What is the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, Helicobacter?
Helicobacter pylori (Helicobacter pylori bacteria, HP) is currently considered the leading etiological factor in chronic gastritis, gastric ulcers, and gastric cancer. Helicobacter pylori causes 85% of chronic gastritis to be Helicobacter pylori, or HP-associated gastritis (causing serious illness). In the etiology of non-atrophic gastritis, nutritional disorders (improper diet, abuse of spicy, hot or cold foods), disorders of neurohumoral regulation, smoking, strong alcoholic drinks (alcohol, vodka, cognac, whiskey, tequila, moonshine) are of great importance.
Gastritis and Helicobacter pylori bacteria, Helicobacter pylori, HP
Helicobacter pylori (HP) is the cause of the development of Helicobacter pylori chronic gastritis, the most important factor in the pathogenesis of duodenal ulcer and gastric ulcer, low-grade gastric lymphoma (malt-lymphoma, from MALT - mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue), as well as gastric cancer. In 1994, experts from the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) under the WHO (World Health Organization) classified Helicobacter pylori as a class 1 carcinogen, which means that HP infection is unconditionally linked to the occurrence of stomach cancer. In 1983, Barry J. Marshall and Robin Warren identified the presence of a microorganism in the stomach of patients with peptic ulcers, which was initially called Campylobacter pylori, and since 1989 it has been called Helicobacter pylori (HP), as it belongs to to a separate genus.
Stomach biopsy - interpretation of the results, sensations after the biopsy
This term refers to the analysis of the composition of cells of abnormal stomach tissues, which involves taking individual sections of the mucous membrane and conducting a microscopic examination.
There are two types of this type of diagnostics – search and targeted. In the first case, the procedure is carried out using a special probe. Particles of the mucous membrane are taken for analysis without visual control.
Taking material for research
To perform a targeted biopsy, a special device is used - a gastroscope. This is a special tube that is equipped with a built-in optical system and a micro-instrument for collecting particles of affected tissue. Loops or forceps can be used for this purpose. The device may also include a knife or electromagnetic devices.
Using a gastroscope, it is possible to remove certain particles of the mucous membrane from specific areas of the gastric wall.
Indications for the procedure
The study is carried out if other methods do not provide the required amount of information. With its help, it is possible to differentiate pathologies of different etiologies with similar examination results. Biopsy is also an important method for diagnosing malignant lesions of the stomach.
So, this study is usually carried out in the following cases:
- malignant formations in the stomach - a biopsy can detect cancer and precancerous conditions;
- gastric ulcer - this diagnostic method allows you to distinguish ulcerative lesions from cancer;
- different forms of gastritis;
- dyspeptic condition - allows you to determine the presence or absence of Helicobacter pylori infection;
- lesions of the mucous membrane are identified for the purpose of their resection;
- surgical interventions - a biopsy is often performed after operations to assess the condition of the gastric wall.
The procedure does not require additional anesthesia and lasts no more than a quarter of an hour. The biopsy is usually performed on an empty stomach. As a rule, it is recommended to avoid consuming any food 10-15 hours before the test.
Immediately before the procedure, you should not brush your teeth. It is also not recommended to use chewing gum and drink water. To perform a targeted examination, a gastroscope is used. This device has an optical system, lighting and microscopic instruments that allow you to take a biopsy.
Decoding the research results
All types of gastroscopy are based on a special optical effect that transmits images from a remotely located device, allowing the doctor to examine the internal surface of organs.
Thanks to this design of the gastroscope with a fiber-optic system and the ability to refract a light beam, the effect of total reflection is achieved.
This allows you to obtain an undistorted image of the inside of the examined organ.
Diagnostic gastroscopy Therapeutic gastroscopy
| The method is used to assess the type and relief of the mucous membrane. With esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EFGDS), it becomes possible to capture a section of the mucosa for biopsy. If bacterial gastritis is suspected, HP testing is performed for the presence of Helicobacter pylori, the main cause of chronic gastritis and peptic ulcers | During the procedure, planned removal of polyps and benign formations, ligation of dilated veins of the esophagus, as well as elimination of long-term non-healing ulcers on the mucous layer are carried out. In emergency cases, a therapeutic test is used to block ulcer bleeding, remove polyps, administer medications, and also give injections |
The results of the biopsy must be deciphered by a doctor. They are usually provided 2-3 days after the study. The data obtained as a result of the procedure is divided into several categories:
- Incomplete means that too little material was taken during the study. In this situation, the procedure is indicated again.
