In the modern world, pathologies and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract ( GIT)
) are the most common in all age categories. Moreover, dysfunction of the stomach and intestines actively provokes diseases of other organs, reduces performance and negatively affects the quality of life. Unfortunately, most gastrointestinal diseases, including neoplasms, appear at an advanced stage. That is why it is important to undergo timely examinations, especially since with properly selected therapy and a balanced diet, they respond well to treatment.
Indications for laboratory diagnostics of the gastrointestinal tract
In addition to acute manifestations in the form of severe pain, bleeding and critical disorders, primary and secondary symptoms for conducting a diagnostic examination of the gastrointestinal tract can be a whole range of direct and indirect indications. The main clinical syndromes are:
- heartburn;
- flatulence;
- private constipation and diarrhea;
- critical changes in stool consistency;
- chest pain (non-cardiac origin);
- painful discomfort in the iliac region and tenesmus;
- discharge of mucus with feces;
- decreased appetite;
- weight loss.
Moreover, in some patients, the development and course of gastrointestinal diseases may be accompanied by other symptoms: constant or periodic diffuse epigastric pain, aversion to food, belching, dysphagia and vomiting. Changes in microflora, yellowing of the skin, sleep disturbances, and nervous irritability may also occur.
Digestive diseases
Gastroenterology
– a special discipline that studies the structure, physiology and pathology of the digestive system, as well as the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the digestive system. Within gastroenterology there are narrower sections: for example, liver and gall bladder diseases are studied by hepatology, pathology of the large intestine and pararectal space - proctology. The normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is greatly influenced by the state of the endocrine system, oral cavity, and the presence of infectious agents in the body.
The digestive system includes a collection of many organs and glands that provide the nutrients the body needs for development and functioning. It permeates almost the entire body, starting with the oral cavity and ending with the rectum. Therefore, the pathology of even one of the digestive organs entails a disorder in the functioning of the digestive system as a whole. Modern ecology, stress, new foods and additives, as well as medications cause the occurrence or exacerbation of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diseases of the digestive system are so common that every person experiences their manifestations at least once in their life. Among diseases of the digestive tract, the undisputed leaders are inflammatory processes in its various parts, which have an acute or chronic course: inflammation of the esophagus (esophagitis), stomach (gastritis), duodenum (duodenitis), liver (hepatitis), pancreas (pancreatitis), gall bladder and ducts (cholecystitis and cholangitis), small and large intestines (enteritis and colitis), rectum (proctitis). They, in turn, cause changes in the mucous membrane of organs, their motor function and lead to the occurrence of stomach and duodenal ulcers, cholelithiasis, and ulcerative colitis. A serious problem in modern society is intestinal dysbiosis, which occurs in the vast majority of people, including newborns.
Diseases of the stomach, pancreas, and intestines are often the root cause of many skin and metabolic diseases. The symptoms of diseases of the digestive system are very diverse and depend on the affected organ. Common manifestations include loss of appetite, abdominal pain, belching, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, upset stool, weakness, weight loss.
Modern gastroenterology has great diagnostic capabilities that make it possible to recognize diseases of the digestive system in the early stages of their occurrence.
Laboratory tests include tests of blood, gastric and duodenal juice, feces, intestinal microflora, and tissue samples taken during biopsy. To examine the hollow organs of the gastrointestinal tract, X-ray and endoscopic methods are used (esophagoscopy, colonoscopy, gastroduodenoscopy, etc.), and for parenchymal organs, ultrasound diagnostics is used. Many chronic diseases of the digestive system, which subsequently require surgical intervention, are caused by neglect or undertreatment of an acute condition. Therefore, the occurrence of any pathological manifestation in the digestive system should serve as a signal for immediate contact with a gastroenterologist. When treating diseases of the digestive system, the patient will be required to strictly follow the treatment regimen and diet. Further…
Methods of laboratory diagnostics of the gastrointestinal tract
To obtain an objective clinical picture of the nature of the disease and to confirm diagnoses, it is often necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis using invasive and non-invasive methods. The Northwestern Center for Evidence-Based Medicine offers laboratory, instrumental and functional examinations without a queue or registration.
The services of our center will help identify pathologies, determine the dynamics of recovery, confirm the effectiveness of therapy and prevention, as well as diagnose neoplasms and helminth infestations. We offer our clients both traditional diagnostic methods and the most innovative examination methods, and the latest results coding system and automated information support eliminate the possibility of errors and confusion in the analyzes.
Laboratory diagnostics of the gastrointestinal tract
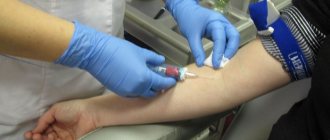
General blood analysis.
