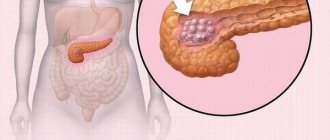
Types of benign intestinal tumor formations and their symptoms
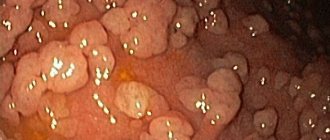
Typically, a polypous formation inside the intestine is benign, forming from epithelial tissue cells and growing into the intestinal lumen. Polyps vary in size, shape, they can “stand” on a stalk or on a broad base, single, multiple (polyposis), soft texture.
Intestinal pathology in the form of polyps is usually observed in older people, overweight people, diabetics, and heavy smokers; it can also be caused by genetic mutations.
Considering the frequency of occurrence of polyps in different parts of the intestine, you can notice that most of them develop in the sections of the colon and rectum, and less in the small intestine. In the duodenum, polyps are diagnosed quite rarely (approximately 0.2% of all endoscopic examinations).
A tumor-like growth in the form of a polyp is not oncology, but over time there is a possibility of its transformation into a malignant tumor.
There are many types of polypous formations in the intestines, but among them the most common are:
- Adenomatous , which are observed in approximately 70% of older patients. It is this type of tumor formation that is more likely than others to degenerate into a low-quality tumor.
- Serrated polyps, depending on their size and location, have varying degrees of malignancy. If small formations are located in the lower region of the colon, the risk is minimal, but if the polyp is large and located in the upper region of the intestine, then the risk of malignant transformation increases.
- Inflammatory polyps are formed when intestinal pathologies such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis occur. Although this type of tumor-like growth has a low percentage of degeneration into oncology, the treatment process should not be neglected.
The effectiveness of treatment of intestinal polyps abroad depends on an accurate diagnosis and determination of the type of pathology.
Treatment
Diagnostics allows us to develop a treatment and rehabilitation plan for the patient.
The main method of helping to identify formations in the lower gastrointestinal tract in adults and children is surgery. Treatment of intestinal polyps without surgery is ineffective. The exception is elements up to 5 mm of the hyperplastic type, total polyposis. In this case, observational tactics are used. A conservative approach is used in a limited category of patients when polyp removal is impossible for objective reasons.
The treatment protocol includes:
- dietary nutrition;
- invasive intervention (surgical removal);
- drug correction when preparing the patient for surgery.
Medications
Specific therapy that can eliminate mucosal growths has not currently been developed. Some information sources talk about the advisability of using aspirin tablets or drugs that are selective COX-2 inhibitors. Studies show a reduction in the likelihood of developing adenomatous elements and colorectal cancer by up to 50% in people at risk. But such drugs for polyps are not prescribed for a wide range of people.
Conservative therapy is recommended as a preparatory stage before surgery. Medicines are prescribed that eliminate the inflammatory process, normalize intestinal motility, and restore normal microflora. Depending on the clinical manifestations, the following medications are used:
- sorbents;
- prebiotics and probiotics;
- laxatives;
- anti-inflammatory suppositories;
- antidiarrheal substances;
- antibacterial drugs;
- enveloping substances.
Important!
For constipation due to intestinal polyposis, it is recommended to use microenemas to avoid traumatizing the formations with solid feces.
Diet food
When tumors are detected in the lower gastrointestinal tract, the diet is developed taking into account clinical characteristics. Depending on the type of functional impairment, table 3 or 4 is prescribed. However, there are general recommendations for the menu.
Nutrition for intestinal polyps should not irritate the mucous membrane and provoke inflammatory changes. Therefore, it is recommended to steam, boil or stew dishes. Excludes:
- fatty, fried, spicy foods;
- dishes made from coarse vegetable fiber.
In this case, the daily diet must include the necessary nutritional components, vitamins and minerals to ensure normal metabolism.
Allowed to eat:
- porridge;
- potato;
- carrot;
- pumpkin;
- spinach;
- lean meat;
- thermally processed fish.
Includes fresh diluted juices and fermented milk products.
It is prohibited to use:
- strong broths;
- full fat milk;
- Rye bread;
- coffee;
- tomatoes;
- citrus;
- yeast baked goods;
- canned food;
- marinades;
- drink alcohol;
- carbonated drinks.
The diet involves split meals up to 5-6 times a day so that the ingredients are better absorbed.
Symptoms of polyps in the intestines
The presence of polyps in the intestines is difficult to determine by any specific clinical signs. The degree of symptomatic manifestation depends on the volume and location in the intestine, the number of formations, their structure, the transformation process and other factors.
However, among the key symptoms that may indicate polyps in different parts of the intestine, the following manifestations should be mentioned:
- the presence of bloody and mucous discharge;
- periodic pain in the lower abdomen, cramping in nature;
- abnormal bowel function (constipation, diarrhea);
- sensation of a foreign body in the anal area with large polyps;
- fullness of the stomach, belching, nausea;
- rectal bleeding;
- changes in stool color (from dark with blood streaks to black);
- anemia due to constant intestinal bleeding.
