A test for Helicobacter pylori should be done in case of unexplained heaviness in the stomach.
Most often, if abdominal pain occurs in the stomach area, we take out the no-shpa and try to suppress this pain. But this is wrong! First you need to understand the causes of pain. The best thing to do is visit a gastroenterologist. Please note that heaviness in the stomach after eating is one of the symptoms of the presence of Helicobacter pylori bacteria in the stomach. And it is the gastroenterologist who will give a referral for analysis in case of suspected inflammation.
A modern person who often eats on the go, gets nervous a lot, eats junk food, and suffers from stomach diseases. But, as it turned out, the cause of gastritis, stomach ulcers and other diseases is the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. If it is detected immediately and treatment is started, the occurrence of these serious diseases can be avoided. To identify the parasite, you need to take a Helicobacter test.
A timely test for Helicobacter can help eliminate the disease even at an early stage of its development. But provided that the most effective research and treatment methods are chosen.
There are several ways to get tested for Helicobacter pylori: donate blood or stool for analysis, or do a breath test. Careful preparation is needed.
Attention. We will tell you what a lack of understanding of the possible cause of heaviness in the stomach leads to using a specific example.
Who needs to get tested for Helicobacter
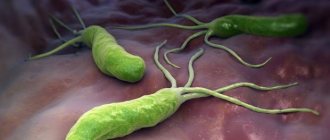
For reference. The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is a parasite that lives in the stomach or duodenum.
They can become infected within a family or in groups where children and adults communicate closely and do not follow hygiene rules. Infection occurs through saliva, mucus, and when using the same utensils. This disease is called Helicobacteriosis.
Sometimes a person may not even suspect that these bacteria already live in his body until the development of diseases is triggered by stress, poor diet, alcohol abuse, smoking, etc. According to statistics, more than 70% of people over 40 years of age are carriers of Helicobacter pylori, but those infected do not experience symptoms of the disease.
If a person is weakened, then bacteria begin to multiply rapidly and release toxins, which, accumulating in large quantities, affect the mucous membrane of the internal organs. Inflammation appears first. If you do nothing, erosions or ulcers will soon appear, and tumors may also make themselves felt.
For reference. Anyone can take a test for Helicobacter pylori, but doctors prescribe it for those who already suffer from stomach or duodenal ulcers, gastritis, or if these bacteria were found in one of the family members (living with them), or in a loved one a relative was diagnosed with stomach cancer.
Also, the attending physician may be alerted by the following symptoms, in the presence of which he will be asked to take a test for Helicobacter:
- The patient suffers from heaviness in the stomach.
- It is difficult for him to digest protein foods, i.e. eat meat.
- He developed heartburn, flatulence, belching, and often felt sick and vomited.
- The stomach hurts, the pain subsides if a person has eaten.
- The patient complains of loss of appetite or difficulty swallowing.
- The man has lost a lot of weight.
- He has constant constipation or diarrhea.
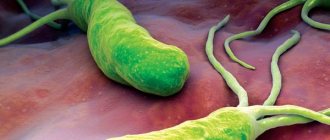
Features of the bacterium and its danger
Before we figure out what the analysis is, let’s find out what the characteristics of the bacterium are and what its danger to health is. Helicobacter pylori is one of the pathogenic microorganisms that can interfere with the production of gastric juice in humans. It moves quite quickly thanks to its flagella. In addition, the ammonia produced by the bacterium has a detrimental effect on stomach acid.
Helicobacter pylori is very dangerous for the body, causing gastritis, ulcers and other stomach diseases
Penetrating into the mucous membrane of the digestive organs, the uninvited guest provokes the appearance of ulcers and foci of inflammation. The bacteria multiplies quickly, poisoning the body more and more every day. It is transmitted through close household contact, sharing utensils and other hygiene items. Therefore, if this microorganism is detected in one of the household members, other family members are recommended to donate blood for Helicobacter pylori.
Important! The bacterium is resistant to gastric juice, but under the influence of antibacterial drugs it dies quite quickly.
