Capsule endoscopy
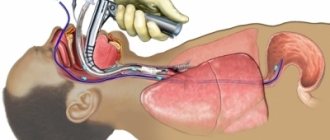
When using this technique, the study is carried out in a special capsule equipped with cameras and other sensors, which the patient must swallow. It scans the digestive tube as it naturally progresses and transmits data via wireless communication systems. This technique is one of the options for examining the intestines for diseases without the use of colonoscopy.
Main advantages:
- Simplicity and painlessness.
- Extensive data on the state of the digestive tract.
- High quality images and a lot of additional data.
Capsule endoscopy also has disadvantages, the main one being the inability to take a biopsy and perform other manipulations. The movement of the capsule cannot be controlled, so the suspicious area cannot be examined in more detail.
What examination can replace intestinal colonoscopy?
Colonoscopy is one of the methods for examining the rectum, cecum and colon for various diseases, including cancer. However, due to the specifics of the research process, this method is not suitable for all patients. In modern medicine, there are several alternative procedures that can be used to check the intestines without a colonoscopy.
Advantages and disadvantages of colonoscopy
Alternative bowel examination methods
MRI and MR colonoscopy
Comments and Reviews
Irrigoscopy
The procedure consists of injecting a contrast agent into the large intestine (barium enema) and taking x-rays in several projections.
This allows you to accurately localize pathological areas of the intestine, detect peristalsis disorders, diverticulosis and other diseases. Irrigoscopy is safe, painless and does not take much time.
The main disadvantage of irrigoscopy is its low information content. There is also a fairly high probability of receiving false data when part of the intestinal contents is mistaken for a tumor or other pathology. As a result, a colonoscopy will still be required to clarify the diagnosis.
PET – positron emission tomography
The procedure lasts 1.5 hours. The patient waits one hour for the results. Radioactive sugar is used in the examination method. Administered intravenously. With its help it is possible to diagnose oncological diseases and tumors. Pathological cells absorb the substance - it is easy to see their location.
This is from the field of nuclear medicine, created by using a special type of scanner and atoms to establish an assessment of the functioning of organs. The effectiveness of the method depends on the drug used.
The method is prescribed together with CT. The combination of PET results with CT images allows one to acquire detailed information about the location of radioactive elements. Determine the stages of oncology, checking the function of blood flow or organ function.
Such an examination without a colonoscopy makes it possible to detect cancer at an early stage.
For tumors, the method will help:
- reveal distant metastases;
- assess the process of tumor spread;
- diagnose relapses
- detect stages of cancer
- monitor the condition of the organ after surgery.
Magnetic resonance and computed tomography
Whether an MRI can be done instead of a colonoscopy depends on the intended diagnosis and other individual characteristics of the patient. This procedure has a number of advantages:
- Simple and fast procedure.
- There is no radiation exposure to the body and no discomfort.
- Quite high accuracy.
This type of diagnosis makes it possible to detect pathological changes in the intestinal wall that are 1 cm or more in size. The main disadvantage of the method is the inability to take material for biopsy and low resolution. Typically, MRI is used to clarify data obtained by other methods, for example, to accurately localize metastases in cancer.
CT scans also provide fairly detailed images. To increase the resolution of the procedure, complete bowel emptying and the introduction of a radiocontrast agent are required. Regular air is often used for this purpose.
The main disadvantage of computed tomography is its high radiation exposure. If the patient is not properly prepared, false results can be obtained. Therefore, CT is used relatively rarely in the diagnosis of colon diseases.
What examination can replace intestinal colonoscopy?
Colonoscopy is one of the methods for examining the rectum, cecum and colon for various diseases, including cancer. However, due to the specifics of the research process, this method is not suitable for all patients. In modern medicine, there are several alternative procedures that can be used to check the intestines without a colonoscopy.
Advantages and disadvantages of colonoscopy
Alternative bowel examination methods
MRI and MR colonoscopy
Comments and Reviews
Stool tests
How to check in another way is a question that is relevant for most people over 40 years old. Regularly performing this endoscopic procedure is associated with quite a lot of inconvenience for the patient and requires careful preparation and diet. An alternative may be DNA testing of stool. They are aimed at identifying specific DNA molecules belonging to tumor cells.
