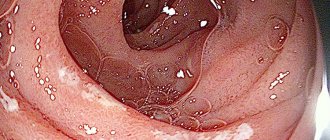
Modern medicine offers a wide selection of diagnostic procedures that allow the most complete examination of the stomach. All methods are conventionally divided into the following types: physical, clinical, instrumental diagnostics. Each type of research and method allows you to obtain a certain picture and, with a general analysis and interpretation of the results, make a diagnosis.
Diagnostic methods
Methods for examining the stomach are prescribed and carried out by a gastroenterologist based on the patient’s complaints about indigestion, abdominal pain, heaviness, bloating, heartburn, belching, and stool disorders.
The most common and effective traditional methods of examining the stomach are esophagogastroscopy (EGD), ultrasound, and fluoroscopy with contrast. Modernized, modern procedures that allow for a more accurate examination of the stomach include CT and MRI. Today medicine offers alternative options for diagnosing gastrointestinal diseases, such as video pill, electrogastrography and electrogastroenterography.
Depending on the type and power of the device, you can examine all organs of the gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, duodenum), take biomaterial for histology and cytological analysis. Methods for examining the stomach can be used in combination in complex cases, or only some of them can be prescribed.
First, the doctor analyzes the complaints, examines the patient, palpates and listens to his abdomen.
All manipulations performed by a gastroenterologist are combined into three large groups:
- A physical examination, when the doctor analyzes complaints, examines the patient, palpates and listens to his abdomen, determines how much the epigastric region hurts.
- Laboratory tests that involve examining the patient’s biological fluids and tissues for hemoglobin, general and biochemical parameters.
- Hardware techniques, when the patient is examined using certain devices, instruments and instruments.
Not always gastroscopy. Examination for abdominal pain
I have a stomachache? Which doctor should I go to? What is the best research to determine the cause of this pain? Is there even a “best”?
Especially for readers of our site, we organized a consultation on diagnostic methods for abdominal pain with specialists from the Expert Clinic Kursk.
Gastroenterologist: Soshnikova Natalya Vitalievna
- The stomach can hurt for a variety of reasons. Natalya Vitalievna, tell us how to understand that abdominal pain is probably associated with problems in the gastrointestinal tract?
If the cause lies in problems of the gastrointestinal tract, then, in addition to pain, there may be other symptoms. Among them:
- nausea, vomiting;
- heartburn;
- belching;
- rumbling in the intestines;
- bloating.
These additional signs do not always occur in diseases of the digestive system. For example, during an acute process there may only be pain.
— What specialty should you consult with a doctor if you discover any abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract?
If there is a gastroenterologist in a medical institution, then go see him. If not, see a surgeon or therapist. According to indications, other specialists can also be involved, since there are many diseases of the digestive system.
— What is included in the complex of patient examinations for suspected gastrointestinal diseases?
Primary screening includes:
— Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (more information about preparing for an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity can be read here);
— fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- General and biochemical blood test.
Based on their results, the doctor decides whether in-depth studies are needed or not.
Are you afraid to undergo gastroscopy? Read our material on the topic: Where can you find the courage to make up your mind? Gastroscopy – without fear!
— Is there a uniform standard for examining patients with abdominal pain caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or is the diagnostic complex selected individually in each specific case?
The standard includes the studies I mentioned above. If necessary, other examinations may be prescribed in each specific case. For example, stool analysis for occult blood, consultations with related specialists, etc.
CT specialist: Acting Head of the Department of Radiation Diagnostics Strokov Roman Aleksandrovich
— Roman Aleksandrovich, in what situations with abdominal pain can you not do without a computed tomography scan? When is this research method indicated?
In practice, the first will be an ultrasound. If the results obtained with its help are not enough or the cause of the complaints remains unclear, then more complex methods are used - such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
Read the material on the topic: What does an MRI of the abdominal cavity show and what is included?
CT most often helps in diagnosing pathologies such as acute calculous cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis, abdominal aortic aneurysm, urolithiasis (it can also cause abdominal pain), chronic intestinal ischemia. In addition, this diagnosis can be prescribed to detect:
- inflammatory bowel diseases (including acute appendicitis);
- complications and outcomes of inflammatory processes of the pancreas;
- some neoplasms of the abdominal organs.
— Is CT an independent diagnosis or, in order for the picture to be complete, does the patient need to undergo other methods of examining the gastrointestinal tract?
It all depends on the specific clinical situation. It happens that a computed tomography scan is sufficient to make a diagnosis. But it is also possible that it - like, in principle, any type of diagnostics - is used to complement another research method.
