Helicobacter pylori infection and its symptoms
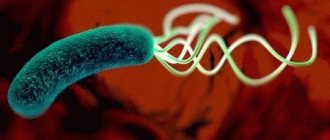
In appearance, the bacterium resembles a spiral surrounded by hairs. With their help, it quickly moves along the walls of the organs and chooses the pylorus of the stomach as its abode - the pyloric lower tier, which smoothly passes into the duodenum.
If a person has a strong immune system, then when a bacteria appears, the body can cope with it. However, it can cause harm that will be global in the future. In the area where the microbe resides, the amount of protective mucus is significantly reduced, hydrochloric acid actively moves towards it, and subsequently inflammation of the mucous membrane appears.
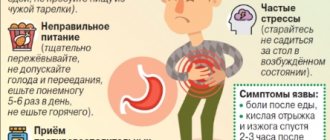
Symptoms of the presence of bacteria in the body are as follows:
- heartburn, belching;
- bleeding gums, coated tongue;
- nagging pain in the stomach;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- constant nausea.
These symptoms are characteristic of a disease called helicobacteriosis. They may indicate the appearance of ulcers and chronic gastritis.
Risk factors
Among the risk factors are the following:
- male gender and middle age;
- inadequate social and living conditions;
- ignoring the rules of personal hygiene;
- the presence of a microorganism in parents;
- working with carriers of bacteria (medical staff);
- promiscuity;
- swimming in open springs and drinking water from them;
It is worth noting that strong immunity is not always able to protect against bacteria. It multiplies well in the intestines even with normal natural defenses, since it can hide from immune mechanisms.
General characteristics of Helicobacter pylori in cats
Helicobacter spp. are gram-negative, microaerophilic, curved spiral motile bacteria
, which live in the stomach and, to a lesser extent, in the intestines and liver of cats. They break down urea into ammonia and bicarbonate and thus create a less acidic microenvironment in order to survive. Overall prevalence rates of Helicobacter are high in both cats (80-100%) and humans (20-100%, with higher rates in older people and poorer countries). Most Helicobacter infections are not associated with clinical signs. However, these bacteria can cause disease, such as the association with feline lymphoma due to the presence of the carcinogen Helicobacter.
Routes of transmission
The bacterium is transmitted from person to person and from animal to person. Research has found it in some species of monkeys and cats. There are three routes of infection that have been proven, and one more that has not yet been scientifically proven.
Fecal-oral
Heliobacter is excreted from the body in the feces and turns into a coccal form. In the latter, it can exist in the external environment for a long time. The microbe can enter the body of another person through objects on which it ends up and through contact with the dirty hands of the patient. You can become infected by not washing your hands before eating or by licking certain objects. This mechanism is typical for children who like to taste everything.
You can become infected through the fecal-oral route from sick animals. Most often this applies to cats. Infection is also common in Africa, where there are many monkeys, and the population has an extremely low level of hygienic education.
A variant of this route of transmission is infection of infants. During lactation, a mother does not properly handle her nipples, and bacteria can be transferred to them from her hands. The child swallows it with milk, then it inseminates the intestinal mucosa and develops rapidly.
Oral-oral
This method of transmission mainly occurs in adults, family members or couples. You can become infected through kissing. To some extent, the bacterium lives on the oral mucosa and dental plaque. The risks of infection increase if hygiene rules are not followed . When kissing, the bacterium can be transmitted to children from parents, but such cases are very rare.
Through the water
When the bacterium was first discovered, it was believed that it did not live in water. However, over time, research has discovered that Heliobacter is present in large quantities in water reservoirs and can be transmitted through water. Interestingly, chlorination, which prevents many infections, does not prevent the transmission of this microbe. It was discovered that in water with the addition of chlorine, pylori transformed into a coccal form and stopped growing, but did not die and retained its infectious properties.
Transplacental route
A blood test of babies born to infected mothers can detect antibodies to the microorganism. The child does not develop any symptoms of pathology. Observation of newborns with stool analysis shows the absence of bacteria in the intestines. Shortly after birth, the antibody titer decreases. All this is reason to believe that antibodies are transmitted to the baby through the mother's blood. The bacteria themselves in the blood do not penetrate or pass through the transplacental barrier, and infection does not occur.
Video on the topic: How to get rid of Helicobacter pylori and excess weight
Epidemiology and methods of transmission of infection
People living in developed countries are more susceptible to helicobacteriosis than others. Thus, preschool children become infected in 10% of cases, and the infection rate in adults is about 100%. Despite this, low economic and social status also increases the risk of bacterial infection.
Since helicobacteriosis is often asymptomatic and long-term, we can say that the level of infection increases with age. According to statistics, Helicobacter is detected in 20% of patients over 40 years of age. And in people over 60 years of age, these bacteria are found in 50% of cases.
In addition, there are occupational risks of infection. For example, bacterial Helicobacter gastritis is often diagnosed by gastroenterologists.
