Indications for testing for Helicobacter pylori
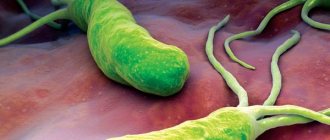
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative spiral-shaped pathogenic microorganism that inhabits the antrum of the stomach and intestines. The waste products of the bacteria lead to the fact that the mucous membrane of these organs of the digestive system will become inflamed, ulcers and erosions will appear on it. In the future, if left untreated, this will lead to the development of diseases such as gastritis, stomach ulcers and even stomach cancer. For the discovery of this bacterium, two scientists (Robin Warren and Barry Marshall) received the Nobel Prize.
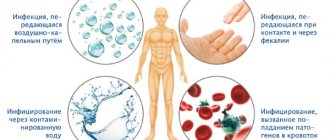
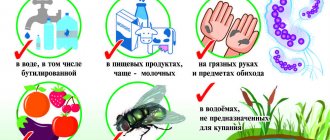
Helicobacter pylori can be transmitted from one person to another by kissing or by using common household items. Therefore, the bacterium first enters the body most often in childhood. The acidic environment of the stomach is not capable of destroying the microorganism, since it has its own defense mechanisms against it.
Sometimes the disease begins to develop immediately after the infection has occurred, and sometimes after a certain time interval. Often, a bacterium can exist completely asymptomatically in the body for several years and manifests its activity only as a result of a combination of certain factors, for example, after suffering stress or against the background of a sharp decrease in immunity.
A test for the presence of Helicobacter pylori should be done for those people who have symptoms of disorders of the digestive system, including:
- Frequent belching.
- Heartburn with secretion of acidic contents.
- Hiccups.
- Bad breath due to the health of the oral cavity itself.
- Stomach pain, feeling of discomfort.
- Abnormal bowel movements, in which diarrhea may be replaced by constipation.
- Symptoms indicating a failure in metabolic processes: hair loss, dry skin, increased brittleness of nails.
- Rapid saturation with small portions of food, disturbances in its digestion.
- Meat intolerance.
If a person has any of the above symptoms, they should be tested for Helicobacter pylori. Also, all family members should be tested, provided that one of them was found to have this bacterium.
When is it worth testing for Helicobacter?
Today, there are several diagnostic methods that can detect the presence of Helicobacter bacteria in the body. First of all, you can perform an FGDS or fibrogastroduodenoscopy. During this procedure, the doctor uses an endoscope to examine the stomach and capture a tiny piece of tissue from the mucous membrane - the so-called biopsy - for further histological examination.
In addition, Helicobacter infection can be detected using a blood test. The thing is that in the presence of this bacterium, the production of special antibodies-immunoglobulins begins. They can be detected during enzyme immunoassay. You can also determine whether the bacterium is present in the body using the polymerase chain reaction method to detect a DNA fragment of the bacterium in the stool. This bacteriological analysis determines the presence of parasites extremely accurately
However, recently another method of detecting infection has become particularly popular - the Helicobacter breath test. This is a quick, simple and non-traumatic procedure for the patient, with highly accurate results.
It is worth conducting a test for the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter Pylori in the body for any manifestations of problems with the digestive system. The following symptoms should alert you:
- frequent heartburn, belching of air or food;
- feeling of discomfort, heaviness, pressure in the stomach after eating;
- nausea after eating even in the absence of errors in the diet;
- aversion to meat food;
- sudden signs of metabolic disorders: brittle nails, increased hair loss, dry and flaky skin, unexpected allergic reactions.
In addition, it is mandatory to conduct a test for Helicobacter if this infection has been identified in one of your family members, as well as in diseases such as gastritis, peptic ulcer, gastroduodenitis. Only after diagnosis, the doctor can prescribe treatment that will prevent the development of severe complications caused by Helicobacter infection.
This is a spiral-shaped gram-negative bacterium, which is found in 90% of cases in patients with diseases of the stomach and duodenum. To date, the connection between H. pylori infection and the occurrence of these diseases has been proven. The bacterium enters the body with food, or by contact - from one person to another (through shared dishes, household items, etc.).
