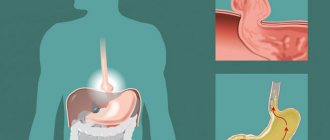
The full functioning of the gastrointestinal system is carried out thanks to several functions. One of them is the movement of the food bolus through the digestive tract. Alternately in different departments, food is retained and processed using enzymes and juices. After completion of the next stage of splitting, the contents are released into the underlying sections of the gastrointestinal tract through the sphincters, which are regulated by the nervous system.
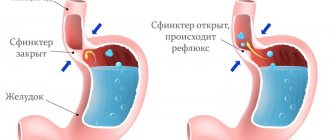
There is also a sphincter between the stomach and duodenum; there are sphincters at the mouths of the bile ducts and the excretory ducts of the pancreas. Under the influence of various factors, muscle sphincters (sphincters) become incompetent.
In pathological cases, bile enters the stomach. Casting is formed under the influence of unfavorable factors. Bile reflux (reflux of bile into the stomach) leads to damage to the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus. As a result, biliary gastritis and esophagitis occur.
Physiology of bile secretion
Bile formation is a continuous process carried out by liver cells. Its accumulation and concentration occurs in the gallbladder.
When food enters the upper parts of the digestive tract under the influence of nerve impulses, the secretion of the common bile duct enters the duodenum through the sphincter of Oddi, where it participates in the digestion of the bolus of food. In a healthy person, motor and secretory function is a harmonious system. However, if its functioning is disrupted, bile reflux into the stomach and food may enter the upper digestive tract.
Diagnostics
The examination of the patient begins with collecting an anamnesis, where the doctor listens to the patient’s complaints, learns about the duration of the disease and the severity of symptoms. To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to identify bile in the stomach. For this purpose the following may be carried out:
- Examination of the mucous membrane of the lower esophagus (esophagogastroduodenoscopy).
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
- Clinical analysis of blood, feces and urine.
- Additional examinations of the tone of the gallbladder.
- Choledochoscintigraphy (allows you to study the contractile function of the esophageal sphintker.
Based on the collected data, the doctor diagnoses bile reflux and prescribes a diet for the patient.
Why is there a lot of bile in the stomach?
Reflux is more common in people of middle and older age groups. Less commonly seen in children. Let's look at the reasons for the reflux of bile into the stomach and esophagus and give advice from gastroenterologists that reduce the risk of developing the disease. There are pathophysiological factors that cause secretions to accumulate in the intestines and move up. These include conditions:
- decreased tone in the lower parts of the digestive tract;
- dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi;
- changes in the nervous coordination of the gastrointestinal system;
- thickening and stagnation of bile in the gallbladder;
- increased pressure in the abdominal cavity.
Gallbladder dyskinesia in adults: causes, symptoms, treatment
If there is a lot of bile in the stomach, external reasons may be:
- Inflammatory processes of the liver, gall bladder and bile ducts.
- Formation of stones in the lumen of the bile ducts and bladder.
- Taking medications for a long time, which leads to a decrease in sphincter tone (NSAIDs - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
- Tumors of benign and malignant nature.
- Surgical interventions: removal of the gallbladder, radical surgical techniques for stomach cancer, reconstruction of the pylorus and bile ducts.
- Constant physical activity, which leads to increased intra-abdominal pressure.
- Overeating, especially fatty foods.
- Alcohol abuse and smoking.
- Overweight.
- Long-term exposure to stress factors.
- The release of bile into the stomach is also observed during pregnancy.
Important!
The combination of several unfavorable factors increases the likelihood of developing pathological reflux of bile into the stomach and esophagus.
Classification of this pathology
The criterion for this classification is the height of bile penetration through the esophagus. In this regard, bile reflux occurs:
- duodengastric;
- duodengastroesophageal;
- duodengastroesophageal.
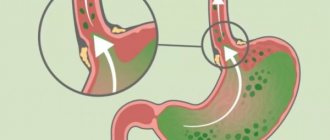
The first type of pathology occurs when the pylorus, which separates the stomach from the duodenum, fails to cope with its functions, and bile enters the stomach. Stagnation of bile in the stomach causes irritation of its mucous membrane, and the organ tends to push this fluid upward.