An invasive clinical study that allows you to obtain detailed information about the main indicators of the patient’s capillary or venous blood:
- number of leukocytes, platelets and red blood cells;
- hemoglobin and ESR levels;
- color index.
The assay is widely used to provide an overall clinical picture and monitor therapy or disease progression. SZTSDM specialists use high-quality consumables and perform blood sampling as comfortable as possible for the patient. Combined with full compliance with all medical and sanitary standards, it guarantees maximum reliability of the result.
Examination of stool for the presence of protozoa.
This microbiological analysis makes it possible to detect cysts of protozoan microorganisms in the feces, which enter the human body with poorly washed vegetables, poor-quality water, traces of soil substrates or from an infected carrier (animals, people, birds). Microspopia can accurately detect giardiasis, balantidosis, amebiosis and toxoplasmosis, which affect the gastrointestinal tract and suppress the immune system.
Examination of stool for worm eggs.
As a rule, microscopic analysis for helminths reveals the presence of worms and eggs of parasites such as ascorids, necator, pinworms or hookworms in feces. But in the SZDCM laboratory, a full-fledged study is carried out, which makes it possible to accurately identify the facts of infection of children and adults with various genera of parasitic helminths and cross-reactions with the antigens of other parasites, which means that the patient will be prescribed correct and effective treatment.
Analysis of microflora for dysbacteriosis.
Bacterial research reveals quantitative and qualitative changes in intestinal biocinosis. Allows you to determine the increase or decrease in pathogenic and healthy microflora (bacteroides, bifidobacteria, candida, Klebsiella, clostridia, Proteus, Escherechia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, strepto-, entero- and staphylococci) and initially determine the degree of dysbiosis.
It should be noted that for each age group special methodologies are used for interpreting the results of this analysis. In this case, the study can also be prescribed to newborns, people with allergic manifestations and patients who have undergone intensive anti-inflammatory, hormonal and chemotherapy.
Coprogram.
A comprehensive chemical, macro- and microscopic laboratory study of a wide range of stool, widely in demand among clinicians and easily interpreted. The analysis assumes:
- determination of enzyme activity of the digestive organs, evacuation capacity of the stomach and intestines;
- study of pH reaction, state of microflora, color and consistency of feces;
- detection of bile pigments, fatty acid salts and mucus.
This non-invasive study also involves identifying inflammatory processes and conducting an analysis for the presence of hidden traces of pus and blood in the stool (Gregersen reaction). It allows you to accurately detect altered erythrocyte hemoglobin and cloudy exudate and thereby identify hidden bleeding and pathology of the gastrointestinal tract.
Antigen screening
rotavirus, norovirus, astrovirus. The analysis is carried out using the polymerase reaction method (PCR) and enzyme immunoassay. This ensures high analytical accuracy and makes it possible to identify infectious pathogens of gastrointestinal diseases in the stool with maximum reliability.
As a rule, infectious agents are actively transmitted through the oral-fecal route from an infected person, so it is extremely important to correctly and timely identify pathogens. The study will determine the etiological factor of acute intestinal infections and will allow a differentiated approach to the treatment of inflammatory processes.
Modern methods of examining the stomach
How much does the examination cost?
The average price of gastroscopy in Moscow starts from 4000–5000 rubles, and the cost of an X-ray examination of the stomach is 3000–4000 rubles.
The approximate cost of an ultrasound scan ranges from 2000–3000 rubles. How much a laboratory examination of the stomach costs depends on the set of laboratory tests chosen and methods for studying the biomaterial. We asked a representative of the INVITRO network of independent laboratories what gastric studies are most in demand today, and how much they cost those suffering from gastroenterological diseases: “Due to the close relationship of the abdominal organs, functional stomach disorders lead to disturbances in the functioning of all gastrointestinal organs - decreased immunity, Metabolism suffers, the absorption of biologically valuable substances in the intestines is impaired, and this entails the development of chronic diseases and a deterioration in the quality of life.
Therefore, a comprehensive examination of the entire gastrointestinal tract is the only method to see in the smallest detail the condition of such an important organ of the digestive system as the stomach. Only based on the results of several studies can various gastroenterological diseases be diagnosed with high reliability. In addition, this allows an individual approach to the choice of treatment for each patient, preventing the development of complications.