But where does Helicobacter pylori come from? Like other pathogenic bacteria, this parasite is not particularly adapted to survive in the environment. For these reasons, most microbes that are eliminated from an invasive organism die before they can find a host.
The best environment for preserving the microorganism is fresh and sea water, where it can live for 14 days. Consequently, transmission of bacteriosis occurs through the consumption of raw water.
In addition, a significant epidemiological danger is the consumption of raw vegetables watered with stagnant water stored in artificial or natural reservoirs.
What precautions should be taken to prevent family transmission?
If one of the family members has become infected with the bacteria, it is important to prevent its occurrence in other relatives. First of all, it is important to get tested. Precautionary measures focus on personal hygiene. Each family member should have their own dishes, towels and other household items . Bed linen, door handles and other items must be constantly processed. It is important to take care of proper nutrition, giving up bad habits and strengthening the immune system.
How to detect the disease
The bacterium can reside in the body without causing any inconvenience to the host. In this case, only research - blood and stool tests - will help identify it. It is also worth paying attention to the characteristic symptoms of its presence, which are listed above.
Is it possible to get infected again?
It is possible to become infected again, since a person does not have immunity to this microorganism. Often, re-infection occurs in the first 10-12 months after completion of therapy. This may be due to just one surviving bacterium.
Secondary pathology is very dangerous, as it can provoke relapses of ulcers, gastritis and gastric erosion.
Is joint treatment necessary in cases where one of the family members tests positive for Helicobacter pylori?
First, all family members need to be tested for helicobacteriosis. Moreover, this is also recommended for friends, other relatives and neighbors, since you can catch the bacteria even through a door handle. If the analysis confirms the presence of the microbe, then therapy is necessary.
What causes Helicobacter in dogs? How do we know if our pet is contagious?
In humans and animals, the bacterium spreads in the same way - through contaminated food and water. Naturally, protecting a pet is more difficult. The main sign of bacteria in dogs and cats is vomiting.
Healthy carriage is also common, when the microorganism is present but does not cause any inconvenience. In any case, only an examination by a veterinarian can reveal it. Pets can be carriers of many pathologies that are dangerous to humans, so owners must carefully monitor their health and observe hygiene standards that are necessary for the health of all family members.
Locations of Helicobacter
Each reader can imagine how Helicobacter pylori becomes infected by comparing facts from everyday life with the dislocation of the microbe:
- Stomach cavity.
- duodenum.
- Cal.
- Bile.
- Liver tissue.
- Skin.
- Saliva.
- Plaque.
From here, the transmission routes of Helicobacter pylori become obvious. Hypothetically, it is not difficult to catch the infection even on a public beach. However, the microbe is transmitted to humans primarily through the mouth. Although it is not a fact that the air route is excluded, as was found out in relation to salmonella. Simply put, doctors today themselves do not yet know the answer to questions about how to become infected with Helicobacter pylori. Although no one doubts whether the infection is transmitted from person to person.
Of course it is transferable! To avoid getting infected, behave carefully in public places, avoid eating places, and filter your social circle. Which of these postulates will surprise polite society? These are typical rules, following which you will avoid a number of problems. Cook food thoroughly and eat mostly home-cooked meals; avoid animals or maintain hygiene measures.
Prevention
Prevention of helicobacteriosis comes down to the following measures:
- The main thing is compliance with the rules of personal and household hygiene. It is important to thoroughly wash dishes and hands before eating, not touch dirty objects, and use personal household items. Children should be supervised to ensure that they do not put any foreign objects in their mouths. Only boiled water should be used.
- The body must receive sufficient amounts of vitamin C and beta-carotene. Their regular use helps reduce the likelihood of infection.
- To reduce the risk of infection, it is recommended to avoid promiscuity. Couples need to undergo appropriate examinations regularly.
Secondary prevention also includes the listed measures. It is also important that all family members are treated with antibiotics and regularly tested for bacteria in stool and exhaled air.
Prevention also includes strengthening the immune system. Proper nutrition and giving up bad habits are important.
Diagnosis and treatment
To accurately determine the presence of bacteria, the gastroenterologist prescribes a series of laboratory tests. The patient must undergo a blood and exhaled breath test. These two methods can give quick results. To obtain a detailed respiratory analysis, the patient must stop taking medications, especially antibiotics and alcohol, 14 days before the procedure. You will also need to refrain from eating legumes and chewing gum. According to indications, a biopsy of the stomach and duodenum is prescribed. With this method, a fragment of the mucous membrane is taken from the stomach. Using this procedure, you can find out the level of organ damage. Therapy, complex and multi-stage, is carried out with the help of medications: antibiotics and drugs that block the secretion of gastric juice.
PAY ATTENTION! Do not prolong gastritis or an ulcer until stomach cancer, it is better to be on the safe side, but this will be necessary. read the story of Galina Savina >>