Ways of infection with Helicobacter
Helicobacteriosis is an intestinal infection caused by the specific bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
The specificity of this bacterium is determined by its habitat. It is no secret that the human body is home to many bacteria and viruses. All of them parasitize under favorable conditions created by the human body.
For reference. But only the bacterium Helicobacter pylori is able to live in the acidic environment of the stomach. In direct contact with oxygen it dies.
Almost any person can develop helicobacteriosis. According to medical statistics, Helicobacter bacteria live in 95% of the population. They can live with a person his entire life without complications. And only under certain conditions (usually with a decrease in immunity) can uncontrolled inflammation (helicobacteriosis) of the gastric or duodenal mucosa develop, which can develop into gastritis or an ulcer.
In persons infected with Helicobacter, stomach cancer develops several times more often. The risk of cancer increases significantly due to the presence of a large number of long-term non-healing ulcers and erosions on the mucous membrane.
For reference. The bacterium is capable of releasing strong toxins that cause inflammation of the gastric mucosa and its rejection. In some cases, the microorganism provokes a decrease in the synthesis of gastric juice. This leads to atrophy of the gastric mucosa.
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori can enter the human body in 3 ways:
- Fecal-oral. Bacteria present in the stool of a sick person enter a healthy body through the oral cavity. Penetration can be accomplished through food, water;
- Oral-oral. Infection occurs through kissing through saliva. Children from sick parents can also get the disease through spoons and forks;
- Iatrogenic. It is very rare, but there are cases of infection with Helicobacter pylori through medical instruments used during examination of the gastrointestinal tract.
And although in most cases, infection with this type of intestinal infection occurs from humans, this infection can also penetrate through pets, dogs, pigs or cats.
When favorable conditions for reproduction appear in the form of stress or decreased immunity, the infection actively begins to reproduce, provoking the development of pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract.
Types of tests for Helicobacter
For reference. You can immediately say which Helicobacter test is the most accurate - this is a histology test.
The problem is that it is possible to take material for histological examination either through a biopsy (biopsy) or during gastric surgery. This is the most difficult way to take tissue,
To confirm or deny the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the body, at least two tests are required. After all, there is always a risk of error, and a lot depends on what second type of analysis the doctor chooses.
The following tests are used to identify Helicobacter pylori:
- Bacteriological;
- Histological;
- Urease respiratory;
- PCR;
- Immunological;
- Serological.
For reference. It is worth knowing that each method has its own advantages and certain disadvantages. Therefore, to determine the exact result, it is recommended to take 2 - 3 different types of analysis. The answers received will make it possible to more accurately determine the presence or absence of Helicobacter pylori.
Preparation
An analysis for Helicobacter pylori involves the detection of specific antibodies in the blood serum, which are produced by the immune system when the pathogenic organism enters a person. These antibodies can be detected in the laboratory using simple chemical reactions. When detecting uninvited guests, the doctor must take into account that a sufficient amount of time must pass for the development of immune agents. That is, the formation of antibodies requires at least 7–10 days. It is this interval that is necessary for the appearance of an immune response to the pathogen.
The most accurate data can be obtained with the help of special preparation for analysis. It includes the following activities:
- a few days before the study, it is important to give up alcoholic beverages;
- 24 hours before blood sampling, you should avoid heavy physical activity and intense sports;
- Before the procedure you should not eat food, you are only allowed to drink water:
- collection of biological material is carried out in the morning;
- The study is carried out before the person starts taking any medications. If the patient is already undergoing therapy with certain medications, this must be reported when donating blood.
Accurate results can be obtained with proper preparation.
If the preparation rules are violated, a false positive response is possible. An incorrect result also often occurs in cases where the patient has undergone treatment, but antibodies are still present in the blood.
Important! A false negative analysis is observed if too little time has passed after the body has been damaged and the immune system has not had time to develop antibodies.
How to get tested
You have decided to get tested for Helicobacter pylori. How to do this, how to prepare for analysis?
First of all, you need to know that there are several ways to do this, and it is better not to rely on one of them, but to conduct at least 2 studies. Let's give the simplest ones.
Blood analysis
Your doctor may ask you to take a blood test to see if you have antibodies to Helicobacter pylori.