Before any hardware examination of the stomach, especially before gastroscopy and biopsy, you can conduct a set of venous blood tests for antibodies to H. pylori, the level of pepsinogen enzymes and gastrin-17, included in the “Gastropanel”, which was developed by the Finnish company BIOHIT. These blood tests make it possible to identify pylori-associated chronic gastritis at an early stage, narrow down the causes of dyspeptic disorders - heartburn, pain, nausea, heaviness and other types of discomfort in the stomach, and assess the risk of developing peptic ulcers and even oncology. "Gastropanel" is indicated for unidentified forms of anemia, if hidden blood loss is suspected. Its cost is 3300 rubles. By the way, the following are usually held together with Gastropanel:
- examination of feces for occult blood using a quantitative immunochemical method (benzidine test) - 340 rubles;
- determination of antibodies to gastric parietal cells, total IgG, IgA, IgM - 1,435 rubles;
- determination of lipase level - 425 rubles;
- determination of Ca 72-4 (carbohydrate antigen 72-4) - 1230 rubles;
- determination of Ca 19-9 (carbohydrate antigen 19-9) - 840 rubles,
- determination of carcinoembryonic antigen (CAE, Carcinoembryonic antigen, CEA) - 805 rubles,
- cytological examination of endoscopic material for the presence of Helicobacter pylori - 845 rubles.
Of course, you cannot decide on your own which tests should be taken and which should not. This decision is made solely by a gastroenterologist. Only he should interpret the test results. By the way, you can also have a consultation with a gastroenterologist at one of the INVITRO medical offices.
PS "INVITRO" is a private medical company that provides laboratory and instrumental diagnostic services both in Russia and throughout the post-Soviet space. The results of any research conducted at INVITRO are accepted by all Russian clinics and clinical hospitals as reliable.
License to carry out medical activities LO-50-01-008046, 09.13.2016
Functional diagnostics of the gastrointestinal tract
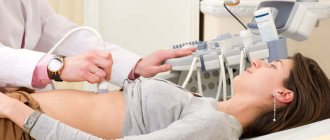
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound)
. A modern and highly informative method of non-invasive diagnostics. Its principle is based on the Doppler effect (a change in the frequency and wavelength of ultrasound as a result of perception or reflection by matter), which makes it safe for adults and children and allows the examination to be performed quickly and without prior preparation of the patient.
Ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract can be prescribed:
- children;
- pregnant women;
- people after chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Depending on the doctor’s recommendations and symptoms, the procedure may involve a comprehensive examination of the abdominal cavity or only the stomach and intestines, including the cecum, sigmoid, rectum, ascending and descending colon. In some cases, an examination of the intestines is carried out with the introduction of a rectal sensor. Ultrasound of the stomach is inferior in information content to gastroscopy. But given the non-invasive nature of the procedure, it allows diagnosis even in infants and people with inflamed and damaged food tracts.
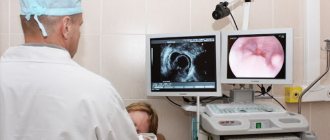
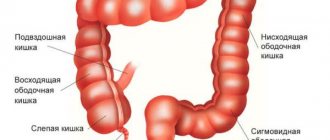
Colonoscopy.
An endoscopic method for diagnosing the condition of the entire large intestine, the length of which reaches more than a meter. It is characterized by the highest information content and allows you to:
- visually determine the nature of the development of ulcers and the relief of the internal walls of the entire large intestine;
- detect even microscopic tumors and polyps;
- perform a biopsy.
Colonoscopy allows early diagnosis of ulcers and neoplasms. Therefore, doctors recommend that even in the absence of obvious symptoms, people over 50 years old should be examined every 5 ÷ 7 years.
Diagnosis is based on the introduction of an endoscope and is associated with flushing and distension of the intestines, which causes significant discomfort and pain. Therefore, it is carried out after deep cleansing and using anesthesia.
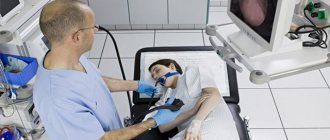
Endoscopy.
A modern method that offers wide possibilities for examining the mucous surfaces of the gastrointestinal tract. Allows:
- take a tissue sample for laboratory testing;
- determine the narrowing and expansion of the esophagus;
- diagnose fibrous layers.
Diagnosis is based on the introduction of a flexible endoscopic sensor into the esophagus naturally. The endoscope is equipped with fiber optic illumination and transmits a high-quality magnified image to the monitor. Thus, gastroendoscopic diagnostics provides a complete clinical picture of the presence of erosions, ulcers, and inflammatory processes on the mucous membrane of the stomach, esophagus and duodenum. Allows you to diagnose gastrointestinal cancer in the early stages and objectively monitor the dynamics of pathology or remission. It should be noted that the procedure is strictly carried out only on an empty stomach.
Laparoscopy.
A minimally invasive method of examining the abdominal cavity, performed using a rigid endoscope. Widely used in the postoperative period to diagnose complications and in cases where X-ray and other clinical and laboratory methods have proven ineffective.
It is highly informative, reliable and technically simple, but requires local or general anesthesia. Applicable for children and older patients.
Radiation diagnostics (CT)
A modern method that combines digital technologies with x-ray examination. The SZTsDM has a latest generation tomograph installed, which made it possible to extremely reduce the impact of radiation on the patient, obtain diagnostic 2D and 3D images of excellent resolution and analyze them from any angle.