Stool can also be analyzed for the presence of occult blood and a fecal immunochemical test can be performed. All these laboratory techniques make it possible to accurately detect cancer, even at the earliest stages of development.
Important
Please note that any intestinal examination cannot serve as a complete replacement for colonoscopy. In most cases, they are used as screening, that is, to detect signs of pathology in the early stages of development.
Intestinal examination, which method to choose instead of colonoscopy?
Dina
303 views
May 27, 2020
Please advise which diagnostic method is best for me to use to examine the intestines and abdominal organs? I am 55 years old, I have been taking hormone replacement therapy (Livial, the main substance is tibolone) for 2 years. Last summer, after switching to proper nutrition (excluding bread, sugar, introducing a water regime of 1.5 liters per day) and cleansing the intestines and lymphatic system with natural preparations, I lost a lot of weight by 14 kg (from 67 kg to 53 kg over 4 months). In December I turned to a preventive medicine physician. Various examinations were prescribed: general blood, blood biochemical analysis, general urine analysis, feces for several types of studies, incl. for dysbacteriosis, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, gastroscopy. After receiving the test results, appropriate treatment was prescribed. I took treatment for 3 months, my condition was good, but my weight did not increase. Currently, I am worried about sensations of being sucked into the upper part of the stomach, a vacuum state (the same symptoms existed before treatment), not related to food intake (they arise suddenly and go away on their own); periodic painless sensations of the presence of something incomprehensible in the solar plexus area, closer to the right side, under the ribs (an ultrasound of the liver in December 2019 revealed a questionable hemangioma), which also suddenly arise and also suddenly go away. The doctor recommended that I have a colonoscopy of my intestines (the results of gastroscopy done in January 2020 were without pathology). I have had many operations on the intestines in the past (at the age of 14 I suffered peritonitis due to appendicitis, 10 days after appendicitis (the intestines were punctured during the operation) - intestinal obstruction, then adhesive disease, infertility 1, in 2006 an endometrioid cyst of the left ovary, tubal plastic surgery (in the hope of getting pregnant). I can’t stand a colonoscopy without anesthesia, because my adhesive process has not gone away. I’m afraid to do a colonoscopy under anesthesia, because there may be a puncture of the intestine again. Currently, there are several alternative methods for examining the intestines and abdominal organs - MRI or CT with and without contrast. Which examination is best for me to do instead of a colonoscopy, taking into account my problems?
Age:
55
Chronic diseases:
Chronic adhesive pelvioperitonitis. Chronic migraines.
The question is closed
intestines
constipation
discomfort in the right hypochondrium
Hydrogen test
A hydrogen breath test is a diagnostic method that does not involve penetration into the body, but allows one to detect pathological changes in it, especially in the digestive tract. In this way, it is possible to establish the true cause of chronic dysbiosis, abdominal pain, lactose intolerance or fructose malabsorption.
The human intestine is filled with a large number of anaerobic bacteria, which produce hydrogen in large quantities. During the breath test, the time of increase in hydrogen concentration is recorded and then, based on these indicators, the section of the intestine in which fermentation processes occurred intensively is determined.
The test is indicated in the following cases:
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- suspicion of intolerance to sugars (lactose, fructose, sorbitol, xylitol);
- inability to digest certain foods or their components (whole milk, fruits, honey);
- increased concentration of microorganisms in the small intestine;
- insufficient secretion of pancreatic juice necessary for digestion;
- irreversible process of replacement of parenchymal liver tissue with fibrous connective tissue;
- symptoms of disturbed microflora (bloating, diarrhea, constipation);
- assessment of the effectiveness of treatment of intestinal diseases associated with atrophy of the small intestinal villi.
In healthy people, hydrogen is practically not formed in those parts of the digestive tract where there is no fecal flora.
Basic methods of intestinal examination
The main examination methods for checking the intestines without colonoscopy include superficial and deep palpation. It helps to detect the place where pain is localized, enlargement of internal organs, and compactions. Next, the patient is sent for a series of tests:
- Blood. She gives in on an empty stomach in the morning. The analysis helps determine infectious pathologies, inflammation, the presence of parasites, and internal bleeding.