Increased gas formation in the intestines can reduce the information content of ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs
Ultrasound doctor: Zotolokin Sergey Vladimirovich
— Sergey Vladimirovich, how can ultrasound examination help in identifying the causes of abdominal pain?
Ultrasound is one of the leading methods with which you can answer a number of diagnostic questions. The fundamental difference, for example, from gastroscopy is that we examine “dense” organs (liver, pancreas, spleen and a number of others), and not tubular ones and not containing mainly or only air.
Ultrasound examination can detect signs of inflammatory processes, neoplasms, stones in the gall bladder, kidneys and a number of others.
— Is there an ultrasound examination of the stomach? How informative is it?
It is described in the literature, but in practice it is of little use due to its low information content. If, for example, there is a large tumor in the stomach, we will be able to notice it. For small formations and inflammatory processes, the diagnostic value of ultrasound in relation to the stomach is minimal.
— In what situations will ultrasound not give a clear picture of the state of the gastrointestinal tract?
This is possible, for example, if:
— Ultrasound is used to evaluate organs for which it is not intended due to its limitations as a diagnostic method;
— there is gas in the path of the ultrasonic wave (for example, in the intestines).
Read the material on the topic: You have been prescribed an ultrasound. What do you need to know before the study?
Endoscopist: Kalinina Yulia Nikolaevna
— Yulia Nikolaevna, why do you need gastroscopy? When is it prescribed and what does it reveal?
It is used for early diagnosis of diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract - esophagus, stomach, duodenum (for example, gastritis, erosive-ulcerative and tumor lesions).
It is prescribed for various symptoms:
- stomach pain;
- belching;
- nausea;
- loss of appetite.
A person can undergo this examination on his own initiative, without a doctor’s referral.
— In what situations is gastroscopy uninformative and cannot help identify the cause of abdominal pain?
This is possible when the cause or source of pain is not the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum, since this method is intended specifically for examining these organs. For other organs, it will not provide the necessary diagnostic information.
— Can capsule endoscopy replace conventional gastroscopy?
No. Firstly, the capsule cannot be controlled in any way while it moves through the digestive tube. In particular, in the stomach, she - purely statistically - may not “see” any pathological formations. Secondly (and this is a fundamental limitation of the method), with capsule endoscopy it is not possible to take a piece of tissue for histological examination.
When applied to the abdominal cavity, MRI has limitations in assessing hollow organs
MRI specialist: Acting Head of the Department of Radiation Diagnostics Strokov Roman Aleksandrovich
— Roman Aleksandrovich, how does magnetic resonance imaging help gastroenterologists diagnose patients with abdominal pain?
MRI is capable of detecting many pathologies of inflammatory, tumor nature, stones in the biliary tract, etc.
But, despite the fact that this method is good at identifying changes in parenchymal, solid organs, it has limitations when assessing the hollow organs of the abdominal cavity.
In many cases, MRI helps resolve questions that remain, for example, after an ultrasound.
— The condition of which organs of the gastrointestinal tract can be assessed by an MRI diagnostic physician during magnetic resonance imaging?
First of all, these are the parenchymal organs of the abdominal cavity (liver, pancreas, spleen), surrounding tissue, lymph nodes, and large vessels. The condition of hollow organs (intestines, stomach) is indirectly assessed: the prerogative in diagnosing their diseases belongs to endoscopic methods.
Acting Head of the Department of Radiation Diagnostics: Strokov Roman Aleksandrovich
— Of the methods we examined for diagnosing the causes of abdominal pain, which is the most informative?
If we talk about the number of situations where the method is the most informative, then this is MRI. However, one must always remember that depending on the organ, the disease and its stage, and the individual characteristics of the clinical situation, different methods may take precedence.
The research method(s) must be chosen by the doctor.
Gastroenterologist: Soshnikova Natalya Vitalievna
— Natalya Vitalievna, as a gastroenterologist, do you only need instrumental methods of examining the stomach to diagnose the patient?
No. Laboratory tests are also important. For example, with their help it is possible to establish the presence of the microorganism Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), which plays a significant role in the development of a certain form of gastritis, erosive and ulcerative lesions and stomach cancer.
You also need to remember that instrumental diagnostic methods make it possible to evaluate the structure and structural changes of an organ, while laboratory methods make it possible to study its functions.
— Can a patient independently understand the variety of diagnostics of stomach pathologies and choose the method that is suitable for him or should a doctor do this?
The research method(s) should be chosen by the doctor, since the same symptom may indicate different diseases and organs. For example, if the upper half of the abdomen hurts, then the problem may not only be in the stomach. Whether the doctor will prescribe gastroscopy, ultrasound, CT, MRI, etc., or a combination of them, will depend on his diagnostic assumptions.