- Normal - considered the ideal option, since questionable fragments do not belong to the category of anomalous.
- Benign - in this situation, tissue growth is recorded. In this case, the results indicate which benign neoplasm is present in the stomach. In some situations, repeat biopsy is indicated.
- Malignant – When cancer appears, data will be provided regarding its type, tumor size, margins and location.
A biopsy is considered a fairly accurate diagnostic method, and therefore there are almost no errors when performing it. Thanks to this study, it is possible to make an accurate diagnosis and select adequate therapy.
Source: https://sarpages.ru/biopsiya-zheludka-oznachaet/
Description of the analysis
The urease breath test detects the presence of the Helicobacter pylori bacterium in the body. This microorganism lives in the stomach of people suffering from pathologies of the digestive system.
The bacterium is found in the patient's saliva and dental plaque. Infection occurs through kissing, violating hygiene rules, or sharing utensils and a toothbrush with an infected person.
Helicobacter pylori is the causative agent of gastritis, as well as ulcers and malignant tumors of the stomach.
The bacterium secretes a special enzyme - urease. This substance is capable of reacting chemically with urea (urea). This produces carbon dioxide and ammonia.
The urease test for Helicobacter pylori is based on this reaction. During the study, the patient consumes urea orally.
The doctor measures the concentration of carbon dioxide or ammonia in the exhaled air before and after taking the drug.
Advantages of the method
In the past, the following types of research were used to diagnose diseases caused by Helicobacter pylori:
- gastric mucus analysis;
- blood test for antibodies to Helicobacter pylori;
- stool examination using PCR diagnostics.
Nowadays, a breath test for the presence of urease is more often used. Let's consider the main disadvantages of the above methods:
- Gastric mucus testing is an invasive version of the urease test. What it is? Biomaterial is obtained during gastroscopy. The doctor inserts a special probe into the patient’s stomach and removes mucus for analysis. Then the laboratory determines the concentration of urease in the material. This is an informative and reliable method, but the gastroscopy procedure is quite unpleasant for the patient. The urease breath test does not cause any discomfort.
- A blood test for antibodies does not always reliably indicate the presence of infection. Quite often, false test results are observed.
- Examination of stool for Helicobacter pylori is an informative diagnostic method. It shows the presence of infection in 95% of cases. However, the release of bacteria continues even after recovery. In stool analysis, Helicobacter pylori can be determined after a pathology. Based on the results of this study, it is difficult to judge the patient's health.
We can conclude that a breath test is the most gentle and reliable method of diagnosis. If the patient follows all the necessary rules for preparing for the test, then false results are extremely rare.
Indications
A urease breath test for Helicobacter pylori is prescribed if an inflammatory infectious process in the stomach is suspected. Indications for the test are patient complaints about the following pathological manifestations:
- Heartburn. During an infectious process in the gastrointestinal tract, hydrochloric acid penetrates from the stomach into the esophagus. This is accompanied by a burning sensation due to irritation of the mucous membrane.
- Pain syndrome. With inflammation of the stomach, pain in the epigastrium of a stabbing or pressing nature is noted. Unpleasant sensations worsen after eating or during long breaks between meals.
- Belching. The infectious process is accompanied by increased gas formation in the stomach. Excess gases, along with food particles, come out through the oral cavity. The exhaled air has a sour or unpleasant odor.
- Plaque on the tongue. This is a characteristic sign of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including those of infectious origin. In chronic gastric pathologies, the tongue is constantly coated with a white coating. The patient feels dryness and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. In the acute form of gastritis, a gray coating forms.
- Dyspeptic phenomena. During an infectious inflammatory process, the digestive function of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted. Patients are concerned about nausea, periodic vomiting, frequent diarrhea followed by constipation, and loss of appetite. There is often bloating of the abdominal cavity due to the accumulation of gases.
Such symptoms indicate an inflammatory process or ulcer in the gastrointestinal tract. The test helps to establish the infectious etiology of diseases.
The test is also carried out during the treatment of pathologies caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. The study allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy.
Biological basis of the technique
Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped bacterium that affects the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. Persistence of the microorganism leads to the development of gastritis, gastroduodenitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers.