However, when the polyp is small in size, symptoms do not appear in any way. Tumor-like growths of this nature are detected during screening, which is an integral part of the cancer treatment program abroad.
Causes of polyps in the rectum
The real reason for the formation of polyps is still unknown. A number of factors have been discovered that can provoke their appearance and growth:
- chronic inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract;
- stagnation of feces caused by constipation and, as a result, irritation of the rectum;
- diarrhea also irritates the intestinal mucosa;
- hereditary factor - the risk of occurrence is 10 times higher in those whose immediate relatives suffered from the pathology;
- chronic diseases in the intestines, such as colitis, proctosigmoiditis and ulcerative colitis - leave scars on the mucous membrane, which serves as a medium for the development of polyps;
- viral infections in the acute phase - violate the integrity of mucosal cells;
- unhealthy diet and bad habits, as well as a sedentary lifestyle, excess weight - create stagnant zones in the intestine through the outflow of lymphatic fluid and venous blood, causing constipation. Eating fatty and heavy foods disrupts digestion and negatively affects the mucous membranes of the rectum;
- unfavorable environment and harmful working conditions;
- intrauterine pathologies during the development of polyposis in children;
- endocrine diseases and menopause in women disrupt hormonal levels in the body.
More often, residents of developed countries and wealthy people suffer from polyposis. This is most likely due to dietary culture: in developed countries the population is accustomed to consuming fatty and meaty foods, Americans love fast food. In developing countries, national dishes include mainly plant foods, where polyposis is quite rare. In Russia, nutrition began to resemble European food, and therefore the formation of polyps among the population increased.
Causes of intestinal polyps
It is quite problematic to unequivocally answer the question about the reasons for the appearance of polyps in the intestines. But there are factors that can lead to the formation of tumor-like growths of a benign nature, among them:
- heredity;
- elderly age;
- disorders associated with hormonal levels and metabolism in the body;
- gender (polyposis is more often diagnosed in men);
- inactive lifestyle;
- smoking;
- environmental degradation;
- poor nutrition with a predominance of foods high in fats and carbohydrates and lack of fiber in the menu;
- food allergies associated with gluten intolerance;
- chronic and inflammatory diseases of the digestive tract;
- predisposition to constipation;
- disturbances in the intestinal microflora;
- atherosclerosis.
Diagnosis of the disease
Periodic examination by a proctologist will help identify polyposis in the large intestine. Some people are embarrassed to see a doctor, not realizing how important it is to find out about the disease at the initial stage.
For women, polyps in the intestines can lead to infertility if complications arise.
The following methods are used to diagnose the disease:
- Palpation of the rectum. The doctor determines by touch the presence of areas of the epithelium on which there are growths or formations. If polyposis is suspected, the patient is referred for additional examination.
- Colonoscopy. Examination of the rectum using an endoscope. This procedure allows you to check the entire length of the large intestine.
- Sigmoidoscopy. An examination similar to a colonoscopy, but the available examination depth is only 30 cm.
- Irrigoscopy. Examination of the intestines by introducing a contrast agent.
Colonoscopy has wider diagnostic capabilities and is less traumatic in comparison with irrigoscopy and sigmoidoscopy.
Konstantin Tishchenko
Orthopedist, Traumatologist
In all cases, patients should have their stool analyzed for signs of internal (occult) bleeding.
How are intestinal polyps diagnosed abroad?
In the early stages of the development of such a pathology in the intestines, there are no pronounced symptoms, therefore, in some foreign countries, in order to most effectively prevent cancer, annual special tests have been introduced for the population. One of them, the hemocult test, makes it possible to see, using certain chemical reactions, hidden blood in the stool, which occurs even with very small polyps and may indicate more serious diseases. Timely detection of pathology in a patient helps reduce the cost of cancer treatment abroad.
Digital examination is a traditional diagnostic method when the doctor detects tumor-like growths and other pathologies in the lower parts of the intestine.
The use of MRI and CT makes it possible to observe tumor-like formations in some parts of the intestine. But to diagnose them in the rectum or sigmoid colon, it is better to undergo sigmoidoscopy. A special device, a rectoscope, helps visualize the internal walls of the organ more carefully. Doctors recommend that people who have already crossed the 50-year mark undergo such an examination at least once every 5 years.
Irrigoscopy makes it possible to see polypous formations larger than 10 mm. It is performed using a contrast agent, which is injected into the colon. Then irrigograms are performed similar to X-rays.
Today, the most informative way to diagnose polyps is still a colonoscopy. This method allows you to learn about all intestinal pathologies. When examining a polyp, a biopsy may also be performed. The removed tissue sample is immediately sent for research (histology and cytology). Such an examination also precedes the start of treatment for intestinal cancer abroad.
The use of the latest laboratory testing techniques helps to diagnose polyposis as accurately as possible and find the most effective treatment method.
How to treat polyps?
The main method of treating polyposis is surgical removal of even the smallest growths detected. Both in the situation with single formations and with multiple ones, therapeutic treatment does not make sense. If the diagnosis reveals polyps, you need to get rid of them without delay, and then conduct histology of the removed formations.