Other materials on topics:
X-ray of the stomach: an eternal classic or a step back?
What does an MRI of the intestine show?
What to do if your child has a stomach ache?
Our doctors
Physical methods
The first way to make a diagnosis is to talk with the patient and perform a physical examination. It is carried out in several stages:
- Conversation, history taking, analysis of the patient’s complaints, especially the nature of the pain.
- General examination: evaluates the patient’s appearance, changes in skin color and structure. Pale skin, exhaustion, cachexia indicate cancer, advanced pyloric stenosis, and lack of hemoglobin. Grayish skin, anorexia, and a doomed look signal a stomach ulcer, bleeding, and decreased hemoglobin.
- Examination of the oral cavity. Caries indicates infection, missing teeth indicates poor digestion. The condition of the tongue is also used to diagnose the disease:
- clean, moist - ulcer in remission;
- grayish coating, bad odor - acute gastritis;
- dry tongue, acute abdomen - peritonitis, perforation of deep erosions, acute pancreatitis, lack of hemoglobin due to bleeding;
- atrophic, smooth surface - stomach cancer, chronic gastritis with low acid content in gastric juice;
- ulceration - poisoning with acids, alkalis.
- Palpation of the abdomen. In severely malnourished patients, the contours of the stomach are visualized, which can be used to determine pyloric stenosis, gross peristalsis, and tumors in the organ. When palpating, it is determined how much the epigastrium hurts, an acute abdomen, irritation or tension of the peritoneum are detected.
- Percussion. In a certain position of the body, for example, when you need to lie down and raise your arms up, conditions are created under which noises, splashes, high or low tympanitis are heard from the stomach.
- Auscultation. Listening allows you to evaluate the peristaltic sounds of the intestines and stomach.
Based on a physical examination, the doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis and can determine priority methods in order to conduct a more detailed examination of the stomach and duodenum.
Diagnostic procedures
Even an experienced doctor cannot always determine the cause of the illness based on external symptoms. Moreover, not every person can describe what he feels. Therefore, the diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases has its own sequence and cannot be done without instrumental and laboratory examinations. Some pathologies do not manifest specific symptoms at the initial stage, but gradually progress. Therefore, examination of the gastrointestinal tract is very important for the timely detection of diseases and prescribing the correct treatment. It is recommended that even healthy people undergo it periodically.
Before making a preliminary diagnosis and choosing examination methods, the doctor conducts a conversation with the patient. It is necessary to tell in detail about your feelings, what provokes them, when they arise. At the same time, the doctor is interested not only in the patient’s complaints. The specialist will definitely ask about habits, diet, and the presence of chronic diseases. It is also very important what illnesses parents and close relatives have. After this, the patient is examined. The doctor does this using physical methods.
These include palpation, percussion and auscultation. At first glance, it may seem that such an external examination is useless in determining the condition of the internal organs. But for an experienced specialist, even such an examination is informative. First, an examination of the oral cavity is performed, where the digestion process begins. The condition of the mucous membrane, teeth, and color of the tongue are important.
The examination begins with a conversation and general examination of the patient.
Then the doctor feels the patient’s stomach, determining whether the organs of the digestive system are enlarged, whether there are hardenings, scars, or enlarged veins. Palpation also allows you to determine the shape of organs, their pain and location. Auscultation or auscultation allows you to hear what sounds the intestines make as they work. Percussion is tapping, which allows you to clarify the shape, location and condition of internal organs.
After this, the doctor determines what other methods of examining the gastrointestinal tract the patient needs. There are quite a few of them, but usually 2-3 methods are chosen. It can be:
What does gastroscopy of the stomach show?
- pH-metry;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- probing;
- X-ray examination;
- colonoscopy;
- Ultrasound;
- scintigraphy;
- CT or MRI;
- blood, urine and stool tests.
Instrumental examination methods make it possible to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, the secretion of gastric juice, the level of acidity, and motor function. With their help, you can detect the presence of tumors, cysts, erosions or ulcers. Usually, to diagnose gastrointestinal diseases, the doctor prescribes FGDS and blood tests. Sometimes it is also necessary to check the condition of the liver, bile ducts and pancreas. Such a complete examination of the digestive system is necessary when it is difficult to make a diagnosis.
If a person doubts whether his digestive organs are functioning normally and whether he should go to the doctor, you can check the stomach and intestines yourself. To do this, you need to squeeze half a glass of juice from raw beets and leave it for a couple of hours. Then drink and observe bowel movements. If it happens quickly and the stool is beet-colored, it means the stomach and intestines are working normally. If your urine is colored and you don’t have bowel movements for a long time, you should consult a doctor.
