: since the procedure used a thinner and more flexible endoscope. This significantly facilitated the passage of intestinal bends and reduced discomfort for the patient. Currently, these terms are used as synonyms for the same survey. Colonofibroscopy: what is it? An examination under this name is completely similar to a colonoscopy.
Indications and contraindications for examination
Absolute indications for colonoscopy include:
- bleeding from the lower intestines;
- Crohn's disease;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- colon polyps;
- assumption of intestinal obstruction of unknown nature.
Relative indications are symptoms such as:
- stool disorders (frequent constipation or, conversely, diarrhea);
- chronic abdominal pain;
- the appearance of blood or mucus in the stool;
- weight loss with a normal calorie diet;
- anemia of unknown origin.
In addition to diagnostic purposes, FCS is also prescribed to perform various manipulations on the intestines (using local anesthesia or intravenous anesthesia).
The decision to perform fibrocolonoscopy in these conditions is made by the doctor, taking into account the general picture of the disease and the results of other studies.
Absolute contraindications for performing FCS include:
- acute myocardial infarction;
- stroke;
- atherosclerosis;
- aortic aneurysm;
- hypertension stages 2 and 3;
- the presence of an artificial valve on the heart muscle;
- peritonitis;
- intestinal perforation;
- ulcerative colitis in the acute phase;
- recovery period after recent surgery on the large intestine.
It is better to postpone colonoscopy if there are relative contraindications, including the following:
- poor intestinal preparedness for examination;
- pregnancy;
- stomach or intestinal bleeding;
- presence of hernias;
- history of multiple surgical operations on the pelvic region.
In the above cases, performing FCS can be dangerous for the patient or uninformative. The question of the advisability of performing a colonoscopy, if there are relative contraindications, is decided by the doctor individually.
Preparation for the procedure
FCS of the intestines is a study that necessarily requires cleansing of the colon. You need to start preparing for the procedure three days before it takes place.
How to eat, recommendations
There is no need to fast to prepare for a colonoscopy, but you should exclude from your diet foods that are difficult to digest and cause increased gas formation in the intestines:
- any fruits and vegetables;
- greenery;
- berries;
- nuts;
- legumes;
- porridge (oatmeal, pearl barley, millet);
- pasta;
- black bread;
- fatty meat, fish;
- sausages;
- whole milk;
- coffee;
- carbonated drinks.
The following products are allowed for consumption:
- wheat bread made from wholemeal flour;
- lean boiled meat (beef, poultry) or fish;
- fermented milk products (yogurt, kefir);
- low-fat broths;
- dry biscuits (biscuits).
The last meal before the FCS should be no later than 20 hours before the examination. Immediately before the procedure, you can only drink water or weak tea.
Enema or drug method of bowel cleansing
There are two ways to prepare the intestines before a colonoscopy: mechanically using enemas or using special medications.
The second option is more convenient for patients and does not create additional trauma if:
- anal fissures;
- hemorrhoids;
- other painful formations in the rectal area.
Cleansing with an enema
In the evening before the examination, the enema should be performed twice with an interval of 1 hour. To perform intestinal cleansing, one and a half liters of distilled warm water are used per procedure. The morning before the colonoscopy, you need to repeat the enema twice more. For better results, you can use mild laxatives or castor oil the day before you begin your colon cleansing.
Medicinal cleansing
An alternative to enemas is the use of the drug “Fortrans” (or its analogues), specially created to cleanse the intestines before diagnostic procedures. The medication option for preparing for the examination should begin the day before the colonoscopy, 2 hours after the last meal.
The dosage of Fortrans should be selected individually by the doctor: approximately one sachet per 20 kg of the patient’s body weight. The drug must be dissolved in warm boiled water at the rate of one sachet per liter of water.
Since it is not possible to drink several liters of liquid at once, it is recommended to consume the solution in small portions over 2–4 hours. It is better to drink the drug quickly, without holding the solution in your mouth so as not to feel its taste. After a portion of Fortrans, you can take a sip of lemon juice - this will eliminate nausea.
Gastrocenter Ufa tells you more about proper preparation for the FCC examination.
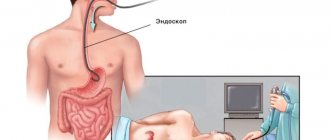
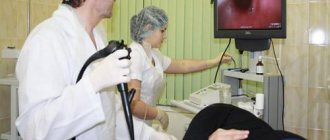
How is it done?
During a colonoscopy, a person lies on a couch on his left side with his knees pressed to his stomach. The anal area is treated with an antiseptic and lubricated with a special anesthesia gel, then the doctor carefully inserts the fibrocolonoscope probe into the rectum. At the next stage of the procedure, the doctor begins to slowly push it into the intestines to examine the walls. To make the study more informative, you need to straighten the folds of the colon: for this, air is pumped into it.