For reference. Our body fights infection and produces special antibodies that bind to the pathogen to neutralize it. If the patient’s blood contains these antibodies, then we can say that he is infected.
A blood test is given in the morning, blood is collected from the cubital vein.
The preparation for it is standard, but it still doesn’t hurt to remind you about it:
- You should not take medications or drink alcohol 2 days before the test.
- Before going to the laboratory, you should not play sports or go to the bathhouse.
- Before taking the test, you should not eat fatty or spicy foods.
- You need to avoid stress, take care of yourself, and don’t get nervous.
- Blood for Helicobacter pylori analysis must be taken on an empty stomach, i.e. The last meal should be the night before. In the morning you cannot have breakfast, even drink juice, coffee or tea, or smoke.
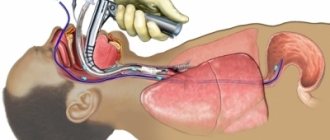
Urease breath test
For reference. The bacterium Helicobacter pylori synthesizes urease, this is a special enzyme. It can affect urea, breaking it down into carbon dioxide and ammonia in the intestines.
When conducting a study, they look at the concentration of these substances in the exhaled air before and after taking urea.
First, the patient breathes through a special tube. There is no need to worry or worry, breathing should be the same as in normal life. After the results have been obtained, the person is asked to drink a solution of urea (5%). You must wait 5 minutes and then take the sample again.
To determine whether a person is infected or not, it is necessary to check the concentration of ammonia in the exhaled air. If it is high enough (more than 0.5 mg/ml), then the test is positive. For the test to be correct, no saliva must enter the tube. If you can’t swallow it, you can sometimes pull out the tube.
In case of saliva contamination, the examination will have to be repeated.
How to prepare for the study:
- You should not take medications that reduce the acidity of gastric juice. It is worth abandoning them 3 weeks before the examination. These are antacids, antibiotics, etc.
- You will have to forget about alcoholic drinks for a while. You should not take them at least 3 days before the examination.
- The day before you go for the test, you should not eat foods that contribute to gas formation: brown bread, cabbage, peas, potatoes, etc.
- You must take the test on an empty stomach and have a light dinner beforehand.
- Before being examined, i.e. in the morning, you can’t smoke and have breakfast.
- During the day, do not chew chewing gum, which promotes strong salivation.
As we can see, preparing for the test is not difficult, but it is better to start it in advance.
Stool analysis
To determine whether the bacteria Helicobacter pylori is present in the body, you can take a stool test. Before taking stool for analysis, 3 days before you collect the material, you must give up dyes and dietary fiber, and you cannot take medications for constipation.
How to prepare for the analysis?
For reference. 72 hours before submitting stool for analysis, you should stop taking medications and medicinal suppositories in order for the result to be correct. A person must go to the toilet himself, without the help of laxatives. Do not stain biomaterial with urine or blood.
Feces should be stored in clean containers. It is better to go to the toilet in the morning and immediately take the stool to the laboratory. If that doesn’t work, you can do it in the evening, but the material should not be stored for more than 10 hours. And in this case, it must be kept in the refrigerator, at a temperature not exceeding 8 degrees.
Helicobacter pylori: diagnostic methods, complications after infection
Since the discovery of the bacterium, new diagnostic methods have appeared, but none of them can be considered universal. The possibilities of research methods are limited by the patient’s age, stages of infection, and taking certain medications.
All diagnostic methods are divided into direct and indirect. The first group includes:
- bacteriological;
- histological;
- molecular biological (PCR - study of feces and blood);
- contrast microscopy;
- immunohistochemical.
Indirect methods are:
- urease test;
- serological diagnosis.
Also, examinations used to make a diagnosis can be invasive or non-invasive. The first require the collection of biopsy material during fabrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) and blood. This:
- bacteriological and morphological (histological or cytological) methods;
- urease test;
- PCR of biopsy samples;
- ELISA;
- microscopy.
Non-invasive techniques for detecting Helicobacter are becoming increasingly popular, especially for preventive examinations and diagnosis at an early age. These include:
- determination of antibodies to Helicobacter in feces, saliva and urine;
- polymerase chain reaction study of feces, saliva, and dental plaque.