Polyp removal
More often, the procedure for removing polyps is performed using endoscopic equipment and may not even require general anesthesia. An endoscope with a lighting device, at the end of which there is a loop electrode, is inserted through the patient's anus. The doctor places a loop over the polyp, grasping it at the base, tightens it and cuts it off at the base, along with the stem.
There is also a method of electrocoagulation - cauterization or excision of polyps with a laser. This intervention is suitable for removing small polyps, since working with a laser on space-occupying formations risks unintentional perforation of the rectal wall. The good thing about the procedure is that, in parallel with the removal of the polyp, the laser seals and seals the vessels and mucous membrane, eliminating bleeding and complications after surgery. Laser exposure also has a disinfecting effect, and the risk of infection entering wounds is significantly reduced. The only condition is that electrocoagulation is applied only to polyps located no deeper than eight centimeters from the anus.
The two above-mentioned methods are minimally traumatic; after the intervention, patients can walk independently and the next day continue to live in a normal rhythm, without unnecessary stress.
Endoscopic polyp removal process
If the polyps affect a significant part of the intestine, are located too close to each other, or there are a large number of them, the surgeon performs abdominal surgery and excises part of the intestine. This procedure requires a long recovery period. After the operation, the excised part of the organ along with the polyps is sent for examination, based on the results of which it becomes clear whether malignant transformation has occurred in the formations.
After the polyps have been removed by any means (or they have “gone away” on their own during conservative treatment of the underlying disease), a year later the patient must undergo a routine colonoscopy to ensure that there are no new formations. If no polyps are found during diagnosis, the procedure can be performed every three years. According to statistics, in 14% of patients, formations may recur at the site of removal, and in 7%, relapse occurs in other, previously unaffected areas of the epithelium. Therefore, you need to be understanding of the need for preventive diagnostics.
More detailed information about polyp removal can be found in our special article.
Video - Consultation with a proctologist: intestinal polyps
Treatment of intestinal polyps abroad
The most effective way to remove intestinal polyps is surgery. The desire to cure a tumor formation at home will not bring the desired results, but will only aggravate the situation, since the pathology can go into a malignant stage, and valuable time will be lost.
Nowadays, to remove polyps, they resort to a treatment method such as TAMIS (transanal minimally invasive surgery). Previously, it was first tested in cancer centers in Israel, but now high-tech equipment and qualified doctors allow this procedure to be performed quickly and painlessly in leading clinics in post-Soviet countries.
In some cases, a combined surgical intervention is used: excision of a tumor formation and electrocoagulation of small polyps. Foreign surgeons perform polypectomy on an outpatient basis using a proctoscope and an elastic ligature. In their opinion, this method is quite simple, low-traumatic, and occurs without side complications when removing even large polyps.
If malignant degeneration of a tumor-like formation in the intestine is suspected, resection of the membrane surrounding the polyp is performed. Next, the doctor sends these removed tissues for histological and cytological tests to confirm the diagnosis. This approach is actively used in the treatment of cancer in Israel and other countries.
Forecast
The most favorable prognosis is given to patients with uncomplicated growths without signs of malignancy. In all other cases, the prognosis directly depends on the general condition of the patient and the severity of the disease.
After resection, regular examinations by a proctologist and endoscopic examinations of the intestine are recommended in order to timely detect relapses.
Depending on the type of growth, the doctor individually sets the required duration of observation and the frequency of colonoscopies.
Prognosis for intestinal polyps
It must be emphasized that the prognosis for intestinal polyps is favorable in most cases, provided they are removed in a timely manner. Long-term single or numerous polyps of large or small size have a tendency to transform into malignant formations, so treatment should not be delayed. Patients who have been diagnosed with tumor-like growths in the intestines should undergo an annual endoscopic examination in order to exclude the possibility of relapse even after the removal of a benign formation.
Classification
Depending on the morphological structure, the following types of polyps are distinguished:
| View | Characteristic |
| Adenomatous (glandular or tubular) | They are diagnosed most often, in almost 50% of patients. They consist of glandular epithelium and are dense hyperplastic growths of a mushroom shape with a pinkish or reddish tint. Less common are branching outgrowths spreading along the intestinal mucosa. Their average diameter reaches from 2 to 3 cm, they are not prone to bleeding and ulceration, and can degenerate into malignant neoplasms |
| Papillary (villous) | Found in 14% of patients. They look like creeping formations or nodes of a rich red color. In size they reach up to 5 cm or more. Prone to malignancy, ulceration and bleeding |
| Glandular-villous | They are a transitional form of glandular and villous growths. Prone to malignancy, detected in 20% of cases |
| Hyperplastic | Formed in 75% of patients. They look like nodes slightly elevated above the mucous membrane, soft in consistency. Do not exceed 5 mm in diameter and are not prone to malignancy |
| Juvenile | They are considered a developmental anomaly that occurs in childhood and adolescence. Can be large, usually have a thin stalk and do not become malignant |