Once in the stomach cavity, the bacterium penetrates the mucous membrane. There, having secured itself with the help of flagella, it begins to produce the enzyme urease. The pH around the bacterial colony increases due to the enzyme, which leads to the activation of compensatory mechanisms for the production of hydrochloric acid by stomach cells. Gastrin and pepsin are also produced in increased quantities.
How to prepare for research
In order for these samples to be reliable, you must follow the following rules for preparing for the urease test:
- The test is carried out on an empty stomach. The test is usually scheduled for the morning; the last meal is allowed 10-12 hours before the test. On the eve of the test, you can only drink clean water, but 1 hour before the test you must stop even drinking liquid.
- 14 days before the test, stop taking medications that suppress the secretion of gastric juice, as well as antibiotics. 2 days before the test, you must stop using antacids and analgesics.
- You should not eat legumes for 24 hours before the test.
- Alcohol is completely avoided 2-3 days before the test.
On the day of the examination, you should not smoke or chew chewing gum. Before the test, you need to thoroughly rinse your mouth and brush your teeth.
Preparation
Preparation for the 13C urease breath test is that the patient must stop taking antibiotics 4 weeks before testing, and NSAIDs, proton pump inhibitor drugs (which reduce stomach acidity) and antacids or adsorbents used for heartburn at least two weeks before. Taking any medications should be stopped five to six days, and drinking alcohol and smoking three days before the test.
It is also recommended not to eat legumes for about a week before testing, since beans, peas, lentils, soybeans and beans contain urease (which protects plants from diseases and insect pests).
Source: https://hospitalvv.ru/diagnostika/test-na-hp.html
Carrying out the test
Before testing for Helicobacter, you need to refrain from eating food.
The patient is almost always advised to fast before testing.
Before the procedures, each patient is given a specially prepared solution, which includes urea.
When the patient takes the solution, you need to insert a mouthpiece into his mouth, through which he needs to breathe for about nine minutes. Breathing should be as normal as possible.
In this way, the digital device can accurately determine the components contained in exhaled carbon dioxide. All results of the examination will be displayed on the monitor.
Read: Stomach lymphoma: symptoms, diagnostic methods and treatment
The main mechanism for identifying bacteria is based on a biochemical method for determining the infection of various microorganisms when they exhibit so-called urease activity.
The possibility of ensuring hydrolysis of urea due to the activity of bacteria is the basis of this testing method. When using a urea solution in people, the hydrolysis process is activated, and the gases formed during this process are eliminated through the oral cavity.
Then comes the procedure of comparing the gases generated as a result of hydrolysis with the original content. It is by determining the difference between gas compositions that a specific diagnosis can be determined.
Such a survey is carried out for the entire population, regardless of category. This technique is considered completely harmless, since it involves kerbamide, which is absolutely harmless to humans.
After completing all research procedures, the attending physician must conduct the most accurate analysis of the information provided to him, after which a specific diagnosis can be determined.
Each patient can receive all the results of such testing in the form of a written protocol, which indicates the most detailed information about the procedures performed.
2Characteristic symptoms
The presence of the following signs should prompt you to get tested for Helicobacter pylori:
- Abdominal pain during or immediately after eating.
- Heartburn.
- Problems with bowel movements.
- In the intervals between meals, “hunger pains” appear.
- Causeless nausea.
- Heaviness in the stomach, even if a person has eaten very little.
- Poor digestion of meat dishes or meat intolerance.
- Aching pain in the stomach that is constantly present.
- Mucus in stool.
- Belching and vomiting.
All these symptoms indicate the activity of Helicobacter, and therefore the presence of a disease associated with the gastrointestinal tract.
Test norm for Helicobacter pylori
This bacterium should not exist in the body of both adults and children. Therefore, the norm for any test for this microbe is a negative result:
- The absence of the bacterium itself when examining smears of the gastric mucosa under a microscope. The eye of a diagnostician under multiple magnification does not reveal S-shaped microbes with flagella at the end of the body.
- The indicator in the test system will not turn crimson when conducting a urease test. After the mucosal biopsy is placed in the express kit environment, nothing will happen: the color of the indicator will remain the original (light yellow or another as stated by the manufacturer). This is the norm. In the absence of bacteria, there is no one to decompose the urea, turning it into ammonia and carbon dioxide. The environment to which the indicator is sensitive does not become alkalized.