Clinical and biochemical types
The laboratory examination technique involves taking blood samples (they are given from a finger and a vein), urine, feces, followed by their examination for specific parameters, in particular, hemoglobin.
Blood is analyzed in two ways:
- standard, when it is necessary to assess the degree of inflammation, anemia, determine the level of total hemoglobin and blood particles (erythrocytes, platelets, lymphocytes);
- biochemical, when low or high levels of bilirubin, amylase, hemoglobin, ALT, AST, and general characteristics of the blood serum are assessed. You should also take samples of biomaterials for cytology, histology and other specific tests.
A urine test allows you to judge the general condition of the body. For example, if the diastase level is increased, pancreatitis is suspected; if urobilin increases, jaundice is suspected.
Fecal analysis allows you to determine the presence of helminthic infestation, giardiasis, and detect hidden blood. The quality of digestion is also assessed. If you submit the material for culture, you can determine the state of the colon microflora.
Ultrasound examination of the stomach
The first instrumental, probe-free method for examining the stomach when the stomach hurts is ultrasound. However, ultrasound allows one to assess the condition of only the terminal, exit zones of the organ due to the peculiarities of its location and filling. Consequently, ultrasound allows us to examine part of the stomach, the duodenal bulb, the pyloric canal and cave, areas of the lesser and greater curvature, and the sphincter in the pyloric region. Advantages:
- ease of tracking peristalsis;
- duplex scanning;
- multi-positionality;
- high speed of the procedure.
Types and classification of gastritis
The disease is divided into two types:
- acute gastritis – characterized by a one-time exposure to irritants, manifests itself once;
- chronic gastritis - the disease systematically recurs.
Acute gastritis, in turn, is divided into four types:
- Catarrhal. It appears under the influence of food poisoning or poor nutrition.
- Fibrinous. Occurs under the influence of sublimate poisons or acids, as well as in complex infectious diseases.
- Corrosive. Appears after alkalis, heavy metal salts, and concentrated acids enter the stomach.
- Phlegmonous. It occurs as a result of complications or injuries after ulcers or stomach cancer and some infectious diseases.
In accordance with the classification according to the pathogenetic mechanism, when diagnosing gastritis (including chronic), it can be classified as one of the following types:
- type A, or autoimmune, is gastritis that appears under the influence of antibodies to the lining cells of the stomach;
- type B, or bacterial gastritis, occurs due to the harmful effects of the bacteria H. pylori;
- type C, or chemical gastritis, it appears under the influence of the reflux of lysolecithin and bile into the stomach.
Mixed AS or AB and alcoholic, drug-induced and other types of gastritis are also distinguished, depending on the origin.
X-ray
The method is carried out using a contrast agent in the form of a suspension of barium sulfate. Before the procedure, the patient drinks a solution that slowly fills the gastrointestinal tract. As the sulfate passes through, x-rays of different sections are taken. Decoding is carried out according to the following indicators:
- shape of a filled stomach;
- organ contours;
- uniformity of contrast distribution;
- structure, motor activity of the gastrointestinal tract.
Based on the combination of symptoms, peptic ulcer, tumor, gastritis, and evacuation dysfunction are diagnosed.
The most accurate data can be obtained by radial fluoroscopy on the condition of the laryngeal part, narrowing of the esophagus, diaphragm, codial parts and curvature of the stomach. Flaws:
- limited information content;
- constipation, difficulty passing hard, discolored stool.
Gastropanel
The methods are the fastest and most effective options for preliminary diagnosis of gastric pathologies. Gastropanel (cytology, histology) includes a set of safe tests that detect:
- dyspepsia;
- Helicobacter infection;
- atrophic form of gastritis.
At the same time, the risks of transformation of stomach diseases into cancer, peptic ulcer in the curvature, into severe atrophic forms with anemia with low hemoglobin, osteoporosis, pathologies of the heart, blood vessels, and central nervous system are assessed.
The essence of gastropanel diagnostics is the study of the patient’s venous blood according to a special program. The result includes a decoding and comparison of indicators with norms, a detailed description and recommendations for treatment, graphic diagrams of possible risks of developing a serious illness and complications.
Probing, endoscopy, biopsy
Probing represents methods for studying the secretory function of the stomach. This procedure allows you to obtain samples and evaluate the contents of the stomach according to a number of parameters: acidity, enzymatic activity, etc. For this, a special thin, flexible tube is used, which is inserted through the patient’s mouth into all organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Depending on the diagnostic purposes, the contents of the stomach and duodenum are selected from different parts.