It is believed that, in the absence of treatment, H. pylori colonizes the gastric mucosa and can exist throughout a person's life, despite the host's immune response. The ability of H. pylori to colonize the mucous membrane and cause gastritis or gastric ulcers depends not only on the state of the host’s immunity, but also on the individual characteristics of a particular strain of the bacterium. Infection with H.
pylori may be accompanied by symptoms or be asymptomatic (without any complaints from the infected person). It is estimated that up to 70% of infections are asymptomatic and about 2/3 of the world's population is infected with Helicobacter, making this infection the most common in the world. The percentage of infection in the Russian population, according to various sources, reaches 60–80%.
This bacterium can survive in the acidic environment of the stomach, gradually impairing its functioning. Infection with H. pylori sometimes leads to very serious illnesses. Many cases of gastric and duodenal ulcers, gastritis, duodenitis, and even stomach cancer are etiologically associated with Helicobacter pylori infection.
There are several methods to confirm or refute the presence of infection. Endoscopic examination (FGS) with the removal of fragments of the gastric mucosa (biopsy) makes it possible to detect H. pylori bacteria during microscopic examination of a biopsy of the gastric mucosa or when cultured on nutrient media.
Unlike fibrogastroscopy (FGDS), the helic test does not require intervention in the body and is applicable to any category of patients. Such an examination is often prescribed if other methods are contraindicated (pregnant women, old age, children). The only exceptions can be patients with individual intolerance to urea solution.
Benefits of the breath test:
- no contraindications;
- high reliability – sensitivity up to 95%, specificity – up to 92%;
- speed – the test takes about 15 minutes, the result is ready immediately;
- non-invasive and painless (you only need to breathe into the tube);
- low price.
The only drawback of the method is that you need to carefully prepare for it, excluding almost all medications.
You can find out the cost of the procedure in the clinic and sign up for a urease breath test by phone.
The essence of the urease breath test for Helicobacter pylori
The breath test is based on the ability of bacteria to secrete a special enzyme - urease. It is necessary for Helicobacter pylori to prevent human gastric juice from destroying its lining.
In the stomach, urease breaks down urea into ammonia and carbon dioxide. The gas is released into the external environment. This is what the analyzer picks up.
There are several types of urease breath test for Helicobacter pylori, including:
- Breath urease test using isotope-labeled urea. In this case, during the procedure, the subject drinks a solution of urea, which was previously labeled with isotopes.
- 13C-urease breath test. In this case, urea labeled with the stable non-radioactive isotope C13 acts as a loading solution.
- Helic test. When conducting a helic test, they use not urea, but a urea solution.
Regardless of what type of examination is performed on the patient, they all have a high degree of accuracy.
Description of the analysis
The urease breath test detects the presence of the Helicobacter pylori bacterium in the body. This microorganism lives in the stomach of people suffering from pathologies of the digestive system. The bacterium is found in the patient's saliva and dental plaque. Infection occurs through kissing, violating hygiene rules, or sharing utensils and a toothbrush with an infected person. Helicobacter pylori is the causative agent of gastritis, as well as ulcers and malignant tumors of the stomach.
The bacterium secretes a special enzyme - urease. This substance is capable of reacting chemically with urea (urea). This produces carbon dioxide and ammonia. The urease test for Helicobacter pylori is based on this reaction. During the study, the patient consumes urea orally. The doctor measures the concentration of carbon dioxide or ammonia in the exhaled air before and after taking the drug.
Preparation for the procedure
Before being tested for Helicobacter pylori, the patient must carry out a number of preparatory measures.
- The study is prescribed no earlier than 3-6 days after taking antibiotics or antisecretory drugs. Also, 5 days before the procedure, you should avoid taking painkillers, antacids and NSAIDs. If a person takes any medications on an ongoing basis, he should consult a doctor about this to clarify the possibility of the procedure.
- At least 3 days before the study, you will need to avoid drinking alcoholic beverages.
- The day before the procedure, you should not eat foods that increase gas formation. It is recommended to remove potatoes, bakery and confectionery products, cabbage, peas and beans from the menu.
- The evening before the test, you should have a light dinner. Meals should take place 2-3 hours before bedtime.
- At least 6 hours must pass between the study and the last meal. The procedure is performed on an empty stomach.
- It is forbidden to eat in the morning; you should refrain from using chewing gum.
- You are not allowed to smoke before the procedure. You need to give up tobacco 3-4 hours before the procedure.
- Before performing the test, you should brush your teeth and rinse your mouth.
- You can drink water for the last time an hour before the test, but its volume should not exceed 100 ml.