Performing a colonoscopy
Typically, a total colonoscopy takes no more than 15 minutes, but if the doctor has identified any pathologies or surgical manipulations are necessary during the procedure, it may take longer.
The channel “Mikhail Valivach” tells more about the FCC procedure.
Colonoscopy under anesthesia
Colonofibroscopy is also performed under intravenous anesthesia (drug sleep).
This type of diagnostic procedure is used for such categories of patients as:
- adults with a low pain threshold;
- children under 12 years of age;
- persons suffering from adhesive obstruction.
After FCS using anesthesia, you need to stay in the clinic for some time under the supervision of specialists.
How is fibrogastroscopy performed?
The patient is placed on his left side with his back straight. The nurse sprays the oropharynx with an anesthetic spray, which begins to act instantly, reducing the sensation of the tube. The patient is asked to hold the mouthpiece between his teeth to prevent him from accidentally clenching his teeth and damaging the endoscope tube.
The endoscopist asks the patient to make a swallowing movement - at this time the endoscope is carefully inserted into the esophagus and subsequently into the stomach. The patient is recommended to take slow deep breaths through the nose, which helps relax the muscles and facilitate manipulation.
Particularly sensitive patients may experience discomfort from stomach bloating, drooling, or involuntary belching. Salivation is understandable, but other phenomena arise as a result of forced air supply through the endoscope to improve visualization of organs.
The duration of fibrogastroscopy is no more than 5-10 minutes. If a biopsy is performed at the same time, the time may increase to half an hour. The endoscope is then carefully pulled out and the patient can walk. If FGS was performed under anesthesia (recommended in some cases), then the patient remains under the supervision of doctors for another couple of hours.
Biopsy during fibrogastroscopy
A fibrogastroscopy biopsy is usually prescribed for patients with ulcers, because it causes mutations in cells, and for gastritis, to determine the stage of the disease and identify its cause - in particular, the presence of Helicobacter pylori. When performing a biopsy, a piece of tissue is pinched off either from one place or from several areas.
What the diagnostics will show: deciphering the results
With fibrocolonoscopy, the doctor can see signs of the following diseases:
- Polyposis of the large intestine. The formation of benign growths (polyps) on the intestinal walls. They can transform into malignant tumors and therefore require removal. In most cases, polyps can be removed without surgery, during a colonoscopy.
- Nonspecific ulcerative colitis. Inflammatory bowel disease, the etiology of which is unknown. Usually the process begins in the rectum and spreads higher. A timely examination helps to identify nonspecific ulcerative colitis in the early stages of development. The doctor may also prescribe a repeat colonoscopy during treatment to monitor the healing of the ulcers.
- Colon cancer. A malignant tumor growing from its mucous membrane. FCS is one of the main methods of screening for colon cancer, recommended for preventive purposes every five years.
- Crohn's disease. A chronic inflammatory disease that can affect the gastrointestinal tract throughout its entire length, including the colon. Colonoscopy in this condition can determine the degree of inflammatory changes, the presence and number of ulcers, and identify sources of bleeding.
- Intestinal tuberculosis. Usually, it is a secondary disease, that is, this microbacterium develops in the primary focus (most often in the lungs), and then spreads to other organs. During fibrocolonoscopy, the doctor will see characteristic inflammatory changes, and will also be able to take a biopsy sample and send it for analysis to confirm the diagnosis.
Advantages and disadvantages
Intestinal FCS has advantages and disadvantages:
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Direct visual examination of the mucous membrane, which can reveal the most minor defects | According to patients, the procedure is extremely painful |
| It is possible to perform endoscopic manipulations (stop bleeding, remove polyps) and/or take tissue for biopsy | Uncomfortable for the patient, long preparatory period |
| The study lasts no more than half an hour | A fiber colonoscope cannot always overcome areas of stenosis and examine some hard-to-reach areas |
Benefits of fiber scanning
- The short examination is performed on an outpatient basis; hospitalization and anesthesia are not required;
- The painless procedure does not require a rehabilitation period;
- Elastometry is performed without skin punctures, which eliminates bleeding and infection;
- The accuracy of the results is not affected by the professionalism of the diagnostician; the conclusion is issued by the Fibroscan device;
- The study is prescribed for any liver disease, the results are available immediately after the scan.
A puncture (needle) biopsy is classified as an invasive technique. Taking a small section of liver tissue does not allow reliably assessing the degree of fibrosis, which leads to erroneous study results. Only fiber scanning gives the doctor a real opportunity to identify compacted areas.