During gastroscopy, colonoscopy or esophagogastroduadenoscopy of the stomach, a visual assessment of the condition of the organ is performed using an endoscope - a probe with an optical tube at the end of which there is a video camera and a lighting device. Using the procedure, superficial changes in the mucosa are detected that are not visualized by other methods. Goals of traditional gastroscopy or colonoscopy:
- differential diagnosis of neoplasms;
- recognition of the early stages of malignancy;
- tracking how deep erosion heals;
- identifying sources of blood loss;
- conducting biopsy histology;
- choice of treatment regimen.
During the manipulation, tissue samples are taken from the gastric walls for biopsy with cytology and histology, which involves examining tissue if polyposis or organ cancer is suspected. The main advantage is the ability to determine the onset of a malignant process at an early stage.
Analyzes
At the stage of making a preliminary diagnosis, laboratory diagnostic methods must be used. These include analysis of biological fluids of the body: blood, urine, and feces. They allow you to determine the activity of enzymes, the presence of inflammation, infections, parasites, and the state of the intestinal microflora. These tests do not make a diagnosis on their own, but are necessarily included in a comprehensive examination of the gastrointestinal tract:
- Diagnosis always begins with blood tests. It is taken on an empty stomach, it is advisable to stop taking alcohol and medications the day before. The blood is checked for ESR to detect the presence of an inflammatory process, pancreatic enzymes, antibodies to Helicobacter pylori or helminths.
- A general urine test is necessary for severe diarrhea and vomiting, as well as for suspected cancer. The density of urine, its color, and composition are assessed.
- To assess the state of the gastrointestinal tract, stool analysis or coprogram is very informative. It allows you to identify the presence of bleeding in the digestive tract, the presence of parasites, and infections. Undigested food remains indicate indigestion. You can also assess the state of the intestinal microflora.
Blood tests can reveal an inflammatory process, impaired enzyme activity, and the presence of parasites
Alternative Methods
Until now, to visualize the entire gastrointestinal tract, in particular the stomach, it was necessary to use unpleasant procedures involving swallowing a gastroscope. But the main advantage of such a device is its versatility, which consists in the ability to conduct an internal examination, take a biopsy for cytology with histology, carry out treatment (stopping bleeding that causes a drop in hemoglobin) or minor operations, for example, to remove small polyps.
But there is a category of people who cannot undergo gastrobiopsy according to indications, or who have an overestimated sensitivity threshold. For such patients, an alternative is offered - tubeless procedures, such as:
- capsule endoscopy;
- CT (virtual colonoscopy/gastroscopy);
- X-ray contrast examination;
- electrogastrography (EGG) and electrogastroenterography (EGEG).
Instrumental methods for examining the stomach
The stomach is examined using special devices that show the condition of the organ from the inside: structural changes, inflammation of the mucous membrane, an increase in the size of the organ. The doctor orders the test. A full examination is carried out in a medical institution under the supervision of doctors and in the absence of contraindications.
Ultrasound of the gastric cavity
This method examines almost all organs. Therefore, ultrasound examination of the stomach is a popular and effective method with which many diseases are diagnosed. The method is considered effective for identifying tumors and polyps, since it clearly projects dense tissue. Using ultrasound without FGS is not enough; a full examination involves the use of ultrasound in parallel with other techniques.
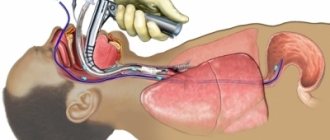
Gastroscopy
This method allows you to diagnose diseases not only of the stomach, but also of the esophagus. The research is carried out with a special instrument. The patient needs to swallow a colon, inside of which there is a fiber-optic system that displays the results on a screen. This examination of the stomach determines the presence of the following diseases:
- gastritis;
- duodenitis;
- esophagitis;
- peptic ulcer;
- neoplasms of various nature.
Magnetic resonance and computed tomography
These instrumental research methods are used quite rarely. These types involve emitting a magnetic field followed by receiving impulses from internal organs. The indicators are recorded on film, the cut of which is specified by the doctor. MRI shows every millimeter of the organ, and CT records changes in each layer. These modern types also have contraindications - pregnancy, the presence of a pacemaker.
Capsule gastroscopy
This is an alternative method that can replace gastroscopy.
This is an alternative method that can replace gastroscopy. The stomach and esophagus are examined using a special apparatus - a capsule with a lens at the end. If during a conventional gastroscopy the intestine is swallowed, then with this method the patient, swallowing the device, can go about his business. The doctor's assessment is carried out after 8-9 hours, when the capsule comes out naturally. Using this method, the doctor evaluates not only the stomach, but also the esophagus.