If you follow all the suggested recommendations, the test result will be as reliable as possible.
How is the urease breath test performed with carbon-labeled urea?
The procedure begins with the patient being asked to breathe through a tube. It is located deep in his mouth, the oral cavity itself will be slightly open. You need to breathe calmly and smoothly. At this time, the doctor takes two air samples.
The patient is then asked to drink an isotope-labeled urea solution. After 15 minutes, another 4 air samples are taken. Care must be taken to ensure that the subject’s saliva does not enter the tube. To do this, he can remove it from time to time and smooth out the accumulated liquid. If it happens that saliva does get inside the sample, then the test should be stopped and repeated after an hour. Although modern devices make it possible to protect air samples from saliva.
Permits for test systems
The HELIC®-scan system is a combined device with a high-precision optical system and an air sampling pump.
- The disposable HELIK® indicator tube has been tested over many years of clinical practice and provides high sensitivity (95%) and specificity (97%).
- The disposable mouthpiece for the HELIK® indicator tube allows you to take an air sample in the most convenient way for the patient, while protecting against the risk of saliva contamination.
- A card with a QR code downloads information for adjusting the HELIC® scan and for subsequent interpretation of the results.
During the examination, two air samples are taken from the patient: before exercise and after. As a load, the patient takes a solution of 0.5 g of urea (this is safe). If the patient is infected with H pylori, then after taking urea, the ammonia content in the air of the oral cavity will increase and the indicator composition in the tube will significantly change its color relative to the initial (basal) level. The device reads and compares color changes and then interprets the result.
Main advantages of the method:
|
The use of the innovative HELIK®-scan test system makes it possible to obtain reliable results.
How is the 13C-urease breath test performed?
It is the 13C-urease test that is the most commonly used test for identifying Helicobacter pylori. During the procedure, only two air samples are taken from the subject.
The first sample is obtained in the morning on an empty stomach, and the second sample is taken half an hour after taking a solution of urea labeled with the stable isotope C13. The person exhales air into disposable bags that are specially designed for this procedure.
This type of research has a number of advantages, including:
- The diagnostic accuracy is high, reaching 100%.
- The procedure is safe for health, since no radioactive substances are used during its implementation.
- The research doesn't take much time. In general, 40 minutes is enough to complete it.
Types of testing for the presence of Helicobacter
- Respiratory diagnostics. The study is effective and absolutely safe; it allows you to accurately detect traces of bacterial waste products during two exhalations of the test subject. The test is based on the ability of the pathogen to produce urease, which protects the amoeba from the aggression of gastric juice. The result of urease tests is the reaction of Helicobacter pylori to a solution taken by the patient with a special type of isotope substance. The process of rapid diagnosis, which has no contraindications, is highly reliable (up to 95%), but only with proper preparation for the procedure.
- Blood test testing. The purpose of the test is to determine the presence in the blood of antibodies that are produced by the human immune system upon contact with the pathogen. The presence or absence of a foreign microbe is determined by the reference (threshold) value of the volume of immunoglobulins. If foreign proteins are absent, the result is considered negative; the presence of antigens (positive result) indicates infection. However, even with a negative test there is no guarantee that there will be no infection.
- Stool examination. The test, called PCR diagnostics, refers to polymerase chain reaction methods and is considered the most sensitive way to recognize pathogen DNA. To obtain reliable results, you should prepare for the collection of material in a certain way, then the accuracy of detecting DNA fragments of the microbe Helicobacter pylori reaches 96%.
- Gastroscopy with taking a sample for research. The endoscopic procedure has the unique ability to visually examine the walls of the digestive tract through the eyepiece of a gastroscope to determine the cause of the disease. If problem areas are detected, the doctor takes a biopsy sample for subsequent diagnosis of the presence of Helicobacter pylori in the cells of the stomach walls. The invasive method is called the HP test; the study eliminates the possibility of a false result.
An unexpected aspect: some gastroenterologists are not inclined to classify Helicobacter pylori as a group of harmful microbes. The bacterium is considered part of the protective microflora of the human body (by analogy with lactobacilli). A person requires treatment only if an ulcer or erosion is detected. It turns out that the microbe is considered a protector against intestinal infections, asthma (bronchial), and some types of oncology.
How is the helic test performed to identify Helicobacter pylori?