Duodengastroesophageal reflux is a consequence of weakening muscle tone, which leads to a weakening of the sphincter of the lower esophagus and the penetration of bile from the stomach up into the esophagus.
The third type of reflux is characterized by bile entering the oral cavity.
The liquid that penetrates up the gastrointestinal tract is, strictly speaking, not pure bile. It is called refluxate and consists of the bile itself and the juice secreted by the pancreas. This mixture has a destructive effect on the mucous membranes of the digestive organs and leads to the occurrence of many diseases of the digestive system.
Read also: How does yoga help the liver and gallbladder?
Gastritis, which occurs due to reflux, is divided into duodenal gastritis and the so-called biliary reflux gastritis.
Symptoms
If a lot of bile is released into the intestines, it stagnates and is subsequently released into the upper sections. When motor function is impaired, it enters the stomach. The secretion containing bile acids causes inflammation of the mucous membrane. In the absence of timely treatment, biliary gastritis develops. Excess gastric juice leads to reflux into the esophagus with the formation of esophagitis. Symptoms of bile reflux into the stomach depend on the duration of the disease and the degree of organ damage. Pathology can be suspected if the following manifestations are present:
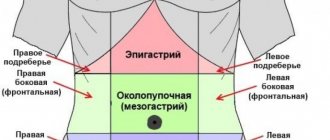
- The occurrence of discomfort during or after eating, which is localized in the upper abdomen and right hypochondrium.
- Dyspeptic syndrome: belching mixed with bitterness, bloating, nausea, and sometimes vomiting bile.
- Changes in bowel habits - alternating constipation and diarrhea.
- Asthenic signs: lethargy, weakness, disability.
- Loss of body weight.
- Anemia.
- Dry, brittle hair and nails.
Symptoms and methods of diagnosing this pathology
The low intensity and mild severity of the symptoms of bile reflux makes it difficult to diagnose in the early stages of the development of the pathology. For some time, the disease may be asymptomatic and not cause any discomfort to the patient. Symptoms and treatment may vary depending on the type of pathology.
Externally, this pathology manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- urge to vomit after eating;
- feeling of nausea;
- the appearance of heartburn;
- deterioration or complete loss of appetite;
- the occurrence of unpleasant belching;
- ulcers appear in the corners of the lips;
- weight loss;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- sensation of pain and burning (stomach pain and, in some cases, in the sternum area).
Young children with this pathology may burp after feeding and cry during this process. Older children may experience negative symptoms such as sleep disturbances and night vomiting. All these signs are a signal to immediately seek medical help.
The following diagnostic techniques are used to diagnose bile reflux:
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | Ultrasound (ultrasound examination) |
| 2 | Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) |
| 3 | monitoring the acidity of gastric juice and gastric microflora throughout the day |
| 4 | gastroduodenoscopy |
| 5 | X-ray examination of the stomach (polypositional) |
| 6 | fibrogastroscopy, in which a sample is taken for histological examination |
Read also: What does a small gallbladder mean?
What to do
Accumulation and stagnation of bile occurs due to a number of factors. Therefore, before treating the reflux of bile into the stomach, it is necessary to find out the cause of the development of the pathology. Medical care for the disease includes several areas:
- diagnostic measures;
- diet;
- conservative therapy;
- alternative methods.
A systematic, comprehensive approach allows you to cope with the problem and helps prevent the development of relapse of reflux.
Attention!
If there are tumors or stones in the gallbladder, doctors discuss radical intervention and decide whether and when surgery is necessary.
Diagnostics
If biliary reflux is suspected, the doctor ascertains the medical history, examines the patient, and prescribes general clinical and instrumental examinations. The release of bile into the stomach is characterized by symptoms that are quickly determined by a specialist based on objective data. Questioning the patient allows you to find out about the duration of the disease, signs of pathology that characterize excessive accumulation and penetration of bile into the upper sections. The gastroenterologist recommends additional diagnostic methods:
- A blood test - general and biochemical - to identify signs of inflammation, thickening of bile, liver dysfunction.
- Carrying out FGDS with histological sampling of material. During fibrogastroscopy, you can see a lot of mucus, a strong release of secretions, determine the degree of damage to the mucosa and the extent of the process with the development of duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum), esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus).
- Detection of the pathogenic pathogen Helicobacter pylori using various tests - PCR, ELISA, urease diagnostics.