X-ray examination
In addition to CT and MRI, a radiograph is also used. Testing in this way involves the use of a contrast agent. During the first sip of the substance, the first recording of the results is carried out and then the images are taken in stages. The duration of the procedure is 30-45 minutes. During the session, to get a complete picture, the patient is asked to change body position. After checking the stomach in this way, preparation for irrigoscopy, a contrast study of the large intestine, can be prescribed.
FGDS of the stomach
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is one of the most popular and accurate research methods. This technique not only shows the location of the pathological process, but also its root cause. In addition, through FGDS, it is possible to precisely apply medications and remove foreign bodies from the gastric cavity. For the study to be successful, it is necessary to prepare for it correctly: do not eat 10 hours before the test, and also become familiar with the contraindications.
Other methods
Checking the stomach can also be carried out using additional techniques such as chromoscopy and chromoendoscopy. These methods involve the use of a special substance that stains the mucous membrane of the organ to obtain a complete picture of deformation processes. Chromoscopy is safe for the body and is contraindicated only for people with individual intolerance to the components of the substance.
Another popular method is endoscopy, which involves inserting a sensor into the gastric cavity. In addition, deep palpation plays an important role, allowing a preliminary diagnosis to be made. If there is a suspicion of the development of neoplasms of any nature, a biopsy is prescribed - a microscopic examination of a fragment of the gastric mucosa, thanks to which the presence of oncology can be checked.
"Video Pill"
Capsule endoscopy is a minimally invasive, probe-free option for examining the gastrointestinal tract in real time. Advantages:
- more accurate data and breadth of assessment of the condition of the mucosa and walls;
- the ability to detect diseases in the early stages;
- absolute absence of pain;
- the ability to choose the optimal treatment regimen.
The essence of the procedure:
- the patient absorbs an 11x24 mm capsule equipped with a video sensor and goes home;
- as it passes, the device captures several thousand frames.
You need to start the manipulation on an empty stomach, after which you can eat regular food. The operating time of the capsule is 6-8 hours. During this time, it is allowed to lead a normal lifestyle, with the exception of playing sports and performing sudden movements. At the end of the specified time, the patient returns to the hospital to transfer data from the device. The capsule itself leaves the body naturally after a few days. Flaws:
- the impossibility of approaching the suspicious area for a more detailed examination;
- inability to take a biopsy for histology.
How to identify gastritis?
The disease usually appears unexpectedly. Pain in the upper abdomen begins sharply. They usually occur on an empty stomach and are cramp-like in nature. The pain is accompanied by nausea or vomiting, as well as heartburn, “sour” belching, a feeling of pressure and fullness in the epigastric region, as well as bloating. In the chronic form of gastritis, the patient often experiences diarrhea or constipation. The disease affects the general well-being of a person. He feels lethargic and drowsy, fatigue increases and irritability occurs. Gastritis affects the tone of the body and can affect the cardiac system, causing numbness in the upper and lower extremities and a burning sensation in the mouth and tongue.
The disease can occur without obvious signs, especially in a chronic form. But, as a rule, the first symptoms of gastritis are sharp pain in the epigastric region, which lasts a short time. The patient also periodically experiences heartburn and nausea. He has problems with bowel movements, which may alternate between constipation and diarrhea. The pain is often accompanied by vomiting, bleeding and dizziness.
After the first signs appear, diarrhea may occur throughout the day. If this happens, you need to completely stop eating food and urgently go to the hospital where your stomach will be washed out. If the symptoms are accompanied by bleeding, the patient is injected with drugs that reduce the synthesis of hydrochloric acid. In this case, medications are prescribed to promote the healing of erosions.
MRI
A modern non-invasive procedure for examining the entire body, in particular the stomach, is magnetic resonance imaging. It is performed on a special tomograph equipped with a movable electromagnetic table, a camera, and a computer with a powerful OS for visualizing the stomach and processing the data obtained. To do this, the patient lies down on a table that slides into the tomograph. While the patient lies motionless, following the doctor’s instructions, pictures are taken and transferred to the PC. Advantages:
- minimal preparation for the procedure;
- no pain during conduction;
- obtaining a clear 3D image of the affected areas;
- no problems with the removal of solid feces.
Flaws:
- high price;
- the need for the patient to have no metal implants or pacemakers.
Diagnostics
When the first signs of stomach disease appear, you should contact a gastroenterologist as soon as possible. After an initial examination and palpation of the abdomen, the doctor may ask several questions about previous diseases and chronic pathologies.