The helic test is carried out according to the same scheme as the 13C-urease breath test. The only difference is that instead of isotope-labeled urea, a person receives a solution of urea. Air is taken in 2 samples: before taking the solution and after taking it.
The undoubted advantage of the study is its complete safety for human health. This is the best test for detecting Helicobacter pylori in pregnant women and children. However, a number of experts question the accuracy of the results obtained. Therefore, the helic test is carried out only in Russia.
Interpretation of the results of a breath test for Helicobacter pylori
A breath test can give two results: positive or negative. The patient either has Helicobacter pylori in the body or has not been infected.
Also, using a special device called a mass spectrometer, the quantitative values of Helicobacter pylori in the body are determined.
The data obtained can be interpreted as follows:
- If the stabilized isotope in the exhaled air contains from 1 to 3.4%, then the degree of infection is mild.
- When the isotope concentration is in the range of 3.5-6.4%, they speak of an average degree of infection.
- Severe Helicobacter pylori infection will be indicated by rates of 6.5-9.4%.
- Extremely severe is indicated by values greater than 9.5%.
As a rule, the accuracy of the test is beyond doubt. It is possible to obtain a negative result only if the conditions for preparing for the study are not observed. Some drugs can reduce the activity of gastric juice production, which will make it impossible to break down urea.
Test results will be available 1-2 days after the test. The storage period for collected samples is 10 days, but no more.
Decoding the results
Analyzing the information received, the doctor makes a conclusion that the patient is infected.
The breath test is based on measuring the concentrations of urea and its breakdown products in exhaled air.
If there are no bacteria in the body, then the concentration of carbon dioxide with carbon 13C in the exhaled air will be equal to its concentration before taking an aqueous solution of urea. If the stress test contains a lot of carbon dioxide with labeled carbon 13C, this means that the patient is infected with Helicobacter Pylori.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
What to do if the test is positive?
If the test for Helicobacter pylori is positive, then the patient will need to undergo a comprehensive examination of the digestive system. The patient must be sent for an FGDS, which will provide information about the condition of the stomach and duodenum. He will also donate blood for biochemical and general analysis; other studies may be required.
Helicobacter pylori requires treatment. Depending on the severity and nature of the damage to the inner wall of the stomach, a therapeutic regimen is selected. However, to eliminate bacteria, antibiotics are always used, which are combined with proton pump inhibitors. In this case, two antibacterial drugs will be prescribed. This may be Amoxicillin, Levofloxacin, Metronidazole, Clarithromycin, etc.
During treatment or after its completion, the doctor may suggest that the patient take another test for Helicobacter pylori. This is required to monitor the effectiveness of ongoing therapy or to evaluate treatment already performed. A gastroenterologist treats diseases of the digestive system.
Biological basis of the technique
Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped bacterium that affects the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. Persistence of the microorganism leads to the development of gastritis, gastroduodenitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers.
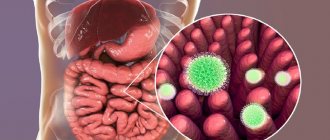
Bacteria on the stomach lining
Once in the stomach cavity, the bacterium penetrates the mucous membrane. There, having secured itself with the help of flagella, it begins to produce the enzyme urease. The pH around the bacterial colony increases due to the enzyme, which leads to the activation of compensatory mechanisms for the production of hydrochloric acid by stomach cells. Gastrin and pepsin are also produced in increased quantities.
In addition to urease, Helicobacter secretes mucinase, lipase and protease - enzymes that break down the upper protective layer of the gastric mucosa. As a result, hydrochloric acid, pepsin and gastrin enter unprotected areas of the gastric epithelium and begin to corrode it. At the site of exposure, inflammation appears first, then erosion and eventually an ulcer.
The bacterium itself is not exposed to the aggressive gastric environment, as it produces urease, which metabolizes urea to form ammonia. NH3 locally increases the pH to 6, which creates favorable conditions for life for Helicobacter pylori.
The urease test for Helicobacter pylori is based on the ability of the bacterium to break down urea.
Indications
The following categories of patients are recommended to undergo the diagnostic procedure:
- with epigastric pain on an empty stomach and immediately after eating;
- having relatives infected with Helicobacter pylori;
- receiving treatment for gastritis and duodenitis.
Types of tests
There are several types of diagnostic methods for detecting Helicobacter by the presence of the enzyme urease:
- urease breath test (UBT and HELIC test);
- rapid urease test with gastric biopsy.