- Biochemistry. Determines how nutrients are absorbed.
- Urine. Attention is paid to its density and color.
- A coprogram, with the help of which the general condition of the intestines is determined, the presence of foreign impurities (pus, undigested food, blood, etc.).
Most often, colonoscopy is prescribed, which differs from other methods in being more informative. However, a more modern and simpler method is capsule diagnostics. Ultrasound, CT, MRI, and X-rays may also be prescribed. They are used if a colonoscopy cannot be performed for some reason.
Invasive
MRI is a good alternative, but the cost of diagnosis is much higher. This type is sometimes prescribed as an additional study. During MR colonography, 2 liters of contrast is injected into the colon. The intestines are then examined using a 3D image. The duration of the diagnosis is about an hour. Other research methods are listed in the table.
| Examination method | Short description |
| CT scan | A contrast agent is also injected into the body. However, small pathological lesions are quite difficult to evaluate. However, with this diagnosis, the mucous membrane is not damaged, tissues with increased density are well identified, the contours of pathological foci and the condition of nearby organs are assessed. |
| Irrigoscopy | Helps assess the location of tumors, their shape, size and mobility. During the procedure, a barium mixture is injected into the patient's body using an enema. Then pictures are taken. To identify congenital fistulas, scars, ulcers, etc. After barium is removed, air is introduced. This allows you to see the contours of pathological foci. |
| Capsule study | It is mainly used when colonoscopy is hampered by the anatomical features of the structure of organs, there is internal bleeding, or suspected tumors. The patient swallows a capsule approximately 10 mm in diameter and 30 mm in length. It is equipped with mini stones. While the capsule moves through the intestines, pictures are automatically taken. The device is excreted in the feces. Information from the capsule is transferred to a computer, where, after processing, images are displayed on the monitor screen. Diagnostic duration is 5-8 hours. |
| Anoscopy | Used only to examine the lower part of the rectum. An illuminated optical device is inserted into the anus. If necessary, a biopsy is performed. Diagnostics helps to identify polyps, tumors, and hemorrhoidal lesions. |
| PET (positron emission tomography) | A good method for checking the intestines for cancer without a colonoscopy . The patient is injected intravenously with radioactive sugar. This makes it possible to detect malignant neoplasms, since cancer cells absorb the substance in large quantities. The duration of the procedure is 1.5 hours. |
Rectomanoscopy is done once every five years. In this case, only 30 cm of intestine is assessed, and if necessary, a tissue sample is taken. However, this diagnosis does not provide an idea of the presence of pathology and the stage of its development. Rectomanoscopy combines three procedures - proctoscopy, anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy.
Non-invasive
The simplest non-invasive method is palpation. It can be superficial or deep. In the first case, palpation is carried out from bottom to top. This way the entire abdomen is checked. With deep palpation, strong pressure is applied. Palpation causes severe discomfort. However, for a healthy person, deep palpation will not cause anxiety or pain. Other methods:
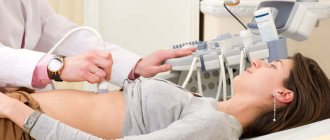
- Ultrasound is a non-invasive research method. The internal organs are assessed using a transducer that picks up an image of sound waves. After processing in a computer, the signals are displayed on the screen as an image. This allows you to visualize tumors and their size, but there is no way to determine the malignancy of the tumors.
- The hydrogen test takes three hours to complete. Every 30 minutes the patient exhales into the tube. This allows you to determine the presence of pathological bacteria in the body.
Non-invasive methods are used when intestinal lesions are superficial or minor and the use of auxiliary instruments or the introduction of substances into the body is not required.
Alternative
Alternative diagnostic methods include ultrasound, CT, MRI . An endoscopy may also be performed. It serves as a good alternative to intestinal colonoscopy. During the examination, polyps, adhesions or neoplasms are detected. The technique is invasive; a small sensor equipped with ultrasound is inserted into the intestine. It is directed as close as possible to the lesion.
Then it is carefully studied and its extent of distribution is revealed. Advantages – techniques – safety and painlessness. With the help of endoscopy, the doctor receives the most accurate information about the condition of the intestines and mucous membranes. At the same time, other organs of the gastrointestinal tract are examined.