- Less than 1% of the labeled 13C isotope in exhaled air is detected in a breath test. This means that Helicobacter enzymes do not work and do not break down the urea drunk for the study. And if enzymes are not detected, we can conclude that the microorganism itself is absent.
- There is no growth of colonies on nutrient media when carrying out the bacteriological method. An important component of the success of this analysis is compliance with all modes of growing the microbe: oxygen in the environment should be no more than 5%, a special blood substrate is used, and an optimal temperature is maintained. If small round bacterial colonies do not appear on the medium over the course of five days, we can conclude that there was no microbe in the biopsy sample under study.
- The absence of antibodies to the pathogen during an enzyme immunoassay of blood or their low titer of 1:5 or less. If the titer is elevated, Helicobacter is present in the stomach. Antibodies or immunoglobulins (IgG, IgM, IgA) are specific proteins of the immune system produced to protect against microbes and increase the body's resistance.
If the test for Helicobacter pylori is positive - what does this mean?
A positive test result means the presence of infection in the body. The exception is a positive result for the antibody titer, which can occur when performing blood ELISA immediately after eradication of the bacterium.
That's the problem:
Even if treatment for Helicobacter is successful and the bacteria is no longer in the stomach, antibodies or immunoglobulins to it remain for some time and can give a false positive result.
Therefore, it is not recommended to donate blood for diagnostics immediately after eradication; it is better to do this a month later. If treatment is successful, all tests will show a Helicobacter-negative result.
In all other cases, a positive test means the presence of a microbe in the stomach: asymptomatic carriage or disease.
Interpretation of cytological examination for Helicobacter
The study of bacteria under a microscope from smears of the gastric mucosa is called cytological. To visualize the microbe, smears are stained with a special dye and then examined under magnification.
If the doctor observes the entire bacterium in the smears, he gives a conclusion about a positive test result. The patient is infected.
Next, he assesses the degree of infection:
- + if he sees up to 20 microbes in his field of vision
- ++ up to 50 microorganisms
- +++ more than 50 bacteria in the smear
If the doctor in the cytological report made a mark of one plus, this means Helicobacter is a weakly positive result: the bacterium is present, but the contamination of the gastric mucosa is not significant. Three pluses indicate significant bacterial activity, there are a lot of them and the inflammation process is pronounced.
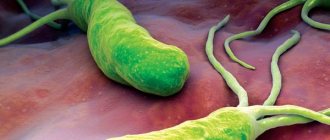
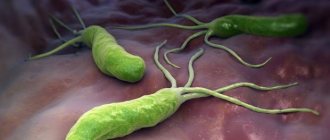
What does Helicobacter pylori look like?
Bacteria Helicobacter pylori, Helicobacter pylori, Helicobacter, HP is a gram-negative microaerophilic bacterium of a curved or spiral shape with many (4 to 6) flagella. Helicobacter pylori (HP) is about 2.9 µm long and 0.8 µm in diameter. Helicobacter pylori , Helicobacter pylori (HP) is found deep in the gastric pits and on the surface of epithelial cells, mainly under the protective layer of mucus lining the gastric mucosa. It can exist in areas of gastric dysplasia with frequent acidification of the duodenal bulb. Directly around the bacterium, the pH is about 7, and the nutrient content is quite sufficient for the life of the microorganism. Helicobacter pylori (HP) is able to exist under conditions of varying concentrations of hydrochloric acid in the gastric cavity. Helicobacter pylori (HP) survives at a pH of 4 to 8. It reproduces successfully at a pH of 6 to 8. The most favorable habitat is the antrum of the stomach. Under unfavorable conditions, Helicobacter pylori (HP) can develop into a coccal form. Helicobacter infection is very dangerous.
What to do if you receive a positive COVID-19 test result
A person can learn about the results of paid or free testing on the clinic’s website, via SMS or email. The responsible laboratory employee will definitely call him to agree on the further course of action. It is determined by two factors:
- the method that was used to detect pathogens of coronavirus infection;
- well-being of the examined person.
If PCR diagnostics were carried out, then the person is sick today or is an asymptomatic carrier. In the latter case, he can infect others, so he must adhere to two weeks of self-isolation. A positive test in combination with severe symptoms of coronavirus (dry non-productive cough, loss of taste and smell, breathing problems) often becomes a serious reason for hospitalization in the infectious diseases department. Treatment and retesting will be carried out.