- Performing pH testing to determine the level of stomach acidity.
- X-ray with barium contrast.
If the patient has symptoms of damage to parenchymal organs, an ultrasound is prescribed. The method allows you to study the structure of organs and their function, and check for the presence of additional formations.
Main reasons
The release of bile does not always occur due to severe illness. Much more often, pathology is provoked by unfavorable factors, and therefore can appear even in a completely healthy person. Because of this, it is usually unsystematic and does not appear often.
- Poor nutrition
- Increased stress after eating
- Regular afternoon naps
- Alcohol
- Long fasts
- Eating stale food
Due to the influence of these factors, the overall tone of the mucous membrane of the digestive organs decreases. In addition, during physical activity, especially if it occurs immediately after eating, disturbances of the valve mechanism develop, as a result of which bile penetrates the digestive organs even when a person has not eaten anything.
Also, the release of bile can occur due to a number of diseases. The most common is hepatitis. Due to the damage to liver cells that occurs against the background of this disease, the patient may experience increased bile production. Similar processes can occur with gastritis and diabetes.
Increased production of bile occurs during food poisoning. The body reacts inadequately to the ingestion of food containing toxins, which is why the production of a substance increases, the action of which neutralizes the poisoned product and accelerates its elimination from the body. Bile emissions are observed in some patients suffering from late forms of dysbiosis and diseases of the bile ducts.
One of the main risk factors is surgical removal of the bladder. This method is used for various diseases, in cases where conservative therapeutic methods do not produce the desired effect. Due to the lack of a reservoir for bile, it constantly enters the digestive organs. In order to slow down this process, the patient is usually prescribed special medications.
Thus, there are different reasons for the release of bile into the intestines, and provoking factors that increase the likelihood of developing such a pathology.
Treatment
Conservative therapy for reflux includes:
- drug correction;
- physiotherapy;
- alternative methods.
Before prescribing a course of treatment, the reasons for the reflux of bile into the stomach and esophagus are determined. Because the choice of funds depends on many factors. If the patient has undergone surgical correction and does not have a gallbladder, some medications are not prescribed. Treatment is recommended to reduce the symptoms of the pathology.
When there is a reflux of bile into the stomach, a group of drugs is included whose action is aimed at:
- normalization of secretory function;
- improvement of motor skills and passage of food masses;
- restoration of acidity;
- elimination of pain syndrome.
Medications
Treatment is prescribed by a gastroenterologist based on objective and additional examination data. The medications presented in the table help get rid of the reflux of bile into the stomach.
Table 1. Drug treatment for the release of bile into the stomach
| Drug groups | Names of tablets | pharmachologic effect |
| Ursodeoxycholic acid | Ukrliv, Ursofalk, Gepaursol, Ursosan | Reduces bile stagnation, restores its composition, improves outflow |
| Prokinetics | Domrid, Motilium | Normalize motor function, reduce the likelihood of reflux, prevent vomiting |
| Choleretic drugs | Allohol, Holosas | Helps thin bile |
| Proton pump blockers | Omeprazole, Omez | Help treat excess secretion, normalize pH balance in the stomach |
| Antacids | Phosphalugel, Almagel, Maalox | Helps reduce irritation of the mucous membrane, create a protective layer on the inner surface of the esophagus and stomach, which neutralizes hydrochloric and bile acids |
| Antispasmodics | Riabal, Dicetel, No-shpa, Mebeverine | Relieves pain, reduces spasm of smooth muscles |
| Analgesics | Paracetamol, Ibuprofen | Relieves pain and discomfort |
Diet
The menu for reflux disease includes products that reduce the irritant effect on the mucous membrane of the esophagus and other parts, do not cause gastritis, and normalize the motor function of the digestive tract. A diet for the reflux of bile into the stomach is recommended by a gastroenterologist for the entire period of treatment and during the rehabilitation period.
How to eat right in this case?
To do this, follow these rules:
- Take food in small portions up to 6 times a day.
- Gentle heat treatment of food is allowed: boiling, baking, stewing, steamed dishes.
- You should not eat 3 hours before bedtime.
- Limit the intake of alcoholic beverages, coffee, sparkling water, and juices.
- Avoid fatty, fried, spicy, smoked foods.
- Fruits and vegetables are not eaten raw.