CT allows you to non-invasively identify tumors and metastases that are not diagnosed by ultrasound, as well as determine:
- inflammatory and erosive processes;
- elasticity and thickness of the walls of the esophagus, stomach and intestines;
- congenital pathologies and postoperative recovery dynamics.
The study was well tolerated by patients of all ages. Requires minimal preparation.
Prevention and recommendations
Most gastrointestinal diseases can be quite easily prevented. It is enough to limit the consumption of fatty and fried foods, introduce fermented milk products, vegetables and dishes rich in fiber into the diet.
Drinking clean water is also of no small importance in the prevention of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. And:
- healthy sleep;
- cardiological and strength physical activity;
- timely treatment of giardiasis, dysbacteriosis, helminthic infestations;
- taking medications strictly according to the instructions and according to the recommendations of doctors;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, abuse of strong brewed tea and coffee, alcohol, including low-alcohol drinks).
How to prepare for tests
Urine and stool tests . The biomaterial is collected in a special sterile container (purchased at the pharmacy). The day before, it is not recommended to take multivitamins and eat foods that can change the color of the biomaterial, as well as laxatives and diuretics.
Urine is collected in the morning, after careful hygiene of the external genitalia. It is necessary to drain the first dose of urine into the toilet, and collect the middle portion (100-150 ml) in a container.
Feces are collected in the morning or no later than 8 hours before the test.
Gastropanel . A week before the study, you should stop taking medications that can affect gastric secretion. The day before, avoid taking medications that neutralize hydrochloric acid. On the morning of the test, do not drink, eat, or smoke.
The study involves donating blood from a vein in two doses: immediately upon arrival at the treatment room and 20 minutes after taking a special cocktail designed to stimulate the hormone gastrin 17.
Blood tests (general, biochemical) . Blood for testing is donated in the morning on an empty stomach. On the eve of the analysis, you should avoid stress, refrain from eating heavy food and alcohol. You should not eat or smoke on the morning of the test. Drinking clean water is allowed.
PH-metry. The probe is installed in the morning on an empty stomach. At least 12 hours must pass since the last meal, and you can drink water no later than four hours before the procedure. Before the planned study, be sure to notify your doctor about the medications you are taking; their use may have to be discontinued several hours (and some medications several days) before the procedure.
It is also recommended that a few days before the study, you refrain from consuming foods that can change the pH of the stomach (we are talking about carbonated and alcoholic drinks, coffee, strong tea, fruit juices, yoghurts, etc.).
Laboratory diagnostics of stomach diseases in “MedicCity”:
- Gastropanel;
- Determination of biochemical parameters;
- Pepsinogen-I;
- Pepsinogen-II;
- Gastrin-17 basal;
- Gastrin-17 stimulated;
- IgG antibodies to Helicobacter pylori;
- PCR stool.
The multidisciplinary clinic "MedicCity" offers patients a wide range of diagnostic and treatment services. You can undergo instrumental diagnostics of stomach diseases, take tests at any convenient time by appointment, without queues and stress, in a pleasant atmosphere and at an adequate cost.
Where to get tested
The Northwestern Center for Evidence-Based Medicine, having a powerful laboratory base and the latest generation diagnostic equipment, offers regular and potential clients to undergo diagnostics of acute, chronic and infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
At SZTsDM JSC you can also order a call from a nurse to collect biological material at home. Contact us, we guarantee high competence of specialists, reliability of diagnosis and complete confidentiality.
Other technologies for diagnosing diseases of the digestive system: probing
As a rule, the above diagnostic methods can reveal only an approximate picture of the disease. If the specialist wants to obtain more accurate information for the diagnosis, he will refer you for additional examinations, which are carried out using special tools and equipment. The simplest and most common method of examining the gastrointestinal tract is probing. The main purpose of intubation is to access gastric juice, which reflects all the necessary indicators of the state of the gastrointestinal tract. Violation of the content of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice causes problems in digestion and becomes the cause of certain diseases. Probing is the only way to examine the balance of acidity in the stomach. In addition, it may be relevant in situations where it is necessary to diagnose certain diseases of the duodenum and even rinse the stomach in case of poisoning.
Endotracheal and nasogastric intubation
The sounding procedure involves inserting a special probe through the esophagus to the stomach. In preparation for this method of examining the gastrointestinal tract, the patient should avoid consuming vegetables, fruits, carbonated drinks, milk and black bread in his diet for two to three days. During this period, it is recommended to take activated carbon in order to reduce gas formation. The procedure itself is carried out ten to twelve hours after the last meal, on an empty stomach. Probing lasts on average no more than two hours and does not entail any consequences for the gastrointestinal tract.