Invasive diagnostic techniques
One of the most informative is bacteriological (cultural) research. Its specificity reaches 100%. The advantage of this technique is the ability to determine antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter. However, this method also has a number of disadvantages. Results are obtained only after 7-10 days; there are also certain difficulties with transporting the biological material being studied. In addition, bacteriological diagnostics do not distinguish coccal forms. However, many doctors consider such a test necessary before starting treatment due to the growing resistance of bacteria to antibiotics.
The specificity of the histological technique is up to 97%. A biopsy is taken from the gastric mucosa with the most severe hyperemia and inflammatory edema. This method allows you to determine the contamination of the mucous membrane and signs of changes in its structure.
A cytological examination is carried out by studying biopsy prints obtained as a result of an endoscopic examination of the stomach and duodenum. The sensitivity of this technique is low (about 20%), but it allows one to detect the first signs of changes in cell structure (metaplasia, neoplasia, etc.).
The rapid urease test is considered the standard for diagnosing Helicobacter infection. It is based on the characteristics of the life activity of the bacterium. Helicobacter, using urease, breaks down the urea contained in the stomach, releasing ammonia and carbon dioxide; as a result, the pH becomes alkaline, which is recorded using a special indicator. The rate of change in shade indicates the degree of infection. The sensitivity of the urease test is up to 98 - 99%; it is often used for the primary diagnosis of Helicobacter.
Phase-contrast microscopy is convenient at high speed, but is informative only when there are a large number of pathogenic microorganisms. Immunohistochemical analysis involves treating the biopsy material with antibodies that selectively stain Helicobacter. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique allows you to determine Helicobacter not only in a smear or biopsy, but also in non-invasive studies. In addition, such an analysis allows you to accurately identify the strain of the bacterium.
Non-invasive diagnostic methods
The urease breath test is performed using 13C labeled urea. It is offered to the patient during breakfast. Helicobacter decomposes urea, but 13C carbon markers are retained in the carbon dioxide released. The patient exhales into a special test tube, and its contents are further examined using spectrometers, infrared or laser devices.
However, this technique is not performed on patients with ulcer bleeding, atrophic gastritis, or stomach cancer. The widespread use of this diagnostic method is hampered by its high cost.
It is important
In St. Petersburg, a device was developed for performing the ammonia breath test; its performance is similar to the urease test.
The specificity of detecting Helicobacter pylori in feces using the PCR method reaches 100%. However, the results of such an analysis are distorted due to the therapy being carried out, in addition, false negative data are possible in elderly patients.
ELISA is considered the most suitable method for diagnosing Helicobacter. A few weeks after infection, the patient’s body produces specific antibodies to Helicobacter, which are determined by enzyme immunoassay. Detection of immunoglobulins is possible in saliva or gastric juice. But they persist for many years, so this technique is not suitable for assessing the effectiveness of therapy.
Particular attention is paid to the early identification of patients at increased risk of developing gastric cancer. To do this, screening is carried out to determine specific markers of atrophy (types 1 and 2 pepsinogen, gastrin - 17). However, effective therapy aimed at eradicating bacteria significantly reduces the likelihood of malignant degeneration of cells.
Diseases and syndromes associated with Helicobacter
Currently, doctors are confident that Helicobacter pylori infection is a determining factor for the development of:
- chronic gastritis type B;
- gastroduodenitis;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- stomach cancer;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease.
It is important
In the early 1990s, Helicobacter was classified as a risk factor in the first group for the development of malignant lesions of the digestive tract.
In addition, experts associate Helicobacter infection with:
- iron deficiency anemia (occurs in 40% of patients);
- platelet purpura (in half of the patients);
- lack of cyanocobalamin;
- atopic dermatitis.
In recent years, evidence has emerged of the connection between Helicobacter pylori and stroke, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and coronary heart disease. However, this information has not been clinically confirmed. In addition, the bacterium affects the bioavailability of a number of drugs, which requires adjustment of their dosage.