- Avoid snacking and chew food thoroughly.
- The diet should include cereals, soups, milk and ready-made dairy products, and fruit infusions.
Foods that are good for the stomach
Treatment of bile reflux with folk remedies
When the duodenum and stomach are full of bile, its accumulation causes unpleasant symptoms. Alternative medicine allows you to remove stagnation of secretions and restore their normal release. Healing herbal remedies can be prepared at home. If there is a reflux of bile into the stomach, treatment with folk remedies shows good results and helps get rid of unpleasant symptoms.
13 recipes for jelly for the stomach with gastritis
Popular recipes are presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Recipes for folk remedies for bile reflux into the stomach
| Natural remedy | Admission rules |
| Chamomile decoction | 15 grams of raw materials are poured into 200 ml of boiling water, brought to a boil and left in a water bath for 10 minutes. Drink ½ glass up to 3 times a day. |
| Dandelion root infusion | 15 grams of crushed raw materials are poured into 200 ml of boiling water and left for 20 minutes. Drink 50 ml 3 times a day. |
| Corn silk | 3 teaspoons of the mixture are poured into 200 ml of boiling water, heated in a water bath for half an hour. Dilute with boiled water 1:1 and filter. Drink ¼ glass before meals. |
Reviews and results
Nutritional therapy can be performed for a long time by patients whose work activities do not involve hard work. Everyone who has encountered this problem admits that the diet must be followed. It helps to avoid discomfort, belching, bitterness in the mouth, heartburn and heaviness in the stomach. Usually these phenomena disappear within the first week of proper nutrition.
- “... When you have a backlash of bile, you can’t drink choleretic herbs, but I made the situation worse - the bile began to be released even more and more of it was thrown into the stomach. The result was severe inflammation. The first time bile reflux was caused by taking rich village milk, which I drank for a whole month while at the dacha. Now a strict diet is prescribed. At first I ate mashed boiled dishes for 2 weeks, and then regular ones, and by the end of the month I was already baking fish and chicken breast. I excluded irritating foods, tomato paste, pickled vegetables, hot and spicy dishes, adjika, ketchup. Immediately everything became bland and tasteless, but after 2 weeks I felt an improvement. I was also prescribed Ursosan at night. I think I'll have to eat like this all the time. In 3 months I lost 4.5 kg”;
- “... When bile was released and entered the stomach (this was discovered on gastroscopy), I was bothered by pain in the stomach, bitterness in the mouth, and nausea in the morning. Gastroscopy also revealed gastritis, but no erosions. Immediately prescribed a diet and Ursosan. I noticed that after 10 days it became much better. I switched to low-fat boiled food, porridge, cottage cheese, boiled vegetables, dietary soups. In total, I followed the diet for 4 months. Now there is no more belching or stomach discomfort. It turns out that you need to eat like this all the time”;
- “... I had an FGDS and it was determined that there was a lot of bile in the stomach. Now I try to eliminate harmful foods, but it doesn’t really help. I began to eat often and in small portions and eat light foods. In the morning, I definitely have oatmeal - it’s enveloping, and there’s less pain, then I take cottage cheese or steamed cutlets with me to work, and again porridge. I can only eat soups in the evening, as it is inconvenient to take them to work. I think that this problem is associated with nerves - bile directly depends on them. I also noticed that you should not overeat and do intense sports (especially bending and abs). I went to the doctor again and when he prescribed Motilium and Ursosan, things moved in a positive direction.”
Advice from a gastroenterologist
The disease causes discomfort and disrupts a person’s usual way of life. Therefore, the patient’s natural desire is to get rid of reflux and its associated symptoms.
To achieve an effective treatment result, gastroenterologists advise:
- Adhere to the diet and nature of your diet, exclude from the menu foods that provoke bile reflux.
- Reduce the impact of stress factors and other negative causes.
- Treat concomitant diseases in a timely manner.
- Include regular moderate physical activity.
- Stabilize your weight.
- Follow the recommendations of a specialist on taking medications.
- Give up bad habits - alcohol and smoking.
Pathology of the digestive system, which is accompanied by the entry of bile into the upper sections, can be successfully treated thanks to modern methods of diagnosis and treatment. However, the main condition on the path to recovery is the joint work of the doctor and the patient.