A person does not decide on his own what to do after receiving positive results. Moreover, he will not be able to hide testing data. It is performed in laboratories accredited by the Ministry of Health and Rospotrebnadzor. Information about currently identified infected people is immediately sent to these authorities. A team of doctors in special equipment goes to the patient’s home, where the subsequent algorithm of actions is determined.
What should a person do next if an external examination does not reveal pronounced signs of coronavirus:
- isolate yourself for 14 days and call the hotline 8-800-2000-112. If necessary, sick leave will be issued and brought home;
- measure temperature twice a day;
- ventilate the room several times a day;
- when in contact with family members living in the same area, use a mask;
- contact colleagues and friends exclusively by telephone or via the Internet;
- If possible, avoid using fans, air conditioners, or air purifiers.
- change towels, underwear and bed linen daily.
The initial positive test becomes the reason for examining all family members who have been in contact with the infected person. They are not required to observe self-isolation. But at the slightest deterioration in their health, they must report this by telephone to the hospital.
PCR diagnostics
PCR testing is the leading laboratory test for the presence of coronavirus. During the pandemic, it was this that was recommended by WHO as the most sensitive and informative. To carry it out, a swab is taken from the nasal cavity or oropharynx, since the upper respiratory tract is the entry point for coronaviruses.
A positive result appears as orange glowing stripes. These are separated nucleic acids that have been exposed to an electrical current. And the person examined directly sees the positive data in the form, which is issued after their interpretation. In most laboratories, this result is marked with a plus sign.
If you test positive for coronavirus, you must quarantine until recovery
A positive test does not always mean that coronaviruses are replicating (multiplying) in the respiratory tract. Even the most modern test systems can make mistakes. False-positive reactions can be provoked by various factors:
- ingress of blood, epithelial cells, and large amounts of mucus into the biomaterial (smear from the nasal passages or oropharynx);
- violation of sterility, contamination of the smear, as a result of which a non-existent infection is detected;
- unsuitability of reagents;
- violation of the transportation of biomaterial or its storage.
In the absence of symptoms characteristic of coronavirus, the result may be considered doubtful. The doctor prescribes repeat testing to confirm or refute the results of the initial one.
Useful information: Doctors constantly monitor the condition of the patient in self-isolation and his contact persons by phone or come for a regular examination.
ELISA testing
Enzyme immunoassay allows one to detect specific immunoglobulins in the patient’s blood with high accuracy. Antibodies are always produced by the immune system in response to the invasion of the human body by infectious pathogens. All of them are specific, that is, to destroy coronaviruses, immunoglobulins (igg) are synthesized, which are not capable of destroying the cells of other pathogens. Therefore, the detection of a specific antigen in the bloodstream directly indicates a developing coronavirus infection.
A person who tests positive for coronavirus using ELISA can become a plasma donor
During ELISA testing, antibodies to coronaviruses, their quantitative content, and the stage of inflammatory pathology are detected. A positive result does not mean that a person is sick. After all, in response to the invasion of pathogens, various antibodies are produced. This is the positive side of ELISA testing. It is likely that the person has been ill for a long time and has acquired a fairly stable immunity.
The most common results of ELISA analysis:
| ELISA testing results | Data interpretation |
| IgM: ≥ 2.0 and IgG: | Coronavirus infection is currently occurring in the body |
| IgM: 1.0 - 2.0 and IgG: | Borderline result indicating the need for re-evaluation |
| IgM: ≥ 2.0 and IgG: ≥ 10.0 | The person recovers, his immunity is formed, but there are still coronaviruses |
| Ig(M) | Antibodies are present in small quantities in the body. The person has been ill and is not able to infect others, but re-infection is possible |
It is unlikely that a person far from medicine will be able to decipher ELISA data. If he has doubts about the reliability of a positive result, this does not serve as a basis for immediate re-testing. It will be carried out within the time limits established by law.
Helicobacter pylori: analysis, test, methods for detecting Helicobacter pylori
What is the diagnosis of Helicobacter, how to detect the bacterium? Basic methods for detecting Helicobacter pylori (HP) :
1) Analysis for Helicobacter pylori: bacteriological (culture of a biopsy of the mucous membrane on a differential diagnostic medium).
2) Morphological (is the “gold standard” for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori; staining of the bacterium in histological preparations of the gastric mucosa according to Giemsa, Ghent, Warthin-Starry, toluidine blue, with the cytological method staining according to Gram, Giemsa).