How long does it take for repeat tests to be taken?
For reference. Each method used in identifying Helicobacter has its own characteristics, which are present not only in the conduct and delivery of the analysis, but also in the timing.
After all, tests to detect an intestinal infection will be necessary even after the course of treatment. And from what research method will be prescribed it will be clear not only how to get tested for Helicobacter pylori, but after what period of time after the course of treatment.
If a doctor prescribes a urease breath test for re-examination, it is better to do it 4 to 6 weeks after the end of the course of treatment. An immunological study can show a more accurate result. But only if there is an intestinal infection in the body.
Unfortunately, the negative answers they often show turn out to be erroneous. Constipation is often the cause of a false answer. It is best to conduct a study using this method 2 weeks after treatment.
For reference. Gastroscopy is an effective method. It allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membrane and clarify the likelihood of developing cancer pathology. But due to the specifics of its implementation, many refuse to conduct it.
If you decide which method is better and simpler, then, of course, urease respiratory. But if you are interested in which one is more accurate, the result will be FGDS.
Types of analysis
A blood test for Helicobacter pylori is carried out using two methods:
Linked immunosorbent assay
An antigen to a bacterium causes a specific immune response. At the same time, it produces antibodies called immunoglobulins. This is a highly accurate and high-quality analytical method. Venous blood is collected for biomaterial.
Such an analysis can be prescribed as a preventive study for all persons who have had everyday contact with people suffering from pathologies of the digestive tract.
Western blot method
An examination is prescribed in cases where immunoglobulins to the pathogen are detected in the plasma. Test results provide detailed information about the presence of antibodies in the blood.
High accuracy of examination can be achieved by electrophoresis: this separates the proteins of the microorganism extract. For biological material, venous blood is collected.
How I removed polyps in the stomach
We will describe a real case that shows typical human behavior in the face of a lack of understanding of the reasons for what is happening. The situation lasted for about six months. The patient is a woman aged 60+.
We give her story in the first person as she told it herself. A case is useful as a guide for action in a specific situation.
Heaviness in the stomach after eating
I began to feel abdominal pain in the stomach area quite a long time ago. Maybe a year ago. At first I didn’t pay much attention. The pain was not constant. It will hurt and stop.
For some time I noticed a heaviness in my stomach after eating. This feeling was mixed with pain. Unpleasant.
During the consultation, the gastroenterologist gives recommendations on current treatment. The list of medications includes: trimedat, pancreatin, Creon. This is the main thing.
Three courses of 10 days in different combinations.
Yes, it gets a little easier. Time passes, money is spent on medicine, but the problem does not go away. The natural recommendation of a gastroenterologist is FGDS of the stomach and intestines.
I'm going for an FGDS of the stomach
Preparing for an FGDS is quite stressful. In the evening I do the cleansing by drinking the mixed crap at regular intervals. The body protests against such violence. But it is necessary.
In the morning I go almost across the city to the doctor with whom I managed to make an appointment. As usual, “word of mouth” brings me to a smart doctor. That is, they were recommended by friends.
One of the reasons for traveling across the city is anesthesia for FGDS. The nearest clinic does not provide anesthesia. Only local.
As a result, after waiting in a long line, I end up in the hands of a doctor. He is experienced and the procedure goes quickly and without consequences for me.
I receive the results of FGDS and histology analysis
After lying for an hour and a half in the rest room, I come to my senses after the anesthesia and get the result. Scan in the picture.
The extract identified the main problem - a polyp in the stomach measuring 10 mm. on a wide leg.
They tell me it’s nothing to worry about, but the polyp needs to be removed. In my understanding, the doctor’s opinion does not require verification. It is necessary, it means necessary.
Now we are waiting for the result of the histology analysis. The doctor who did the FGDS does not remove malignant polyps. If the results are appropriate, you will need to look for an oncologist surgeon. If everything goes well, you can contact the same doctor for removal.
Getting ready to remove a polyp in the stomach
Ten days after sending the sample for histology, I receive the result. He is normal from an oncological point of view. But I’m a simple person and it doesn’t occur to me to ask a specialist’s opinion on the histology certificate I received.