The doctor may also ask about complaints and observed symptoms. This is necessary to compile a general history and clinical picture of the disease.
To identify stomach diseases, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- Gastroscopy is a special technique for diagnosing diseases of the stomach and duodenum (gastritis, ulcers, duodenitis, etc.). Thanks to it, you can get a clear image of the organ, which is taken with a gastroscope camera and transmitted to the monitor screen.
After this, the results are recorded and printed. The doctor re-examines the image and makes a diagnosis.
The gastroscopy procedure is performed by a doctor using special equipment. The patient is prohibited from eating and drinking ten hours before the appointment. Before the study begins, the patient's throat is treated with lidocaine for pain relief. Next, the person clamps the mouthpiece and a gastroscope is inserted into his oral cavity. Gradually the person relaxes their throat and the tube is inserted further into the throat.
After the procedure, the unpleasant sensation in the throat remains for another day.
- Endoscopic diagnosis is done using a device - an endoscope. It allows you to most accurately identify all pathologies in the stomach.
- Fluoroscopy is used to identify not only pathologies of the stomach, but also all organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Using this technique, you can save the obtained research result and record it on film.
The procedure itself is painless. It is done in 5-10 minutes.
The main disadvantage of fluoroscopy is considered to be radiation exposure, but with the advent of modern techniques, the dangerous effects have been minimized.
- Computed tomography is the type of test most often used to diagnose stomach cancer. With its help, you can most accurately identify the stages of cancer and forms (early, middle, advanced), and the location of the tumor.
The procedure is painless for the patient and completely non-traumatic.
- Ultrasound is a quick and painless way to accurately diagnose stomach diseases. During this procedure, the patient needs to lie on the couch while the doctor moves a special sensor across the abdomen. In this case, the image will be transmitted to the monitor screen.
Using ultrasound, you can see the location, shape and structure of the stomach. This will help you choose the right treatment.
- As laboratory diagnostic methods, general blood tests and urine and stool tests are used.
CT
Computed tomography is a virtual gastroscopy/colonoscopy. The stomach is viewed using X-rays in a tomograph. The presence of pathological seals is determined by the throughput of X-rays:
- dark, clear tissue indicates polyposis disease;
- light, gray - absence of formations.
By rotating the device, you can obtain a slice of an organ or seal. Disadvantages of virtual colonoscopy:
- inability to identify small seals;
- the need to insert a tube into the colon to supply air and expand the gastrointestinal tract, which improves visibility, and this can cause pain and discomfort;
- careful preparation with a consistent diet is required.
Virtual beam colonoscopy is contraindicated:
- pregnant women;
- for obesity.
How can you check the gastrointestinal tract using hardware techniques?
At the next stage, proven instrumental techniques are used. They are not able to replace each other. Each examination is prescribed after studying the clinical picture in order to assess the morphological and structural features of the organ.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound of the stomach is also called echography. This is a technique based on the ability of tissue to reflect passing high-frequency sound waves. Simply put, ultrasound is an ultrasound examination. It is not very informative for an adult, but it is used quite often in children. The fact is that echography does not make it possible to see the entire pathology, perform a biopsy, or study the nature of the changes. But since other hardware methods can cause discomfort in the child or are generally contraindicated for him, doctors begin the examination with an ultrasound - to confirm the suspicions of the gastroenterologist. It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis this way.
Using ultrasound, the epigastrium is checked in the following cases:
- increased gas formation;
- pain in the organ area;
- problems with digestion;
- suspicion of gastritis, ulcers, polyps or cancer.
The procedure does not take much time. The patient learns the results immediately.
CT scan
If diagnosis is difficult, doctors refer the patient to a CT scan (computed tomography). The study provides information about the shape and size of the organ, the condition of the musculoskeletal system, the thickness of the abdominal wall and the presence of foreign bodies. CT is more informative than x-rays and is characterized by less radiation exposure.
MRI
MRI is a method that allows you to obtain accurate information about the condition of the stomach. The images obtained during the examination make it possible to assess the condition of the vessels and lymph nodes, whether there are stones or cysts, polyps or tumors in the organ, and also to study the structure of the tissue.
X-ray with contrast
X-ray is the most accessible and inexpensive diagnostic method. It is used to evaluate parameters such as:
- Wall thickness;
- shape and size;
- the presence of ulcers, neoplasms.
Even more information can be obtained by irrigoscopy, or x-ray with contrast. Barium is used as a contrast agent. The patient drinks a capsule containing barium and is then examined. Barium is opaque to X-rays, so the image is more accurate than without contrast.