3) Test for Helicobacter: breath test (determination of 14C or 13C isotopes in exhaled air; they are released as a result of the breakdown of urea in the patient’s stomach under the influence of urease from the bacterium Helicobacter pylori (HP)).
4) Urease test for the bacterium Helicobacter pylori (determination of urease activity in a biopsy of the gastric mucosa by placing it in a liquid or gel-like medium containing a substrate, buffer and indicator).
5) PCR, polymerase chain reaction (extremely sensitive method).
6) Immunological methods (blood test, blood for Helicobacter, antibodies for Helicobacter): enzyme immunoassay and rapid tests based on immunoprecipitation or immunocytochemistry, including determination of IgM, IgA, IgG, their titer (1: 10, 1: 20, 30, 40, 50). ELISA, what is antigen, antibodies, AT?
The Helicobacter result will be ready in a few days (positive - 1, 2, 3, 4 or negative test, positive or negative).
Helicobacter pylori (HP) stimulates the human immune system to produce systemic antibodies, but at the same time helps to suppress local immunity.
Diagnostic results
The results of the study are interpreted as follows:
- SARS-CoV-2 RNA was not detected: the test is negative - there is no virus in the biomaterial;
- SARS-CoV-2 RNA has been detected: the test is positive – the infection is present in the body.
Depending on the location of the test, the answer may be sent by the clinic to the user by email or communicated to the patient by the attending physician. If you doubt the reliability of the results, it is recommended to undergo PCR testing again - after 4-5 days. A re-examination is also required for those who have completed treatment for COVID-19 to confirm recovery.
How to treat Helicobacter?
Sarklinik knows how to treat and cure Helicobacter , how to get rid of Helicobacter. In the treatment of Helicobacter pylori, effective procedures, antibiotics, means of protecting the gastric mucosa, and medications that normalize acid production in the stomach are used. Unfortunately, homeopathy, folk remedies, medicine, treatment with folk remedies at home, left pills, drugs do not eradicate Helicobacter pylori (bacillus), and anti-Helicobacter therapy will not succeed. On the medical website sarclinic.ru you can read reviews from patients.
Urease test during gastroscopy
A feature of the bacterium that can be used when testing for Helicobacter is the release of urease, which can break down urea. As a result of this reaction, carbon dioxide is formed, which is vital for the bacteria itself to protect against the acidic contents of the stomach. This urease activity can be detected by gastroscopy.
The study of urease activity is of great diagnostic value, since only Helicobacter is capable of producing this enzyme.
The use of fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGS) allows the doctor to visually assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the digestive system. For this, a small flexible fiberscope with a video camera and a light source at the end is used. By visually examining the inner layer of the stomach and duodenum, an experienced doctor may notice altered areas characteristic of a peptic ulcer. Carrying out a biopsy, i.e. taking a small piece of suspicious mucous membrane can be used for further diagnosis.
After a piece of mucous is taken, it is placed in a special chemical environment that can determine the activity of urease in bacteria. If the mucous membrane contained Helicobacter, then the medium will change its color to crimson due to a change in the pH solution to the alkaline side. If the color has not changed, then the presence of such a bacterium is unlikely, but it cannot be completely ruled out.
How to fight Helicobacter pylori?
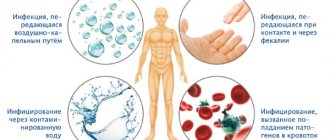
At the first consultation, the doctor will tell you about current problems. What is the importance of nutrition, diet, de-nol, garlic, propolis (propolis), stool analysis (stool). Why are they called pilari - hilary, pillori, pilor, is it necessary to identify it, is it a virus? Where to get tested for Helicobacter in Saratov. What is the most effective eradication regimen? Where is diagnostics carried out, how to donate blood, how to kill bacteria, effective destruction? How to treat gastritis associated with Helicobacter? How to treat without antibiotics? How do people become infected with Helicobacter, where does the bacterium come from, how is it transmitted, how can one become infected, how do they become infected, what are the routes of transmission, methods of infection, is gastritis contagious, what is prevention? Call us, we know how to fight Helicobacter pylori .
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo of Helicobacter pylori: (©) Knorre | Dreamstime.com\Dreamstock.ru
Related posts:
Helicobacter pylori: treatment, symptoms, test, analysis, bacteria, norm
Lectins – informative molecular probes