Bile reflux into the intestines - causes, symptoms, treatment and diet
For the normal functioning of all organs of the digestive tract, it is necessary for bile to enter the intestines.
The volume of enzyme production must correspond to the volume of food consumed, moving along with it through all parts of the intestine. Bile has normal indicators - biochemistry, concentration. Disturbances in the process of enzyme production and its release into the intestinal lumen provoke the development of pathological processes: the flow of bile into an empty stomach with burns of its walls, the production of a substance in a larger volume than is objectively required, etc. Identifying symptoms helps to establish the nature of the pathology, begin treatment on time and prevent more severe complications. Bile in the intestines in too large a volume is far from normal and a dangerous disorder.
Treatment of the disease
If attacks occur rarely (once every 2 months), then there is no need to resort to radical measures. All bad habits are eliminated and the patient’s diet is normalized.
If there are other diseases that contribute to the reflux of bile, then 2 main principles of treatment are applied: eliminating symptoms and normalizing the outflow of bile.
Drug treatment
When treating pathology with medications, they use medications that relax smooth muscles, suppress mucous secretion, and improve the structure and motility of the bladder.
To stimulate the gastrointestinal tract, take the following tablets:
They activate digestion, accelerating the movement and excretion of feces. This cleanses the entire system.
The aggressive effects of hydrochloric acid are alleviated by antacids (Nexium, Maalox, Almagel). With their help, the pH balance of the microflora is normalized due to their effect on the secretory glands.
When there is a lot of bile, it is neutralized with ursodeoxycholic acid (Ursofalk). The chemical substances included in its composition pass into a water-soluble form directly in the stomach, from where they are excreted from the body.
Pain syndrome is relieved with antispasmodics (No-spa).
Surgery
Gastrointestinal diseases accompanied by the release of bile often require surgical treatment. Modern medicine has reached a high level, so there are gentle treatment methods that avoid serious injuries:
- Laparoscopy . The operation is performed through a small hole with a diameter of no more than one and a half centimeters. The surgeon makes several punctures in the abdominal cavity. Next, an instrument and a probe with a camera are inserted. In most cases, patients tolerate this type of surgery well. Recovery occurs under the supervision of doctors. The necessary medications and procedures are prescribed. Seams are inspected regularly.
- Laparotomy . If it is impossible to carry out the operation described in the previous paragraph, doctors resort to this method. In this case, it is possible to remove the diseased organs. The risk of complications is high, rehabilitation is long. Medications are prescribed and physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out. Inspection and treatment of seams is carried out more often and more thoroughly.
Folk remedies for neutralizing bile
Traditional medicine can also be effective in combating large amounts of bile in the stomach. The main thing is to consult a doctor and not self-medicate.
Prescriptions are prescribed that can drive away excess bile from the epigastrium, relieve pain and neutralize unpleasant bitterness in the oral cavity.
You can eliminate pain with a decoction of rowan or rosehip. At the same time, combining them with herbal infusions (birch, dandelion leaves, immortelle).
To cleanse the stomach, it is recommended to drink a decoction of flax seeds. The walls of the stomach are strengthened. To prepare it, you need to grind the seeds and pour warm water over them, leave to swell for a while. The resulting porridge is eaten for breakfast.
To eliminate the unpleasant bitter taste in the mouth, just drink a couple of glasses of warm boiled water. Thus, the gastric mucosa is cleansed and bile is removed.
If stagnation appears in the upper parts of the digestive tract, propolis is used. 10 grams should be dissolved in ½ glass of vodka, left for 3 days and strained. Take 60 drops half an hour before meals.
Causes of the disease
The factors causing the constant reflux of bile into the esophagus are internal (physiological) and external (nutritional) reasons.
Internal:
- stomach pathologies: reflux esophagitis, gastritis, ulcer;
- chronic inflammation of the duodenal mucosa;
- gallbladder disease;
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- structural features of the sphincter between the stomach and duodenum;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- oncological neoplasms in the abdominal cavity;
- obesity;
- pregnancy.
External:
- unbalanced diet;
- drinking water at the same time as eating;
- dry food, snacks;
- binge eating;
- tobacco and alcohol abuse;
- long course of taking painkillers and analgesics;
- playing sports after eating;
- lifting heavy objects;
- uncomfortable posture during sleep;
- stress;
- passive lifestyle.