EGG and EGEG
The methods of electrogastrography (EGG) and electrogastroenterography (EGEG) are based on the assessment of peristalsis of the elements of the digestive system. A special device reads impulses of electrical signals coming from the organ during the digestion of food. The study is used as an auxiliary study. Its main disadvantage is the long period of time (three hours), and in this way it is not possible to examine the stomach completely.
The difference between the methods is that during EGEG the electrical activity of the stomach and intestines is examined, while during EGG only the stomach is examined.
Gastroscopy and sounding
Examination of the stomach using a flexible probe, to the end of which a mini-camera is attached, is called gastroscopy or EGDS (esophagogastroduodenoscopy). The examination is prescribed before planned surgery, in case of significant weight loss, as well as any symptoms of gastric pathologies. The procedure has contraindications:
- respiratory failure;
- heart rhythm problems;
- hypertensive crisis;
- stroke;
- mental disorders.
Proper preparation for the examination plays a major role in obtaining a reliable result. Usually the doctor tells the patient about this in detail.
The procedure does not take more than ten minutes. The subject swallows the endoscope, which transmits the image to the monitor, and the specialist conducts an examination.
In case of chronic gastritis and stomach ulcers, it is necessary to examine gastric juice. For this purpose, probing is carried out. You should prepare for the study:
- do not eat the day before (a light dinner is allowed no later than 20:00);
- In the morning, do not smoke, do not drink, do not take medications, do not eat.
Gastric juice is taken using a special probe. It is administered through the mouth and esophagus, and biomaterial is removed. Then the probe is removed, the patient has breakfast, after which another portion of gastric juice is taken.
The examination results include a description of such characteristics of the biomaterial as:
- color;
- quantity;
- smell;
- acidity.
In this way, the functional and morphological state of the mucosa is assessed and the secretory function of the stomach is determined.
Capsule endoscopy
Capsule endoscopy is the newest instrumental method for examining the esophagus and stomach. This is an excellent replacement for gastroscopy. For the study, a special apparatus is used - a small capsule with a built-in lens that allows you to take many pictures as it moves through the digestive tract.
The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach, the patient washes down the capsule with water and can go about his business. After 8-9 hours, the capsule will leave the body naturally, but before that it will transmit information to the doctor’s computer. After reviewing the data obtained, the specialist can draw conclusions about the condition of the gastric mucosa.
Barium porridge and x-ray
X-ray contrast diagnostics involves examining the lumen of the stomach, its performance, motility, and ability to evacuate by obtaining X-ray images after ingesting barium porridge. To obtain detailed images, the patient must constantly turn over and may need to raise his arms above his head. The procedure lasts 2-4 hours. Disadvantages of the method:
- lack of information in the initial stages of inflammatory processes or pathologies with minor deviations from the norm;
- thorough preparation for manipulation;
- the need to fast for some time and come for manipulation on an empty stomach;
- abdominal pain, constipation;
- You may begin to pass hard white stool containing barium after the procedure.
Instrumental methods for studying the digestive organs
Endoscopic examination
- esophagoscopy;
- gastroscopy;
- duodenoscopy;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- colonoscopy (flexible colonoscope) with multiple step-by-step targeted biopsy.
During endoscopy, according to indications (for example, for ulcerative and erosive processes), a targeted biopsy is performed with material taken for microbiological testing for the presence of H. pylori.
The presence of H. pylori can be determined by the results of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) and PCR with this antigen.
Plain radiography of the abdominal cavity
Allows you to detect structures containing air or calcifications, tumors, etc.
- perforation of any department; gastrointestinal tract into the abdominal cavity;
- calcifications and stones in the hollow organs of the abdominal cavity.
X-ray contrast studies
X-ray contrast study allows you to evaluate:
- stomach position;
- its shape;
- the nature of the relief of the mucous membrane;
- contours and elasticity of the stomach wall;
- state of its towing function
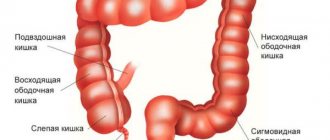
A study with barium passage through the small intestine reveals:
- intestinal villous atrophy;
- dilatation of intestinal loops;
- defects in the filling of the small intestine.
Irrigoscopy allows you to evaluate:
- position;
- shape;
- colon displacement;
- the state of its lumen and the severity of haustra;
- relief of the mucous membrane.
Laparoscopy
It makes it possible to directly visualize internal organs, which makes it possible to confirm the presence and extent of the disease, in particular, the involvement of the peritoneum in the inflammatory process.