With the certificate I received, I go to the doctor who did the FGDS and agree on the removal of the polyp.
The doctor sends me for coronavirus testing. He cannot perform an operation without a conclusion. I pay 1800 rubles for the test. As a result, the test is negative - everything is fine and the polyp can be removed.
To prepare, I'm going on a strict diet.
Consultation with a gastroenterologist
The morning of the day of surgery arrives. With the morning comes a hypertensive crisis. I don’t know what caused it. There was no particular excitement. There was more than one experience of surgical intervention. Moreover, removing a polyp during the FGDS procedure is not such an operation.
One way or another, the procedure is not performed at high blood pressure.
While discussing the situation with my loved ones, we decide that I need to visit a gastroenterologist for consultation.
The next day I go to the clinic. I show the gastroenterologist the result of the histological examination. Here is a picture with this result.
The doctor points to the underlined line in the picture - this is the reason for your heaviness in the stomach. Well, yes. I am not an expert and could not understand what was written.
As a result, inflammation and the presence of Helicobacter bacteria are clearly indicated. In the underlined line, HP (+) indicates a positive result.
The question remains about removing the polyp. The gastroenterologist sends me to an oncological surgeon, because only he can give a recommendation on the removal of the polyp.
Consultation with an oncologist
The oncologist looked at the results of FGDS and histological examination. He chuckled. It turns out that the size of a 10 mm polyp was reduced by half due to taking a tissue sample. For a biopsy, the sample taken must be at least 5 mm thick.
That is, the remaining 5 mm does not greatly affect the situation.
Then the oncologist is dumbfounded by the fact that polyps do not create pain. Also, according to statistics, polyps extremely rarely degenerate into malignant formations.
Conclusions from the patient's story
It is no coincidence that we included the story of our interlocutor in this material. This is an experience. Here are the points you should pay attention to in certain cases.
Among the conclusions, let us pay attention to the following:
- the symptoms of “heaviness in the stomach” and “abdominal pain in the stomach area” are quite common. Especially the first one. However, in a search of articles on these symptoms, we did not find any indication that these are possible symptoms of the presence of the Helicobacter pylori bacterium in the stomach. That is, if these symptoms are present, it is advisable to do a Helicobacter test.
- Read the test results given to you carefully. It is better to consult a doctor. It’s good that the interlocutor did not have an operation to remove a polyp due to a hypertensive crisis. After all, this operation did not eliminate the problem with which she came to the FGDS. First you need to remove the bacteria (Helicobacter eradication).
- The most accurate analysis for Helicobacter is histological examination. This is a rather complicated procedure and is not possible in every situation. The easiest option for preliminary analysis is a breath test. Can be used for preliminary assessment.
Similar articles:
- By what symptoms can Helicobacter pylori be recognized? The appearance of acne on the face, belching, lichen planus, gastritis, and many...
- Stool analysis for Helicobacter pylori Every person with stomach problems should know what this is...
- Analysis for Helicobacter pylori: What is it, interpretation of the analysis, norm One of the most insidious and dangerous bacteria in the human body...
- Which one is better to take the Helicobacter pylori test and which one is more accurate? Attention! Read the extended text of the article here. Helicobacter pylori is a serious…
Preparation stage
The helic test is quite simple to perform, but it requires careful preparation. This is the most important step to obtain the most accurate result.
Rules for preparing for the Helicobacter breath test:
- in the morning before the procedure, you need to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with plain water;
- the procedure is carried out strictly on an empty stomach;
- It is permissible to drink some water (1/2 glass) 1 hour before the test;
- on the day of the analysis, smoking and chewing gum are excluded;
- the dinner menu on the eve of the test should be dietary and can be eaten no later than 22:00;
- 2 weeks before the test, cancel all antibiotics and agents that inhibit the secretion of hydrochloric acid;
- a week before the examination, you should not take painkillers, antacids, anti-inflammatory medications and bismuth preparations;
- 3 days before the test, alcohol and all legumes are excluded.
Any medications the patient is taking should be consulted with a physician. He can give additional recommendations regarding preparation for the helic test.